6f517013cc720fbbd57e701a3fc9a311.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 and not Conflict Management Resource Management and Resource Planning Conflict Planning J. J. Verplanke INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION
and not Conflict Management Resource Management and Resource Planning Conflict Planning J. J. Verplanke INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION
 Framework: issues Context of PSP § Planning of Resources § Management of Resources § Use of Resources GI as record of Changes and Dynamics Specific actors
Framework: issues Context of PSP § Planning of Resources § Management of Resources § Use of Resources GI as record of Changes and Dynamics Specific actors
 Framework: actors l Planners Experts l Managers Decision-makers l Users Stakeholders SCI to show Changes and Dynamics Specific knowledge
Framework: actors l Planners Experts l Managers Decision-makers l Users Stakeholders SCI to show Changes and Dynamics Specific knowledge
 Framework: knowledge § Expertise Science & Technology § Policy Governance & Institutions § Indigenous Experience/operational Combining/sharing information = knowledge Specific environment
Framework: knowledge § Expertise Science & Technology § Policy Governance & Institutions § Indigenous Experience/operational Combining/sharing information = knowledge Specific environment
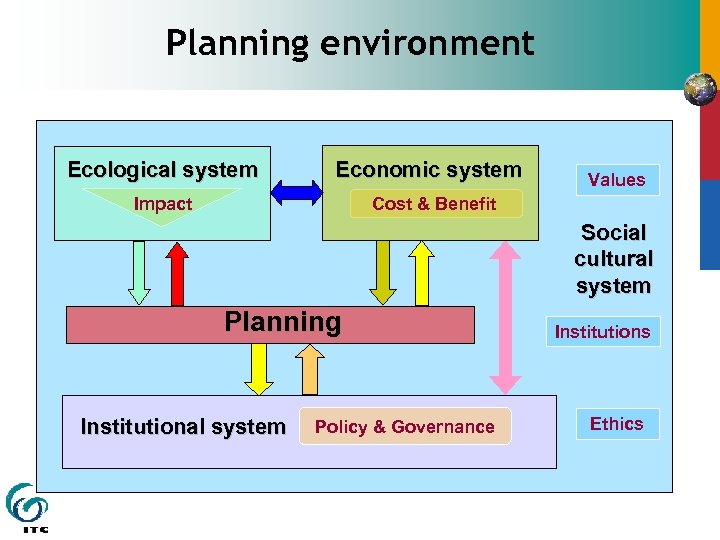 Planning environment Ecological system Economic system Impact Cost & Benefit Values Social cultural system Planning Institutional system Policy & Governance Institutions Ethics
Planning environment Ecological system Economic system Impact Cost & Benefit Values Social cultural system Planning Institutional system Policy & Governance Institutions Ethics
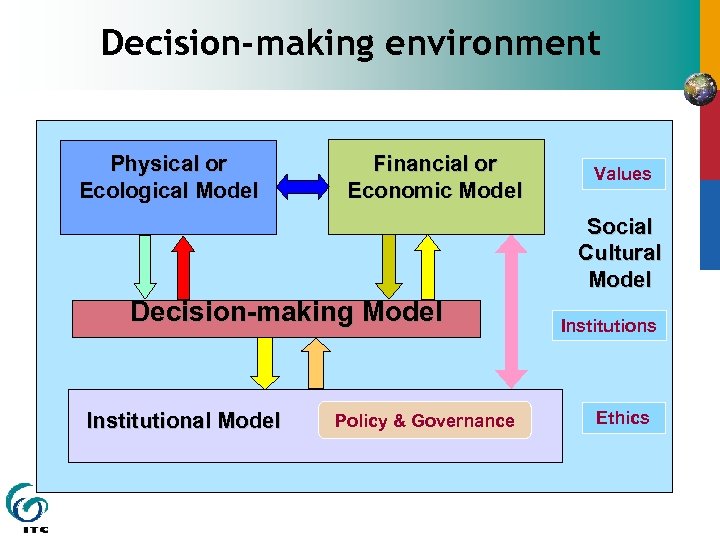 Decision-making environment Physical or Ecological Model Financial or Economic Model Values Social Cultural Model Decision-making Model Institutional Model Policy & Governance Institutions Ethics
Decision-making environment Physical or Ecological Model Financial or Economic Model Values Social Cultural Model Decision-making Model Institutional Model Policy & Governance Institutions Ethics
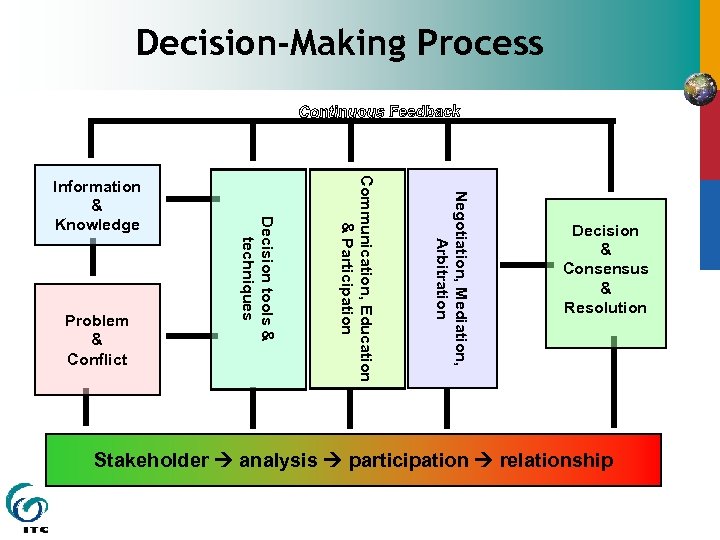 Decision-Making Process Negotiation, Mediation, Arbitration Communication, Education & Participation Problem & Conflict Decision tools & techniques Information & Knowledge Decision & Consensus & Resolution Stakeholder analysis participation relationship
Decision-Making Process Negotiation, Mediation, Arbitration Communication, Education & Participation Problem & Conflict Decision tools & techniques Information & Knowledge Decision & Consensus & Resolution Stakeholder analysis participation relationship
 Planner § Planner as a coordinator, § Planner as a facilitator, § Planner as a negotiator, § Planner as a meddler?
