756506759e440be57a333f5c245e476e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 ancient egypt chapter 4
ancient egypt chapter 4
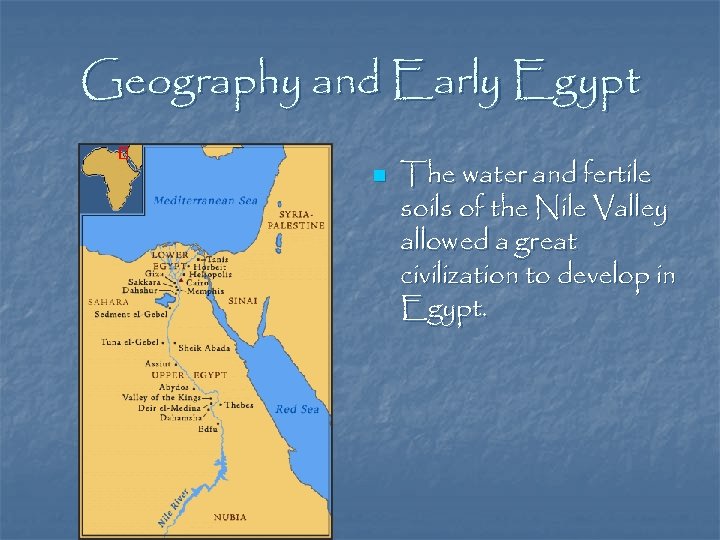 Geography and Early Egypt n The water and fertile soils of the Nile Valley allowed a great civilization to develop in Egypt.
Geography and Early Egypt n The water and fertile soils of the Nile Valley allowed a great civilization to develop in Egypt.
 n Egypt as it appears today….
n Egypt as it appears today….
 Egypt: The Gift of the Nile n n Nile River brought Egypt to life and allowed it to thrive. Biannual flooding of the Nile made farming possible
Egypt: The Gift of the Nile n n Nile River brought Egypt to life and allowed it to thrive. Biannual flooding of the Nile made farming possible
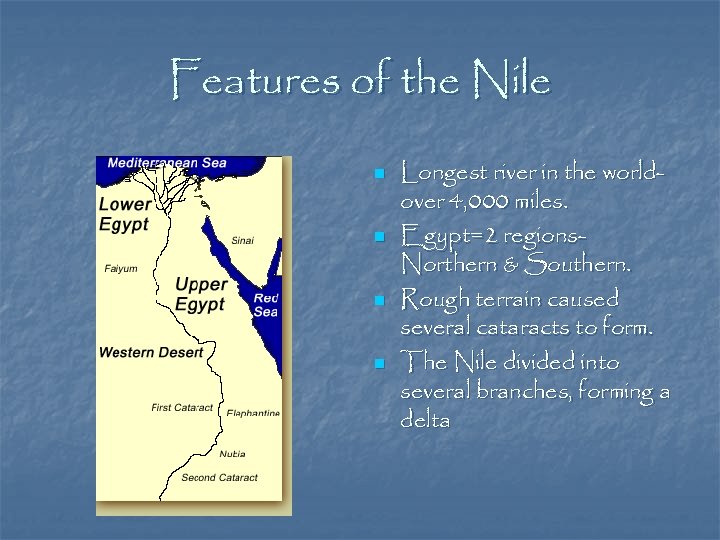 Features of the Nile n n Longest river in the worldover 4, 000 miles. Egypt=2 regions. Northern & Southern. Rough terrain caused several cataracts to form. The Nile divided into several branches, forming a delta
Features of the Nile n n Longest river in the worldover 4, 000 miles. Egypt=2 regions. Northern & Southern. Rough terrain caused several cataracts to form. The Nile divided into several branches, forming a delta
 The floods of the Nile n n Little rain fell in the Egyptian desert, but the Nile flooded every year-summer & fall The flooding created a rich silt-ideal for farming. Without the floods, people couldn’t have farmed there. The location was also ideal because natural barriers made it hard to invade.
The floods of the Nile n n Little rain fell in the Egyptian desert, but the Nile flooded every year-summer & fall The flooding created a rich silt-ideal for farming. Without the floods, people couldn’t have farmed there. The location was also ideal because natural barriers made it hard to invade.
