99064dc613d8847c64efa20004ae7c54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

An Overview of the Reliability and the Fault Trends of the SRS Cheryl Hodgkinson Daresbury Laboratory Synchrotron Radiation Department WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Contents • Introduction • SRS Operational Statistics • Analysis of the Operational Data – Efficiency – Fault Statistics – Ageing and Obsolete Equipment • Maintaining Reliability – – Capital Investment and Redundancy Risk Analysis Post Incident Investigation and Modifications Preventative Maintenance and Scheduling • Conclusions and Acknowledgments WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Introduction • The Synchrotron Radiation Source – 2 Ge. V, 2 nd Generation Light Source – Constructed between 1975 and 1980 – Began scheduled user operations in 1981 – Some SRS systems, mainly injector components were salvaged from a previous accelerator – Operational user facility for 26 years and scheduled for closure December 2008 WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
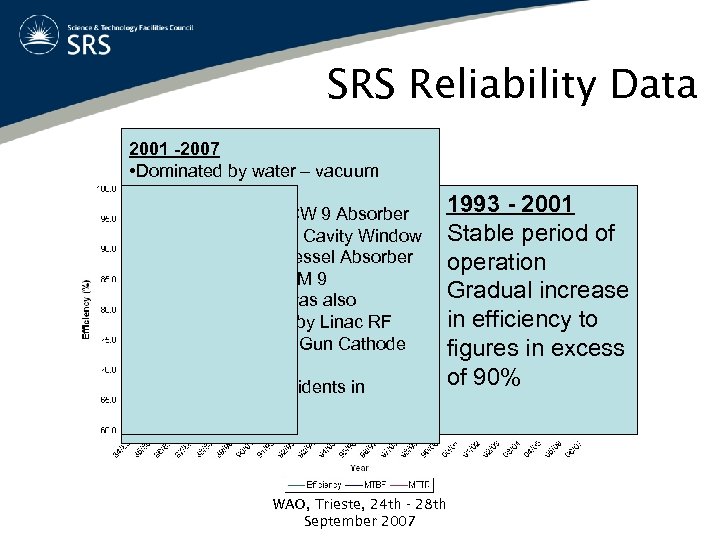
SRS Reliability Data 2001 -2007 • Dominated by water – vacuum incidents 1984 – 1992 1993 - 2001 • 01/02 (65%) SCW 9 Absorber • A number of upgrades • 04/05 (85%) RF Cavity Window Stable period of & Quadrupole Vessel Absorber operation • HBL • 06/07 (78%) TVM 9 Gradual increase • Undulator • Efficiency in 06/07 was also in efficiency to • SC Wavelength significantly effected by Linac RF and HT systems and Gun Cathode figures in excess Shifters issues. • in of 90% • Periods between incidents Erratic efficiency profile due to new systems excess of 90%. WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
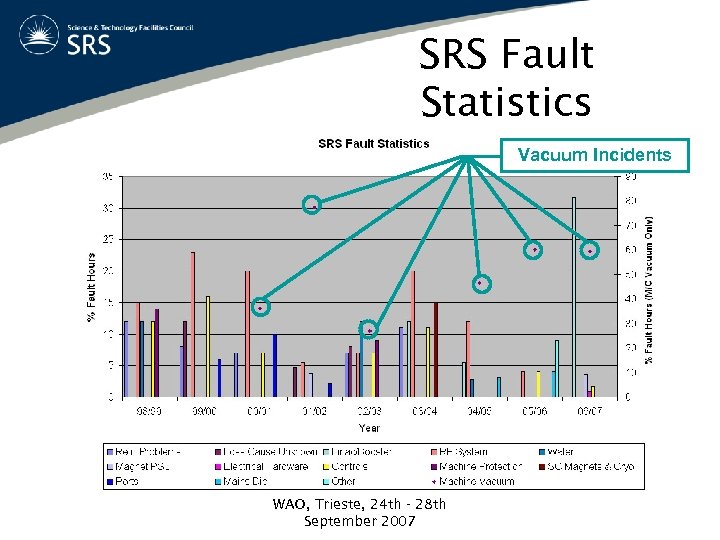
SRS Fault Statistics Vacuum Incidents WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
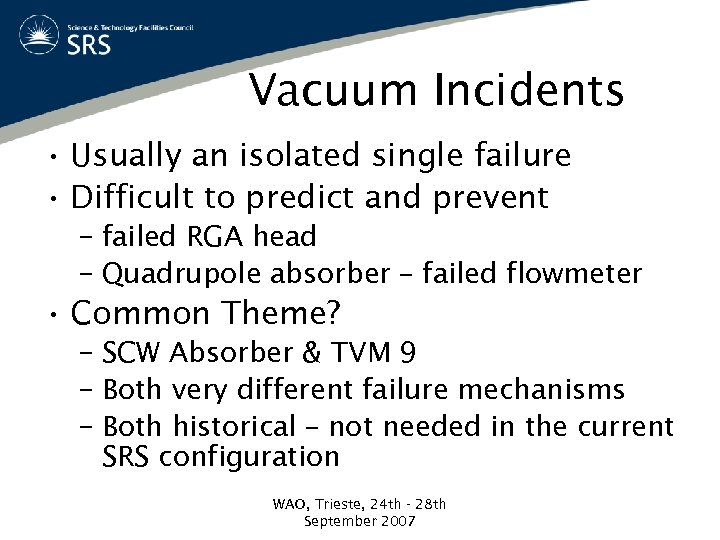
