4eebddb761acd4012b7cddd6cd4bd48a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Ancient Rome Chapter 5

Beginning of Civilization • Geography – Small mountains, large fertile plains • Settlement – Latins on the seven hills – Etruscans N. of Rome – Rome was built on Etruscan learning • Engineering, alphabet, architecture, and religion

Establishment of the Republic • 509 B. C. end of Etruscan rule • Establish a Republic – People choose some of the officials

The Republic • Original: – Patricians + 2 consuls = Senate – Patricians – members of the land-holding upper class – Consuls – elected to lead the Senate and control the Army • Serve one term, have to agree – Dictator – Emergency general for 6 Months • Cincinnatus – 15 days

Plebians want power • Plebians – mass population – Citizens with little political power – Later elect tribunes with veto • Laws of the Twelve Tables • How are you affected by this government set-up?

Assignment • Create a Pie Graphic Organizer that gives all of the information found in the Roman Cursus Honorum found on Page 152. Include the position of Dictator in your Organizer.
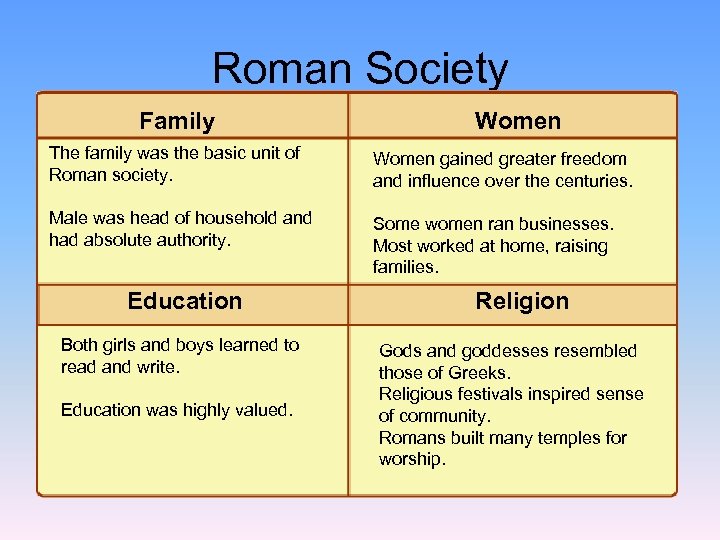
Roman Society Family Women The family was the basic unit of Roman society. Women gained greater freedom and influence over the centuries. Male was head of household and had absolute authority. Some women ran businesses. Most worked at home, raising families. Education Both girls and boys learned to read and write. Education was highly valued. Religion Gods and goddesses resembled those of Greeks. Religious festivals inspired sense of community. Romans built many temples for worship.

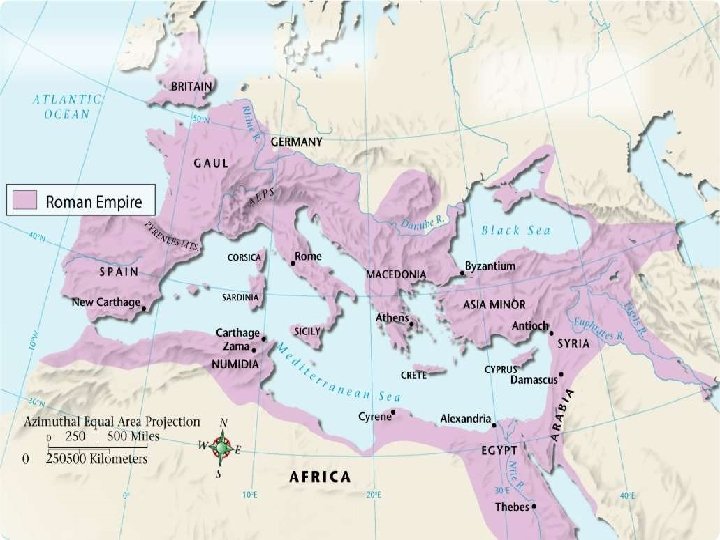
Roman Expansion • By about 270 B. C. , Rome controlled most of the Italian peninsula. • Why was Rome’s expansion in Italy successful? • Skilled diplomacy • Loyal, well-trained army – Army was organized into legions or groups of about 5000 men • Treated defeated enemies fairly – Let them keep their customs • Gave rights to conquered people

