7e0082454b8a29e0830bdd40c17cb45e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
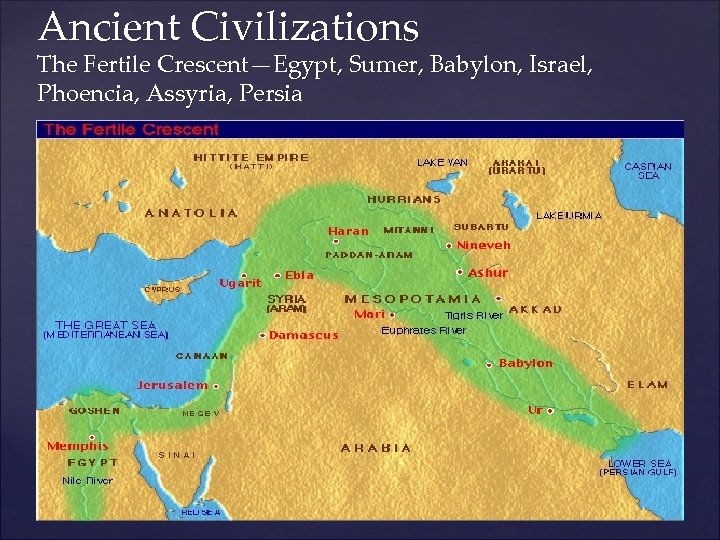
Ancient Civilizations The Fertile Crescent—Egypt, Sumer, Babylon, Israel, Phoencia, Assyria, Persia {

Ancient Egypt {

Gift of the Nile I. "Gift of the Nile" A. Ancient Egypt was a river valley civilization 1. Very dry climate 2. 9/10 of the land is desert. 3. Almost the entire population lived within ten-fifteen miles of the Nile River.

The Nile River I. Nile River A. The world's longest river, approximately 4, 000 miles. 1. Overflowed each year around the month of April and subsided around October. a. The flood waters were caused by rains in Eastern Africa spread rich deposits of fertile soil along the banks of the Nile River called Silt. b. Enabled food to be easily grown. 2. During the dry season, farmers learned to irrigate the land. a. Irrigation- The watering of dry land by means of streams, canals, and pipes. B. Economy was based on farming. 1. Crops were usually planted in October and were harvested in the spring.
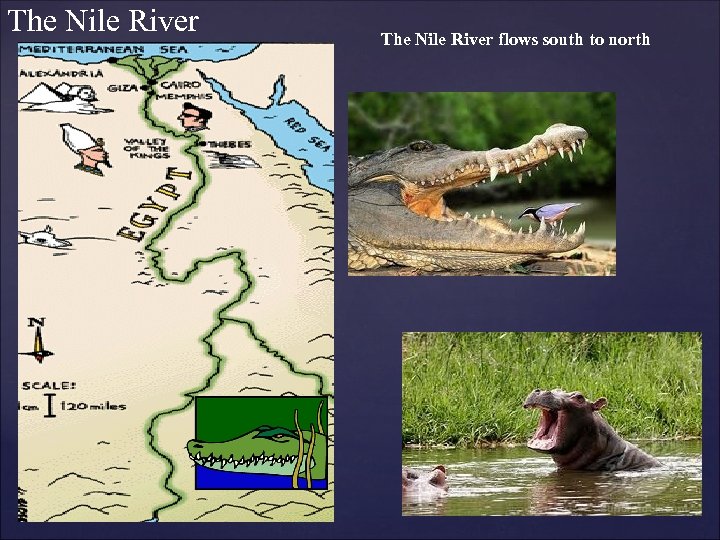
The Nile River flows south to north
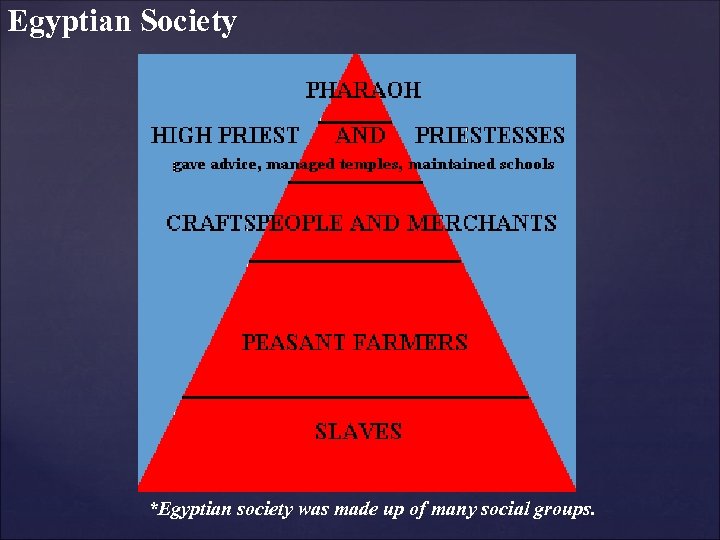
Egyptian Society *Egyptian society was made up of many social groups.

