Andreas Vesalius.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius
 n n Andreas Vesalius (1514 -1564) scientist, founder of anatomy. Born in Brussels. Vesalius activity took place in many European countries. One of the first to explore the human body through autopsies. Most of the work "On the structure of the human body" (books 1 -7, 1543) Vesalius gave a scientific description of the structure of all the organs and systems have many errors of his predecessors, including Galen. Persecuted church. Died in the shipwreck. Andreas Vesalius is rightly considered the founder of modern anatomy and founder of the school of anatomists. He enjoyed success as a physician practices.
n n Andreas Vesalius (1514 -1564) scientist, founder of anatomy. Born in Brussels. Vesalius activity took place in many European countries. One of the first to explore the human body through autopsies. Most of the work "On the structure of the human body" (books 1 -7, 1543) Vesalius gave a scientific description of the structure of all the organs and systems have many errors of his predecessors, including Galen. Persecuted church. Died in the shipwreck. Andreas Vesalius is rightly considered the founder of modern anatomy and founder of the school of anatomists. He enjoyed success as a physician practices.
 n Andreas Vesalius was born in Brussels in 1514 to a family of doctors. Doctors were his grandfather and greatgrandfather, and his father served as an apothecary at the court of Emperor Charles V. Interests of others, no doubt, influenced by the interests and aspirations of the young Vesalius. Andreas studied first at school and then at the University of Louvain, where he received a broad education, studied Greek and Latin, so that could get acquainted with the works of scientists already in his early years. Obviously, he read a lot of books about medicine of ancient and contemporary scholars, as his works show deep knowledge. Vesalius executed independently of the bones collected a full human skeleton. It was the first anatomical manual in Europe.
n Andreas Vesalius was born in Brussels in 1514 to a family of doctors. Doctors were his grandfather and greatgrandfather, and his father served as an apothecary at the court of Emperor Charles V. Interests of others, no doubt, influenced by the interests and aspirations of the young Vesalius. Andreas studied first at school and then at the University of Louvain, where he received a broad education, studied Greek and Latin, so that could get acquainted with the works of scientists already in his early years. Obviously, he read a lot of books about medicine of ancient and contemporary scholars, as his works show deep knowledge. Vesalius executed independently of the bones collected a full human skeleton. It was the first anatomical manual in Europe.
 n n Every year more and more evident passion for Vesalius to the study of medicine, for anatomical research. In his spare time, he exercises at home carefully dissected animal bodies of mice, cats, dogs, studying the structure of their body. In an effort to improve their knowledge in the field of medicine, especially anatomy, Andreas Vesalius at the age of seventeen went to the University of Montpellier, and in 1533, first appeared in the medical faculty of the University of Paris, to attend the lectures of the famous enatoma Sylvia. Young Vesalius was able to critically method of teaching anatomy.
n n Every year more and more evident passion for Vesalius to the study of medicine, for anatomical research. In his spare time, he exercises at home carefully dissected animal bodies of mice, cats, dogs, studying the structure of their body. In an effort to improve their knowledge in the field of medicine, especially anatomy, Andreas Vesalius at the age of seventeen went to the University of Montpellier, and in 1533, first appeared in the medical faculty of the University of Paris, to attend the lectures of the famous enatoma Sylvia. Young Vesalius was able to critically method of teaching anatomy.
 n n n In the preface to the treatise "On the structure of the human body, " Andreas Vesalius wrote: "My work would not have been successful if, during his medical work in Paris, I did not apply to the case of his hands. . . And I myself, a few sophisticated personal experience, publicly held independent third of autopsies. " A. Vesalius gives lectures on issues that show his doubts about the truth of the teachings of Galen - the unquestioned authority, his teaching should be taken without any reservations, and Vesalius trust my eyes more than the works of Galen. Scientist rightly believed anatomy basis of medical knowledge, and the purpose of his life was the desire to revive the experience of the past, to develop and refine a method for studying human anatomy. However, the church that prevented the development of natural sciences, prohibited autopsies man, since it is blasphemy. Many difficulties had to be overcome young anatomist Andreas Vesalius. In order to be able to do dissections, he used every opportunity. If the plants in your pocket money, he agreed with the cemetery caretaker, and then got into his hands the body, fit for an autopsy. If there was no money, Vesalius, hiding from the guard was opening the tomb itself, without his knowledge. What had to take risks! Vesalius so well studied the bones of the human skeleton and animals that could, without looking at them, called the touch any bone.
