de33e85b15a05825c9c29f306d6447fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece
 Greek Mythology • What is Mythology? • Trojan War – Homer • Iliad • Odyssey • Olympic Gods/ Creation of the World
Greek Mythology • What is Mythology? • Trojan War – Homer • Iliad • Odyssey • Olympic Gods/ Creation of the World
 Greece • • • Mythology Philosophy Democracy Architecture Arts Olympics • • City-States Persian Wars Peloponnesian War Phillip II of Macedonia • Alexander the Great
Greece • • • Mythology Philosophy Democracy Architecture Arts Olympics • • City-States Persian Wars Peloponnesian War Phillip II of Macedonia • Alexander the Great
 Greek City-States • Sparta • Athens
Greek City-States • Sparta • Athens
 Sparta
Sparta
 Spartan Society • Agriculture Based • Invaded neighboring city-states and enslaved the captured • Demographics – 10, 000 Spartans – 200, 000 Other • Perioeci- artisans, merchants • Helots- slaves • 650 BC Helots revolted • Militaristic Society
Spartan Society • Agriculture Based • Invaded neighboring city-states and enslaved the captured • Demographics – 10, 000 Spartans – 200, 000 Other • Perioeci- artisans, merchants • Helots- slaves • 650 BC Helots revolted • Militaristic Society
 Militaristic Society • Spartan Men starved to be soldiers • Women starved to have soldier sons • Spartans hated Greeks who lived behind walls • Inspected babies and if unhealthy they would be left on the hillside to die
Militaristic Society • Spartan Men starved to be soldiers • Women starved to have soldier sons • Spartans hated Greeks who lived behind walls • Inspected babies and if unhealthy they would be left on the hillside to die
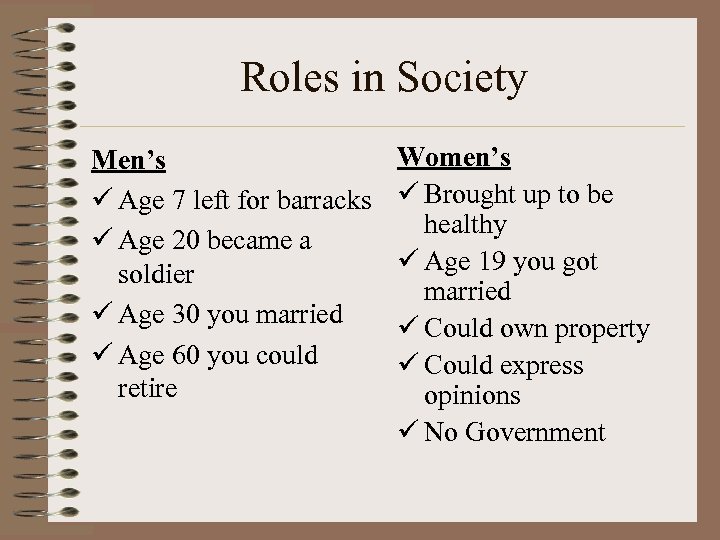 Roles in Society Men’s ü Age 7 left for barracks ü Age 20 became a soldier ü Age 30 you married ü Age 60 you could retire Women’s ü Brought up to be healthy ü Age 19 you got married ü Could own property ü Could express opinions ü No Government
Roles in Society Men’s ü Age 7 left for barracks ü Age 20 became a soldier ü Age 30 you married ü Age 60 you could retire Women’s ü Brought up to be healthy ü Age 19 you got married ü Could own property ü Could express opinions ü No Government
 Spartan Government • • Two Joint Kings ruled over Military Assembly/ All men over 20 Five overseers –ephors. Counsel of Elders Drawbacks • No new ideas • Lagged behind on literature
Spartan Government • • Two Joint Kings ruled over Military Assembly/ All men over 20 Five overseers –ephors. Counsel of Elders Drawbacks • No new ideas • Lagged behind on literature
 Athens
Athens
 Athens • Pre-Athens • 4 Tyrants • Athenian Democracy
Athens • Pre-Athens • 4 Tyrants • Athenian Democracy
 Athens Pre- Athens 600 BC - Government needs to change Ø Only men whose father and grandfather lived in Athens could participate in government Ø Non land owning citizens could not participate in government Ø Free foreigners could not own land nor participate in government
Athens Pre- Athens 600 BC - Government needs to change Ø Only men whose father and grandfather lived in Athens could participate in government Ø Non land owning citizens could not participate in government Ø Free foreigners could not own land nor participate in government
 Athens 507 BC a new constitution was written “All free men could participate in government regardless of their class”
Athens 507 BC a new constitution was written “All free men could participate in government regardless of their class”
 Athens Four Tyrants • 621 BC- Draco: – written law code/ harsh • 594 BC- Solon: – – Freed all Debts Turned Grain to cash crops Fathers teach trade to sons Extended citizenship to artisans and merchants – Created a two house legislation/ Council of 500 and Assembly • 546 BC Peisistratus – Divided large estates – Extended citizenship : more citizens – Provided poor w/ loans – Put poor to work • 508 BC Cleisthenes – Set up Democracy