 Increased Food Production n Canals: carry water to fields of wheat, barley, fruits, & vegetables. Raised animals: cattle & sheep River-fish, ducks, & geese
Increased Food Production n Canals: carry water to fields of wheat, barley, fruits, & vegetables. Raised animals: cattle & sheep River-fish, ducks, & geese
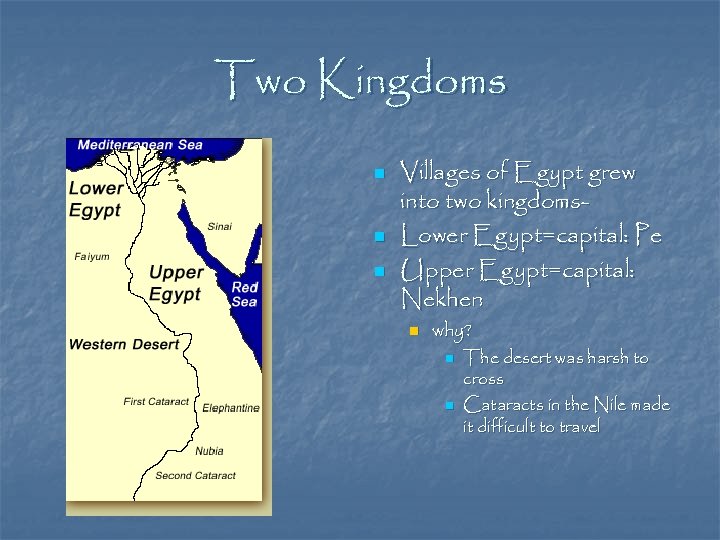 Two Kingdoms n n n Villages of Egypt grew into two kingdoms. Lower Egypt=capital: Pe Upper Egypt=capital: Nekhen n why? n n The desert was harsh to cross Cataracts in the Nile made it difficult to travel
Two Kingdoms n n n Villages of Egypt grew into two kingdoms. Lower Egypt=capital: Pe Upper Egypt=capital: Nekhen n why? n n The desert was harsh to cross Cataracts in the Nile made it difficult to travel
 Strong kings unified all of Egypt n According to tradition, Menes rose to power in Upper Egypt and unified the two kingdoms by taking control of Lower Egypt and marrying a Lower-Egyptian princess
Strong kings unified all of Egypt n According to tradition, Menes rose to power in Upper Egypt and unified the two kingdoms by taking control of Lower Egypt and marrying a Lower-Egyptian princess
 Strong Kings Unified all of Egypt n n Menes was probably Egypt’s first pharaoh Also founded Egypt’s first dynasty in the same day.
Strong Kings Unified all of Egypt n n Menes was probably Egypt’s first pharaoh Also founded Egypt’s first dynasty in the same day.
 The Old Kingdom n Egyptian Government and religion were closely connected.
The Old Kingdom n Egyptian Government and religion were closely connected.
 Life in the Old Kingdom was influenced by pharaohs, roles in society & trade n n n Old Kingdom=pharaoh was both king & god As population grew, social classes appeared. Egypt began to trade goods with it’s neighbors.
Life in the Old Kingdom was influenced by pharaohs, roles in society & trade n n n Old Kingdom=pharaoh was both king & god As population grew, social classes appeared. Egypt began to trade goods with it’s neighbors.
