c46ce468016546167ab19f1f0f905520.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Ancient Egypt Unit Test Study Guide
Ancient Egypt Unit Test Study Guide
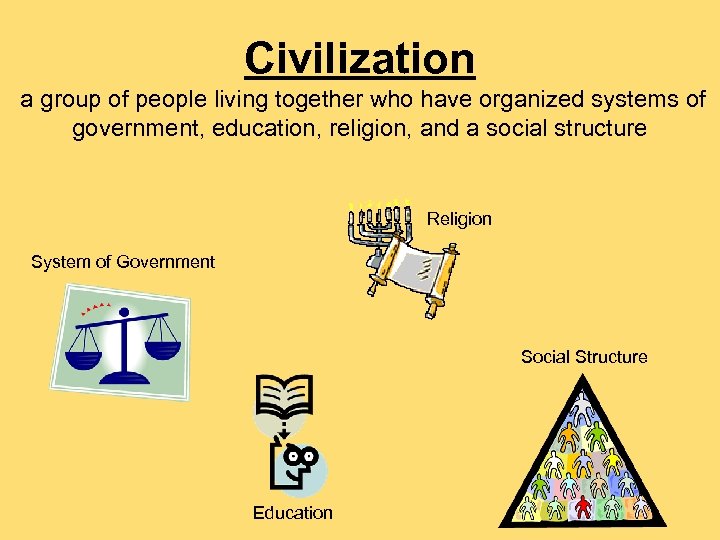 Civilization a group of people living together who have organized systems of government, education, religion, and a social structure Religion System of Government Social Structure Education
Civilization a group of people living together who have organized systems of government, education, religion, and a social structure Religion System of Government Social Structure Education
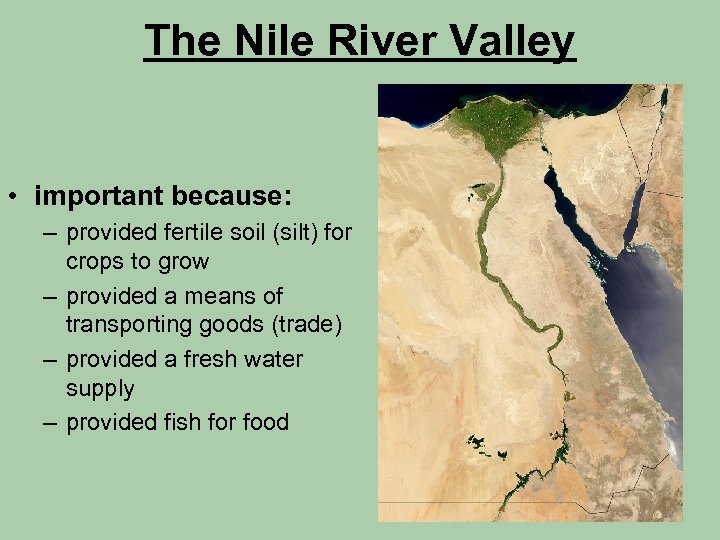 The Nile River Valley • important because: – provided fertile soil (silt) for crops to grow – provided a means of transporting goods (trade) – provided a fresh water supply – provided fish for food
The Nile River Valley • important because: – provided fertile soil (silt) for crops to grow – provided a means of transporting goods (trade) – provided a fresh water supply – provided fish for food
 Egypt’s Geography How did the geography affect Egypt’s civilization? • Nile River: • Nile flows north so they had to use sails on their ships • cataracts made it difficult to travel up and down the river • vast deserts: • “red land” where no crops could grow • Egyptians had to develop irrigation ditches to get water from Nile to crops
Egypt’s Geography How did the geography affect Egypt’s civilization? • Nile River: • Nile flows north so they had to use sails on their ships • cataracts made it difficult to travel up and down the river • vast deserts: • “red land” where no crops could grow • Egyptians had to develop irrigation ditches to get water from Nile to crops
 f form o d a se ng ba writi s icture on p Why were Hieroglyphics important? Hieroglyphics • scribes wrote religious and official documents • to record information • how much wheat was harvested • taxes farmers owed
f form o d a se ng ba writi s icture on p Why were Hieroglyphics important? Hieroglyphics • scribes wrote religious and official documents • to record information • how much wheat was harvested • taxes farmers owed
 Rosetta Stone The discovery of the Rosetta Stone was important because archaeologists used it to decode hieroglyphics and learn about ancient Egyptian civilization. The Rosetta Stone contained a passage written in both Greek & hieroglyphics – so we could compare the two writings and decode the 700 symbols.
