fd5def4216578496f6411986313ec3f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71

Ancient Israelites They believed in one God who set down moral laws for His people. They recorded their history in the Hebrew Bible.

Ancient Israel

Who were the Israelites? Monotheism Spoke Hebrew Judaism – Jews Influenced Christianity and Islam Helped shape beliefs and practices of societies in Europe and America Hebrew language Wrote down their history and religious beliefs in the Hebrew Bible known as the Old Testament Herders and traders Came from Mesopotamia to Canaan (present day Lebanon, Israel, and Jordan) Descendents of Abraham

Abraham God (Yahweh) told him to leave Mesopotamia and go to Canaan. God’s promise (covenant) Lived in Canaan for 100 years then a drought occurred and some went to Egypt
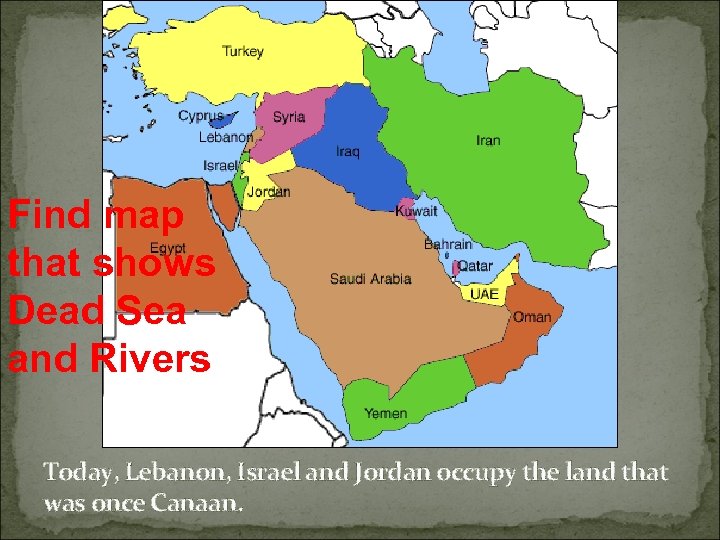
Find map that shows Dead Sea and Rivers Today, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan occupy the land that was once Canaan.

Jacob Abraham’s grandson Also called Israel – means “one who struggles with God” Later given to his descendants 12 sons divided into tribes (12 tribes of Israel)

From Slavery to Freedom Israelites were enslaved to build pyramids for the Pharaoh. Baby boys –Nile River Moses – tended sheep Burning bush 10 plagues

Moses An illustrated story of Moses

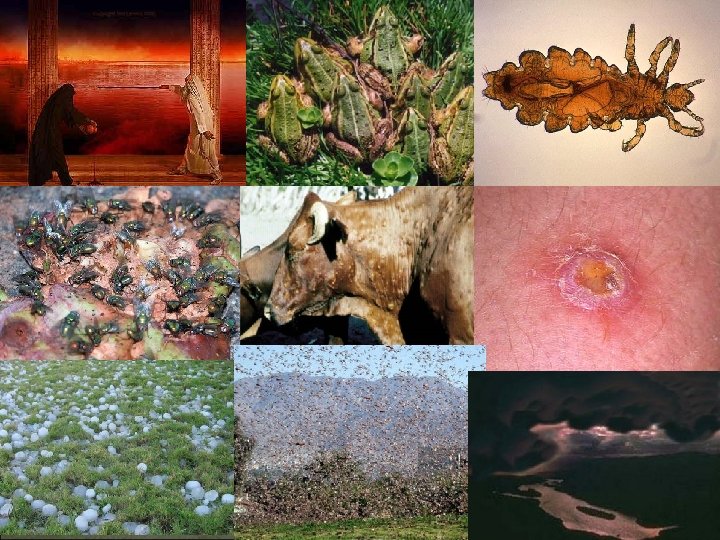
10 Plagues Turn Water to blood 2. Frogs 3. Lice 4. Flies 5. Disease on livestock 6. Boils 7. Hail 8. Locusts 9. Darkness 10. Death of 1 st born of all Egyptian humans and animals Exodus 7: 19 -11: 5 1.