Planner § Planner as a coordinator, § Planner as a facilitator, § Planner as a negotiator, § Planner as a meddler?
 Planning in Theory 1. Find a problem 2. Make people aware 3. Let people participate 4. Make people understand 5. Construct a solution 6. Involve people in decision
Planning in Theory 1. Find a problem 2. Make people aware 3. Let people participate 4. Make people understand 5. Construct a solution 6. Involve people in decision
 Planning in Practice 1. Find a problem 2. Make people aware 3. Propose a solution 4. Make people angry 5. Try to explain 6. Control damage
Planning in Practice 1. Find a problem 2. Make people aware 3. Propose a solution 4. Make people angry 5. Try to explain 6. Control damage
 Planning as a means to: § § l l Make choices Allocate resources Achieve goals Schedule future activities Create conflicts Mitigate conflicts (inherent) (consequence)
Planning as a means to: § § l l Make choices Allocate resources Achieve goals Schedule future activities Create conflicts Mitigate conflicts (inherent) (consequence)
 Achieving Objectives § Impossible to satisfy everybody § NIMBY § LULU § BANANA § Not In My Back Yard § Locally Unwanted Land Use § Build Absolutely Nothing Anywhere Near Anyone
Achieving Objectives § Impossible to satisfy everybody § NIMBY § LULU § BANANA § Not In My Back Yard § Locally Unwanted Land Use § Build Absolutely Nothing Anywhere Near Anyone
 Stakeholders with different interests Get Discount Sell fuel Buy fuel Make Profit Conflicting Interests ? Who looks after my interests ? Matching Interests Stakeholders Natural Resources
Stakeholders with different interests Get Discount Sell fuel Buy fuel Make Profit Conflicting Interests ? Who looks after my interests ? Matching Interests Stakeholders Natural Resources
 Stakeholders and stakes (exercise) § Who are stakeholders? § § §
Stakeholders and stakes (exercise) § Who are stakeholders? § § §
 Stakeholders § Who are stakeholders? § Government § Directly affected (groups) § Indirectly affected (groups) those who are affected, but also those who can affect (the outcome)
Stakeholders § Who are stakeholders? § Government § Directly affected (groups) § Indirectly affected (groups) those who are affected, but also those who can affect (the outcome)
 Stakeholders § active and passive stakeholders: those who affect (determine) a decision or action, and those affected by this decision or action § primary stakeholders are the heart of interest or the intended beneficiaries of a project and secondary stakeholders § key stakeholders: significant influence
Stakeholders § active and passive stakeholders: those who affect (determine) a decision or action, and those affected by this decision or action § primary stakeholders are the heart of interest or the intended beneficiaries of a project and secondary stakeholders § key stakeholders: significant influence
 Stakeholder Analysis an instrument for understanding a system, and changes in it, by identifying stakeholders and assessing their relationships and their respective interests in that system.
Stakeholder Analysis an instrument for understanding a system, and changes in it, by identifying stakeholders and assessing their relationships and their respective interests in that system.
