dba8a044bdf4a05248ddfbff2c87bee1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
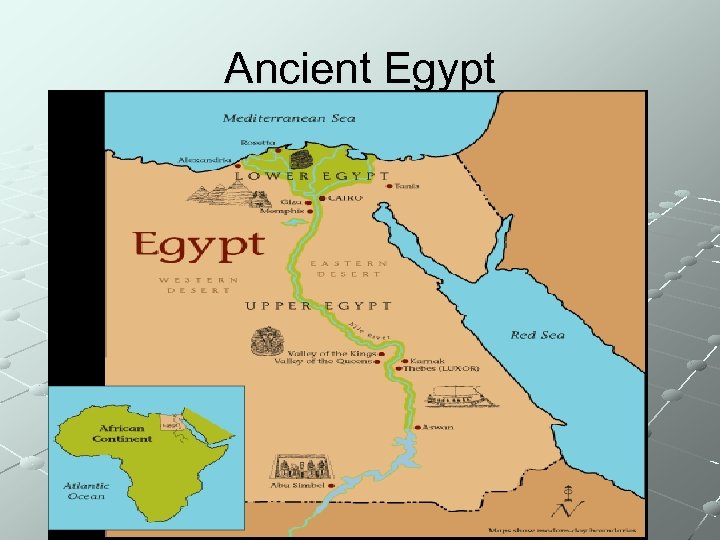
Ancient Egypt

Ancient Egypt 3100 BCE – Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by Narmer (aka Menes)- capital placed at Memphis 2900 BCE – Hieroglyphics develop (Egyptian writing) 2700 BCE – 365 solar calendar develops – June 21 is beginning of year - greatest Egyptian scientific achievement 2686 -2613 BCE – Pharaoh Djoser orders first pyramid built by Imhotep (step pyramid) 2585 – 2470 BCE – Khufu, Khafre (also builds Sphinx) and Menkaure order the 3 pyramids of Giza built.

Ancient Egypt 2100 BCE – capital is moved to Thebes by the priesthood under Mentuhotep II of the 11 th Dynasty 1674 BCE – Egyptian former capital of Memphis falls to Hyksos; Hyksos conquer Lower Egypt and rule it for the next 100 years 1567 - 1550 BCE – Ahmose I conquers the Hyksos and reunites Upper and Lower Egypt to begins 18 th Dynasty

Ancient Egypt 1478 – 1458 BCE – Hatshepsut rules as first female pharaoh with her son Thutmoses III 1479 – 1425 BCE – Thutmoses III builds the largest Egyptian Empire conquering Israel, Mesopotamia and Nubia 1352 – 1336 BCE – Amenhotep IV changes his name to Akhenaten; changes Egyptian religion to monotheism; moves capital from Thebes to Akhetaton (Amarna) 1336 – 1327 BCE – Tutankhamen restores capital to Thebes; restores old religion; dies shortly after

Ancient Egypt 1299 BCE – Rameses II fights Hittites at Battle of Kadesh which ended in the world’s first peace treaty. Rameses II goes on to build many temples, buildings and even cities during his reign. 1224 – 1165 BCE – Rameses III repulses the invasion of the Indo-European Sea People; he is considered the last of the great Egyptian pharaohs