Parting of the Red Sea Known as the Exodus Passover, Jewish holiday celebrates this event

Journey to Canaan Sinai Desert Mount Sinai – where Moses received laws from God or the Torah

Torah Later became the 1 st part of the Hebrew Bible Torah described a covenant (agreement) with God in which God promised to return the Israelites to Canaan if they followed His laws. Explained what God considered to be right and wrong Ten Commandments

Ten Commandments Shaped basic moral laws of many nations Helped develop a belief in the “rule of law”– idea that laws should apply to everyone equally Exodus 20: 1 -17

Ten Commandments How many of the commandments tell people how to interact with other people? 6 (commandments 5 - 10) How many tell them how to worship and show respect for God? 4 (commandments 1 - 4)

Ark of the Covenant Ark of A gold-plated wooden box (acacia wood) 45” long and 27” wide and 27” deep 4 gold rings on corners with 2 gold rings on side where poles of acacia wood overlaid in gold were used to carry it Contents: stone tablets on which the Ten Commandments were carved, a golden pot of manna from the wilderness journey, and Aaron’s rod Most sacred artifact of the Israelites

The Promised Land 40 years Moses never lived to see it. Joshua – new leader Had to fight to regain it Jericho marched around walls for 6 days while 7 priests blew their trumpets on 7 th day – trumpets blew one last time and Israelites raise a great shout 3 more wars Land divided by 12 tribes

Judges Leadership Usually a military leader Commanded 1 or 2 tribes (seldom all 12) Barak, Gideon, Samuel, Eli, Samson, and others including Deborah told Barak to attack the army of the Canaanite king Jabin and went along to battlefield as an adviser. King Jabin was destroyed around 1125 B. C. Walled towns for protection Created an alphabet

Phoenician Alphabet Phoenicians were skilled sailors and traders (with Greece, Spain, and western Africa). Spread ideas and goods like an alphabet Alphabet made writing simpler and easier to keep records. Brought the idea to Greeks who passed it on to the Romans which is the basis for most Western alphabets


Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Why was the religion of Israel unique in the ancient world? What is the Torah, and how did the Israelites obtain it? What was the importance of the Phoenician alphabet? What problems did the Israelites face when they returned to Canaan? Which one of the Ten Commandments do you think is most important today?

Belief that God gave Canaan to the Jews Belief in one god Jewish Ideas Ten Commandments Hebrew Bible

The Kingdom of Israel Creation of the kingdom of Israel; its great kings (Saul, David, and Solomon); and the challenges Israel faced
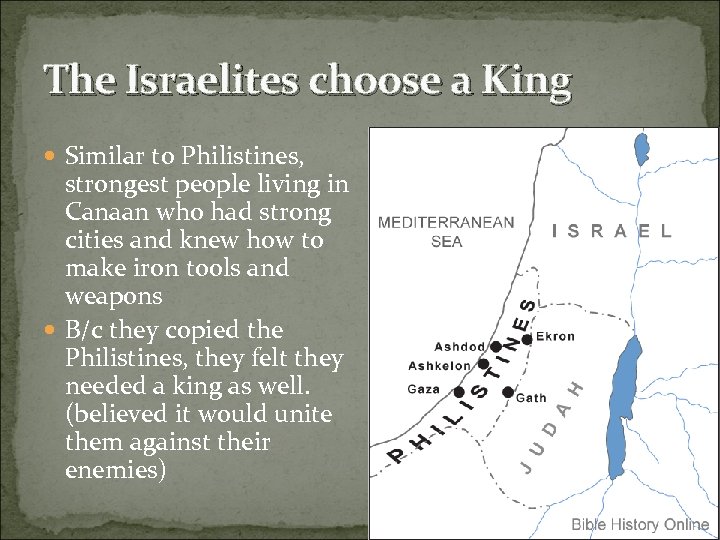
The Israelites choose a King Similar to Philistines, strongest people living in Canaan who had strong cities and knew how to make iron tools and weapons B/c they copied the Philistines, they felt they needed a king as well. (believed it would unite them against their enemies)

The Rule of Saul 1020 B. C. – Samuel asked to choose a king. What is a prophet? Samuel’s warning Samuel anointed their choice, Saul (warrior-farmer) as king. What does this mean? Saul – tall, handsome, and had won many battles Saul disobeyed some of God’s commands. Samuel was instructed by God to anoint a new king (David) in secret.

David Known for his bravery and leadership David and Goliath Put in charge of army by Saul “Saul has slain his thousands, and David his ten thousands. ” Took throne in 1000 B. C. Drove Philistines from the area Created an empire Tribute Heavy taxes to expand Israel’s capital, Jerusalem. temple

Solomon David’s son Built splendid stone temple in Jerusalem In Hebrew Bible, he is known for his proverbs.

