89f7320bfd555cfd7f5043555c240af3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 An Overview of the History and Current Status of Telehealth in Canada INET MINI-CONFERENCE June 20, 2007 Laurie Poole, BSc. N, MHSA, CHE President, Canadian Society of Telehealth
An Overview of the History and Current Status of Telehealth in Canada INET MINI-CONFERENCE June 20, 2007 Laurie Poole, BSc. N, MHSA, CHE President, Canadian Society of Telehealth
 Outline • The Canadian Society of Telehealth • What is Telehealth? • Update on Telehealth Activities in Canada • Barriers to Success • Requirements for a Shared Vision • Questions and discussion
Outline • The Canadian Society of Telehealth • What is Telehealth? • Update on Telehealth Activities in Canada • Barriers to Success • Requirements for a Shared Vision • Questions and discussion
 The Canadian Society of Telehealth • The National Voice of Telehealth in Canada • Affiliated with other e-health organizations (Collaboration Agreement with COACH) • Leadership, Advocacy, Policy & Education • Forum for exchange of ideas and knowledge • Subject Matter Expertise (e. g. Canada Health Infoway) Slide #: 3
The Canadian Society of Telehealth • The National Voice of Telehealth in Canada • Affiliated with other e-health organizations (Collaboration Agreement with COACH) • Leadership, Advocacy, Policy & Education • Forum for exchange of ideas and knowledge • Subject Matter Expertise (e. g. Canada Health Infoway) Slide #: 3
 Telehealth: the use of information & communication technology to exchange health information and provide health care and wellness services Telecommunication infrastructure is a pre-requisite Telehealth solutions enable health service delivery channels: Tele-Consultations Videoconferencing stations, communication enabled medical devices Tele-Education Videoconferencing stations used for training/education Home Telehealth Active or passive monitoring of remote patients for pre/ post-op procedures, CDM etc. Tele-triage Centralized health call centers to offer first line delivery of service to clients as part of primary care and emergency response Scheduling Solutions – a key enabler required for the effective use of telehealth service delivery EHR Infostructures support telehealth applications as per any other Point-of-Service Application
Telehealth: the use of information & communication technology to exchange health information and provide health care and wellness services Telecommunication infrastructure is a pre-requisite Telehealth solutions enable health service delivery channels: Tele-Consultations Videoconferencing stations, communication enabled medical devices Tele-Education Videoconferencing stations used for training/education Home Telehealth Active or passive monitoring of remote patients for pre/ post-op procedures, CDM etc. Tele-triage Centralized health call centers to offer first line delivery of service to clients as part of primary care and emergency response Scheduling Solutions – a key enabler required for the effective use of telehealth service delivery EHR Infostructures support telehealth applications as per any other Point-of-Service Application
 Benefits of Telehealth • Increase access to health care services • Improve quality of care • Reduce health care costs Slide #: 5
Benefits of Telehealth • Increase access to health care services • Improve quality of care • Reduce health care costs Slide #: 5
 Telehealth in Action Telehealth Consultations in a one year period: Nova Scotia : 2, 573 total telehealth sessions 1, 170 clinical telehealth sessions Manitoba: 4, 842 total telehealth sessions 3, 149 clinical sessions Ontario: 33, 000 total telehealth sessions 25, 000 clinical consults Slide #: 6
Telehealth in Action Telehealth Consultations in a one year period: Nova Scotia : 2, 573 total telehealth sessions 1, 170 clinical telehealth sessions Manitoba: 4, 842 total telehealth sessions 3, 149 clinical sessions Ontario: 33, 000 total telehealth sessions 25, 000 clinical consults Slide #: 6
 Telehealth at Work K-net Telehealth • Grew from 5 FN communities in 2003 to 24 communities in 2006 • Vast land mass (average community population 700) • Estimated program costs: $2. 8 million/year • Estimated travel savings: $4. 2 million/year • Patient satisfaction > 90% Slide #: 7