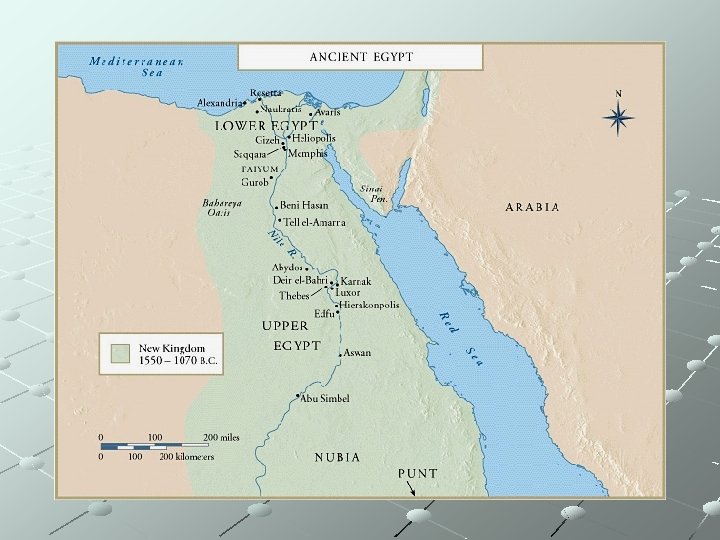
Ancient Egyptian History can be broken down in 3 major periods: Old Kingdom – 2686 – 2181 BCE Middle Kingdom – 2040 – 1700 BCE New Kingdom – 1550 – 1070 BCE most successful period

Ancient Egyptians were Polytheistic Major Egyptian Gods: Ra (later named Amon-Ra or Amon-Re) – sun god; ruler of the gods Osiris – god of underworld, resurrection, and plants Isis – goddess of fertility , wife/sister of Osiris Amen – god of creation; later combined with Ra to create one leading deity Anubis – god of the dead Set- god of chaos Horus – protector of the pharaoh, a sky god Bastet – Egyptian cat god, protector of souls The ka was the Egyptian word for the life force or soul

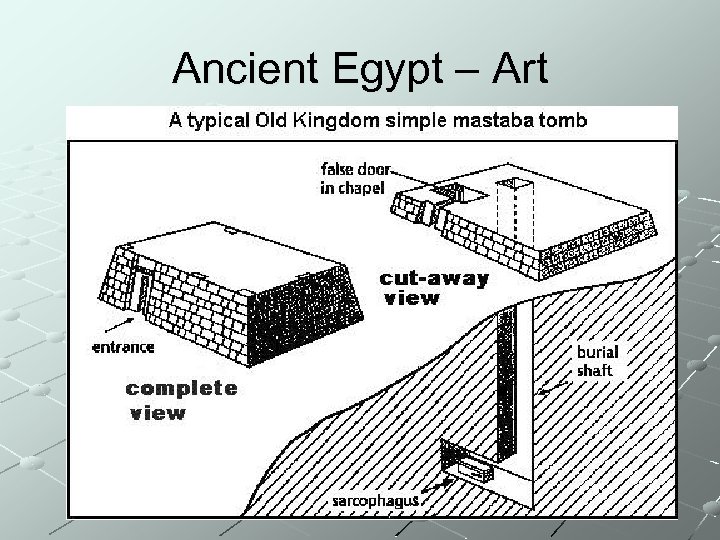
Ancient Egypt – Art Characteristics Strong sense of order All figures must stand on horizontal lines Egyptian canon of proportions is clearly defined Aim at clarity rather than illusion Head, hips, legs and feet always in profile Eyes, shoulders and upper torso seen from front Use of Hierarchic scale Higher ranking officials were depicted within the rules more strictly seeming almost rigid Frozen, timeless quality to Egyptian Art

Ancient Egypt Canon of Proportions – a set of rules governing the proportions of the human body as they must be rendered by the artist Hierarchic Scale – use of relative size to indicate the comparative importance of depicted objects or people