Proverbs Wise sayings Happy the man who finds wisdom, the man who gains understanding! -- Proverbs 3: 13 If you are wise, it is to your own advantage; and if you are arrogant, you alone shall bear it. -- Proverbs 9: 12 Hatred stirs up disputes, but love covers all offenses. -- Proverbs 10: 12

Proverbs Between the devil and the deep sea To choose between two equally bad alternatives in a serious dilemma. Where there's a will there's a way When a person really wants to do something, he will find a way of doing it. A burnt child dreads fire A bad experience or a horrifying incident may scar one's attitude or thinking for a lifetime. First come, first served The first in line will be attended to first. A friend in need is a friend indeed A friend who helps when one is in trouble is a real friend. "Better to remain silent and be thought a fool than to speak out and remove all doubt. ” -- Abraham Lincoln

Benjamin Franklin’s proverbs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. "Well done is better than well said" "A lie stands on one leg, the truth on two" "God helps those who help themselves" "A penny saved is a penny earned" "Early to bed, early to rise makes a man healthy, wealthy, and wise" "There is no little enemy" "It is hard for an empty sack to stand upright" "When the well is dry, they know the worth of water" "Drive the business, let not drive thee" "Kill no more pigeons than you can eat" "The sleeping fox catches no poultry" "Think of the things, whence you came, where are you going, and to whom you must account" "Energy and persistence conquer all things"

Solomon continued Many Israelites hated his rule. Taxed people to pay for his great buildings List positive and negative aspects of paying taxes. Made young men work in mines of neighboring countries to make more money Death – 10 of 12 tribes set up their own nation in the north
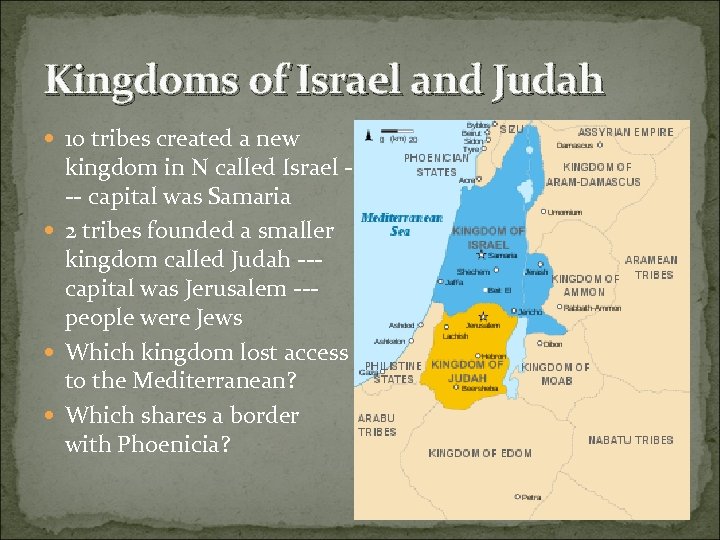
Kingdoms of Israel and Judah 10 tribes created a new kingdom in N called Israel -- capital was Samaria 2 tribes founded a smaller kingdom called Judah --capital was Jerusalem --people were Jews Which kingdom lost access to the Mediterranean? Which shares a border with Phoenicia?

Kingdoms felt threatened by their powerful neighbors. Prophets brought hope – emphasizing that people should please God by leading a moral life and helping others.

The Fall of the Kingdoms Assyrians and Chaldeans were building empires in SE Asia Israel 722 B. C. – were conquered by the Assyrians scattering the 10 tribes across their empire. New culture developed called Samaritans. “lost tribes of Israel”
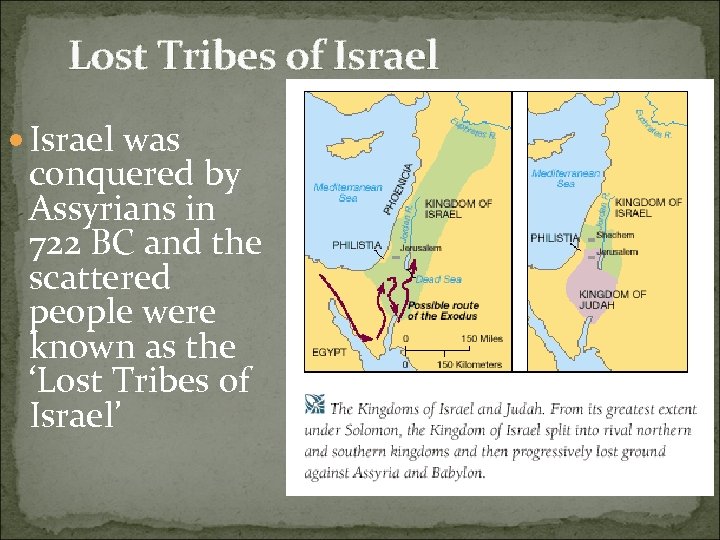
Lost Tribes of Israel was conquered by Assyrians in 722 BC and the scattered people were known as the ‘Lost Tribes of Israel’

