62e5576486839449858bde053de2ee56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 and Unit 3 – Theory of the Firm
and Unit 3 – Theory of the Firm
 This lecture is interactive. Before beginning make sure students are paired with a partner with a whiteboard, marker & eraser. Move your seat together beside your partner’s to where you can comfortably take your own notes & write on the white board together. You don’t need to take notes until you see this sign.
This lecture is interactive. Before beginning make sure students are paired with a partner with a whiteboard, marker & eraser. Move your seat together beside your partner’s to where you can comfortably take your own notes & write on the white board together. You don’t need to take notes until you see this sign.
 4 market structures in which firms compete: #1 – perfect competition #2 – monopoly #3 – monopolistic competition #4 - oligopoly 3 of 34
4 market structures in which firms compete: #1 – perfect competition #2 – monopoly #3 – monopolistic competition #4 - oligopoly 3 of 34
 1. Many buyers and sellers 2. All the products are homogeneous. 3. All buyers & sellers are price takers. 4. There are NO barriers to entry. 5. There is perfect information. 6. There is no chance of long-run profits.
1. Many buyers and sellers 2. All the products are homogeneous. 3. All buyers & sellers are price takers. 4. There are NO barriers to entry. 5. There is perfect information. 6. There is no chance of long-run profits.
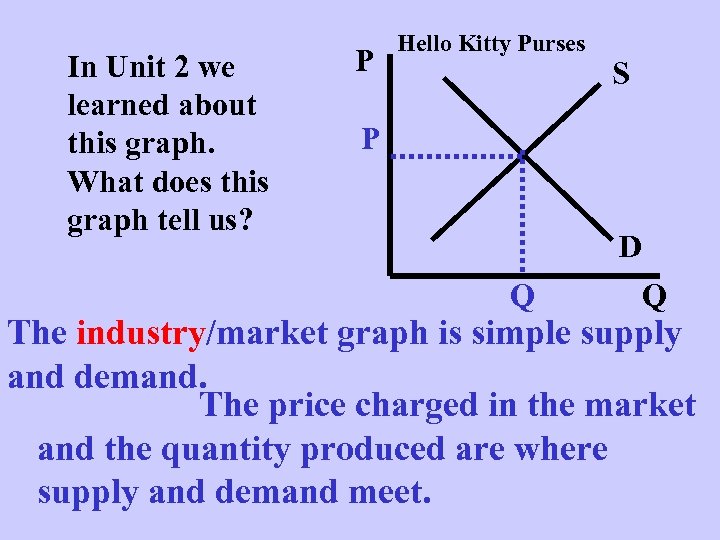 In Unit 2 we learned about this graph. What does this graph tell us? P Hello Kitty Purses S P D Q Q The industry/market graph is simple supply and demand. The price charged in the market and the quantity produced are where supply and demand meet.
In Unit 2 we learned about this graph. What does this graph tell us? P Hello Kitty Purses S P D Q Q The industry/market graph is simple supply and demand. The price charged in the market and the quantity produced are where supply and demand meet.
 In this unit on costs we’re adding to our analysis the individual firm. cost firm On your whiteboard draw the graph for an individual firm correctly labeling the 2 axes & title of graph. 6 of 34 quantity
In this unit on costs we’re adding to our analysis the individual firm. cost firm On your whiteboard draw the graph for an individual firm correctly labeling the 2 axes & title of graph. 6 of 34 quantity