Pre-Dynastic Egypt

Ancient Egypt - Art Palette of King Narmer 3100 BCE Memphis, Egypt Relief Sculpture This work shows Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquering lower Egypt and uniting it with Upper Egypt
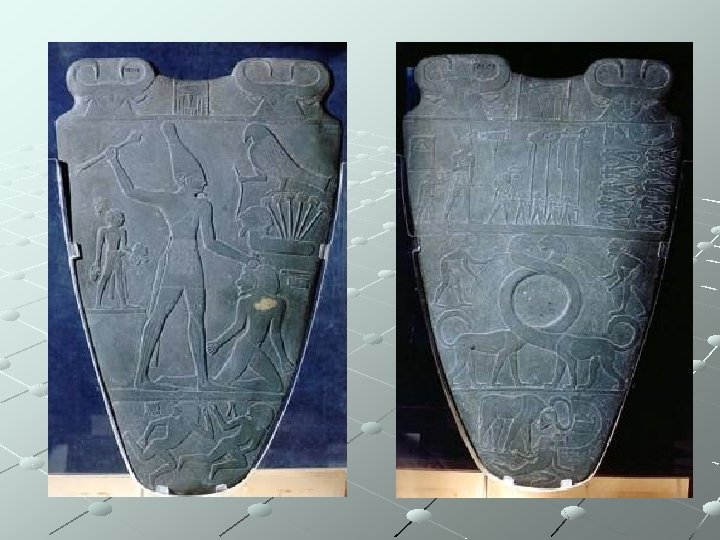

Ancient Egypt – Art
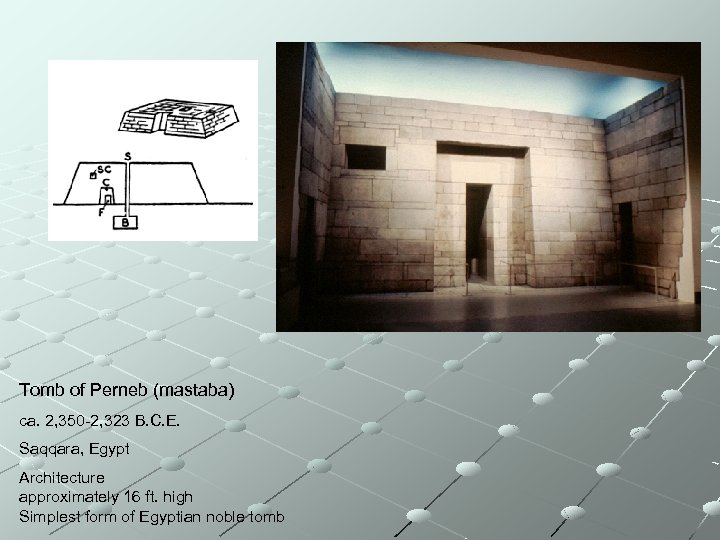
Tomb of Perneb (mastaba) ca. 2, 350 -2, 323 B. C. E. Saqqara, Egypt Architecture approximately 16 ft. high Simplest form of Egyptian noble tomb


Ancient Egypt - Art Step Pyramid of Pharaoh Djoser 2681 -2662 BCE Saqqara, Egypt Architecture Artist: Imhotep First pyramid structure built First known artist – Imhotep as architect Oldest stone structure ever built


Old Kingdom Art

Red Pyramid of Sneferu

Sneferu’s Bent and Collapsed Pyramids

Ancient Egypt - Art Pyramids of Giza 2530 – 2470 BCE Giza, Egypt Architecture Pyramid of Khufu on right; Pyramid of Khafre in center; Pyramid of Menkaure on left in front Served as tombs like all pyramids Face exactly north, south, east and west and are aligned to the stars in Orion’s belt

Ancient Egypt - Art

Ancient Egypt - Art Great Pyramid of Giza 2530 BCE Giza, Egypt Architecture The only surviving member of the Seven Wonders of the World The largest stone structure ever built 480 ft tall – 100, 000 workers – 23 years to build


Ancient Egypt - Art The Great Sphinx 2570 – 2544 BCE Giza, Egypt World’s largest Sculpture In the image of Khafre Size was meant to impress visitors and show pharaoh’s power


Khafre ca. 2, 520 -2, 494 B. C. E. Giza, Egypt Sculpture diorite approximately 66 in. high Seated pharaoh – one of 3 accepted poses

Ancient Egypt - Art Menkaure (Mycerinus) and Queen Khamerernebty 2470 BCE Giza, Egypt Sculpture King slightly taller and much more rigid than wife Canon of proportions followed Queen is allowed to be less rigid – can even place her hand around his waist Weight equally distributed on both feet Note they are not 100% free standing