Egyptian Society: Pharaoh(s) I. Pharaoh A. Made up 1% of the population. 1. Egyptian supreme ruler. (Most powerful) a. People believed that the pharaohs were descended from the gods and ruled as god's representative on earth. 2. The Pharaohs owned all the land made all the laws. a. Farmers had to pay rent to the Pharaohs to farm the land. 1 a. Sometimes 2/3 of all crops had to be given to the pharaohs.
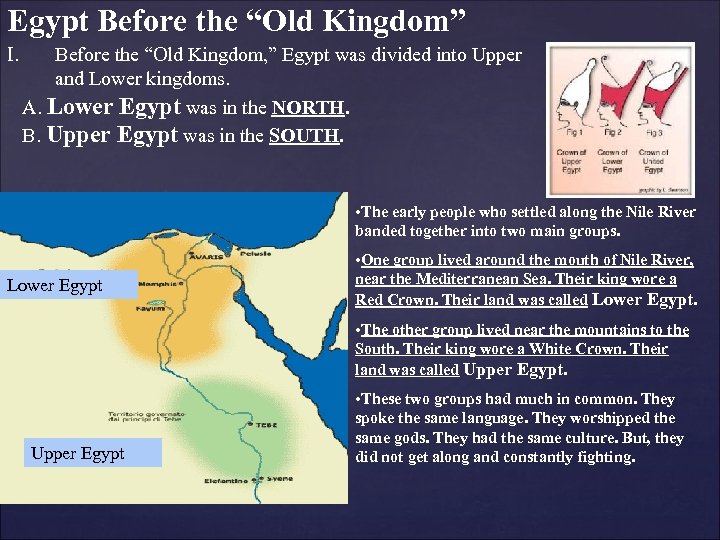
Egypt Before the “Old Kingdom” I. Before the “Old Kingdom, ” Egypt was divided into Upper and Lower kingdoms. A. Lower Egypt was in the NORTH. B. Upper Egypt was in the SOUTH. • The early people who settled along the Nile River banded together into two main groups. Lower Egypt • One group lived around the mouth of Nile River, near the Mediterranean Sea. Their king wore a Red Crown. Their land was called Lower Egypt. • The other group lived near the mountains to the South. Their king wore a White Crown. Their land was called Upper Egypt • These two groups had much in common. They spoke the same language. They worshipped the same gods. They had the same culture. But, they did not get along and constantly fighting.
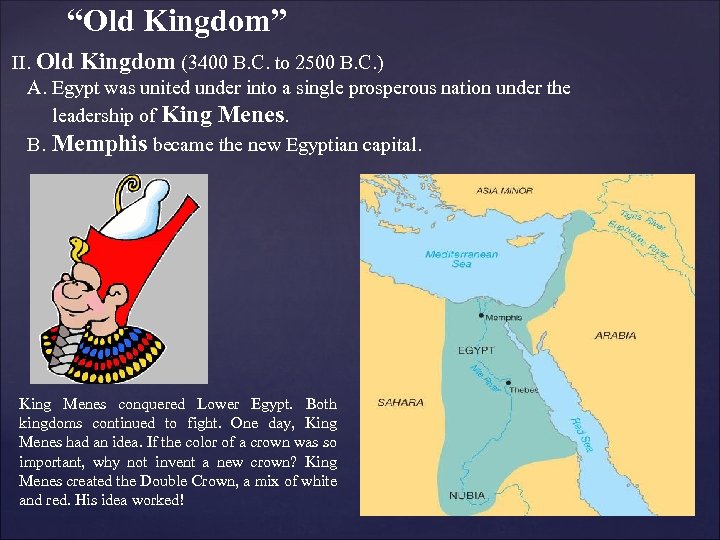
“Old Kingdom” II. Old Kingdom (3400 B. C. to 2500 B. C. ) A. Egypt was united under into a single prosperous nation under the leadership of King Menes. B. Memphis became the new Egyptian capital. King Menes conquered Lower Egypt. Both kingdoms continued to fight. One day, King Menes had an idea. If the color of a crown was so important, why not invent a new crown? King Menes created the Double Crown, a mix of white and red. His idea worked!