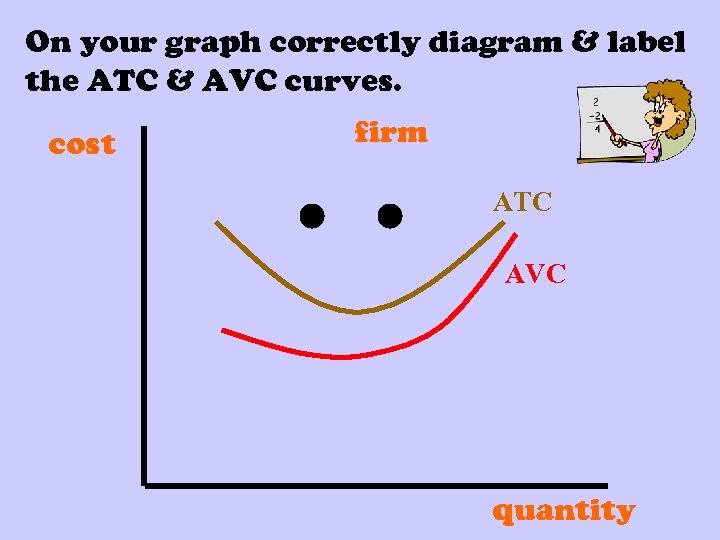 On your graph correctly diagram & label the ATC & AVC curves. cost firm ATC AVC quantity
On your graph correctly diagram & label the ATC & AVC curves. cost firm ATC AVC quantity
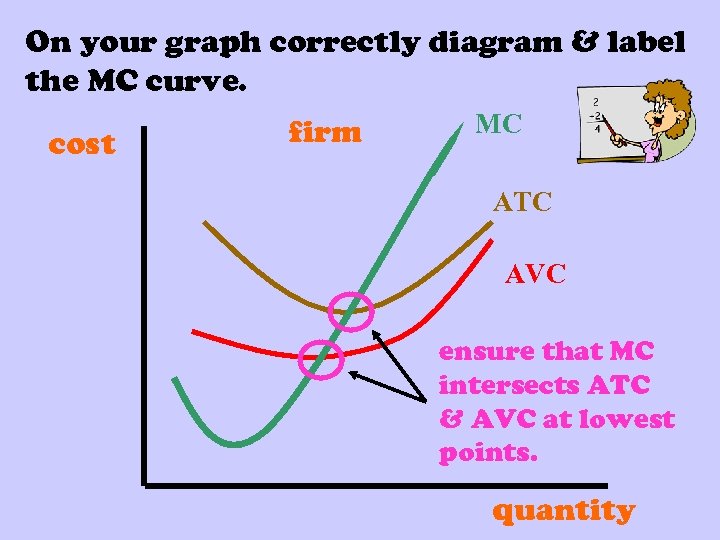 On your graph correctly diagram & label the MC curve. cost firm MC ATC AVC ensure that MC intersects ATC & AVC at lowest points. quantity
On your graph correctly diagram & label the MC curve. cost firm MC ATC AVC ensure that MC intersects ATC & AVC at lowest points. quantity
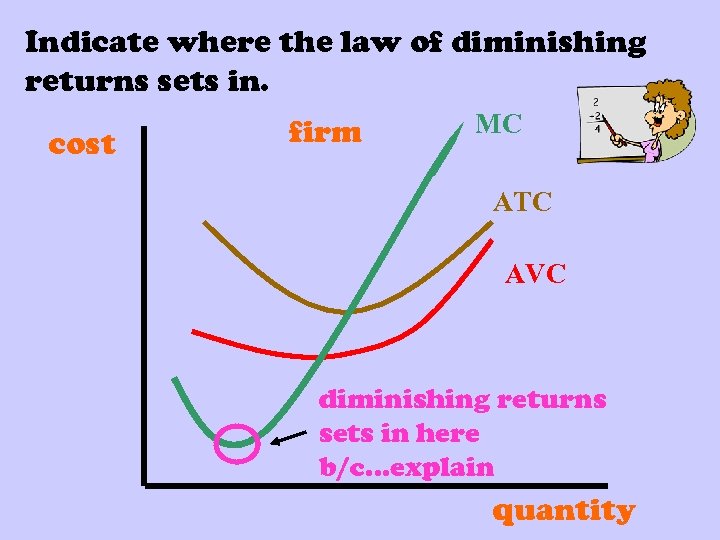 Indicate where the law of diminishing returns sets in. cost firm MC ATC AVC diminishing returns sets in here b/c…explain quantity
Indicate where the law of diminishing returns sets in. cost firm MC ATC AVC diminishing returns sets in here b/c…explain quantity
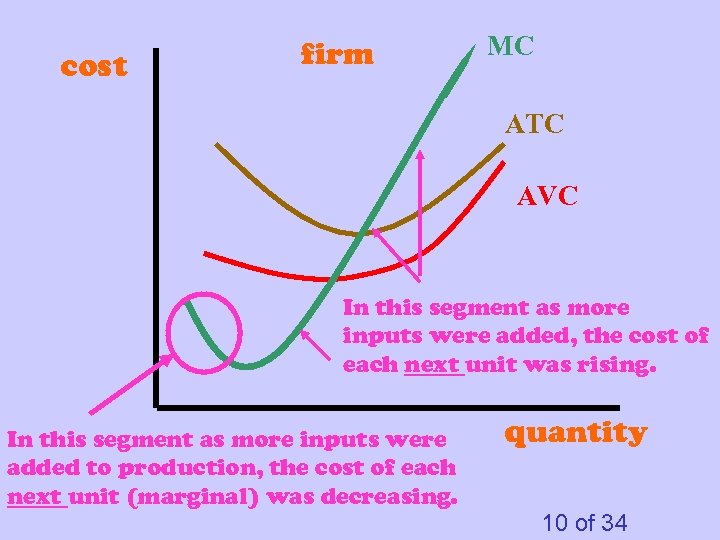 cost firm MC ATC AVC In this segment as more inputs were added, the cost of each next unit was rising. In this segment as more inputs were added to production, the cost of each next unit (marginal) was decreasing. quantity 10 of 34
cost firm MC ATC AVC In this segment as more inputs were added, the cost of each next unit was rising. In this segment as more inputs were added to production, the cost of each next unit (marginal) was decreasing. quantity 10 of 34
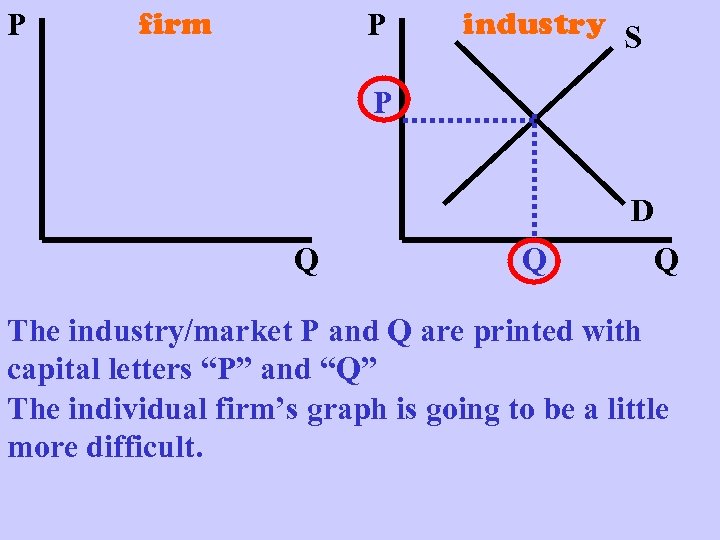 P firm P industry S P D Q Q Q The industry/market P and Q are printed with capital letters “P” and “Q” The individual firm’s graph is going to be a little more difficult.
P firm P industry S P D Q Q Q The industry/market P and Q are printed with capital letters “P” and “Q” The individual firm’s graph is going to be a little more difficult.
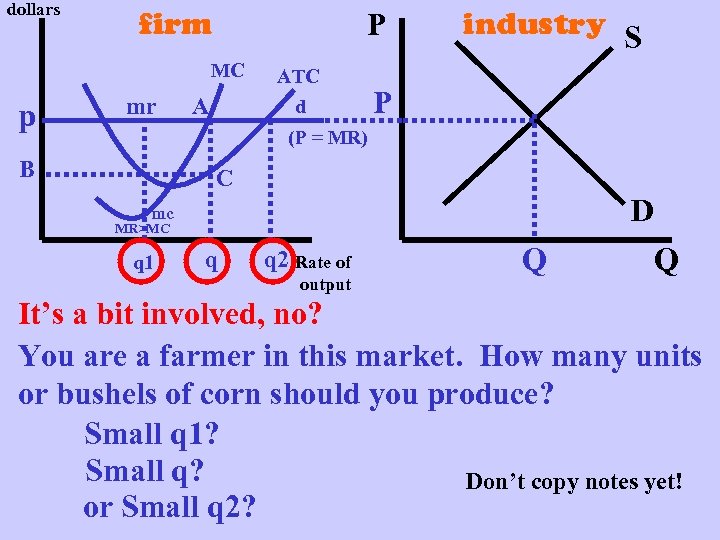 dollars firm P MC p mr A ATC d industry S P (P = MR) B C D mc MR>MC q 1 q q 2 Rate of output Q Q It’s a bit involved, no? You are a farmer in this market. How many units or bushels of corn should you produce? Small q 1? Small q? Don’t copy notes yet! or Small q 2?
dollars firm P MC p mr A ATC d industry S P (P = MR) B C D mc MR>MC q 1 q q 2 Rate of output Q Q It’s a bit involved, no? You are a farmer in this market. How many units or bushels of corn should you produce? Small q 1? Small q? Don’t copy notes yet! or Small q 2?