Athens Four Tyrants • 621 BC- Draco: – written law code/ harsh • 594 BC- Solon: – – Freed all Debts Turned Grain to cash crops Fathers teach trade to sons Extended citizenship to artisans and merchants – Created a two house legislation/ Council of 500 and Assembly • 546 BC Peisistratus – Divided large estates – Extended citizenship : more citizens – Provided poor w/ loans – Put poor to work • 508 BC Cleisthenes – Set up Democracy
 Athenian Democracy • Assembly (ALL) – – Freedom of Speech Pass Laws Supreme Court Choose 10 Generals • Council of 500 (Lottery) – Taxes – Treaties – Public works • Jury System – 201 -1001 members • Ostracism – 6, 000 exiled
Athenian Democracy • Assembly (ALL) – – Freedom of Speech Pass Laws Supreme Court Choose 10 Generals • Council of 500 (Lottery) – Taxes – Treaties – Public works • Jury System – 201 -1001 members • Ostracism – 6, 000 exiled
 Athenian Education • • All sons must be educated Girls learned household duties Wealthy sons learned through private tutors Others paid fee for private school Age 7 -18 Text books Iliad and Odyssey Curriculum: - Arithmetic, Geometry, Drawing, Music, Gymnastics, and Rhetoric (Teens) • Two years of Military, and take oath
Athenian Education • • All sons must be educated Girls learned household duties Wealthy sons learned through private tutors Others paid fee for private school Age 7 -18 Text books Iliad and Odyssey Curriculum: - Arithmetic, Geometry, Drawing, Music, Gymnastics, and Rhetoric (Teens) • Two years of Military, and take oath
 Persian War
Persian War
 Persian Wars • 400’s Persians began to attack the Greeks • Led by Cyrus II in 546 BC Persians conquered Ionia • Ionian’s could keep their own government, but Persians were considered to be barbarians • Other Greeks sent warships, but Persians won • Darius wanted to punish mainland Greeks
Persian Wars • 400’s Persians began to attack the Greeks • Led by Cyrus II in 546 BC Persians conquered Ionia • Ionian’s could keep their own government, but Persians were considered to be barbarians • Other Greeks sent warships, but Persians won • Darius wanted to punish mainland Greeks
 Persian Wars Marathon: Salamis: Ø Athenians- 10, 000 Persians- 20, 000 Ø Persians waited for Athenians in Marathon 25 miles from Athens Ø Athenians did nothing, and waited for Persians to load into boats Ø They than attacked surprising the Persians Ø 6, 400 dead Persians 192 dead Athenians Ø Xerxes sends 200, 000 troops to Greece Ø Oracle at Delphi says battle shall be won behind a wooden wall Ø Themistocles convinced Greek allies this means wooden ships Ø They need to delay Persians on Mt. Thermopylae
Persian Wars Marathon: Salamis: Ø Athenians- 10, 000 Persians- 20, 000 Ø Persians waited for Athenians in Marathon 25 miles from Athens Ø Athenians did nothing, and waited for Persians to load into boats Ø They than attacked surprising the Persians Ø 6, 400 dead Persians 192 dead Athenians Ø Xerxes sends 200, 000 troops to Greece Ø Oracle at Delphi says battle shall be won behind a wooden wall Ø Themistocles convinced Greek allies this means wooden ships Ø They need to delay Persians on Mt. Thermopylae
 Persian War Salmis cont. : Ø 7, 000 Greeks led by Spartan general Leonidas hold them off for three days Ø A traitor shows Persians a secret passage through the hills Ø Leonidas sent everyone home except for 300 Spartans
Persian War Salmis cont. : Ø 7, 000 Greeks led by Spartan general Leonidas hold them off for three days Ø A traitor shows Persians a secret passage through the hills Ø Leonidas sent everyone home except for 300 Spartans
