 AND THE COURTS OF LAWS
AND THE COURTS OF LAWS
 The Code of English Law by Alfred the Great in the 9 th century Witenagemot – the council of powerful lords William the Conqueror – the Great Council (lords and bishops) Everything had been by the will of the monarch until Magna Carta was signed up
The Code of English Law by Alfred the Great in the 9 th century Witenagemot – the council of powerful lords William the Conqueror – the Great Council (lords and bishops) Everything had been by the will of the monarch until Magna Carta was signed up
 The mayor The aldermen (for each district) Constables = The City Watch (useless) Various executions (boiling alive, cutting off the ears, hands, whipping, a ducking stool, hanging at Tyburn…)
The mayor The aldermen (for each district) Constables = The City Watch (useless) Various executions (boiling alive, cutting off the ears, hands, whipping, a ducking stool, hanging at Tyburn…)
 Ludgate prison (for criminals) Newgate prison (for debtors) – was pulled down => The Central Criminal Court of London (Old Bailey) The Bow Street Runners (brothers Fielding)= Robin Redbreasts The Metropolitan Police (Sir Robert Peel) = “Bobbies” / “Peelers”
Ludgate prison (for criminals) Newgate prison (for debtors) – was pulled down => The Central Criminal Court of London (Old Bailey) The Bow Street Runners (brothers Fielding)= Robin Redbreasts The Metropolitan Police (Sir Robert Peel) = “Bobbies” / “Peelers”
 ER – Elisabeth Regina “Black Maries” “Pandas” 999 No weapon
ER – Elisabeth Regina “Black Maries” “Pandas” 999 No weapon
 Acts of Parliament are enforced through the various courts of justice considering the cases of their violation in the country=trying the cases=> trials 2 kinds of cases: - criminal cases (certain state law is broken) - civil cases (quarrels b/n certain people) Þ in England courts of 2 types – criminal and civil
Acts of Parliament are enforced through the various courts of justice considering the cases of their violation in the country=trying the cases=> trials 2 kinds of cases: - criminal cases (certain state law is broken) - civil cases (quarrels b/n certain people) Þ in England courts of 2 types – criminal and civil