Telehealth at Work K-net Telehealth • Grew from 5 FN communities in 2003 to 24 communities in 2006 • Vast land mass (average community population 700) • Estimated program costs: $2. 8 million/year • Estimated travel savings: $4. 2 million/year • Patient satisfaction > 90% Slide #: 7
 Telehealth at Work Slide #: 8
Telehealth at Work Slide #: 8
 Canadian Telehealth Domains Clinical Consultations and Follow-up (Examples) • • • • thoracic psychiatry (adult, geriatric and pediatric) forensic mental health assessments orthopedic ophthalmology pathology live fetal ultrasound interpretation, live paediatric cardiac echo paediatric swallow assessments Oncology - cancer care Dietary (e. g. eating disorders), endocrinology anesthesiology radiology – digital imaging Slide #: 9 • • • • chronic disease mgt (diabetes etc) cardiology pre-op, post Op general surgery gastroenterology physio therapy nephrology neurology wound management and dermatology rheumatology speech and language genetic counseling family visits ergonomic assessments Home Telehealth 24/7 Tele-nurse Lines
Canadian Telehealth Domains Clinical Consultations and Follow-up (Examples) • • • • thoracic psychiatry (adult, geriatric and pediatric) forensic mental health assessments orthopedic ophthalmology pathology live fetal ultrasound interpretation, live paediatric cardiac echo paediatric swallow assessments Oncology - cancer care Dietary (e. g. eating disorders), endocrinology anesthesiology radiology – digital imaging Slide #: 9 • • • • chronic disease mgt (diabetes etc) cardiology pre-op, post Op general surgery gastroenterology physio therapy nephrology neurology wound management and dermatology rheumatology speech and language genetic counseling family visits ergonomic assessments Home Telehealth 24/7 Tele-nurse Lines
 Telehealth Myths • Build it and they will come • All practitioners like it • Training one person is all you need to do • Broadband is everywhere • One size fits all and it’s plug and play Slide #: 10
Telehealth Myths • Build it and they will come • All practitioners like it • Training one person is all you need to do • Broadband is everywhere • One size fits all and it’s plug and play Slide #: 10
 Telehealth Myths • If something goes wrong with a group of physicians, you will get another chance • The government is here to help • New equipment is always backward compatible • Networks never fail • It’s just wires and doctors Slide #: 11
Telehealth Myths • If something goes wrong with a group of physicians, you will get another chance • The government is here to help • New equipment is always backward compatible • Networks never fail • It’s just wires and doctors Slide #: 11
 What are the issues? • Telehealth should not be an additional silo of clinical information • Telehealth should not be an isolated channel of service delivery Slide #: 12
What are the issues? • Telehealth should not be an additional silo of clinical information • Telehealth should not be an isolated channel of service delivery Slide #: 12
 What are the issues? • The core issue is the scope and complexity of telehealth integration: – Technology – Data – Governance and policy – Service planning, delivery and performance measurement – Clinician workflow – Consumer participation Slide #: 13
What are the issues? • The core issue is the scope and complexity of telehealth integration: – Technology – Data – Governance and policy – Service planning, delivery and performance measurement – Clinician workflow – Consumer participation Slide #: 13
 Technology and Data Integration • Point of Service (POS) Systems – – Integrated workstations Laptops and handhelds Kiosks Patient home access • Network infrastructure – Bandwidth management – Wireless capability – Home and office automation Slide #: 14
Technology and Data Integration • Point of Service (POS) Systems – – Integrated workstations Laptops and handhelds Kiosks Patient home access • Network infrastructure – Bandwidth management – Wireless capability – Home and office automation Slide #: 14