 Egyptian Society n Social Classes: Pharaohs ruled Egypt as gods n Nobles were officials and priests who helped run the government. n Scribes and craftspeople wrote & produced goods. n Farmers servants, & slaves made up most of Egyptian Society. n
Egyptian Society n Social Classes: Pharaohs ruled Egypt as gods n Nobles were officials and priests who helped run the government. n Scribes and craftspeople wrote & produced goods. n Farmers servants, & slaves made up most of Egyptian Society. n
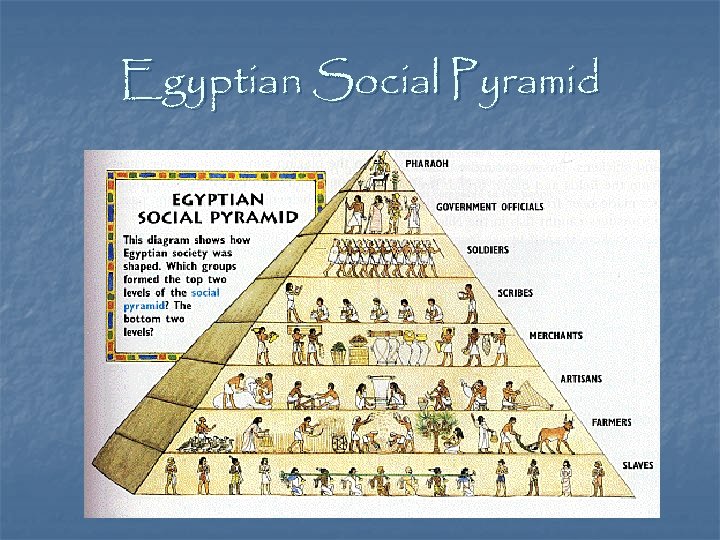 Egyptian Social Pyramid
Egyptian Social Pyramid
 Religion Shaped Egyptian Life n The Egyptians had many gods: n Sun, sky and earth-often mix human and animal forms.
Religion Shaped Egyptian Life n The Egyptians had many gods: n Sun, sky and earth-often mix human and animal forms.
 Religion Shaped Egyptian Life n n n Focused on the afterlife-(life after death) believed that when a person died his or her “ka” left the body and became a spirit. Embalming preserved the bodies to keep the link between the body & the spirit. The bodies were specially treated & wrapped in cloth-mummies!!
Religion Shaped Egyptian Life n n n Focused on the afterlife-(life after death) believed that when a person died his or her “ka” left the body and became a spirit. Embalming preserved the bodies to keep the link between the body & the spirit. The bodies were specially treated & wrapped in cloth-mummies!!
 Pyramids were built as huge tombs for pharaohs n n n Historians are still not sure how the pyramids were built-they displayed amazing engineering. The size and shape of the pyramid showed the importance of the pharaohs. They were the people’s link to the gods, so the Egyptian’s wanted their spirits to be happy.
Pyramids were built as huge tombs for pharaohs n n n Historians are still not sure how the pyramids were built-they displayed amazing engineering. The size and shape of the pyramid showed the importance of the pharaohs. They were the people’s link to the gods, so the Egyptian’s wanted their spirits to be happy.
 Pyramids
Pyramids
 The Middle and New Kingdoms n During the Middle and New kingdoms, order and greatness were restored in Egypt.
The Middle and New Kingdoms n During the Middle and New kingdoms, order and greatness were restored in Egypt.
 The middle kingdom was a period of stable government between periods of disorder n n n After a period of power and competition between the nobles, the middle kingdom was restored. Egypt fell into disorder when a group called the Hyskos invaded… they ruled Egypt for about 200 yrs. The Egyptians fought backn n n Ahmose of Thebes declared himself king Drove out the Hyskos Began New Kingdom
The middle kingdom was a period of stable government between periods of disorder n n n After a period of power and competition between the nobles, the middle kingdom was restored. Egypt fell into disorder when a group called the Hyskos invaded… they ruled Egypt for about 200 yrs. The Egyptians fought backn n n Ahmose of Thebes declared himself king Drove out the Hyskos Began New Kingdom
 New Kingdom: peak of trade & military power…but did not last n n n Fearing future invasions, the Egyptians took over all possible invasion routes into the kingdom. Took over vast lands & was the leading military power in the area. Became rich because of conquered lands.
New Kingdom: peak of trade & military power…but did not last n n n Fearing future invasions, the Egyptians took over all possible invasion routes into the kingdom. Took over vast lands & was the leading military power in the area. Became rich because of conquered lands.
 Growth & Effects of trade n n Trade routes developed as conquests brought traders into distant lands. Queen Hatshepsut encouraged trade & used the profits to support art & architecture.
Growth & Effects of trade n n Trade routes developed as conquests brought traders into distant lands. Queen Hatshepsut encouraged trade & used the profits to support art & architecture.