Republic to Empire • Punic Wars – 1 st Punic War • Rome defeats Carthage and wins the islands of Sicily, Corsica, and Sardinia – 2 nd Punic War • Hannibal marches all around through the Pyrenees and Alps and loses 1/3 of Army, but sweeps across Italy • Never captures Rome • Rome outflanks by sending an army to Carthage
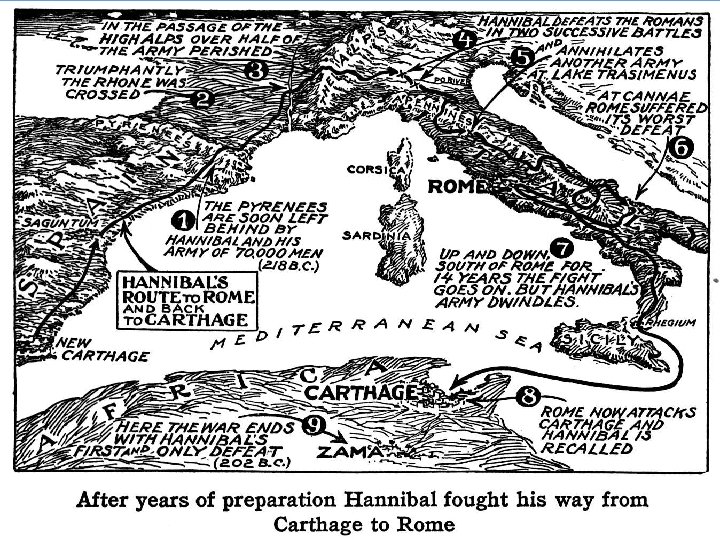

Punic Wars Continued • 3 rd Punic War – Rome destroys Carthage • Kill everyone • Sell survivors into slavery • Pour salt all over

“Supremacy and World Domination. ” • Imperialism – establishing control over foreign lands • Macedonia, Greece, Asia Minor • Egypt allies with Rome

Domestic Rome • New Wealthy Class – Trade, conquest, taxes • Latifundia – large estates bought by wealthy families – Slaves from war • How does Slavery hurt parts of the economy? – Small farmers, exports/imports, growing unemployment, rich/poor, corruption – Can these principles be tied to our economy today?

Attempts at Reform • Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus – Plebian brothers • Tiberius – elected Tribune in 133 – Distributed land to poor farmers • Gaius – elected Tribune in 123 – Use of public funds to buy grain to feed the poor • Both brothers and their followers were assassinated by members of the Senate

Decline of the Roman Republic • Civil Wars • Slave uprisings and revolts • Legions turn into professional armies

Julius Caesar • Military commander, Pompey was other commander • Completed the Roman takeover of Gaul • Pompey persuades Senate • Caesar defeats Pompey • Senate names him Dictator

Reforms of Caesar • • Public works to help unemployment Public land given to the poor Citizenship extended to more people Introduce new calendar – Based on Egyptian calendar – Our basic calendar today • Stabbed by members of the Senate in 44 B. C.

Civil War • Mark Antony + Octavian – Chief General + Grandnephew – Ally to hunt down murderers – Fight for power – Octavian is victorious over Antony/Cleopatra

Roman Empire • Octavian named Augustus – First citizen – Named successor and had absolute power

Government of Augustus • • Kept the Senate Created a Civil Service Opened high level jobs to ALL that qualify Use the census to create more fair taxes – Census – population count • Postal service • Issued new coins • Use jobless to build roads & temples, farming

Succession • Chosen – some good, some bad • Refer to the List

Pax Romana • “Roman Peace” • 200 yr from Augustus – Marcus Aurelius • Stable rule of an area the size of the U. S.