The Pyramids & Great Sphinx III. Pyramids were built. A. Served as royal tombs where Egyptian Pharaohs were buried. Pyramids were huge structures built to hold a royal tomb. Pyramids had storage rooms, courtyards, secret passageways, and traps to catch robbers who might break into the pyramid. The Great Sphinx is a large humanheaded lion that was carved from a mound of natural rock. It is located in Giza where it guards the front of Khafra's pyramid.
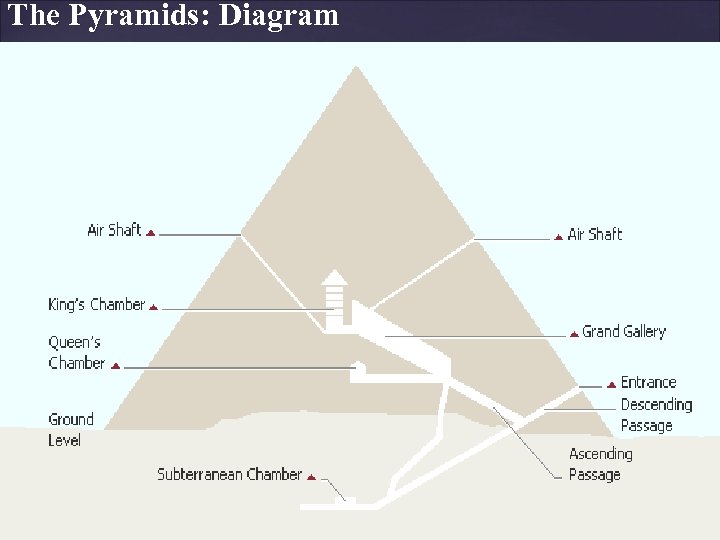
The Pyramids: Diagram

Decline of the “Old Kingdom” IV. Decline of the “Old Kingdom” A. The government during the Old Kingdom grew corrupt. 1. Leaders fought among themselves for power and wealth. a. Civil war erupted and ended the Old Kingdom.

“Middle Kingdom” I. Middle Kingdom: Age of Nobles (2, 500 to 1, 580 B. C. ) A. Egypt was divided into forty regions 1. Governors were appointed to rule each region. B. Egyptian Nobles became very powerful and engaged in a civil war against the Pharaohs. C. Chaos and continued disunity had made Egypt very weak.

Decline of the “Middle Kingdom” II. Decline of the “Middle Kingdom. ” A. About 1700 B. C. , the Hyksos invaded Egypt. 1. Hyksos were desert nomads who were less civilized than the Egyptians. a. The Hyksos had superior weapons and technology. 1 a. Overwhelmed the Egyptians using Chariots. b. The Hyksos conquered and ruled Egypt for over 200 years. 1 b. The Hyksos were very cruel. 2. Egyptians learned to use bronze and horse drawn chariots from the Hyksos and ousted the Hyksos and regained control of Egypt.

“New Kingdom” I. New Kingdom: The Age of Empire (1580 B. C. to 1150 B. C. ) A. The Pharaohs regained full control of Egypt. B. Hatshepsut became the first woman ruler in history. 1. Began the succession of ruling families called dynasties. 2. Expanded Egyptian Empire through trade and conquest. a. Palestine, Phoenicia, Syria, Cyprus, and Nubia. b. Many conquered people became Egyptian slaves. c. Imported gold, ivory, ostrich feathers, fish, and wine. d. Exported glassware, linens, and pottery. 3. Thebes became the new capital of Egypt. In public Hatshepsut dressed like a man and wore a false beard so people wouldn’t know she was a woman.