n n n In the preface to the treatise "On the structure of the human body, " Andreas Vesalius wrote: "My work would not have been successful if, during his medical work in Paris, I did not apply to the case of his hands. . . And I myself, a few sophisticated personal experience, publicly held independent third of autopsies. " A. Vesalius gives lectures on issues that show his doubts about the truth of the teachings of Galen - the unquestioned authority, his teaching should be taken without any reservations, and Vesalius trust my eyes more than the works of Galen. Scientist rightly believed anatomy basis of medical knowledge, and the purpose of his life was the desire to revive the experience of the past, to develop and refine a method for studying human anatomy. However, the church that prevented the development of natural sciences, prohibited autopsies man, since it is blasphemy. Many difficulties had to be overcome young anatomist Andreas Vesalius. In order to be able to do dissections, he used every opportunity. If the plants in your pocket money, he agreed with the cemetery caretaker, and then got into his hands the body, fit for an autopsy. If there was no money, Vesalius, hiding from the guard was opening the tomb itself, without his knowledge. What had to take risks! Vesalius so well studied the bones of the human skeleton and animals that could, without looking at them, called the touch any bone.
 n n Spent three years at the University of Andreas Vesalius, and then the circumstances were such that he had to leave Paris and go again at Louvain. There Vesalius got in trouble. He removed the corpse of an executed criminal gallows and made an autopsy. Louvain clergy demanded strict punishment for such blasphemy. Vesalius realized that the debate is useless, and thought it best to leave Louvain and went to Italy.
n n Spent three years at the University of Andreas Vesalius, and then the circumstances were such that he had to leave Paris and go again at Louvain. There Vesalius got in trouble. He removed the corpse of an executed criminal gallows and made an autopsy. Louvain clergy demanded strict punishment for such blasphemy. Vesalius realized that the debate is useless, and thought it best to leave Louvain and went to Italy.
 n After receiving a doctorate in 1537, Andreas Vesalius began teaching anatomy and surgery at the University of Padua. The Government of the Republic of Venice encouraged the development of the science of nature and sought to extend the work of scientists at the University.
n After receiving a doctorate in 1537, Andreas Vesalius began teaching anatomy and surgery at the University of Padua. The Government of the Republic of Venice encouraged the development of the science of nature and sought to extend the work of scientists at the University.
 n Brilliant talent caught the attention of a young scientist. Vesalius twenty-two, has already received for his work the title of Doctor of Medicine, was appointed to the chair of surgery with the duty to teach anatomy. Andreas with inspiration lectured, have always attracted a lot of students, worked with the students and, most importantly, continued his studies. And the deeper he studied the internal structure of the body, the more strengthened the idea that the teaching of Galen quite a few significant errors, which just did notice who was under the influence galenovskogo authority.
n Brilliant talent caught the attention of a young scientist. Vesalius twenty-two, has already received for his work the title of Doctor of Medicine, was appointed to the chair of surgery with the duty to teach anatomy. Andreas with inspiration lectured, have always attracted a lot of students, worked with the students and, most importantly, continued his studies. And the deeper he studied the internal structure of the body, the more strengthened the idea that the teaching of Galen quite a few significant errors, which just did notice who was under the influence galenovskogo authority.

