50a75328c3703d4ac5dff31081794aeb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Anatomy and Evaluation of the Brachial Plexus San Jose State University Undergraduate Athletic Training Educational Program

Contents l Anatomy of the Brachial Plexus l Mechanisms of Brachial Plexus Injury and Pathologies l Neurological Evaluation for the Brachial Plexus and Related Special Tests
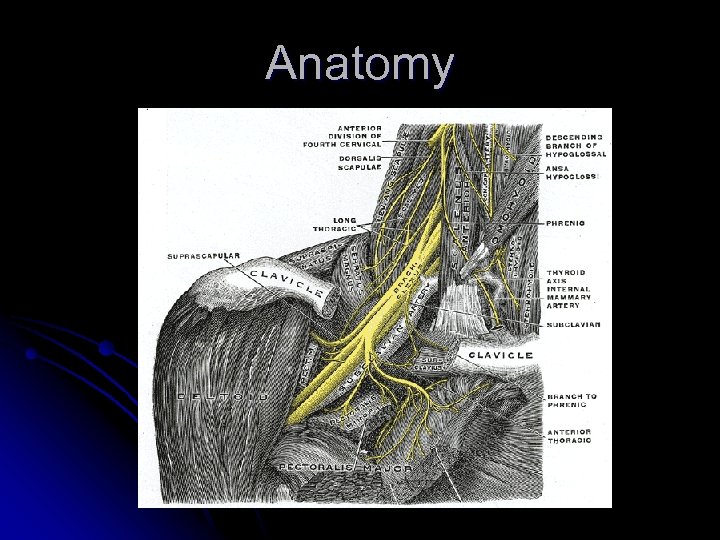
Anatomy