 Technology and Data Integration • Privacy and security – Secure access – Consent management – Secondary use of data • Data capture and exchange – Standards to support technical and semantic interoperability – Comprehensive information to support decision making at the point of care – Minimum data set for longitudinal storage Slide #: 15
Technology and Data Integration • Privacy and security – Secure access – Consent management – Secondary use of data • Data capture and exchange – Standards to support technical and semantic interoperability – Comprehensive information to support decision making at the point of care – Minimum data set for longitudinal storage Slide #: 15
 Governance and Policy • Licensure – Legal, ethical responsibilities – Cross jurisdictional issues – Provincial-territorial response • Credentialing – Credentials for practitioners who provide remote consultations – CCHSA/NIFTE Guidelines Slide #: 16
Governance and Policy • Licensure – Legal, ethical responsibilities – Cross jurisdictional issues – Provincial-territorial response • Credentialing – Credentials for practitioners who provide remote consultations – CCHSA/NIFTE Guidelines Slide #: 16
 Governance and Policy • Reimbursement – Absence of policies impacting telehealth adoption – Coverage is neither consistent nor complete – Being addressed by P/T jurisdictions (e. g. Alberta) • Consent – – Slide #: 17 Type of consent required Who should obtain the consent Where is it stored Specific needs regarding cross-jurisdiction
Governance and Policy • Reimbursement – Absence of policies impacting telehealth adoption – Coverage is neither consistent nor complete – Being addressed by P/T jurisdictions (e. g. Alberta) • Consent – – Slide #: 17 Type of consent required Who should obtain the consent Where is it stored Specific needs regarding cross-jurisdiction
 Service Planning, Delivery and Performance Management • Vision and goal setting • Service design, resourcing and budgeting • Change management and training • Quality Improvement • Accreditation Slide #: 18
Service Planning, Delivery and Performance Management • Vision and goal setting • Service design, resourcing and budgeting • Change management and training • Quality Improvement • Accreditation Slide #: 18
 Clinical Adoption & Consumer Participation • Clinician Adoption and Workflow – Early exposure and demonstration of ‘best practices’ – Physician automation • Consumer participation – Building confidence and competence – Link to providers – Human Factors Slide #: 19
Clinical Adoption & Consumer Participation • Clinician Adoption and Workflow – Early exposure and demonstration of ‘best practices’ – Physician automation • Consumer participation – Building confidence and competence – Link to providers – Human Factors Slide #: 19
 Physicians not integrating ICTs in workflow • Physicians in general early adopters of ICTs, but have difficulty integrating into workflow and patient care • 88% of Canadians use internet, but 1 out of 2 users access it from home, not the office • Demographics are changing use: 53% of Canadians physicians under 35 are using PDAs (compared to less than 33% of physicians over 55). (CMA) • GP offices face the same challenges are other SMEs in using ICTs (lack of time and expertise, transforming business processes) Slide #: 20 Source: Canada Health Infoway, 2005
Physicians not integrating ICTs in workflow • Physicians in general early adopters of ICTs, but have difficulty integrating into workflow and patient care • 88% of Canadians use internet, but 1 out of 2 users access it from home, not the office • Demographics are changing use: 53% of Canadians physicians under 35 are using PDAs (compared to less than 33% of physicians over 55). (CMA) • GP offices face the same challenges are other SMEs in using ICTs (lack of time and expertise, transforming business processes) Slide #: 20 Source: Canada Health Infoway, 2005
 Adoption and Change Management • Quebec Legislation (November 2005) • Technical Advancements • Health Care Restructuring • Move towards the development of Electronic Health Records • Consumer Demand & Expectations Slide #: 21