Decline of the “New Kingdom” C. The Decline of Ancient Egypt (1, 150 B. C. to 31 A. D. ) 1. Egypt was conquered in succession by Libya, Assyria, Persia, and Rome (31 A. D. )

Egyptian Contributions: Religion I. Religion A. Ancient Egyptians worshipped many gods. (Polytheism) 1. Examples included: a. Ra (the Sun God) b. Osiris (the God of the Nile. ) B. First conception immortality (life after death. ) For more info on Egyptian gods and goddesses: http: //www. ancientegypt. co. uk/gods/explore/main. html

Egyptian Contributions: Religion
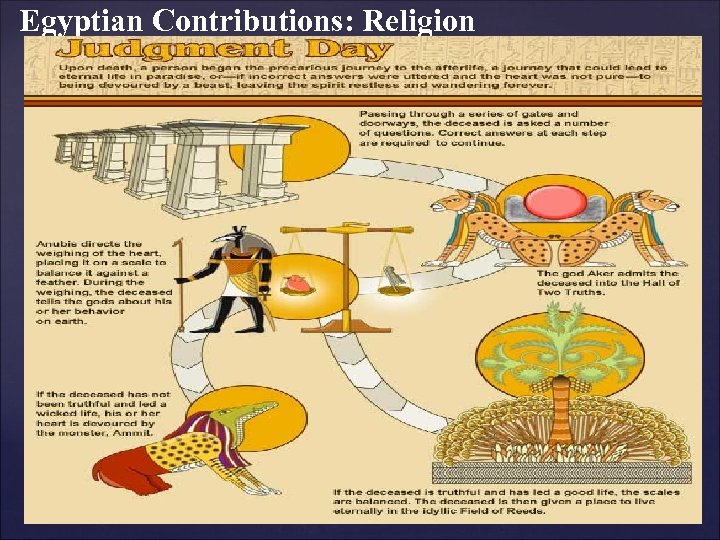
Egyptian Contributions: Religion

Egyptian Contributions: Art II. Art A. The Egyptians excelled in architecture and sculpture. 1. Great temples, pyramids, and other structures were built. B. Egyptian sculptors carved lifelike statues of men and beasts. C. Beautiful jewelry and other objects of copper and bronze were made.

Egyptian Contributions: Writing III. Writing A. Hieroglyphics 1. A crude system of writing using pictures and symbols. B. Rosetta Stone 1. Discovered in 1799, the Rosetta Stone provided the key to understanding the history of Ancient Egypt. a. Written in Hieroglyphics, late Egyptian, and Greek languages. Rosetta Stone

Hieroglyphics Alphabet Can you spell your name using Hieroglyphics?

Other Contributions Credited to Ancient Egypt IV. Other contributions credited to Ancient Egypt. A. Made paper from Papyrus reed. B. Invented the plow and irrigated their fields during the dry seasons. C. Used geometry for building and surveying. D. Invented the decimal system. E. Used a twelve-month calendar of 365 days, based on the movement of the sun. F. Performed surgical operations in which drugs were used as anesthetics. G. Law and order 1. Laws were very strict and stern. a. Those found guilty were whipped, tortured, burned, or thrown to the crocodiles.

Egyptian Contributions: Science V. Mummification A. Egyptians preserved dead bodies by embalming them. Preparing an Egyptian mummy sometimes took up to 70 days. On some mummies that have been unwrapped, the total length of the bandages has been about 1. 5 miles.
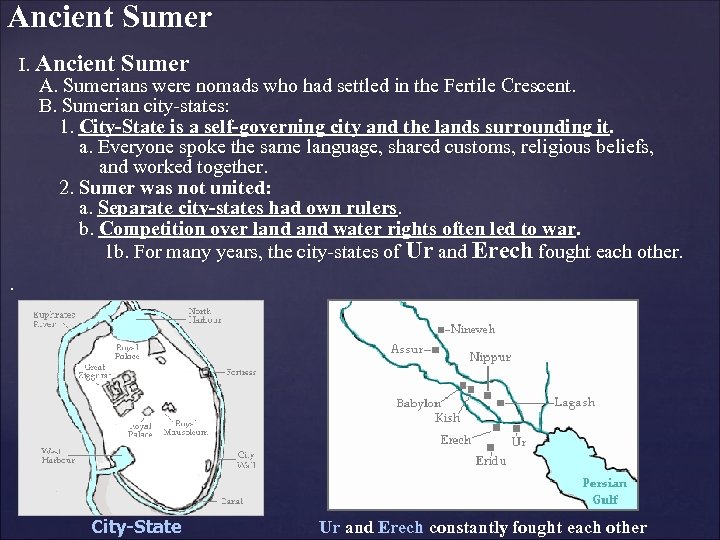
Ancient Sumer I. Ancient Sumer A. Sumerians were nomads who had settled in the Fertile Crescent. B. Sumerian city-states: 1. City-State is a self-governing city and the lands surrounding it. a. Everyone spoke the same language, shared customs, religious beliefs, and worked together. 2. Sumer was not united: a. Separate city-states had own rulers. b. Competition over land water rights often led to war. 1 b. For many years, the city-states of Ur and Erech fought each other. . City-State Ur and Erech constantly fought each other