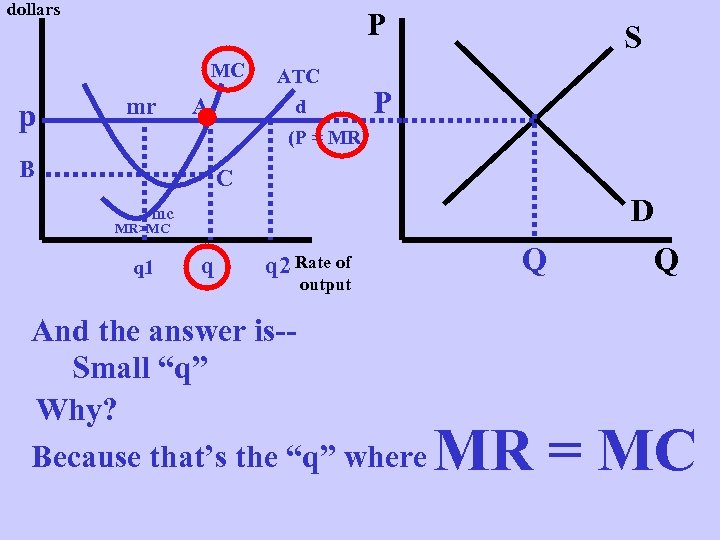 dollars P MC p mr A ATC d S P (P = MR) B C D mc MR>MC q 1 q q 2 Rate of output And the answer is-Small “q” Why? Because that’s the “q” where Q Q MR = MC
dollars P MC p mr A ATC d S P (P = MR) B C D mc MR>MC q 1 q q 2 Rate of output And the answer is-Small “q” Why? Because that’s the “q” where Q Q MR = MC
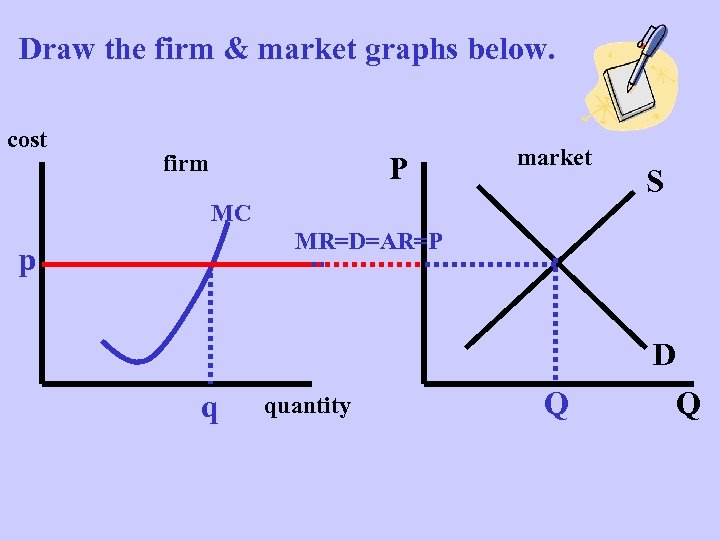 Draw the firm & market graphs below. cost firm P market S MC MR=D=AR=P p D q quantity Q Q
Draw the firm & market graphs below. cost firm P market S MC MR=D=AR=P p D q quantity Q Q
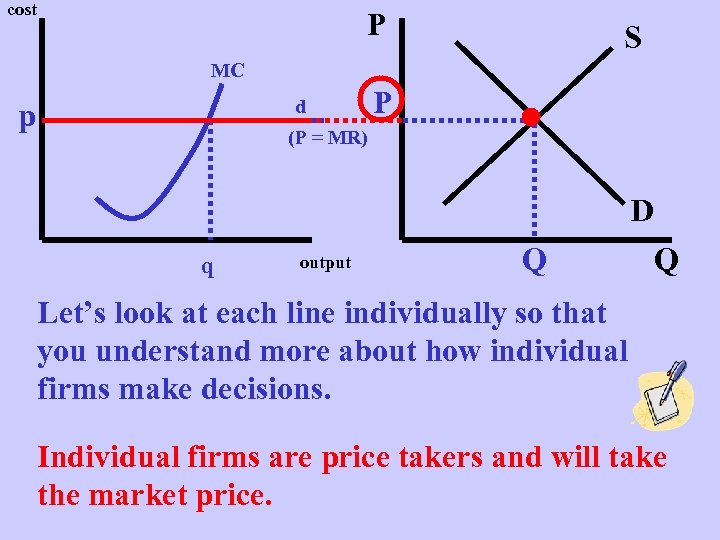 cost P S MC d p P (P = MR) D q output Q Q Let’s look at each line individually so that you understand more about how individual firms make decisions. Individual firms are price takers and will take the market price.
cost P S MC d p P (P = MR) D q output Q Q Let’s look at each line individually so that you understand more about how individual firms make decisions. Individual firms are price takers and will take the market price.