Old Kingdom Art Rahotep and Princess Nofret C. 2620 BCE Sculpture Meidum, Egypt Possibly Sneferu’s daughter In Egyptian canon of colors, size, pose

Seated Scribe ca. 2, 450 -2, 350 B. C. E. Saqqara, Egypt Sculpture painted limestone approximately 21 in. high Note that he is not perfect and is in fact a bit flabby

Ancient Egypt - Art Ka-Aper 2500 BCE Saqqara, Egypt Sculpture Proves Egyptians could create realistic portrayals of people when not of the nobility or royalty Heavy set, older

Ancient Egypt - Art Ti Watching a Hippopotamus Hunt 2500 – 2400 BCE Saqqara, Egypt Relief Sculpture Typical Egyptian pose Ti is larger than servants – watching and not participating in the hunt Hippos were symbols of the god of chaos - Set in Egypt and looked upon unfavorably

Middle Kingdom

Rock cut Tombs Beni Hasan 3 -5 ca. 1950 -1900 B. C. E. Beni Hasan, Egypt Architecture These tombs are cut directly into the cliff

Tomb of Meketre ca. 1, 985 B. C. E. Thebes, Egypt Architecture Many non-royal tombs have been discovered with artifacts

Riverboat from tomb of Meketre, Thebes, Egypt

Granary from tomb of Meketre, Thebes, Egypt

Statuette of an offering bearer from tomb of Meketre, Thebes, Egypt

Hippopotamus 1991 -1783 B. C. E. Thebes, Egypt Sculpture/Craftwork 7 7/8 in. long Egyptians loved to use colored faience Faience -glazed earthenware decorated with opaque colors

New Kingdom

Ancient Egypt - Art Mausoleum of Queen Hatshepsut 1478 - 1458 BCE Thebes, Egypt Architecture Hatshepsut became the first female pharaoh First important historical female Tomb built on terraces – this was a temple – the body not placed here
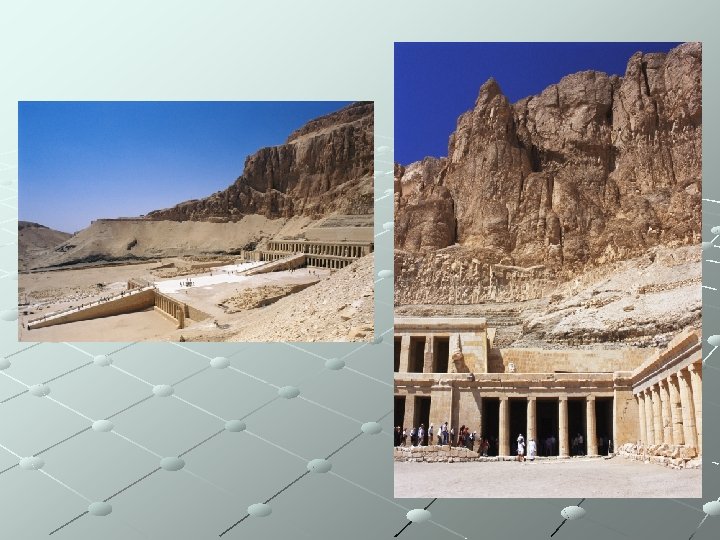


Hatshepsut with offering jars ca. 1, 473 -1, 458 B. C. E. Deir el-Bahri, Egypt Sculpture 8 ft. 6 in. high Although female, she appears male in all public functions and in monuments and sculpture

Ancient Egypt - Art The Weighing of the Heart and The Judgement of Osiris 1285 BCE Thebes, Egypt Illuminated Manuscript Part of the Book of the Dead – Ancient Egypt’s Holy Book