 Ramses the Great n Led by Ramses the Great, Egypt fought invaders for many years, leaving the empire diminished.
Ramses the Great n Led by Ramses the Great, Egypt fought invaders for many years, leaving the empire diminished.
 Daily Life and Work in Egypt n n n Family life was important in Egyptian Society. Most Egyptians had their own homes. Women had many legal rights: Owning property n Making contracts n Divorcing their husbands n
Daily Life and Work in Egypt n n n Family life was important in Egyptian Society. Most Egyptians had their own homes. Women had many legal rights: Owning property n Making contracts n Divorcing their husbands n
 Egyptian Jobs n n Scribes: few people were more respected than scribes. They did not have to pay taxes, and many became wealthy.
Egyptian Jobs n n Scribes: few people were more respected than scribes. They did not have to pay taxes, and many became wealthy.
 Egyptian Jobs n Artisans, Artists, and Architects: these jobs required advanced skills-also very admired in Egypt.
Egyptian Jobs n Artisans, Artists, and Architects: these jobs required advanced skills-also very admired in Egypt.
 Egyptian Jobs n n n Merchants & Traders: Although trade was important, few people held these positions. Some had to travel very long distances to buy and sell goods. Soldiers: Egypt created a permanent army that offered soldiers a chance to rise in social status and receive land as payment.
Egyptian Jobs n n n Merchants & Traders: Although trade was important, few people held these positions. Some had to travel very long distances to buy and sell goods. Soldiers: Egypt created a permanent army that offered soldiers a chance to rise in social status and receive land as payment.
 Egyptian Jobs n Farmers & other peasants: made up the vast majority of the population. n n Grew crops to support their families and pay taxes. Slaves: slaves were usually criminals or prisoners. *they did have some legal rights.
Egyptian Jobs n Farmers & other peasants: made up the vast majority of the population. n n Grew crops to support their families and pay taxes. Slaves: slaves were usually criminals or prisoners. *they did have some legal rights.
 Egyptian Achievements n The Egyptians made lasting achievements in writing, architecture and art.
Egyptian Achievements n The Egyptians made lasting achievements in writing, architecture and art.
 Egyptian writing used Hieroglyphics n n Learned to write hieroglyphics on papyrus-a long lasting paper-like material made from reeds. Scribes used papyrus using brushes and ink
Egyptian writing used Hieroglyphics n n Learned to write hieroglyphics on papyrus-a long lasting paper-like material made from reeds. Scribes used papyrus using brushes and ink
 Egyptian writing used Hieroglyphics n n Historians learned how to read hieroglyphics after studying the Rosetta Stone. Written in three languages: n n n Hieroglyphics A later form of the Egyptian language Greek
Egyptian writing used Hieroglyphics n n Historians learned how to read hieroglyphics after studying the Rosetta Stone. Written in three languages: n n n Hieroglyphics A later form of the Egyptian language Greek
 Egypt’s Great Temples were Lavishly Decorated n n Egyptians believed that massive temples were homes for the gods. People visited to worship, offer gifts to the gods and asked for favors.
Egypt’s Great Temples were Lavishly Decorated n n Egyptians believed that massive temples were homes for the gods. People visited to worship, offer gifts to the gods and asked for favors.
 Egypt’s Great Temples were Lavishly Decorated n Temples had: n n n Stone sphinxes and other statues Obelisk: tall 4 -sided pillar that is pointed at the top. Painted walls and columns that also had hieroglyphics.
Egypt’s Great Temples were Lavishly Decorated n Temples had: n n n Stone sphinxes and other statues Obelisk: tall 4 -sided pillar that is pointed at the top. Painted walls and columns that also had hieroglyphics.
 Egyptian Art Filled Tombs n n Art: lively, colorful scenesbut only kings, priests and other important people could enter the tombs. Tombs contained art such as: n n n Art and hieroglyphics on walls & columns Stone statues and carvings. Jewelry
Egyptian Art Filled Tombs n n Art: lively, colorful scenesbut only kings, priests and other important people could enter the tombs. Tombs contained art such as: n n n Art and hieroglyphics on walls & columns Stone statues and carvings. Jewelry