Rosetta Stone The discovery of the Rosetta Stone was important because archaeologists used it to decode hieroglyphics and learn about ancient Egyptian civilization. The Rosetta Stone contained a passage written in both Greek & hieroglyphics – so we could compare the two writings and decode the 700 symbols.
 Pyramids • Pyramids were huge stone buildings that served as burial places for the pharaohs. • Egyptians believed that kings remained gods after death and the pyramids were like palaces. • Kings were buried with their possessions so they could use them in the afterlife.
Pyramids • Pyramids were huge stone buildings that served as burial places for the pharaohs. • Egyptians believed that kings remained gods after death and the pyramids were like palaces. • Kings were buried with their possessions so they could use them in the afterlife.
 Why was Trade Important? • Trade increased and made the Egyptian economy more prosperous or profitable. • Traded goods such as wheat, gold, and linen to southwest Asia. • They brought back goods that they needed and did not have.
Why was Trade Important? • Trade increased and made the Egyptian economy more prosperous or profitable. • Traded goods such as wheat, gold, and linen to southwest Asia. • They brought back goods that they needed and did not have.
 Pharaoh • Egyptian ruler who was worshipped as a god • referred to as a godking • the word pharaoh means “great house” • pharaohs were believed to be related to Amon-Ra (the sun god) Can you name one of the pharaohs and tell why he/she was important?
Pharaoh • Egyptian ruler who was worshipped as a god • referred to as a godking • the word pharaoh means “great house” • pharaohs were believed to be related to Amon-Ra (the sun god) Can you name one of the pharaohs and tell why he/she was important?
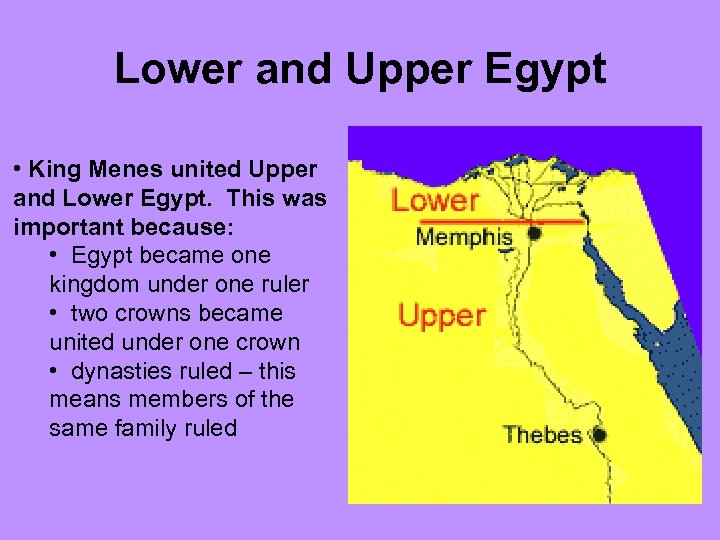 Lower and Upper Egypt • King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt. This was important because: • Egypt became one kingdom under one ruler • two crowns became united under one crown • dynasties ruled – this means members of the same family ruled
Lower and Upper Egypt • King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt. This was important because: • Egypt became one kingdom under one ruler • two crowns became united under one crown • dynasties ruled – this means members of the same family ruled