The Fall of the Kingdoms Judah Judaism developed from the religious practices of the tribes of Judah. 620 B. C. – conquered by Egyptians keeping their king but paying tribute to Egypt Chaldeans conquered Egypt.

King Nebuchadnezzar Chaldean king 597 B. C. – captured Jerusalem punishing the Jews severely Made 10, 000 Jews leave Jerusalem and move to Babylon, Chaldean capital. Appointed a new Jewish king Prophet Jeremiah warned the new Jewish king that planning a revolt would be dangerous. 586 B. C. – destroyed temple; Babylonian captivity

Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Why did the Assyrians and the Chaldeans want to control the land belonging to the Israelites? Why was David anointed king while Saul was still in charge of the Israelites? Who were the prophets, and why were they important to the Israelites? What happened to the Israelites after the death of Solomon? Who were the Samaritans? Why do you think the Assyrians, and later the Chaldeans, moved Jews away from Israel and Judah after those areas were conquered?
King David King Solomon

King David King Solomon Drove the Philistines from Israel and created an empire Built a temple in Jerusalem Built Jerusalem Known for his proverbs Wrote many psalms

The Growth of Judaism Jews continued their religion during their exile in Babylon.

Exile and Return Babylonian exile Their religion became known as Judaism. Sabbath Synagogues Ruins of the Ancient Synagogue at Bar'am

The Torah Ark of the Ari Ashkenazi Synagogue The Karaite Synagogue in the Old City (Jerusalem) Belz Great Synagogue in Jerusalem (largest)

Why did the Jews Return to Judah? 500 s B. C. – Persians defeated Chaldeans and Babylon 538 B. C. – Persian king Cyrus permitted Jews to return to Judah. Rebuilt Jerusalem and the temple Religious leaders Scribes Torah Hebrew Bible

What is in the Hebrew Bible? Series of 34 books collected The Torah, the Prophets, and the Writings –added later Books of poetry, literature, and proverbs Genesis

Genesis 1 st book of Torah Noah, ark, Flood Rainbow Babel

Looking toward the future God’s plan for a peaceful future Book of Daniel Jews believed that evil and suffering would eventually be replaced by goodness. Christians and Muslims share this idea of good triumphing over evil. 334 B. C. – Alexander the Great 331 B. C. – he defeated the Persians and introduced the Greek language and ways to Judah.

Diaspora Jews – Babylon, Egypt, lands bordering Mediterranean Sea This is known as Diaspora --- scattering of Jews outside of Israel and Judah Greek word that means “scattered. ” Jews learned Greek language and ways but remained loyal to Judaism.

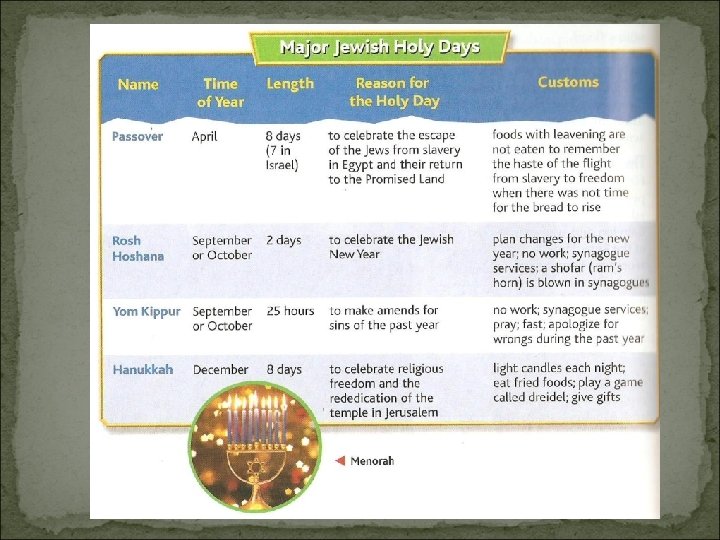
Maccabees 168 B. C. – Greek ruler Antiochus controlled Judah. Jews made to worship Greek gods and goddess. Judas Maccabeus, a priest, along with followers rebelled. The Maccabees Hanukkah