 Stakeholder Analysis means? combining information
Stakeholder Analysis means? combining information
 Stakeholder Attributes § The 4 most relevant attributes are: § interests § influence § importance § interaction
Stakeholder Attributes § The 4 most relevant attributes are: § interests § influence § importance § interaction
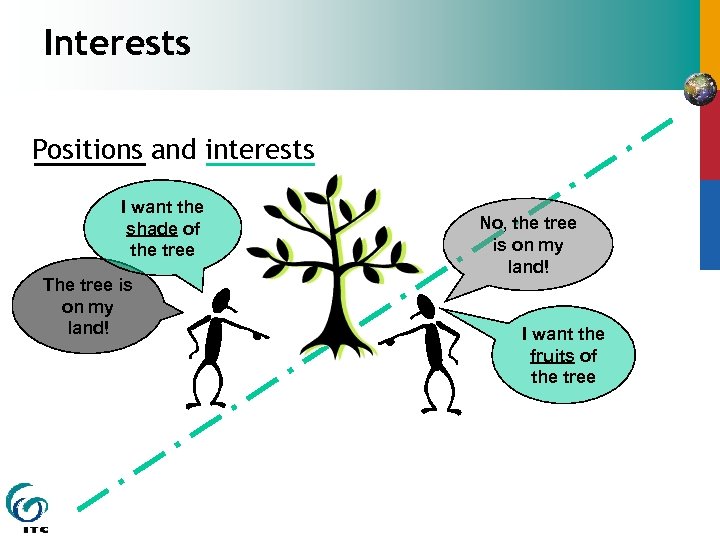 Interests Positions and interests I want the shade of the tree The tree is on my land! No, the tree is on my land! I want the fruits of the tree
Interests Positions and interests I want the shade of the tree The tree is on my land! No, the tree is on my land! I want the fruits of the tree
 Influence = Power § the power to control decisions. § the ability to persuade others into a course of action. § facilitate implementation of a project or affect it negatively. § power, mandate, legitimacy
Influence = Power § the power to control decisions. § the ability to persuade others into a course of action. § facilitate implementation of a project or affect it negatively. § power, mandate, legitimacy
 Importance : is the priority given to satisfying a stakeholders’ needs and interests § is most obvious when stakeholder interests in a project converge closely with the project's objectives. (purpose). § is therefore distinct from influence. (Stakeholders, who have weak capacity to participate and limited power to influence key decisions can have high importance).
Importance : is the priority given to satisfying a stakeholders’ needs and interests § is most obvious when stakeholder interests in a project converge closely with the project's objectives. (purpose). § is therefore distinct from influence. (Stakeholders, who have weak capacity to participate and limited power to influence key decisions can have high importance).
 Influence & Importance High Importance Low interests are. A be to protected ensure coalition of B support unlikely to be subject D of project source of significant C risk Low Influence High
Influence & Importance High Importance Low interests are. A be to protected ensure coalition of B support unlikely to be subject D of project source of significant C risk Low Influence High
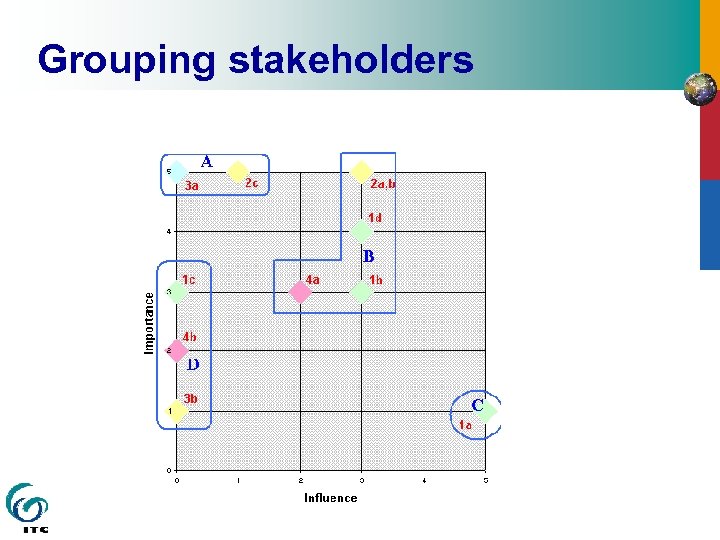 Grouping stakeholders