Religion in Sumer II. Religion in Sumer: A. Sumerians did not worship their leaders as gods, instead they worshipped nature. B. Built tremendous temples called Ziggurats 1. To honor the gods and goddesses of nature. 2. Most important buildings in the city-states. a. Constructed to be the tallest structure. b. Ziggurats were believed to be the stairway to the gods.

Sumerian Writing III. Sumerian writing A. Cuneiform 1. Developed to keep accounts of business deals.

The Babylonians I. Babylonians A. Were Nomads before they conquered Sumer and adopted her ways. B. Contributions of the Babylonians. 1. Code of Hammurabi, written by Hammurabi (c. BC 1792 -1750) a. First account of recorded laws, total of 282 specific laws. b. Known as the "Eye for an Eye" laws 2. Constructed the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. a. A magnificent palace with many levels of gardens and palaces. 1 a. King Nebuchadnezzar built it for his homesick wife. According to accounts, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon were built to cheer up Nebuchadnezzar's homesick wife, Amyitis.

Code of Hammurabi

Birth of Judaism I. The origins of Judaism A. Abraham led his immediate family from Sumer to Canaan. (present day Israel) B. Followers of Abraham became known as Hebrews. C. A great famine forced the Hebrews to flee to Egypt. 1. Life in Egypt was harsh. 2. Hebrews were forced into slavery by the Egyptians. D. Moses and the Hebrews fled Egypt and returned to Canaan.

Judaism

Judaism II. Ten Commandments A. God (Jehovah) gave Moses the laws by which Hebrews would live and abide. 1. Belief in one God (Monotheism) 2. Governed religious beliefs and behavior. a. Laws forbade lying, stealing, murder, etc.

The Kingdom of Israel King Solomon 970 -930 BC United the tribes of Israel into the Kingdom of Israel. Solomon was the son of King David, and was known as a wise king. During this time Jerusalem became the capital of the Kingdom of Israel. Under the leadership of Solomon, Israel reached the height of its power. He built a great temple in Jerusalem which became the focal point of the Jewish Religion. The remains of this temple, now known as the Western Wall or Wailing Wall are still a focal point of the Jewish faith.

The Divided Kingdom After Solomon’s death the kingdom of Israel split into two parts Division: The Kingdom of Israel was the ten northern tribes with the capital city of Samaria. The Kingdom of Judah was the two tribes in the South with the capital of Jerusalem. The Assyrians destroyed the kingdom of Israel and scattered the people in 722 B. C. , these are known as the lost tribes of Israel. The Kingdom of Judah remained until it was destroyed by the Chaldeans (Neo Babylonians) and King Nebuchadnezzar in 586 B. C. beginning the Babylonian captivity which would last until the defeat of the Chaldeans by the Persian Empire and Cyrus the Great.

The Babylonian Captivity of the Jews was known as the first Diaspora The Diaspora is the scattering of the Jewish people. There have been two Diasporas. The first was the Babylonian captivity, which ended when the Persians freed the Jews and the Jews returned to Jerusalem and rebuilt the temple. During the Captivity there was an Age of Prophecy Prophets such as Isaiah and Ezekiel declared that the people needed to return to the original covenant or face punishment.

The Jews stayed in Israel until the Romans destroyed the Temple again in 70 AD, beginning the second Diaspora. After that the Jews were scattered throughout European anti-Semitism in the Middle Ages and the Holocaust of WWII forced many Jews to emigrate to the United States and many began to return to Israel. This led to the formation of the state of Israel by the United Nations in 1948 ending the second Diaspora. Many Jews consider any Jew not living in the Holy Land to still be in the Diaspora.