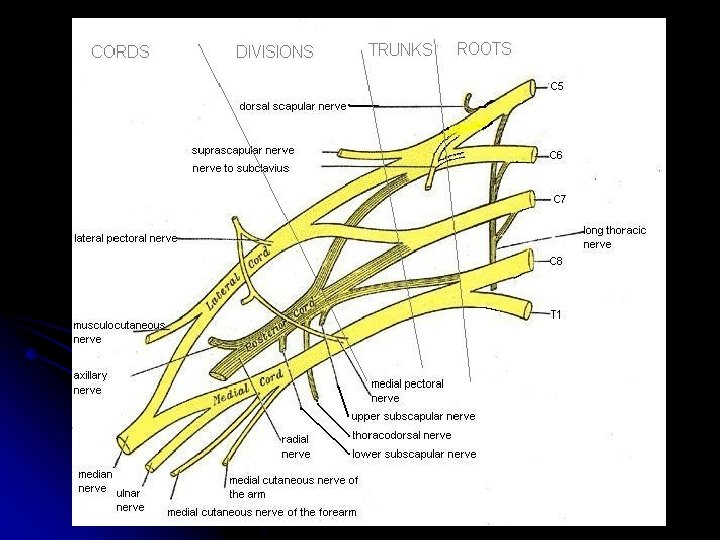
Levels l Roots l Real l Trunks l l Divisions l Drink l Cords l Cold l Branches l Beer Athletic Trainers
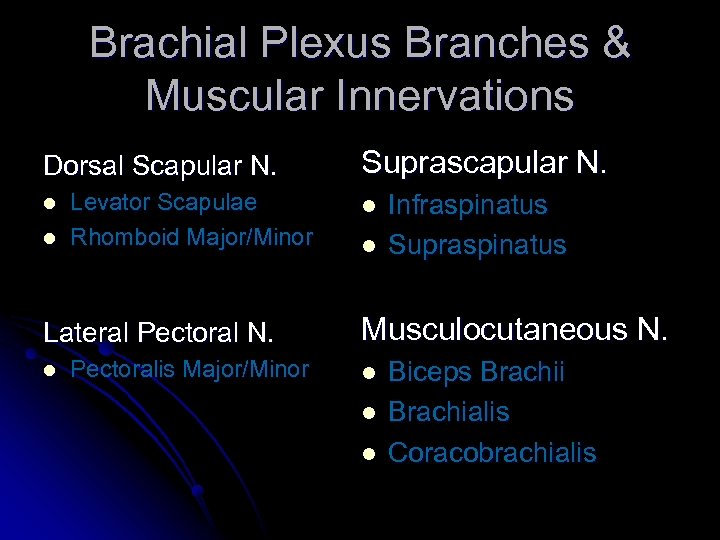
Brachial Plexus Branches & Muscular Innervations Dorsal Scapular N. l l Levator Scapulae Rhomboid Major/Minor Lateral Pectoral N. l Pectoralis Major/Minor Suprascapular N. l l Infraspinatus Supraspinatus Musculocutaneous N. l l l Biceps Brachii Brachialis Coracobrachialis
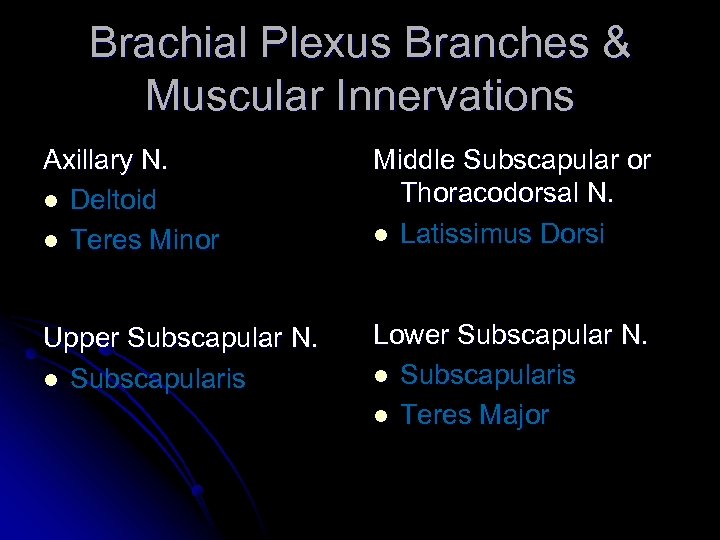
Brachial Plexus Branches & Muscular Innervations Axillary N. l Deltoid l Teres Minor Middle Subscapular or Thoracodorsal N. l Latissimus Dorsi Upper Subscapular N. l Subscapularis Lower Subscapular N. l Subscapularis l Teres Major

Brachial Plexus Branches & Muscular Innervations Median N. l l l l l Abductor Pollicis Brevis/Longus Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Flexor Digitorum Profundus (Lat. 2) Flexor Pollicis Brevis (Lat. ) & Longus Lumbricales (Lat. 2) Opponens Pollicis Palmaris Longus Pronator Quadratus Pronator Teres * Radial N. l l l Abductor Pollicis Brevis Anconeus Brachioradialis Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis/Longus Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Extensor Digiti Minimi Extensor Digitorum Communis Extensor Indicis Extensor Pollicis Brevis/Longus Supinator Triceps Brachii
Brachial Plexus Branches & Muscular Innervations Ulnar N. l l l l l Abductor Digiti Minimi Adductor Pollicis Dorsal Interossei Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Digiti Minimi Flexor Digitorum Profundus (Med. 2) Flexor Pollicis Brevis (Med. ) Lumbricals (Med. 2) Opponens Digiti Minimi Palmar Interossei Long Thoracic N. l Serratus Anterior Medial Pectoral N. l Pectoralis Major Medial Brachial Cutaneous N. (sensory) Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous N. (sensory)

Mechanisms of Injury to the Brachial Plexus

Brachial Plexus Injury Overview l Sports most commonly associated with brachial plexus injuries include: football, baseball, basketball, volleyball, fencing, wrestling, and gymnastics l Nerve injuries can result from blunt force trauma, poor posture, or chronic repetitive stress l Patients generally present with pain and/or muscle weakness l Over time, some patients may experience muscle atrophy (Duralde, 2000)