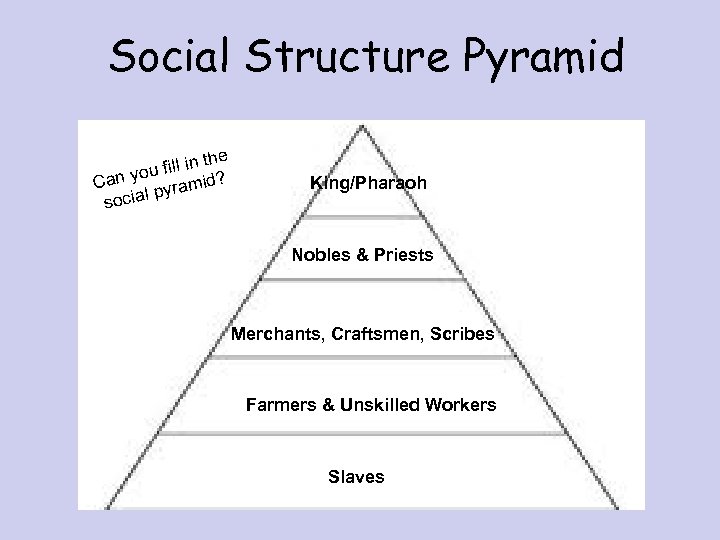 Social Structure Pyramid he fill in t ou Can y yramid? p social King/Pharaoh Nobles & Priests Merchants, Craftsmen, Scribes Farmers & Unskilled Workers Slaves
Social Structure Pyramid he fill in t ou Can y yramid? p social King/Pharaoh Nobles & Priests Merchants, Craftsmen, Scribes Farmers & Unskilled Workers Slaves
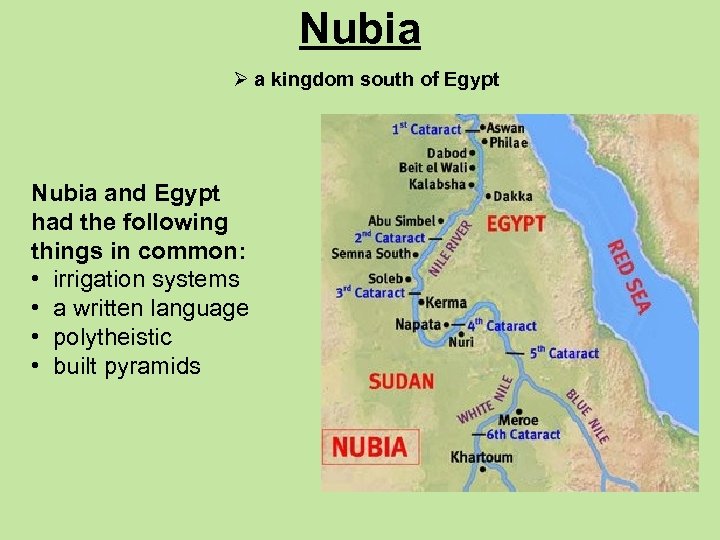 Nubia Ø a kingdom south of Egypt Nubia and Egypt had the following things in common: • irrigation systems • a written language • polytheistic • built pyramids
Nubia Ø a kingdom south of Egypt Nubia and Egypt had the following things in common: • irrigation systems • a written language • polytheistic • built pyramids
 Religious Beliefs: Religious beliefs affected daily life by: • using stories about gods to explain the natural world • making predictions about the Nile flooding • believing in the afterlife: • the afterlife was more important than life on Earth • mummification to prepare kings for the afterlife
Religious Beliefs: Religious beliefs affected daily life by: • using stories about gods to explain the natural world • making predictions about the Nile flooding • believing in the afterlife: • the afterlife was more important than life on Earth • mummification to prepare kings for the afterlife
 Hatshepsut • Hatshepsut was the daughter of a pharaoh who became a ruler of Egypt. She claimed that Ra was her real father. • she was married to Thutmose II and became a pharaoh after his death • she took complete control • sent several trading expeditions in search of riches • peaceful reign
Hatshepsut • Hatshepsut was the daughter of a pharaoh who became a ruler of Egypt. She claimed that Ra was her real father. • she was married to Thutmose II and became a pharaoh after his death • she took complete control • sent several trading expeditions in search of riches • peaceful reign
 GRAPES Geography: Nile River, desert, cataracts Religion: polytheism, Ra, priests Achievements: pyramids, hieroglyphics, papyrus Political: Hatshepsut, Khufu, Menes Economic: farming, traded wheat, scribes Social: pharaoh, merchants, slaves (paper)
GRAPES Geography: Nile River, desert, cataracts Religion: polytheism, Ra, priests Achievements: pyramids, hieroglyphics, papyrus Political: Hatshepsut, Khufu, Menes Economic: farming, traded wheat, scribes Social: pharaoh, merchants, slaves (paper)