The Phoenicians established a trade empire, and colonies, throughout the Mediterranean. They traded several goods including glass and lumber. Their most important product was Tyrian purple, a dye made from boiling the Murex snail. This purple dye was very difficult and expensive to produce. It was very valuable to the rich. Murex snail
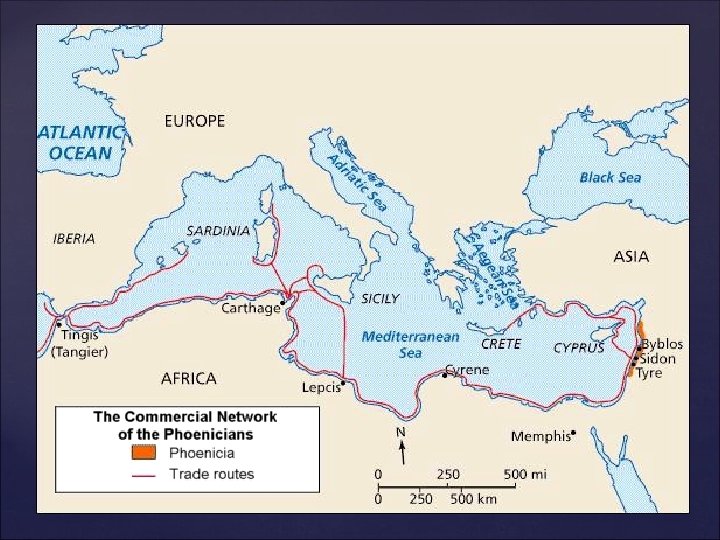

The Phoenicians spread their alphabet throughout the Mediterranean Their alphabet consisted of 22 letters, it did not have vowels. Unlike many early alphabets which were made of pictograms, the Phoenician alphabet was phonic (based on sound). These sounds could be assembled to make words. The Greeks eventually adopted this alphabet, which influenced the Latin Alphabet which we use today.

Phoenician alphabet -- note their writing reads right to left, and that some symbols were later re-used and made into vowels.

Phoenician Artifacts


The Assyrians Semitic-speaking people who exploited the use of iron weapons to build an empire by 700 B. C. Included Territory From Mesopotamia, some of the Iranian Plateau, Asia Minor, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt.

Eventually, the Assyrian Empire fell to several groups including the Chaldeans (Neo-Babylonians) and the Medes. Assyrian kings ruled with absolute power. Kingdoms were well organized and efficient. Kept direct contact with the people who helped administer their empire Assyrians established a system where they could relay messages by horseback and forth in a week’s time. Ashurbanipal Considered the greatest Assyrian King. He collected the writings of Mesopotamia and est. the great library of Nineveh, the capital.
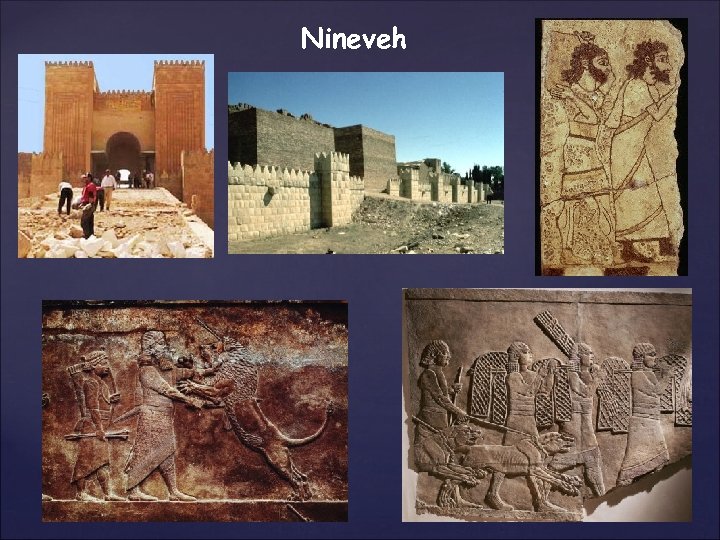

Nineveh

Military Strength The Assyrian military was one of the strongest in the ancient world. They used fierce iron weapons and psychological warfare. The Assyrians would often attempt to get an area to surrender before attack. If people refused and were defeated they were treated harshly. King Ashurnasirpal once stated “ 3, 000 of their combat troops I felled with weapons. . . Many I took alive; from some of these I cut off their hands to the wrists, from others I cut off their noses, ears and fingers; I put out the eyes of many of the soldiers. . I burned their young men and women to death. ”

The Persians Cyrus the Great Persian King who defeated Babylon and ended the Jews’ captivity. Cyrus ruled from 559 to 530 B. C. and was a great leader, hence the name Cyrus the Great. Cyrus was very respectful of other cultures. Not only did he free the Jews, but he also treated conquered peoples fairly. He allowed them to keep their own religions and customs. This respect made the people who lived under him respectful of his rule and less likely to revolt.