Vacuum Incidents • Usually an isolated single failure • Difficult to predict and prevent – failed RGA head – Quadrupole absorber – failed flowmeter • Common Theme? – SCW Absorber & TVM 9 – Both very different failure mechanisms – Both historical – not needed in the current SRS configuration WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
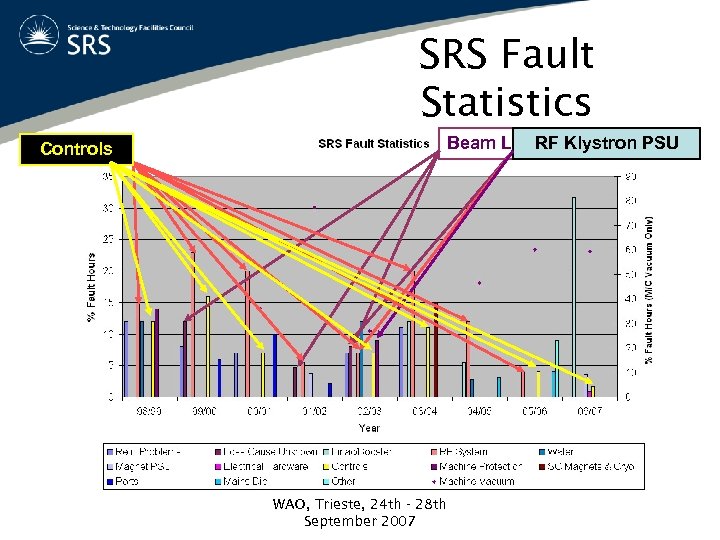
SRS Fault Statistics RF System Controls Beam Loss Cause Unknown RF Klystron PSU WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
Ageing and Obsolete Equipment • Early Equipment – Built in-house – Repairs in-situ (time) – Can be repaired • Later Equipment – – Plug-in Replaced with a spare Return to manufacturer for repair Support issues WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Ageing and Obsolete Equipment • Concern regarding condition of in RESULT vacuum water circuits No evidence of wall thinning or erosion – 17 year old absorber removed from storage ring – Area’s milled away to examine any wall thinning WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Ageing and Obsolete Equipment • External water circuits – Elbows – Near feedthroughs – Potential for vacuum incident during repair – Potential to cause more serious failure WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
Ageing Machine – It’s not just equipment! • It’s about people too! – Loss of design and build knowledge, as staff retire • Less documentation for older equipment, drawings, maintenance schedules, etc. • Can’t teach 20 years design, build and operational knowledge. – Succession planning important – You only know what’s been missed when the fault occurs • Lapses in maintenance schedules • Longer fault rectification WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
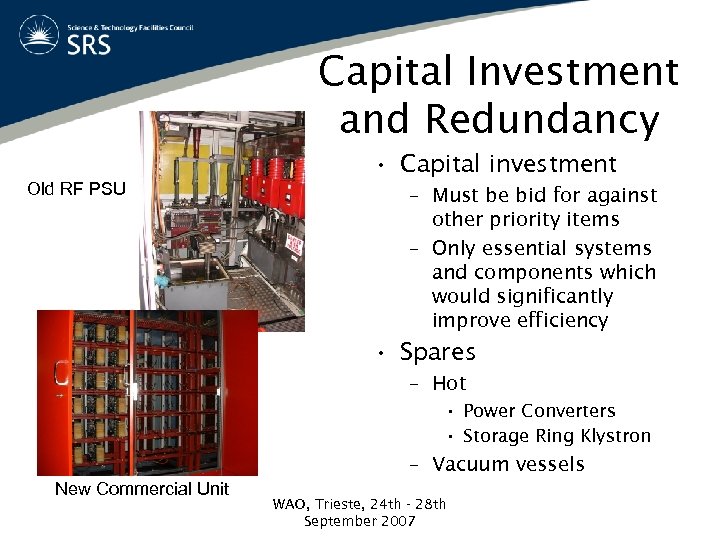
Capital Investment and Redundancy • Capital investment Old RF PSU – Must be bid for against other priority items – Only essential systems and components which would significantly improve efficiency • Spares – Hot • Power Converters • Storage Ring Klystron – Vacuum vessels New Commercial Unit WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Risk Analysis • Benefit difficult to assess – The biggest risk is the one you don’t know about • At top level – Difficult to compare risk and focus resource – How do you compare extremely reliable long lead time items against components that fail frequently, but are a fast repair? – Does highlight major issues • Linac Klystron WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
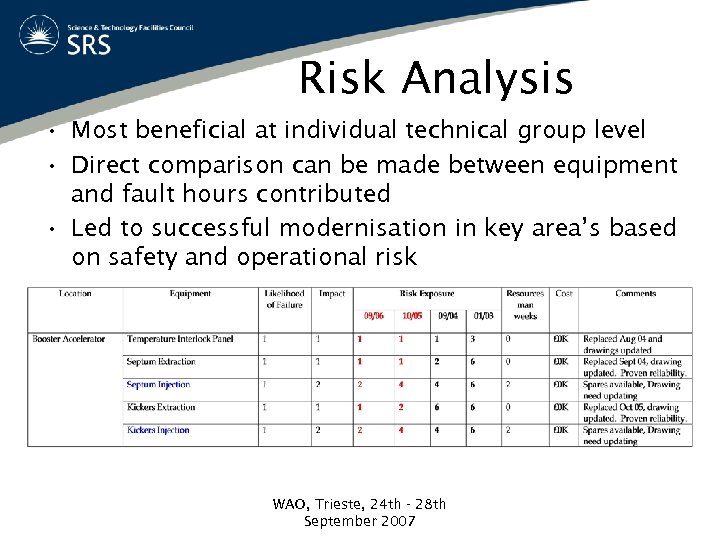
Risk Analysis • Most beneficial at individual technical group level • Direct comparison can be made between equipment and fault hours contributed • Led to successful modernisation in key area’s based on safety and operational risk WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
Post Incident Investigation • Learning from incidents is important • Committee is always formed to recover and also determine actions to prevent reoccurrence. • Actions from recent faults – Modification to TVM cooling pipes – Revised interlock testing schedule – Test rig to test thermionic valves on-site WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
Preventative Maintenance and Scheduling WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Conclusions • The SRS has provided reliable user operations for over 26 years • Vacuum incidents are isolated incidents, which do not indicate any form of systematic failure which would limit the life of the SRS • Only evidence of any systematic failure due to ageing is the failure of copper elbows on water circuits • The high operating efficiency demanded by the light source community can be maintained on an ageing machine using a variety of techniques. WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007

Acknowledgments • The author would like to thank – Previous SRS Operations Managers for compiling these statistics – Current and past Operations Teams for providing the data – Steve Griffiths of EE&PS for providing his Groups Risk Analysis Data And Finally. . . Daresbury Staff past and present for their contributions to SRS Operations WAO, Trieste, 24 th - 28 th September 2007
99064dc613d8847c64efa20004ae7c54.ppt