Jewish Culture Shaped by religion Laws affected daily life

Family life Great importance Sons – valued especially carried on family name Became head of household upon father’s death Education 1 st teachers were their mothers Elders took over religious education of boys (Torah) Mothers educated daughters at home

Ruth and Naomi Their relationship shows importance of family love and devotion. Book of Ruth in Hebrew Bible Naomi wants to return home after death of husband sons. Ruth to Naomi – “Wherever you go, I will go; wherever you lodge; I will lodge; your people shall be my people, and your God my God. ” Boaz marries Ruth and they have Obed is the grandfather of David.

Jewish Diet Under Jewish law, Jews could only eat certain animals. Beef and lamb, not pork scaly fish like salmon not shellfish or smooth skin fish like eel Laws – kashrut – “that which is proper” Kosher Ancient times – meals were made up of fish, fruit, veggies, and barley bread. Beverages were mainly milk, water, wine, and beer.


Jewish Clothing No mixing of fabrics Flax or wool but not combined Men tunics made of linen next to their skin (some layered) Cold weather – wool or sheepskin cloaks Heads – caps or turbans sandals Women Draped in long, simple dresses Covered heads with shawls Wealthy wore leather shoes, makeup, and jewelry

The Jews and the Romans Under Roman rule, the Jews were divided and rebellious. In response, the Romans destroyed the temple and exiled the Jews.

King Herod Most famous king Known for additions made to Jewish temple in Jerusalem Division after the Herod’s death

Pharisees and Taught the Torah and how to apply its laws to daily life Taught in synagogues and were supported by the common people Support of the oral traditions Believed these were very important in helping people obey the commandments Sadducees Accepted the Torah More concerned about how it applied to priests in Temples Disagreed with Pharisees teachings Emphasized written law and commmandments

Essenes A 3 rd group Priests who broke away from the Temple in Jerusalem Desert Praying and waiting for God to deliver the Jews from the Romans Strictly followed written law

Dead Sea Scrolls Ancient scrolls found in A. D. 1947 in caves near the Dead Sea Helped historians know more about Judaism during Roman times

Jewish Revolts Waiting for a messiah Zealots A. D. 66 –Zealot revolt Jews A. D. 70 – Romans retook Jerusalem killing thousands of Jews. Revolted again in A. D. 132 Ended in 3 yrs – Romans forbade Jews to live in or visit Jerusalem Palestine

Jewish Teachers Rabbis – teachers of the Torah Yohanan ben Zaccai – famous rabbi Founded a school in northern Palestine – center of Torah studies Commentaries (Talmud – Hebrew word for “learning or study”) A. D. 1947 – Palestine divided Israel – A. D. 1948

So that lives could be saved and certain important business carried out on the Sabbath, etc.

Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How did Alexander the Great affect the Israelites? What was Diaspora? What was education like within a Jewish family? Who was Yohannan ben Zaccai, and why was he important? Do you think that Jewish beliefs and values would have spread so widely if the lands of Israel and Judah had not been conquered by other peoples? Explain.

1. God exists. 2. God is one and unique. 3. God is eternal. 4. Prayer is to be directed to God alone. 5. The words of the prophets are true. 6. Moses was the greatest prophet, and his prophecies are true. 7. The Torah was given to Moses. 8. There will be no other Torah. 9. God knows the thoughts and deeds of men. 10. God will reward the good and punish the wicked. 11. The Messiah will come. 12. The dead will be resurrected.

Impact of Ancient Israel Covenant = formal agreement between Hebrews and God (Yahweh); Hebrews worshipped God and only God, and in return, they would be God’s Chosen People and given Canaan as the Promised Land Spiritual ideas profoundly influenced Western culture, morality, ethics and conduct Three of the world’s most dominant religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam all derive their roots from the spiritual beliefs of the Ancient Israelites
fd5def4216578496f6411986313ec3f8.ppt