 Four long years, he worked on with their work. Vesalius studied, translated and reprinted works of medical scientists of the past, their predecessors anatomists. And in their writings, he found a lot of mistakes, "Even the greatest scientists - wrote Vesalius – slavishly adhered foreign gaffes and a strange style in their manuals obsolete. " The scientist began to trust the most authentic book - the book of the human body that has no errors. At night by candlelight Andreas Vesalius dissected cadavers. He set a goal to solve the great problem - correctly describe the location, shape and function of the human body. n
Four long years, he worked on with their work. Vesalius studied, translated and reprinted works of medical scientists of the past, their predecessors anatomists. And in their writings, he found a lot of mistakes, "Even the greatest scientists - wrote Vesalius – slavishly adhered foreign gaffes and a strange style in their manuals obsolete. " The scientist began to trust the most authentic book - the book of the human body that has no errors. At night by candlelight Andreas Vesalius dissected cadavers. He set a goal to solve the great problem - correctly describe the location, shape and function of the human body. n
 n The result of a passionate and hard work of the scientist was celebrated treatise in seven books, which appeared in 1543, entitled "On the structure of the human body. " It was a gigantic scientific work in which, instead of outdated dogma presents new scientific views. It reflected the cultural progress of humanity in the Renaissance
n The result of a passionate and hard work of the scientist was celebrated treatise in seven books, which appeared in 1543, entitled "On the structure of the human body. " It was a gigantic scientific work in which, instead of outdated dogma presents new scientific views. It reflected the cultural progress of humanity in the Renaissance
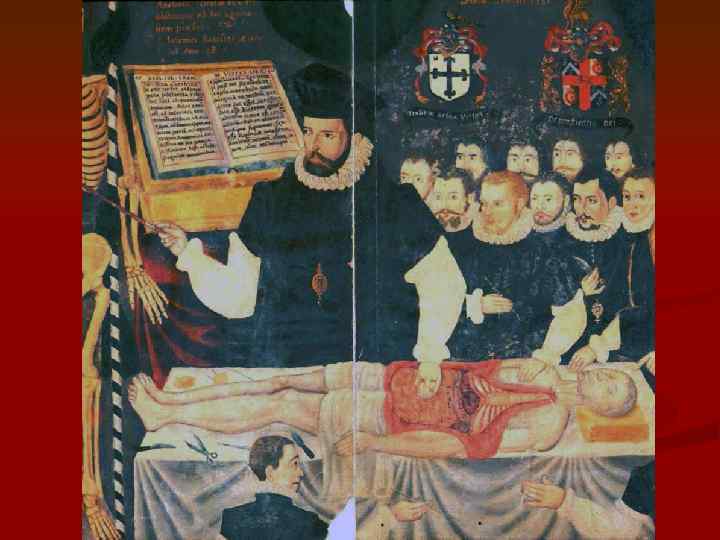
 n Typography has developed rapidly in Venice and in Basel, where Andreas Vesalius published his work. His book is decorated with beautiful paintings of the artist Stefan Kalkar, a pupil of Titian is significant that in the picture below are the skeletons in poses typical of living people, and landscapes that surround some of the skeletons, they say more about life than death. All this work was intended to benefit Vesalius living person, studying his body to preserve his health and life. Each capital letter in a treatise decorated with drawings depicting children studying anatomy. So it was in the ancient art of anatomy taught from childhood, the knowledge passed down from father to son. Gorgeous art composition frontispiece of the book depicts Andreas Vesalius in a public lecture and human autopsy.
n Typography has developed rapidly in Venice and in Basel, where Andreas Vesalius published his work. His book is decorated with beautiful paintings of the artist Stefan Kalkar, a pupil of Titian is significant that in the picture below are the skeletons in poses typical of living people, and landscapes that surround some of the skeletons, they say more about life than death. All this work was intended to benefit Vesalius living person, studying his body to preserve his health and life. Each capital letter in a treatise decorated with drawings depicting children studying anatomy. So it was in the ancient art of anatomy taught from childhood, the knowledge passed down from father to son. Gorgeous art composition frontispiece of the book depicts Andreas Vesalius in a public lecture and human autopsy.