Entertainment • Circus Maximus – Chariot Race • Gladiators – typically slaves – Tame restless mobs

Roman Achievement • Greco-Roman Culture – Greek, Roman, & Hellenistic • Poetry – Virgil tried to show that Rome was as heroic as Ancient Greece • Satirize – to make fun of

Livy • Historian and Philosopher • Tried to establish patriotism and traditionalism • Was disappointed by the lack of heroism in the history of Rome

Art • Stresses Realism and Individualism • Mosaic – picture made from chips of colored stone or glass

Architecture • • • Focused on grandeur Rounded Dome Pantheon Columns Examples around here?

Science and Math • Engineering – use of math and science to develop useful structures and machines – Roads, bridges, harbors, aqueducts – Aqueducts – bridge-like stone structures that carried water from the hills into Roman cities • Ptolemy – Earth is center of the Universe

Law • “Rule of Law” – stability and peace through accepted norms • Influences on the U. S. – Innocent until Proven Guilty – Face accuser and offer defense – Guilt beyond reasonable doubt through evidence – Judges interpret the law – Penalties depend on social class

Early Religion in Rome • Polytheistic, mystery religions, cults • Religious tolerance • Still had to acknowledge the divine spirit of the Roman emperor and honoring the ancient Roman Gods

Judea • Roman controlled • Jews excused from worshipping Roman Gods • Messiah – anointed king sent by God • Jews try to rebel – Rome puts down rebellion and destroys the Jewish temple – Later rebellions result in destruction of Jerusalem

Christianity • • Knowledge of Jesus comes from bible Jesus born about 4 B. C. 12 apostles – assistants of Jesus Teachings – Stemmed from Jewish traditions – Took on the name Christians “followers of Christ”

Paul • Never met Jesus • Was actually a persecutor of Christians • Converted and spread Christianity to many areas of the world

Christian Persecution • Persecuted for not honoring the emperor or Roman Gods • Martyrs - Christians killed by persecution

Spread of Christianity • Spread easily through Greek philosophy and pagan traditions – Method used throughout history • 313 A. D. Constantine – Issued the Edict of Milan – All Roman citizens given freedom of religion

Church Heirarchy • Pope/Patriarchs – Bishop • Priest • Clergy – the group of people who conduct Christian services • Bishop – a high Church official responsible for everyone in the diocese • Patriarch – most important bishops • Pope – Patriarchs in Rome • Heresies - beliefs against the church

Fall of the Empire • Politically – Fighting for the throne – 26 emperors in 50 years • Only one died of natural causes • Socially and Economically – Heavy Taxes – Unofficial Slavery

Diocletian • Tried to restore power • Divided empire into two – He controlled the Rich Eastern Part – Maximian was appointed to rule the Western Part • Fixed prices to try to control inflation – rapid rise in prices • Farmers were required to stay on their land • Sons in Father’s foot steps

Constantine • Granted Religious toleration • Established a new capital at Byzantium -> Constantinople

Invasion • Huns – from central Asia, migrate to Europe – Overran the Visigoths, Ostrogoths, and other Germanic tribes • Invasion causes Rome to give up Britain, France, and Spain • Rome is eventually overrun and sacked by the Visigoths • Attila attacks most of Europe • Odoacer kicks the Roman emperor in the West out of the Throne – This marks the historical end of the Roman Empire

Why did Rome Fall? • Military Attacks – Invasions, military consisted of mercenaries • Political Turmoil – Lost support of the people b/c it was oppressive and authoritarian – Corruption of leaders – Civil Wars – Division of the Empire during a crucial period • Economic Weakness – Heavy taxes – Reliance on Slaves reduced technological innovation

Why did Rome Fall? • Economic Weakness cont. – Farmers abandoned land – Middle class sank into poverty – Population decline from warfare and disease • Social Decay – Loss of values (Patriotism, discipline, devotion to duty) – Upper class quit leading and started spending

Did Rome Fall? • Why or Why not?
4eebddb761acd4012b7cddd6cd4bd48a.ppt