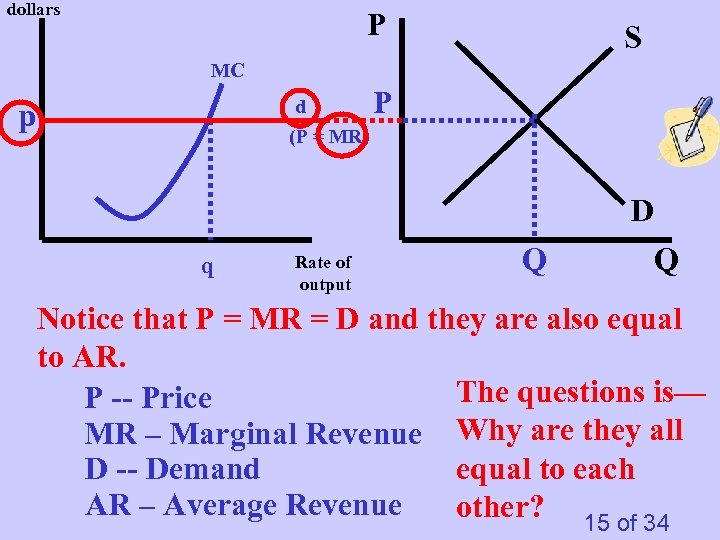 dollars P S MC d (P = MR) p P D q Rate of output Q Q Notice that P = MR = D and they are also equal to AR. The questions is— P -- Price MR – Marginal Revenue Why are they all D -- Demand equal to each AR – Average Revenue other? 15 of 34
dollars P S MC d (P = MR) p P D q Rate of output Q Q Notice that P = MR = D and they are also equal to AR. The questions is— P -- Price MR – Marginal Revenue Why are they all D -- Demand equal to each AR – Average Revenue other? 15 of 34
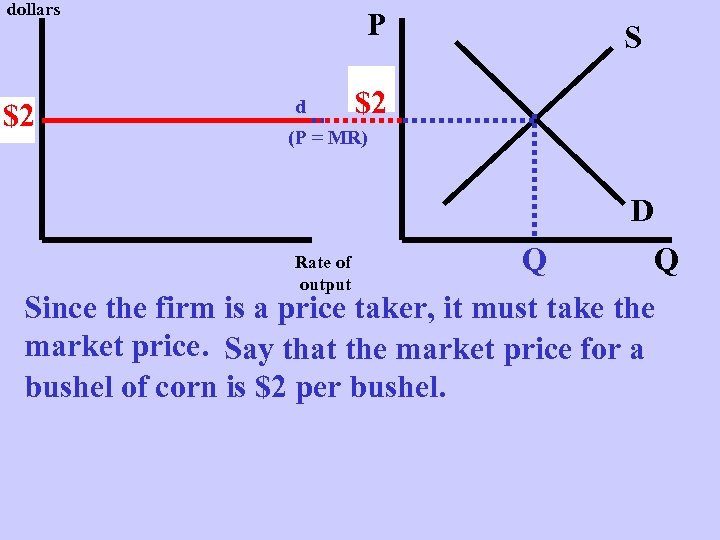 dollars $2 p P d S $2 P (P = MR) D Q Q Since the firm is a price taker, it must take the market price. Say that the market price for a bushel of corn is $2 per bushel. Rate of output
dollars $2 p P d S $2 P (P = MR) D Q Q Since the firm is a price taker, it must take the market price. Say that the market price for a bushel of corn is $2 per bushel. Rate of output
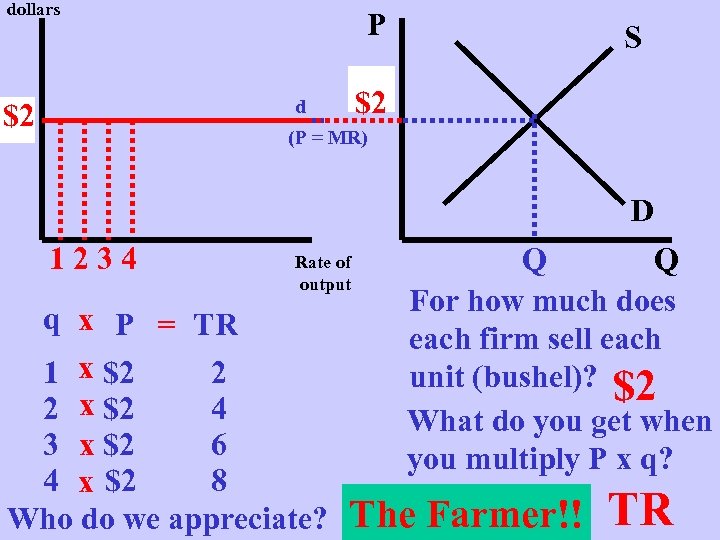 dollars P $2 P d $2 p S (P = MR) D 1234 Rate of output q x P = TR 1 x $2 2 2 x $2 4 3 x $2 6 4 x $2 8 Who do we appreciate? Q Q For how much does each firm sell each unit (bushel)? $2 What do you get when you multiply P x q? The Farmer!! TR
dollars P $2 P d $2 p S (P = MR) D 1234 Rate of output q x P = TR 1 x $2 2 2 x $2 4 3 x $2 6 4 x $2 8 Who do we appreciate? Q Q For how much does each firm sell each unit (bushel)? $2 What do you get when you multiply P x q? The Farmer!! TR
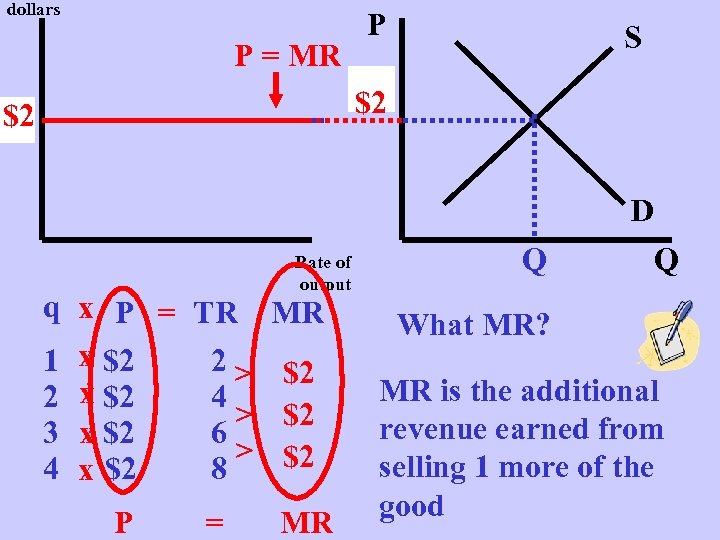 dollars P = MR P S $2 P $2 p D q x P = TR 1 x $2 2> 2 x $2 4 > 3 x $2 6 > 4 x $2 8 P = Rate of output MR $2 $2 $2 MR Q Q What MR? MR is the additional revenue earned from selling 1 more of the good
dollars P = MR P S $2 P $2 p D q x P = TR 1 x $2 2> 2 x $2 4 > 3 x $2 6 > 4 x $2 8 P = Rate of output MR $2 $2 $2 MR Q Q What MR? MR is the additional revenue earned from selling 1 more of the good