 Work Vesalius worried minds of scientists. The boldness of his scientific thought was so unusual that, along with an estimate of its opening followers he had many enemies. Lot of grief and frustration experienced great scientist, even when he left the students. Famous Silvius, teacher Vesalius called "Vezanus", which means - a madman. He came out against him with a sharp pamphlet, which he called "Protection Against Defamation on anatomical works of Hippocrates and Galen on the part of a madman. " n
Work Vesalius worried minds of scientists. The boldness of his scientific thought was so unusual that, along with an estimate of its opening followers he had many enemies. Lot of grief and frustration experienced great scientist, even when he left the students. Famous Silvius, teacher Vesalius called "Vezanus", which means - a madman. He came out against him with a sharp pamphlet, which he called "Protection Against Defamation on anatomical works of Hippocrates and Galen on the part of a madman. " n
 n n He did not disdain in order to appeal to the emperor himself, demanding punish Vesalius, "I beg Tsezarskoe Majesty - wrote Professor Jacob Silvius - that he was severely beaten, and in general has conquered the beast of ignorance, ingratitude, insolence, pernicious piece of wickedness, born and brought up in his house, as this monster deserves to plague his breath is not poison Europe. " Andreas Vesalius foresaw how to wrap the event after the publication of his treatise "On the structure of the human body. " Earlier, he wrote: ". . . my work is subjected to attack by those who did not undertake the anatomy of jealously, as was the case in Italian schools, and who is now in his old age to pine with envy right revelations boys. "
n n He did not disdain in order to appeal to the emperor himself, demanding punish Vesalius, "I beg Tsezarskoe Majesty - wrote Professor Jacob Silvius - that he was severely beaten, and in general has conquered the beast of ignorance, ingratitude, insolence, pernicious piece of wickedness, born and brought up in his house, as this monster deserves to plague his breath is not poison Europe. " Andreas Vesalius foresaw how to wrap the event after the publication of his treatise "On the structure of the human body. " Earlier, he wrote: ". . . my work is subjected to attack by those who did not undertake the anatomy of jealously, as was the case in Italian schools, and who is now in his old age to pine with envy right revelations boys. "
 n n Most eminent doctors really took the side of Sylvia. They joined with his demand to curb and punish Andreas Vesalius, who dared to criticize the great Galen. Such was the power of recognized authorities, such were the foundations of the social life of the time, when every innovation merit caution, every courageous speech, goes beyond the established canon, was regarded as a free-thinking. They were the fruit of centuries of ideological monopoly of the church, which imposed inertia and routine. Exposing dozens of corpses, having carefully studied the human skeleton Vesalius became convinced that the belief that the men on one edge less than women, it is not true. But this belief was beyond medical science. It affected the Church doctrine.
n n Most eminent doctors really took the side of Sylvia. They joined with his demand to curb and punish Andreas Vesalius, who dared to criticize the great Galen. Such was the power of recognized authorities, such were the foundations of the social life of the time, when every innovation merit caution, every courageous speech, goes beyond the established canon, was regarded as a free-thinking. They were the fruit of centuries of ideological monopoly of the church, which imposed inertia and routine. Exposing dozens of corpses, having carefully studied the human skeleton Vesalius became convinced that the belief that the men on one edge less than women, it is not true. But this belief was beyond medical science. It affected the Church doctrine.
 n n n Vesalius did not reckon with another statement of the clerics. In his time maintained the belief that the human skeleton is bone, which does not burn in the fire, indestructible. It is alleged, and laid the mysterious power by which man will rise again in the day of judgment, to appear before the Lord God. Although this stone has not been seen, it is described in scientific works, its existence is not doubted. Vesalius is in describing the structure of the human body, expressly stated that in studying the human skeleton, he found a mysterious stone. Andreas Vesalius was aware of the consequences that may lead to action against Galen. He realized that he was against the established opinion, affects the interests of the church. And what they do with such daring alone, he knew well. Scientists continue to teach at the University of Padua, but every day the atmosphere around him was heating up more and more. He was sad to part with the fall, with the University, to interrupt their work and research. But the other way, he did not see. It was at this time he was invited Spanish Emperor Charles V to take the place of the court physician. Imperial Court was at that time in Brussels. Karl has served as father of Vesalius, and a young professor accepted the emperor. Of course, in Brussels it will not have the department, he can not deal with the students. But the imperial court to serve as a safe refuge from the persecution of the church, leaving the opportunity to engage in anatomy. Thus, the place of the court physician, although it was not like Vesalius, had its advantages.
n n n Vesalius did not reckon with another statement of the clerics. In his time maintained the belief that the human skeleton is bone, which does not burn in the fire, indestructible. It is alleged, and laid the mysterious power by which man will rise again in the day of judgment, to appear before the Lord God. Although this stone has not been seen, it is described in scientific works, its existence is not doubted. Vesalius is in describing the structure of the human body, expressly stated that in studying the human skeleton, he found a mysterious stone. Andreas Vesalius was aware of the consequences that may lead to action against Galen. He realized that he was against the established opinion, affects the interests of the church. And what they do with such daring alone, he knew well. Scientists continue to teach at the University of Padua, but every day the atmosphere around him was heating up more and more. He was sad to part with the fall, with the University, to interrupt their work and research. But the other way, he did not see. It was at this time he was invited Spanish Emperor Charles V to take the place of the court physician. Imperial Court was at that time in Brussels. Karl has served as father of Vesalius, and a young professor accepted the emperor. Of course, in Brussels it will not have the department, he can not deal with the students. But the imperial court to serve as a safe refuge from the persecution of the church, leaving the opportunity to engage in anatomy. Thus, the place of the court physician, although it was not like Vesalius, had its advantages.