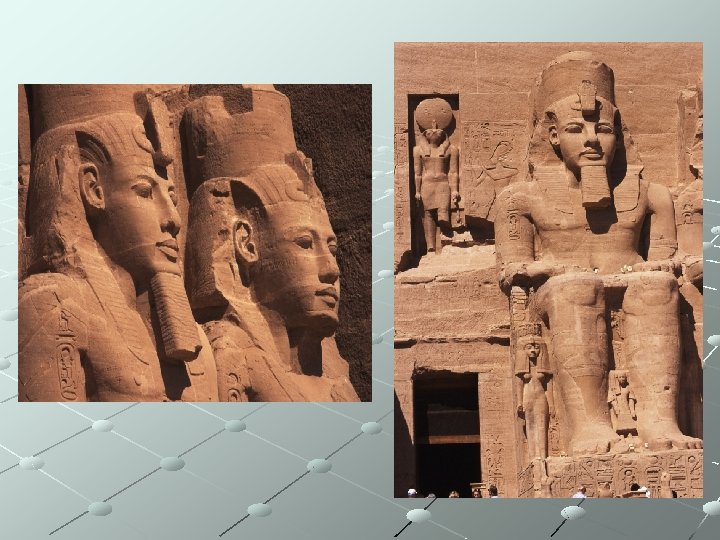
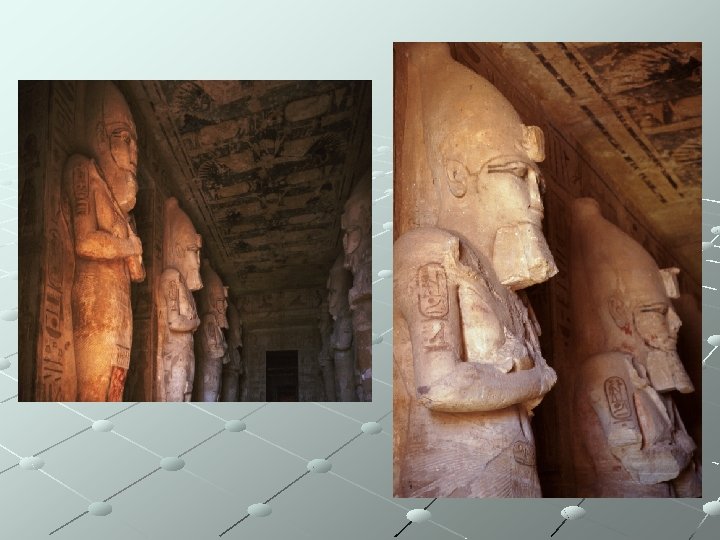
Ancient Egypt - Art Temple of Rameses II 1260 BCE Abu Simbel (Answan), Egypt Architectur/Relief Sculpture Greatest example of all temples Rameses II built Placed his name on over 50% of all New Kingdom monuments Egyptian standards unchanged despite passage of centuries



Temple of Amen-Re (Amon-Ra) ca. 15 th century B. C. E. Karnak, Egypt Architecture World’s largest religious structure

Ancient Egypt - Art Nobleman Hunting in the Marshes 1400 BCE Thebes, Egypt Painting From Tomb of Nebamun Focus on conveying the message of what is going on not in realism Similar to Ti relief from 1100 years earlier

Ancient Egypt - Art Musicians and Dancers 1350 BCE Thebes, Egypt Tomb of Nebamun Painting Combination of innovation and beauty in New Kingdom art; rules a bit more flexible – musicians actually face the viewer

Ancient Egypt - The Amarna Revolution Amenhotep IV’s religious and artistic revolution It started as an attempt to thwart the power of the priests at Thebes and turned into a full blown revolution in religious beliefs Amenhotep IV proclaims Aten as the only god – all others are declared false and their temples are ordered closed Amenhotep IV changes his name to Akhenaten (son of Aten) Akhenaten moves capital from Thebes to new capital called Aketaten (Amarna), basically putting priests out of power