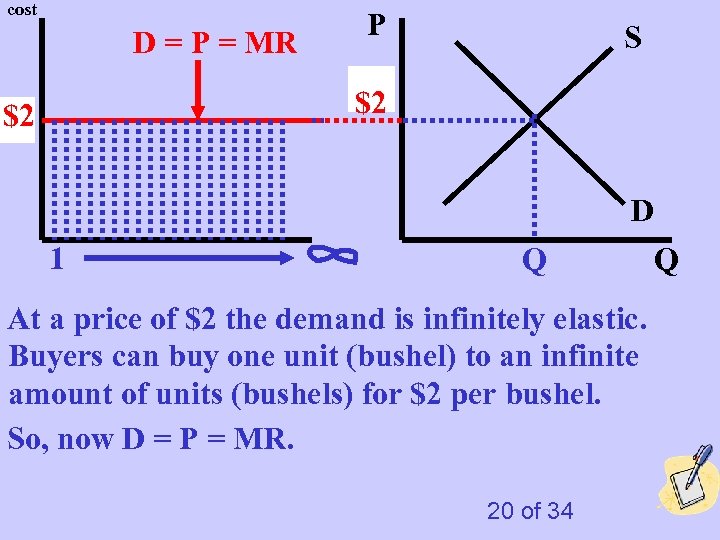 cost D = P = MR P S $2 P $2 p D 1 Q At a price of $2 the demand is infinitely elastic. Buyers can buy one unit (bushel) to an infinite amount of units (bushels) for $2 per bushel. So, now D = P = MR. 20 of 34 Q
cost D = P = MR P S $2 P $2 p D 1 Q At a price of $2 the demand is infinitely elastic. Buyers can buy one unit (bushel) to an infinite amount of units (bushels) for $2 per bushel. So, now D = P = MR. 20 of 34 Q
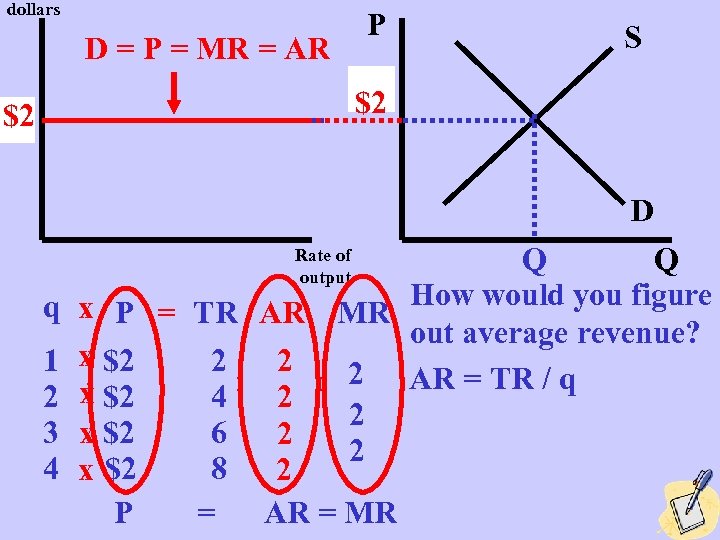 dollars D = P = MR = AR P S $2 P $2 p D Q Q q x P = TR AR MR How would you figure out average revenue? 1 x $2 2 AR = TR / q 2 x $2 4 2 2 3 x $2 6 2 2 4 x $2 8 2 P = AR = MR Rate of output
dollars D = P = MR = AR P S $2 P $2 p D Q Q q x P = TR AR MR How would you figure out average revenue? 1 x $2 2 AR = TR / q 2 x $2 4 2 2 3 x $2 6 2 2 4 x $2 8 2 P = AR = MR Rate of output
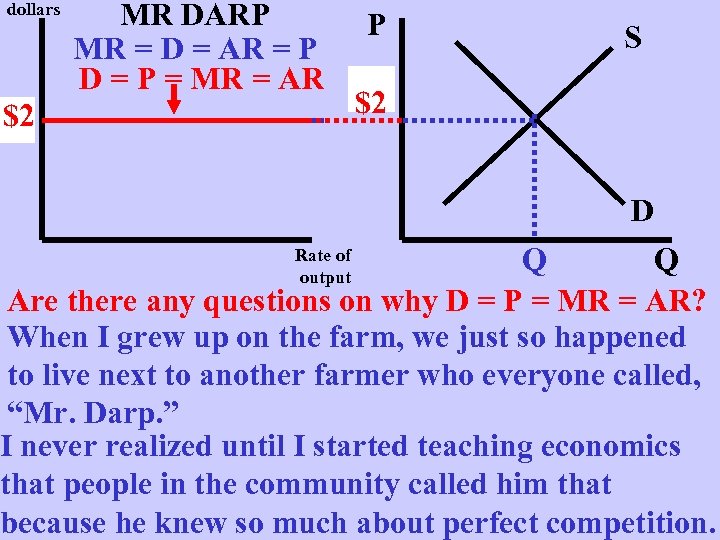 dollars MR DARP MR = D = AR = P D = P = MR = AR $2 p P S $2 P D Q Q Are there any questions on why D = P = MR = AR? When I grew up on the farm, we just so happened to live next to another farmer who everyone called, “Mr. Darp. ” I never realized until I started teaching economics that people in the community called him that because he knew so much about perfect competition. Rate of output
dollars MR DARP MR = D = AR = P D = P = MR = AR $2 p P S $2 P D Q Q Are there any questions on why D = P = MR = AR? When I grew up on the farm, we just so happened to live next to another farmer who everyone called, “Mr. Darp. ” I never realized until I started teaching economics that people in the community called him that because he knew so much about perfect competition. Rate of output
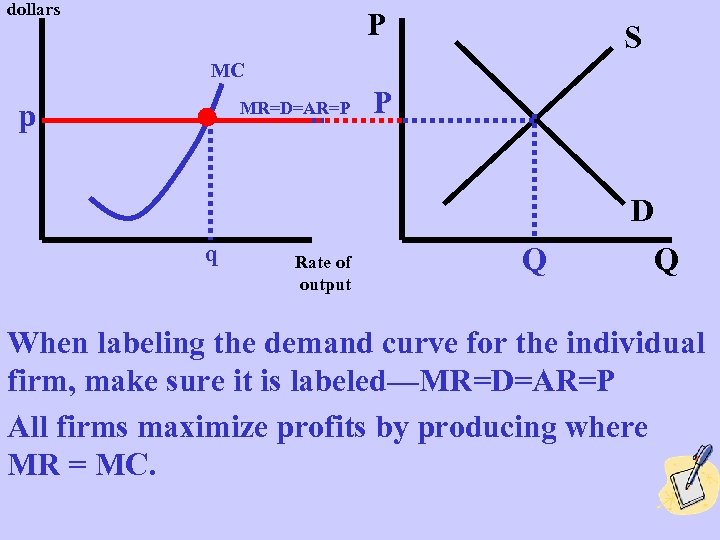 dollars P S MC p MR=D=AR=P P D q Rate of output Q Q When labeling the demand curve for the individual firm, make sure it is labeled—MR=D=AR=P All firms maximize profits by producing where MR = MC.