 n n Still, it was hard to find a more unsuitable for the post of Vesalius. He was a scholar, researcher. Now he had to absorb far removed from the principles of science, the ability to please their noble patients, capture their thoughts, attend all court ceremonies. But even in these circumstances, it did not stop the work to which he devoted life. All the free time Andreas Vesalius gave the treatise "On the structure of the human body. " Modify, add, clarify, what seemed to him not quite convincing. Using every opportunity he did dissections. But the idea that he was cut off from the research centers that research activities was his side business, depressed Vesalius.
n n Still, it was hard to find a more unsuitable for the post of Vesalius. He was a scholar, researcher. Now he had to absorb far removed from the principles of science, the ability to please their noble patients, capture their thoughts, attend all court ceremonies. But even in these circumstances, it did not stop the work to which he devoted life. All the free time Andreas Vesalius gave the treatise "On the structure of the human body. " Modify, add, clarify, what seemed to him not quite convincing. Using every opportunity he did dissections. But the idea that he was cut off from the research centers that research activities was his side business, depressed Vesalius.
 He wanted to go back to the scientific department. But realistically, Vesalius could not even think about to leave Brussels and move to another place where he was able to do the work for everyone. As soon as he left the imperial court, as the Inquisition again would show interest in him. That's why the most melancholy moments of life Vesalius convinced myself that it is necessary to come to terms with the circumstances. n A second edition of Vesalius managed to publish his treatise "On the structure of the human body. " It was only a brief happy moment for all these years, and then everything went still. Stretched a long line, one after another monotonous days. n But then came the end of the stay of Vesalius in the imperial court. His patron, Charles V abdicated, retired to a monastery and died on the throne was Philip II - bile and evil man. He did not like Vesalius, and openly expressed their dislike of him. Quick to take advantage of these many envious enemies of the court physician. Attitude of the new emperor to Vesalius deteriorated even more. Vesalius felt that he had to leave as quickly as possible from Brussels. He tries to break free from the power of the new emperor, sent a request to allow him to Italy. But wayward Philip categorically opposed this. n
He wanted to go back to the scientific department. But realistically, Vesalius could not even think about to leave Brussels and move to another place where he was able to do the work for everyone. As soon as he left the imperial court, as the Inquisition again would show interest in him. That's why the most melancholy moments of life Vesalius convinced myself that it is necessary to come to terms with the circumstances. n A second edition of Vesalius managed to publish his treatise "On the structure of the human body. " It was only a brief happy moment for all these years, and then everything went still. Stretched a long line, one after another monotonous days. n But then came the end of the stay of Vesalius in the imperial court. His patron, Charles V abdicated, retired to a monastery and died on the throne was Philip II - bile and evil man. He did not like Vesalius, and openly expressed their dislike of him. Quick to take advantage of these many envious enemies of the court physician. Attitude of the new emperor to Vesalius deteriorated even more. Vesalius felt that he had to leave as quickly as possible from Brussels. He tries to break free from the power of the new emperor, sent a request to allow him to Italy. But wayward Philip categorically opposed this. n
 n n Severe restrictions under Philip Church dissect corpses again touched Vesalius. Violate their values come into open conflict with the church. Vesalius wrote bitterly about this time - "I could not even touch his hand to the dry skull and the less opportunity I had to make the opening. " But try as he might, Andreas Vesalius did not give rise to any church whatsoever charges, it was not in his power. Vesalius on newly poured streams of slander. On top of that he was falsely accused in the fact that he dissected a live person.
n n Severe restrictions under Philip Church dissect corpses again touched Vesalius. Violate their values come into open conflict with the church. Vesalius wrote bitterly about this time - "I could not even touch his hand to the dry skull and the less opportunity I had to make the opening. " But try as he might, Andreas Vesalius did not give rise to any church whatsoever charges, it was not in his power. Vesalius on newly poured streams of slander. On top of that he was falsely accused in the fact that he dissected a live person.