Brachial Plexus Injury Overview l l Before performing special tests, rule out fractures and dislocations Brachial plexus injuries resolve quicker than spinal cord injuries (Prentice, p. 846) l Evaluation for return-to-play should take into consideration symptoms, resolution time, and prior injuries to this region (Gorden, et al. , 2003) l Evaluate athletes immediately after injury and again after the game/practice (Kuhlman & Mc. Keag, 1998)

Three Mechanisms of Injury l Percussion l Traction l Cervical Nerve Compression

Percussion Occurs with direct blow to the supraclavicular fossa over Erb’s point (Troub, 2001) Example: Cross-check to a hockey player

Traction Occurs with a direct blow to the shoulder with the neck laterally flexed toward the unaffected shoulder (Troub, 2001) Example: Gymnast falls on beam

Cervical Nerve Compression Occurs when the neck is flexed laterally toward the patient’s affected shoulder Caused by compression or irritation of the nerves, resulting in point tenderness over involved vertebrae of affected nerve(s) (Troub, 2001) Example: Football player tackles an opponent
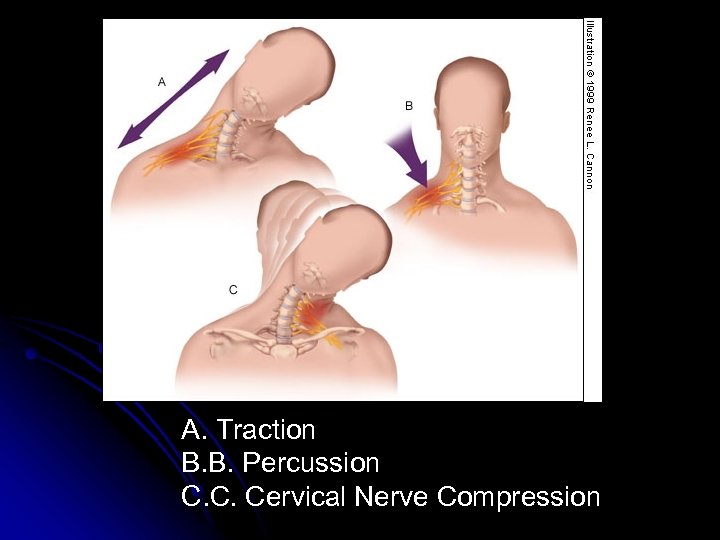
A. Traction B. B. Percussion C. C. Cervical Nerve Compression

Brachial Plexus Pathologies l “Burners” or “Stingers” l Associated with traction and/or compression l Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Burners or Stingers l Mechanisms of injury include cervical flexion away from the limb and hyperextension of the cervical spine l May present with pain, numbness, burning, and/or tingling from the shoulder to the fingers l Possible loss of function in arm and hand for several minutes up to several days (Prentice, p. 846)

Thoracic Outlet Syndrome l Caused by pressure on the brachial plexus and/or subclavian artery and/or vein l May present with numbness, paresthesia, pain, cool and pale skin, cyanosis or edema in upper extremity, and swollen veins (Prentice, pp. 683 -684) l Patient may also develop unilateral atrophy and/or lowered shoulder on affected side (Duralde, 2000)

Three Grades of Injury l Grade 1 – Neuropraxia l Grade 2 – Axonotmesis l Grade 3 – Neurotmesis

Grade 1 - Neuropraxia l Results in a disruption in the function of a nerve that produces numbness and tingling l Most common grade within athletics l Symptoms usually resolve within several minutes (Duralde, 2000)

Grade 2 - Axonotmesis l Damage to the nerve’s axon l Symptoms include numbness, tingling, and affected function (may last several days) l Long nerves have a greater healing time than short nerves l Rare within athletics (Duralde, 2000)

Grade 3 - Neurotmesis l Permanent nerve damage occurs l Very rare within athletics l “Occurs with high-energy trauma, fractures, and penetrating injuries” (Duralde, 2000)