dollars P S MC p MR=D=AR=P P D q Rate of output Q Q When labeling the demand curve for the individual firm, make sure it is labeled—MR=D=AR=P All firms maximize profits by producing where MR = MC.
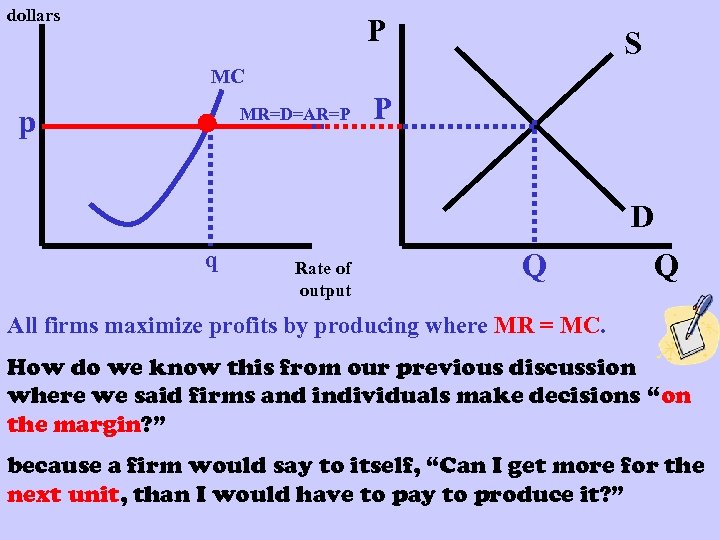 dollars P S MC p MR=D=AR=P P D q Rate of output Q Q All firms maximize profits by producing where MR = MC. How do we know this from our previous discussion where we said firms and individuals make decisions “on the margin? ” because a firm would say to itself, “Can I get more for the next unit, than I would have to pay to produce it? ”
dollars P S MC p MR=D=AR=P P D q Rate of output Q Q All firms maximize profits by producing where MR = MC. How do we know this from our previous discussion where we said firms and individuals make decisions “on the margin? ” because a firm would say to itself, “Can I get more for the next unit, than I would have to pay to produce it? ”
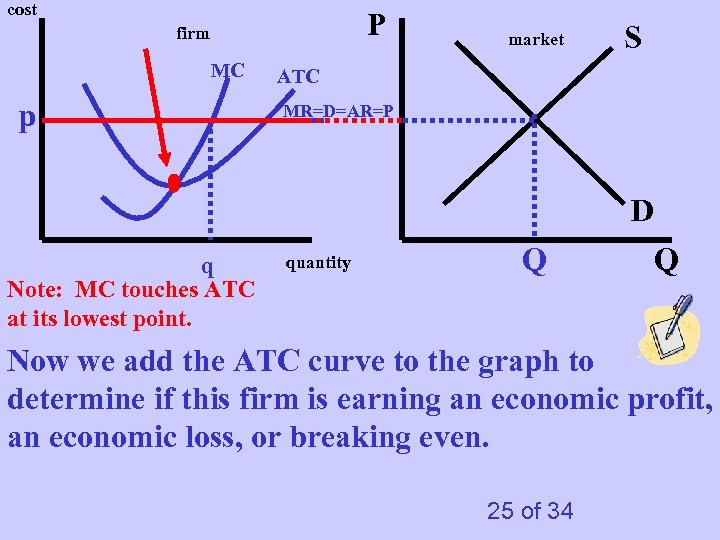 cost P firm MC p market S ATC MR=D=AR=P D q Note: MC touches ATC at its lowest point. quantity Q Q Now we add the ATC curve to the graph to determine if this firm is earning an economic profit, an economic loss, or breaking even. 25 of 34
cost P firm MC p market S ATC MR=D=AR=P D q Note: MC touches ATC at its lowest point. quantity Q Q Now we add the ATC curve to the graph to determine if this firm is earning an economic profit, an economic loss, or breaking even. 25 of 34
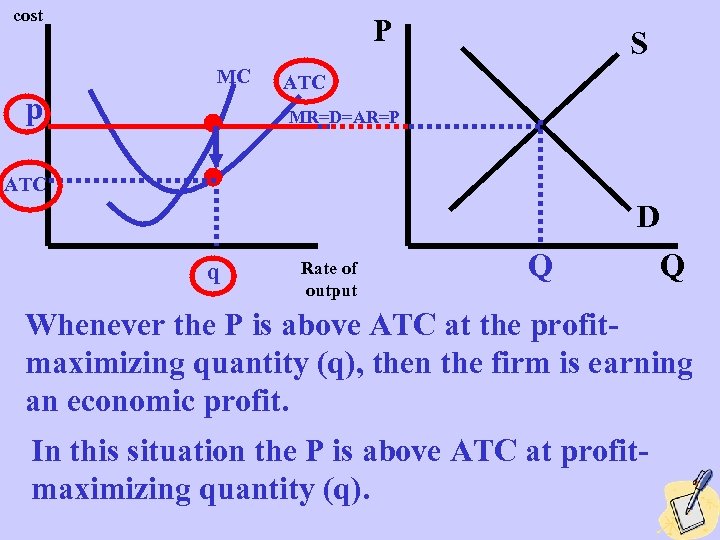 cost P MC p S ATC MR=D=AR=P ATC D q Rate of output Q Q Whenever the P is above ATC at the profitmaximizing quantity (q), then the firm is earning an economic profit. In this situation the P is above ATC at profitmaximizing quantity (q).
cost P MC p S ATC MR=D=AR=P ATC D q Rate of output Q Q Whenever the P is above ATC at the profitmaximizing quantity (q), then the firm is earning an economic profit. In this situation the P is above ATC at profitmaximizing quantity (q).