Expansion of Empire under Darius I Ruled from 521 -486 B. C. added western India to the Persian Empire. Then added Thrace in Europe and expanded the Empire to its greatest size. He also brought the Persian Empire into conflict with the Greeks. Satrapies Darius divided his empire into provinces called Satrapies to make it more manageable. Each province was ruled by a governor called a Satrap. This man was the protector of the kingdom. They collected taxes, provided justice and security, and got soldiers for the army.

The Royal Road The Royal road stretched from Lydia to Susa, the chief capital of the empire. It used a system of couriers similar to the Assyrians. This allowed for efficient communication in the empire Persian Military The Persians had an elite military. It contained people from all over the Persian Empire. The Immortals The Elite fighters of the Persian Empire. They were so called because in battle their numbers were never allowed to fall below 10, 000 men. They were constantly replaced from behind so they appeared to never die.

Persian kings became greedy and so the empire became weak. Family spats and assassinations became the rule of the day. The Empire was defeated by Alexander the Great during the 330’s B. C.
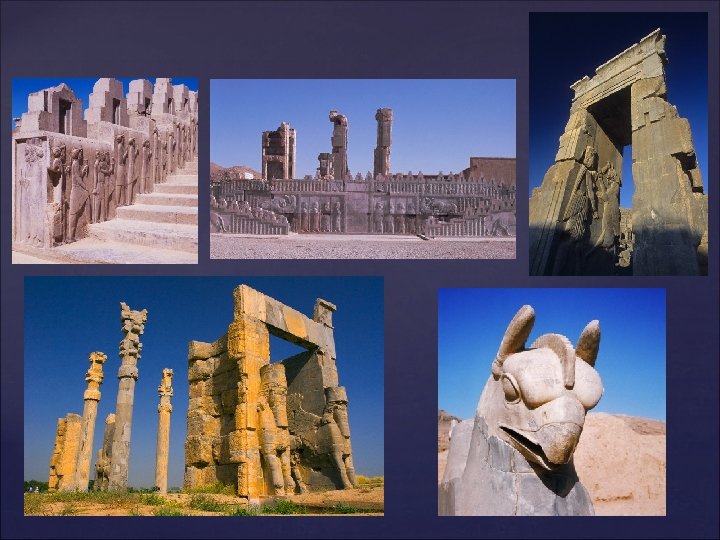
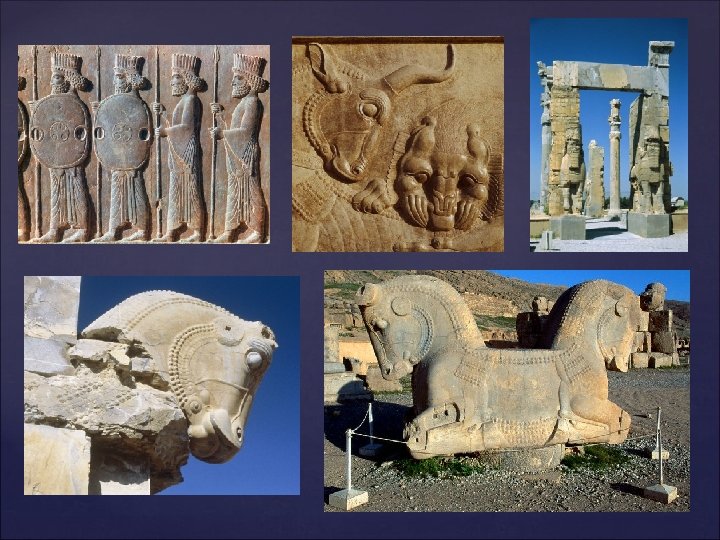



Persian Religion Zoroastrianism--Original Religion of the Zoroastrianism Persian Empire Zoroaster--Founder and Prophet of the Zoroaster-Religion. Also known as Zarathustra. Book: Zend Avesta, the recorded teachings of Zoroaster. Monotheistic--Taught belief in one Monotheistic-universal, all-powerful god. Ahura Mazda--The god of Zoroastrianism
7e0082454b8a29e0830bdd40c17cb45e.ppt