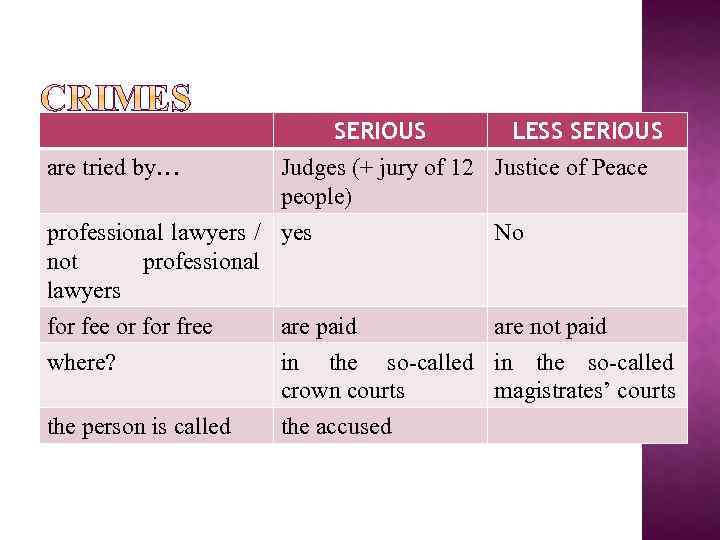 are tried by… SERIOUS LESS SERIOUS Judges (+ jury of 12 Justice of Peace people) professional lawyers / yes not professional lawyers No for fee or free where? are paid are not paid in the so-called crown courts magistrates’ courts the person is called the accused
are tried by… SERIOUS LESS SERIOUS Judges (+ jury of 12 Justice of Peace people) professional lawyers / yes not professional lawyers No for fee or free where? are paid are not paid in the so-called crown courts magistrates’ courts the person is called the accused
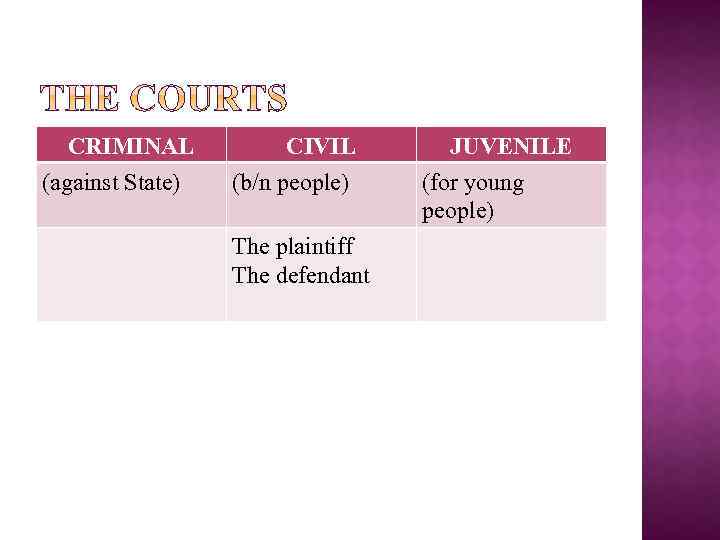 CRIMINAL (against State) CIVIL (b/n people) The plaintiff The defendant JUVENILE (for young people)
CRIMINAL (against State) CIVIL (b/n people) The plaintiff The defendant JUVENILE (for young people)
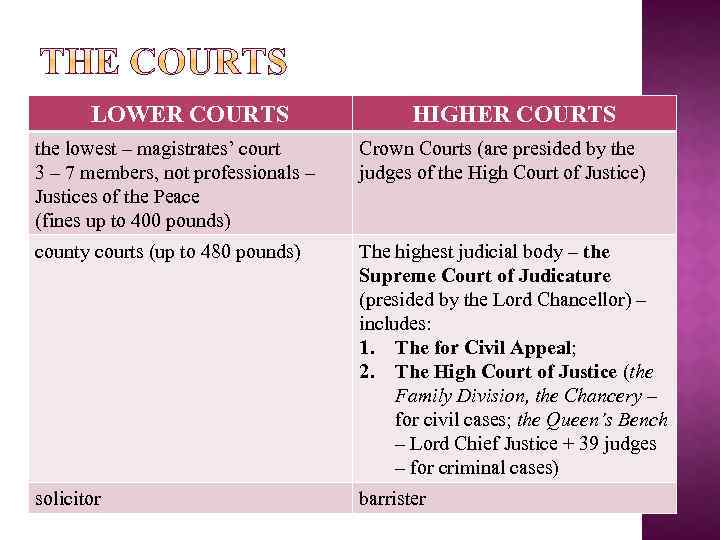 LOWER COURTS HIGHER COURTS the lowest – magistrates’ court 3 – 7 members, not professionals – Justices of the Peace (fines up to 400 pounds) Crown Courts (are presided by the judges of the High Court of Justice) county courts (up to 480 pounds) The highest judicial body – the Supreme Court of Judicature (presided by the Lord Chancellor) – includes: 1. The for Civil Appeal; 2. The High Court of Justice (the Family Division, the Chancery – for civil cases; the Queen’s Bench – Lord Chief Justice + 39 judges – for criminal cases) solicitor barrister
LOWER COURTS HIGHER COURTS the lowest – magistrates’ court 3 – 7 members, not professionals – Justices of the Peace (fines up to 400 pounds) Crown Courts (are presided by the judges of the High Court of Justice) county courts (up to 480 pounds) The highest judicial body – the Supreme Court of Judicature (presided by the Lord Chancellor) – includes: 1. The for Civil Appeal; 2. The High Court of Justice (the Family Division, the Chancery – for civil cases; the Queen’s Bench – Lord Chief Justice + 39 judges – for criminal cases) solicitor barrister