 n n n Vesalius was trying to prove his innocence, but to no avail. He had to obey. The verdict of the church was categorical: the court physician Andreas Vesalius had to atone for their sins go to worship in the "holy places" to the Holy Sepulcher. . . In 1564 Vesalius with his wife and daughter left Madrid. Leaving his family in Brussels, he went to one long journey. On the way to Jerusalem scholar stopped in his beloved Venice, where he spent the best years of his life. Vesalius did not give the idea of returning to their favorite science. There is speculation that the Venetian Senate offered him again to take the chair at the University of Padua. But the dream of the scientist back to the science has not been realized. On the way back from Jerusalem in a shipwreck patient Vesalius was thrown on the island of Zante (Greece), where in 1564 he died. We do not know the place of his burial, but the best monument scientist, a fighter for progressive science is his great work on the structure of the human body.
n n n Vesalius was trying to prove his innocence, but to no avail. He had to obey. The verdict of the church was categorical: the court physician Andreas Vesalius had to atone for their sins go to worship in the "holy places" to the Holy Sepulcher. . . In 1564 Vesalius with his wife and daughter left Madrid. Leaving his family in Brussels, he went to one long journey. On the way to Jerusalem scholar stopped in his beloved Venice, where he spent the best years of his life. Vesalius did not give the idea of returning to their favorite science. There is speculation that the Venetian Senate offered him again to take the chair at the University of Padua. But the dream of the scientist back to the science has not been realized. On the way back from Jerusalem in a shipwreck patient Vesalius was thrown on the island of Zante (Greece), where in 1564 he died. We do not know the place of his burial, but the best monument scientist, a fighter for progressive science is his great work on the structure of the human body.
 n n n More about Andreas Vesalius: Vesalius (Andrew Vesalius) - a famous surgeon and founder of the new anatomy, was born on 31 th December 1514 in Brussels, the group includes among its ancestors several prominent doctors (his grandfather - the author of essays, "Comments on aphorisms of Hippocrates"). Andreas Vesalius was educated at Louvain, Paris and Montpellier, and especially devoted himself studying human anatomy, with the risk of their lives, due to prejudices of his time, taking human corpses. They say that even the Andreas before every corpse dissection fervently asked God's forgiveness for what he was looking for science in the death of the mystery of life.
n n n More about Andreas Vesalius: Vesalius (Andrew Vesalius) - a famous surgeon and founder of the new anatomy, was born on 31 th December 1514 in Brussels, the group includes among its ancestors several prominent doctors (his grandfather - the author of essays, "Comments on aphorisms of Hippocrates"). Andreas Vesalius was educated at Louvain, Paris and Montpellier, and especially devoted himself studying human anatomy, with the risk of their lives, due to prejudices of his time, taking human corpses. They say that even the Andreas before every corpse dissection fervently asked God's forgiveness for what he was looking for science in the death of the mystery of life.
 n n He soon gained notoriety experienced surgeon, and was invited to lecture on anatomy in Basel, Padua, Bologna and Pisa. In 1543 Andreas Vesalius published his famous work «De sorroris humani fabrica libri septem» (Basel), which opened a new era in the history of anatomy: the authority of Galen was finally overthrown and the human anatomy has been put on the ground accurate pilot study. Andreas Vesalius essay has caused, as expected, fierce attacks by doctors obscurantists against which Vesalius protect several polemical writings. Since 1544, as a physician of the Emperor Charles V, Andreas accompanied him in all the travel, but his son, Philip II, the Spanish Inquisition managed to seize a long time enemies lurk. Accusations that during the autopsy of the deceased heart found some signs of life, Andreas Vesalius, was sentenced to death. Only through the intercession of Philip II, the death penalty was replaced pilgrimage to the Holy Sepulchre.
n n He soon gained notoriety experienced surgeon, and was invited to lecture on anatomy in Basel, Padua, Bologna and Pisa. In 1543 Andreas Vesalius published his famous work «De sorroris humani fabrica libri septem» (Basel), which opened a new era in the history of anatomy: the authority of Galen was finally overthrown and the human anatomy has been put on the ground accurate pilot study. Andreas Vesalius essay has caused, as expected, fierce attacks by doctors obscurantists against which Vesalius protect several polemical writings. Since 1544, as a physician of the Emperor Charles V, Andreas accompanied him in all the travel, but his son, Philip II, the Spanish Inquisition managed to seize a long time enemies lurk. Accusations that during the autopsy of the deceased heart found some signs of life, Andreas Vesalius, was sentenced to death. Only through the intercession of Philip II, the death penalty was replaced pilgrimage to the Holy Sepulchre.