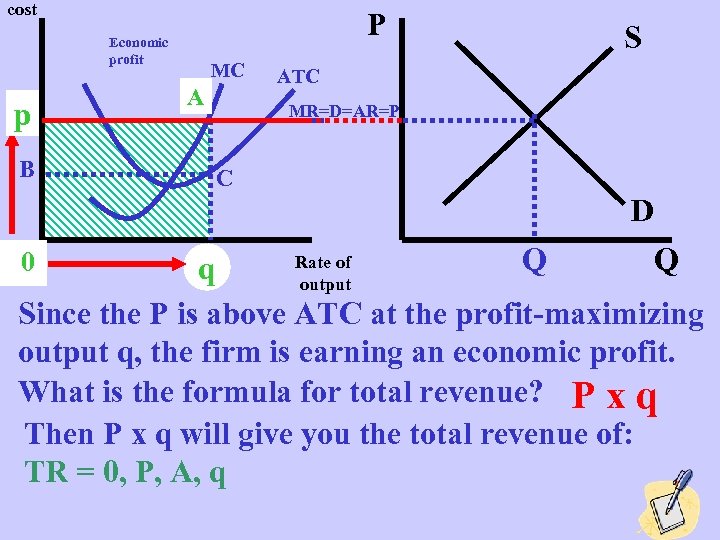 cost P Economic profit p p B MC A A S ATC MR=D=AR=P C D Rate of Q Q q q output Since the P is above ATC at the profit-maximizing output q, the firm is earning an economic profit. What is the formula for total revenue? P x q Then P x q will give you the total revenue of: TR = 0, P, A, q x 00
cost P Economic profit p p B MC A A S ATC MR=D=AR=P C D Rate of Q Q q q output Since the P is above ATC at the profit-maximizing output q, the firm is earning an economic profit. What is the formula for total revenue? P x q Then P x q will give you the total revenue of: TR = 0, P, A, q x 00
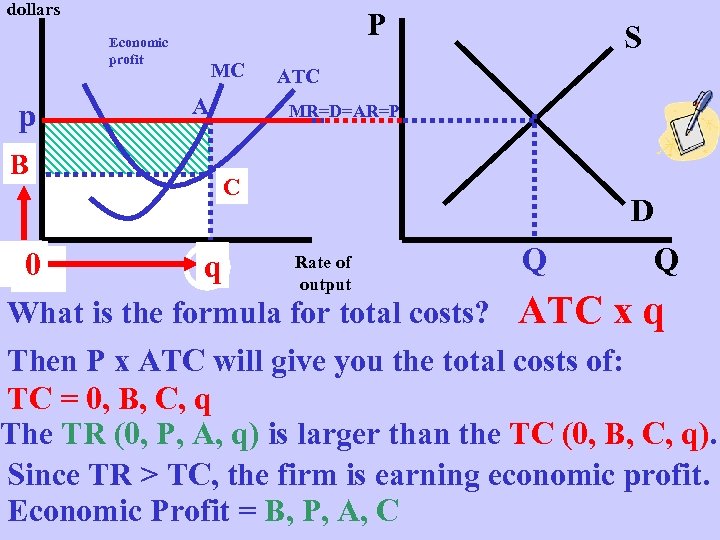 dollars P Economic profit p B B MC A S ATC MR=D=AR=P C C D Rate of Q Q q 0 x 0 output What is the formula for total costs? ATC x q Then P x ATC will give you the total costs of: TC = 0, B, C, q The TR (0, P, A, q) is larger than the TC (0, B, C, q). Since TR > TC, the firm is earning economic profit. Economic Profit = B, P, A, C
dollars P Economic profit p B B MC A S ATC MR=D=AR=P C C D Rate of Q Q q 0 x 0 output What is the formula for total costs? ATC x q Then P x ATC will give you the total costs of: TC = 0, B, C, q The TR (0, P, A, q) is larger than the TC (0, B, C, q). Since TR > TC, the firm is earning economic profit. Economic Profit = B, P, A, C
 Practice on a white board Write both team members’ names on the whiteboard. Draw a correctly labeled diagram showing both the industry and the individual firm where the firm is suffering an economic loss. Draw as large as possible still being easily legible. 29 of 34
Practice on a white board Write both team members’ names on the whiteboard. Draw a correctly labeled diagram showing both the industry and the individual firm where the firm is suffering an economic loss. Draw as large as possible still being easily legible. 29 of 34
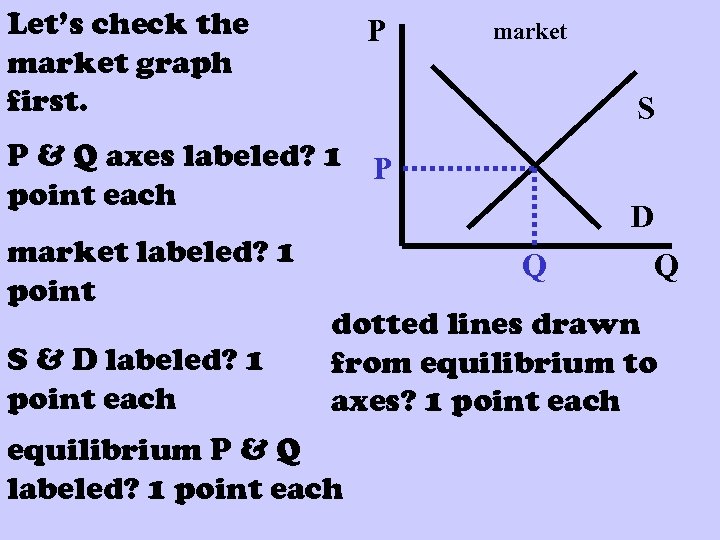 Let’s check the market graph first. P market S P & Q axes labeled? 1 P point each market labeled? 1 point S & D labeled? 1 point each D Q Q dotted lines drawn from equilibrium to axes? 1 point each equilibrium P & Q labeled? 1 point each