Adoption and Change Management • Quebec Legislation (November 2005) • Technical Advancements • Health Care Restructuring • Move towards the development of Electronic Health Records • Consumer Demand & Expectations Slide #: 21
 Why focus on ICT? • Health care is a priority for Canadians • A crucial economic sector – – – 13% of Canada’s GDP (est. 2006) Estimated $142 B spending in 2005 Close to 40% of P/T expenditures Employs over 1. 5 million people (2006) Responsible for estimated 34% of business R&D (2004) • Health care sector is a heavy user of technology for diagnostics, but less for business process efficiency Slide #: 22 Source: Canada Health Infoway, Stat. Can
Why focus on ICT? • Health care is a priority for Canadians • A crucial economic sector – – – 13% of Canada’s GDP (est. 2006) Estimated $142 B spending in 2005 Close to 40% of P/T expenditures Employs over 1. 5 million people (2006) Responsible for estimated 34% of business R&D (2004) • Health care sector is a heavy user of technology for diagnostics, but less for business process efficiency Slide #: 22 Source: Canada Health Infoway, Stat. Can
 Opportunity for Integration Electronic Health Records Electronic health record systems can help improve patient health outcomes, decrease duplication, error and costs; and reduce waits. Without electronic health records, national directions to improve primary health care, public health, drugs drug and patient safety, chronic diseases, cancer and wait times will not be successful. Public Health Primary Health Care Electronic health record systems form the foundation for a health information and communications infostructure that can enable modern health care delivery. Slide #: 23 Source: Canada Health Infoway, 2006 Drugs and Patient Safety Information & Communications Technologies Wait Times Cancer Chronic Disease
Opportunity for Integration Electronic Health Records Electronic health record systems can help improve patient health outcomes, decrease duplication, error and costs; and reduce waits. Without electronic health records, national directions to improve primary health care, public health, drugs drug and patient safety, chronic diseases, cancer and wait times will not be successful. Public Health Primary Health Care Electronic health record systems form the foundation for a health information and communications infostructure that can enable modern health care delivery. Slide #: 23 Source: Canada Health Infoway, 2006 Drugs and Patient Safety Information & Communications Technologies Wait Times Cancer Chronic Disease
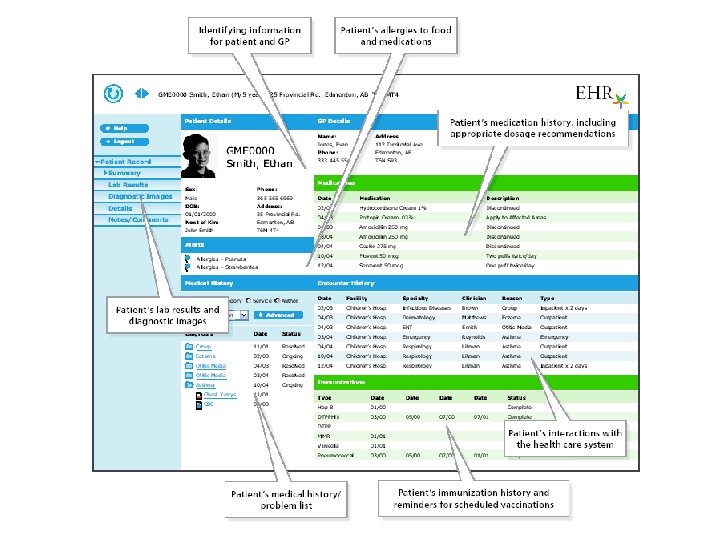
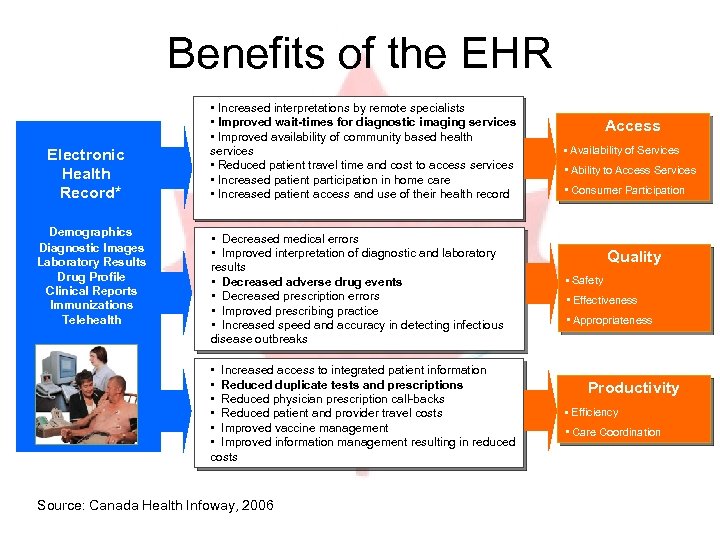 Benefits of the EHR Electronic Health Record* Demographics Diagnostic Images Laboratory Results Drug Profile Clinical Reports Immunizations Telehealth • Increased interpretations by remote specialists • Improved wait-times for diagnostic imaging services • Improved availability of community based health services • Reduced patient travel time and cost to access services • Increased patient participation in home care • Increased patient access and use of their health record • Decreased medical errors • Improved interpretation of diagnostic and laboratory results • Decreased adverse drug events • Decreased prescription errors • Improved prescribing practice • Increased speed and accuracy in detecting infectious disease outbreaks • Increased access to integrated patient information • Reduced duplicate tests and prescriptions • Reduced physician prescription call-backs • Reduced patient and provider travel costs • Improved vaccine management • Improved information management resulting in reduced costs Source: Canada Health Infoway, 2006 Access • Availability of Services • Ability to Access Services • Consumer Participation Quality • Safety • Effectiveness • Appropriateness Productivity • Efficiency • Care Coordination