Grouping stakeholders
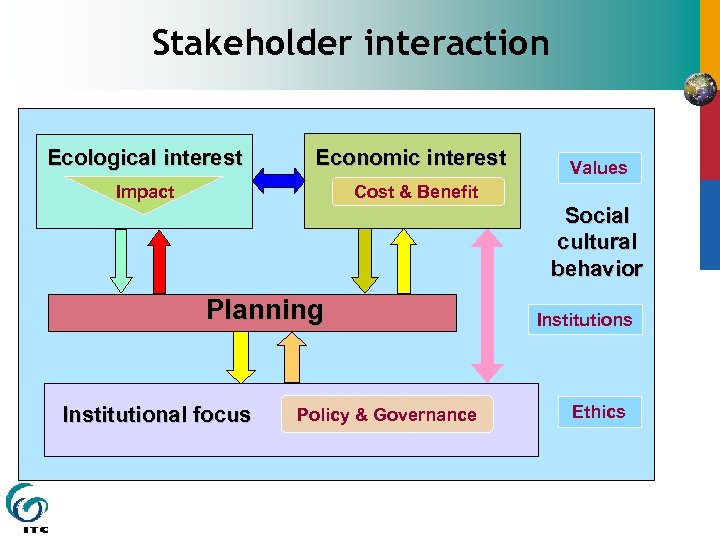 Stakeholder interaction Ecological interest Economic interest Impact Cost & Benefit Values Social cultural behavior Planning Institutional focus Policy & Governance Institutions Ethics
Stakeholder interaction Ecological interest Economic interest Impact Cost & Benefit Values Social cultural behavior Planning Institutional focus Policy & Governance Institutions Ethics
 Conflict sources § Different interests § Factual disagreement § Relational aspects Personal § Interdependence § Scarcity § Communication barriers Structural & Physical
Conflict sources § Different interests § Factual disagreement § Relational aspects Personal § Interdependence § Scarcity § Communication barriers Structural & Physical
 Level of confrontation § The level at which the conflict occurs (international, local). § The relative position or status of the stakeholders (conflicts at the same level or between levels). § The relative power of the stakeholders (who has responsibilities and who represents significant economical interests)
Level of confrontation § The level at which the conflict occurs (international, local). § The relative position or status of the stakeholders (conflicts at the same level or between levels). § The relative power of the stakeholders (who has responsibilities and who represents significant economical interests)
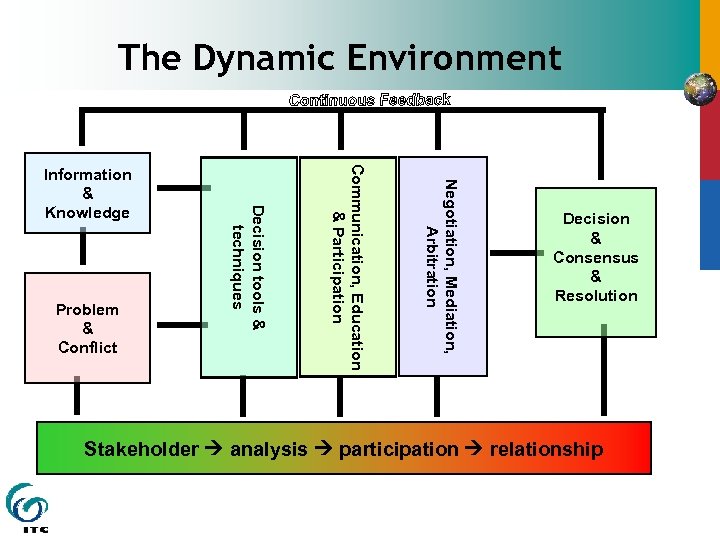 The Dynamic Environment Negotiation, Mediation, Arbitration Communication, Education & Participation Problem & Conflict Decision tools & techniques Information & Knowledge Decision & Consensus & Resolution Stakeholder analysis participation relationship
The Dynamic Environment Negotiation, Mediation, Arbitration Communication, Education & Participation Problem & Conflict Decision tools & techniques Information & Knowledge Decision & Consensus & Resolution Stakeholder analysis participation relationship
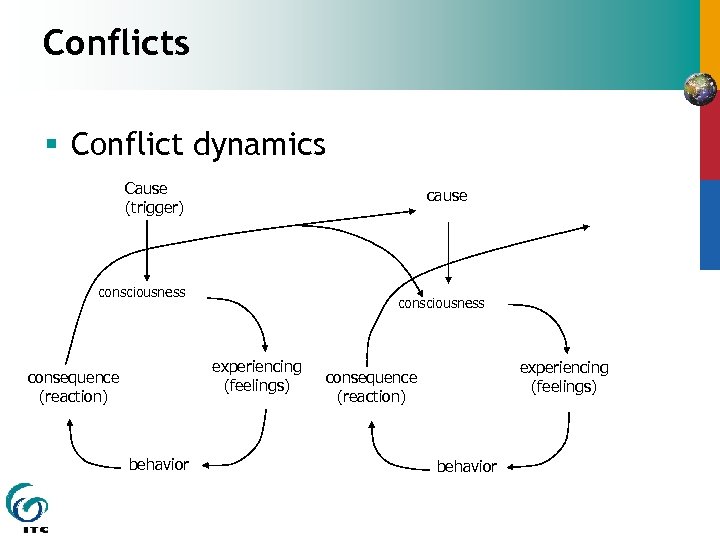 Conflicts § Conflict dynamics Cause (trigger) cause consciousness experiencing (feelings) consequence (reaction) behavior
Conflicts § Conflict dynamics Cause (trigger) cause consciousness experiencing (feelings) consequence (reaction) behavior