 Peloponnesian War • Athenians began to dominate • Spartans grew jealous and formed an anti-Athens league • 431 - 404 Athens held strong • 404 BC Sparta gave Ionia to Persia in exchange for gold to build boats • Typhus wiped out Athens • Athenian allies began to side with Sparta • 404 BC Athens lost
Peloponnesian War • Athenians began to dominate • Spartans grew jealous and formed an anti-Athens league • 431 - 404 Athens held strong • 404 BC Sparta gave Ionia to Persia in exchange for gold to build boats • Typhus wiped out Athens • Athenian allies began to side with Sparta • 404 BC Athens lost
 Peloponnesian War Effects: • Bad for both sides • City-states declined • Unemployment rose • Fields were destroyed • Merchants moved to Persia • People lost faith in government/ stopped discussing politics • 350 BC Macedonians took over
Peloponnesian War Effects: • Bad for both sides • City-states declined • Unemployment rose • Fields were destroyed • Merchants moved to Persia • People lost faith in government/ stopped discussing politics • 350 BC Macedonians took over
 Phillip II/ Alexander
Phillip II/ Alexander
 Phillip the Barbarian • Becomes king of Macedonia in 350 BC • Transforms army • Defeats people in North (wants Greece, and Persia) • Demosthenes warns Greeks to Unite, Athens and Thebes try, but it is too late and in 338 BC Phillip conquers Greece
Phillip the Barbarian • Becomes king of Macedonia in 350 BC • Transforms army • Defeats people in North (wants Greece, and Persia) • Demosthenes warns Greeks to Unite, Athens and Thebes try, but it is too late and in 338 BC Phillip conquers Greece
 Phillip the Barbarian • Had complete control of Macedonia • 336 BC his daughter got married
Phillip the Barbarian • Had complete control of Macedonia • 336 BC his daughter got married
 Alexander The Great • Son of Phillip II • 20 years old when he becomes king • Strong leader • Good Military General • Educated by Aristotle
Alexander The Great • Son of Phillip II • 20 years old when he becomes king • Strong leader • Good Military General • Educated by Aristotle
 Alexander The Great • 334 BC he attacks Persia with 35, 000 troops • Defeats 40, 000 troops at Granicus • Darius III raises 50 -75 thousand more troops • Alexander charges right at Darius III • Alexander gains control of Anatolia
Alexander The Great • 334 BC he attacks Persia with 35, 000 troops • Defeats 40, 000 troops at Granicus • Darius III raises 50 -75 thousand more troops • Alexander charges right at Darius III • Alexander gains control of Anatolia
 Alexander The Great • Persians offer Western empire, Alexander refuses • Alexander was welcomed when he took Egypt in 332 BC • Founded Alexandria • Treated like a Pharaoh
Alexander The Great • Persians offer Western empire, Alexander refuses • Alexander was welcomed when he took Egypt in 332 BC • Founded Alexandria • Treated like a Pharaoh
 Alexander The Great • Moves East to Mesopotamia to confront Darius and 250, 000 Persians • Alexander wins gaining Babylon, Susa, Perapolis
Alexander The Great • Moves East to Mesopotamia to confront Darius and 250, 000 Persians • Alexander wins gaining Babylon, Susa, Perapolis
 Alexander The Great • He than pushed east until he was blocked by 200 elephants • Quit after 11 years of fighting • He died and his empire was divided up: – Antibonus- Macedonia – Ptolemy- Egypt – Seleucus- Persia
Alexander The Great • He than pushed east until he was blocked by 200 elephants • Quit after 11 years of fighting • He died and his empire was divided up: – Antibonus- Macedonia – Ptolemy- Egypt – Seleucus- Persia