Benefits of the EHR Electronic Health Record* Demographics Diagnostic Images Laboratory Results Drug Profile Clinical Reports Immunizations Telehealth • Increased interpretations by remote specialists • Improved wait-times for diagnostic imaging services • Improved availability of community based health services • Reduced patient travel time and cost to access services • Increased patient participation in home care • Increased patient access and use of their health record • Decreased medical errors • Improved interpretation of diagnostic and laboratory results • Decreased adverse drug events • Decreased prescription errors • Improved prescribing practice • Increased speed and accuracy in detecting infectious disease outbreaks • Increased access to integrated patient information • Reduced duplicate tests and prescriptions • Reduced physician prescription call-backs • Reduced patient and provider travel costs • Improved vaccine management • Improved information management resulting in reduced costs Source: Canada Health Infoway, 2006 Access • Availability of Services • Ability to Access Services • Consumer Participation Quality • Safety • Effectiveness • Appropriateness Productivity • Efficiency • Care Coordination
 Disease Management A system of coordinated health care interventions and communications for populations with conditions in which selfcare efforts are significant Disease Management Association of America (DMAA) Slide #: 26
Disease Management A system of coordinated health care interventions and communications for populations with conditions in which selfcare efforts are significant Disease Management Association of America (DMAA) Slide #: 26
 Value Created by Telehealth & EHR • Healthcare professionals make clinical decisions based on knowledge • Better knowledge translates to better care • Knowledge starts with accurate, relevant clinical information • The EHR creates the capability to share relevant clinical information • The 5 Rs of the EHR: – The right information – About the right client – Available to the right person – In the right place – At the right time Slide #: 27
Value Created by Telehealth & EHR • Healthcare professionals make clinical decisions based on knowledge • Better knowledge translates to better care • Knowledge starts with accurate, relevant clinical information • The EHR creates the capability to share relevant clinical information • The 5 Rs of the EHR: – The right information – About the right client – Available to the right person – In the right place – At the right time Slide #: 27
 In Summary… • Telehealth can’t exist in a vacuum • Technology continues to outpace governance, policies and legislation • It’s main principle is more about people and relationships than technology • How will we know when we’re there? Slide #: 28
In Summary… • Telehealth can’t exist in a vacuum • Technology continues to outpace governance, policies and legislation • It’s main principle is more about people and relationships than technology • How will we know when we’re there? Slide #: 28
 Shared Vision • • • Enabler in achieving healthcare goals Standards Development Political Will Integration with the EHR When we no longer use the prefix ‘tele” OR • When we no longer have to ask “what is telehealth” Slide #: 29
Shared Vision • • • Enabler in achieving healthcare goals Standards Development Political Will Integration with the EHR When we no longer use the prefix ‘tele” OR • When we no longer have to ask “what is telehealth” Slide #: 29
 Telehealth Vision Telehealth is a service delivery component within the larger e-health domain and has applicability across the whole continuum of health care delivery. It is a mode of delivery for health care and health education that is becoming more integrated with the overall delivery of health care services. Source: CST White Paper, Telehealth- What the Future Holds, May 2007 Slide #: 30
Telehealth Vision Telehealth is a service delivery component within the larger e-health domain and has applicability across the whole continuum of health care delivery. It is a mode of delivery for health care and health education that is becoming more integrated with the overall delivery of health care services. Source: CST White Paper, Telehealth- What the Future Holds, May 2007 Slide #: 30
 Join us in St. John’s for our 10 th Annual Conference Slide #: 31
Join us in St. John’s for our 10 th Annual Conference Slide #: 31

 Thank You www. cst-sct. org email: lpoole@clinidata. com Slide #: 33
Thank You www. cst-sct. org email: lpoole@clinidata. com Slide #: 33