Ancient Egypt - The Amarna Revolution Major changes are also made in art Amarna Period Characteristics: Exaggerated features – protruding stomach; large lips, elongated heads Sensitive Portrayals – more intimacy and emotion is portrayed More Informal – everyday scenes are depicted Overemphatic Outlines Stylized realism

Ancient Egypt - Art Akhenaten, Nefertiti and Their Children Worshipping the Sun 1348 – 1336 BCE Amarna, Egypt Relief Sculpture Typical Amarna period characteristics: deep outlines, exaggerated features, daily life scene, intimacy Yet still within Egyptian basic rules

Ancient Egypt - Art Bust of Queen Nefertiti 1348 – 1336 BCE Amarna, Egypt Sculpture Limestone Considered the masterpiece of Egyptian Art A symbol of beauty even in modern times

Ancient Egypt - Art Queen Tiye 1390 – 1352 BCE Thebes, Egypt Sculpture Mother of Amenhotep IV, wife of Amenhotep III This sculpture breaks with tradition before the Amarna Revolution Realistic portrayals of royalty are allowed briefly during this time

Death Mask of Tutankhamen ca. 1, 323 B. C. E. Thebes, Egypt Sculpture gold with semiprecious stones 21 1/4 in. high Over 22 lbs. of gold Most famous artifact from Tut’s tomb

Ancient Egypt - Art Cover of Tutankhamen’s Coffin 1336 – 1327 BCE Thebes, Egypt Sculpture Solid gold with gemstones Tutankhamen is most famous of pharaohs Because his tomb was only one ever discovered intact – Howard Carter

Wedjat Eye of Tutankhamen ca. 1, 333 -1, 323 B. C. E. Thebes, Egypt Craftwork gold and precious stones 2 in. wide Symbol of protection for the king

Ptolemaic Egypt

Bast (Cat Goddess) 304 -31 B. C. E. Thebes, Egypt Sculpture 11 in. high Kept evil spirits from tombs
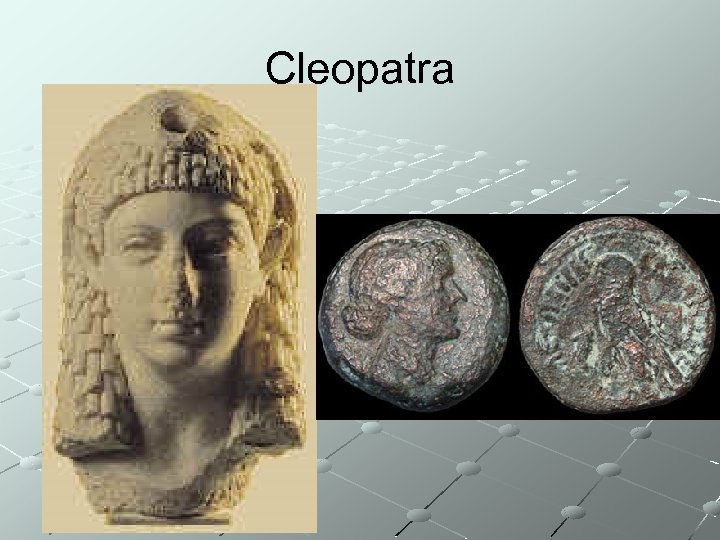

Cleopatra

Ancient Egypt - Art Rosetta Stone 196 BCE Rosetta, Egypt Relief Sculpture Inscription in 3 languages allowed for the decipherment of hieroglyphics by Jean Champolloin The story in the 3 languages tells of Ptolemy V

Roman Egypt

Temple of Dendur from Nubia ca. 15 B. C. E. Architecture 82 ft. long Held inside Metropolitan Museum of Art in NY

Portrait of a boy 2 nd century A. D. Faiyum, Egypt Painting encaustic on wood 15 in. high Placed over the mummies of Roman aristocracy in Egypt

Faiyum portraits 2 nd century A. D. encaustic on wood

Ancient Egypt The End Next Lecture : Aegean Greeks
dba8a044bdf4a05248ddfbff2c87bee1.ppt