C 5 -C 6 Affected l Motor Deficits: Shoulder abduction, shoulder flexion, elbow flexion, and wrist extension l Sensory Loss: Lateral arm, 1 st digit, and 2 nd digit

C 7 Affected l Motor Deficits: Elbow extension weakness and wrist flexion l Sensory Loss: Pad of index finger

C 8 -T 1 Affected (very rare) l Motor Deficits: Finger abduction/adduction and thumb flexors/extensors l Sensory Loss: 4 th digit, 5 th digit, medial forearm, and medial arm

C 5 -T 1 Affected l Motor Deficits: Scapular motion and entire arm l Sensory Loss: Entire arm, forearm, and hand
Process of Evaluation
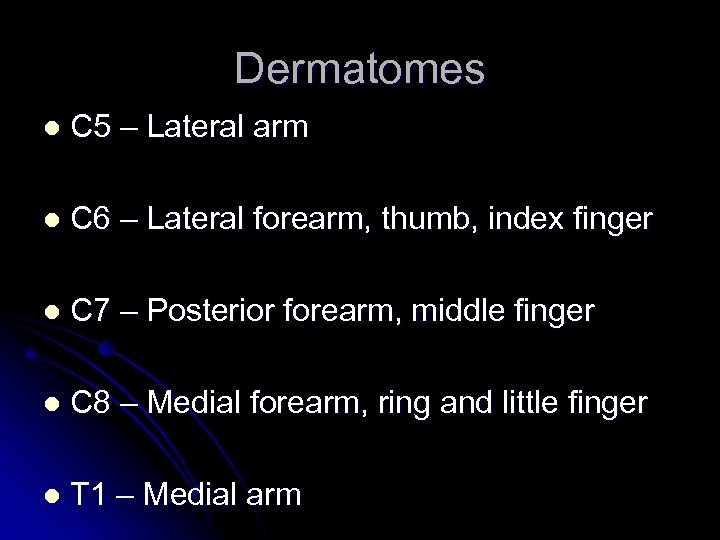
Dermatomes l C 5 – Lateral arm l C 6 – Lateral forearm, thumb, index finger l C 7 – Posterior forearm, middle finger l C 8 – Medial forearm, ring and little finger l T 1 – Medial arm