Let’s check the market graph first. P market S P & Q axes labeled? 1 P point each market labeled? 1 point S & D labeled? 1 point each D Q Q dotted lines drawn from equilibrium to axes? 1 point each equilibrium P & Q labeled? 1 point each
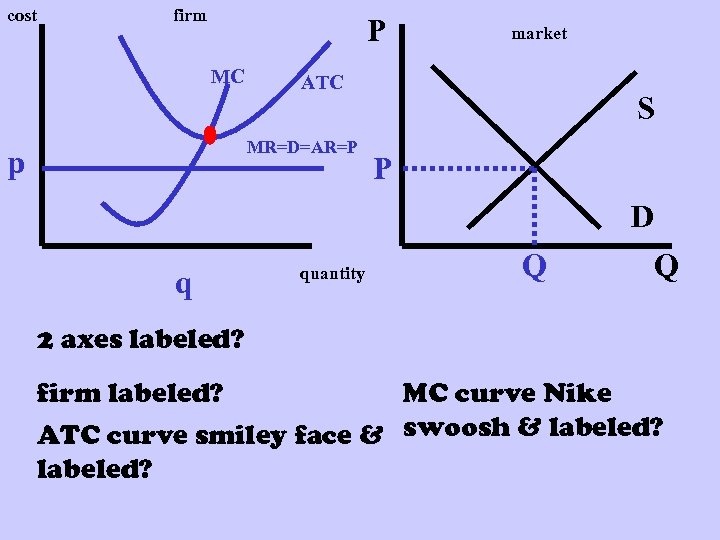 cost firm P MC ATC MR=D=AR=P p market S P D q quantity Q Q 2 axes labeled? firm labeled? MC curve Nike ATC curve smiley face & swoosh & labeled?
cost firm P MC ATC MR=D=AR=P p market S P D q quantity Q Q 2 axes labeled? firm labeled? MC curve Nike ATC curve smiley face & swoosh & labeled?
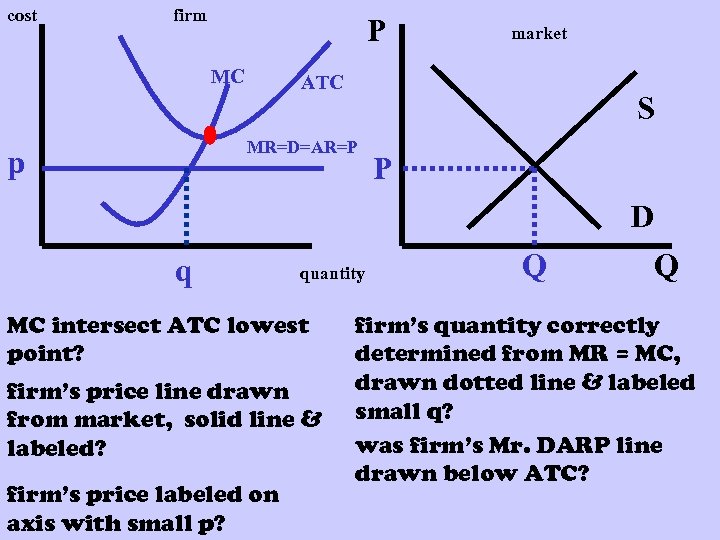 cost firm P MC ATC S MR=D=AR=P p market P D q quantity MC intersect ATC lowest point? firm’s price line drawn from market, solid line & labeled? firm’s price labeled on axis with small p? Q Q firm’s quantity correctly determined from MR = MC, drawn dotted line & labeled small q? was firm’s Mr. DARP line drawn below ATC?
cost firm P MC ATC S MR=D=AR=P p market P D q quantity MC intersect ATC lowest point? firm’s price line drawn from market, solid line & labeled? firm’s price labeled on axis with small p? Q Q firm’s quantity correctly determined from MR = MC, drawn dotted line & labeled small q? was firm’s Mr. DARP line drawn below ATC?
 Erase your white board. Write both team members’ names on the whiteboard. Draw a correctly labeled diagram showing both the industry and the individual firm where the firm is at zero economic profit. Draw as large as possible still being easily legible.
Erase your white board. Write both team members’ names on the whiteboard. Draw a correctly labeled diagram showing both the industry and the individual firm where the firm is at zero economic profit. Draw as large as possible still being easily legible.
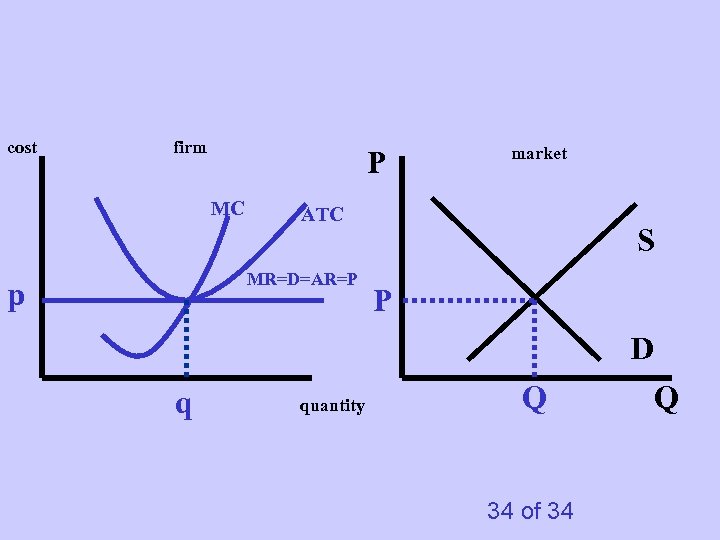 cost firm P MC ATC MR=D=AR=P p market S P D q quantity Q 34 of 34 Q
cost firm P MC ATC MR=D=AR=P p market S P D q quantity Q 34 of 34 Q