Myotomes l C 5 – Shoulder abduction l C 6 – Elbow flexion or wrist extension l C 7 – Elbow extension or wrist flexion l C 8 – Grip strength, shake hands l T 1 – Interossei, spread fingers and resist finger adduction
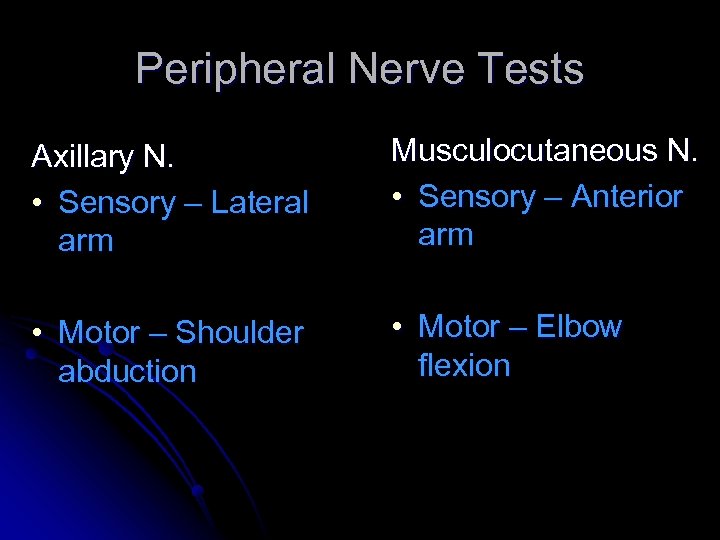
Peripheral Nerve Tests Axillary N. • Sensory – Lateral arm Musculocutaneous N. • Sensory – Anterior arm • Motor – Shoulder abduction • Motor – Elbow flexion
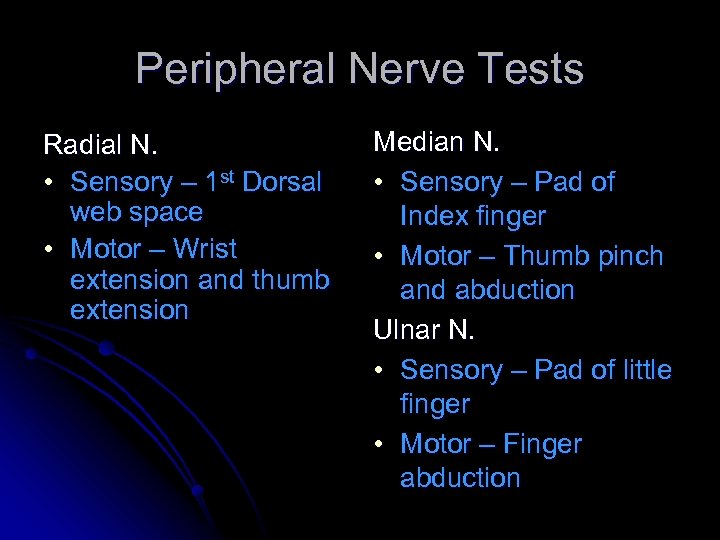
Peripheral Nerve Tests Radial N. • Sensory – 1 st Dorsal web space • Motor – Wrist extension and thumb extension Median N. • Sensory – Pad of Index finger • Motor – Thumb pinch and abduction Ulnar N. • Sensory – Pad of little finger • Motor – Finger abduction

Reflex Tests l C 5 – Biceps brachii reflex (anterior arm near antecubital fossa) l C 6 – Brachioradialis reflex (lateral aspect of forearm) l C 7 – Triceps brachii reflex (at insertion of tricep brachii) l C 8 and T 1 do not have reflex tests

Related Special Tests Brachial Plexus • Cervical Compression Test • Cervical Distraction Test • Spurling’s Test • Brachial Plexus Traction Test Thoracic Outlet Syndrome • Adson’s Test • Allen’s Test • Military Brace Position

References Duralde, X. A. (2000). Neurologic injuries in athlete’s shoulder. Journal of Athletic Training, 35(3), pp. 316 -318. Gorden, J. A. , Straub, S. J. , Swanik, C. B. , & Swanik, K. A. (2003). Effects of football collars on cervical hyperextension and lateral flexion. Journal of Athletic Training, 38(3), pp. 209 -218. Hoppenfeld, S. (1976). Physical Examination of the Spine & Extremities. Upper Saddle River: NJ: Prentice Hall. pp. 93 -127. Kuhlman, G. S. & Mc. Keag, D. B. (1999). The “burner”: A common nerve injury in contact sports. American Family Physician, 60(7). Retrieved April 5, 2006 from the American Academy of Family Physicians database. Martini, F. H. , Timmons, M. J. , & Tallitsch, R. B. (2003). Human Anatomy. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc. Starkey, C. & Ryan, J. (2002). Evaluation of Orthopedic and Athletic Injuries. Philadelphia, PA: F. A. Davis Company. Troub, M. (2001). Brachial plexus injuries in athletics: “Burners”. Northwest Texas Sports Medicine Clinic. Retrieved March 5, 2006 from the Northwest Texas Sports Medicine Clinic website.

Project Participants l Presenters: Heather Terbeek, Hank House, Cesar Cardenas, and Rachel Sorris l Models: Becky Roark & Kevin Geiger l Researchers: Caitlin Wall, Heather Terbeek, Hank House, Cesar Cardenas, and Becky Roark l Special Thanks to Our Faculty: Jeff Roberts, Dr. Leamor Kahanov, and Chris Warden
50a75328c3703d4ac5dff31081794aeb.ppt