d41f5f4fb6d3f74e6916132835c75809.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 An Overview of National Health Reform Presentation Developed for the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy Updated: February 2015
An Overview of National Health Reform Presentation Developed for the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy Updated: February 2015
 Health Care Reform • Comprehensive health reform, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) , signed into law on March 23, 2010 • Significant industry-wide changes – expanded health insurance coverage – control rising costs – improve health care delivery system
Health Care Reform • Comprehensive health reform, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) , signed into law on March 23, 2010 • Significant industry-wide changes – expanded health insurance coverage – control rising costs – improve health care delivery system
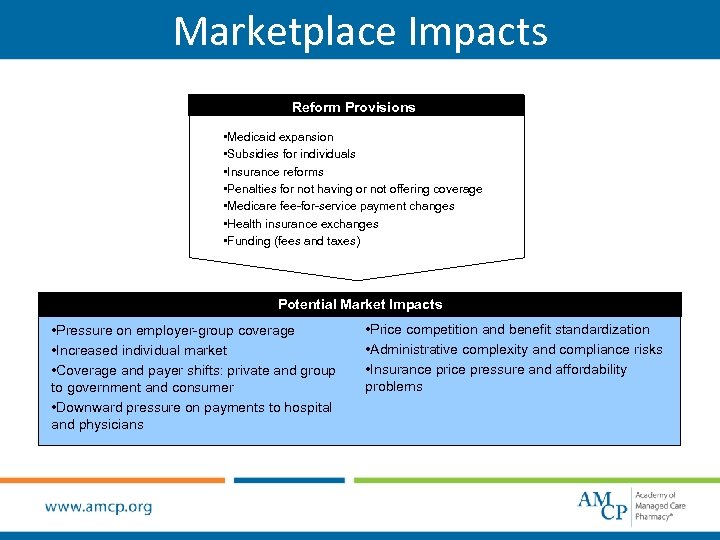 Marketplace Impacts Reform Provisions • Medicaid expansion • Subsidies for individuals • Insurance reforms • Penalties for not having or not offering coverage • Medicare fee-for-service payment changes • Health insurance exchanges • Funding (fees and taxes) Potential Market Impacts • Pressure on employer-group coverage • Increased individual market • Coverage and payer shifts: private and group to government and consumer • Downward pressure on payments to hospital and physicians • Price competition and benefit standardization • Administrative complexity and compliance risks • Insurance price pressure and affordability problems
Marketplace Impacts Reform Provisions • Medicaid expansion • Subsidies for individuals • Insurance reforms • Penalties for not having or not offering coverage • Medicare fee-for-service payment changes • Health insurance exchanges • Funding (fees and taxes) Potential Market Impacts • Pressure on employer-group coverage • Increased individual market • Coverage and payer shifts: private and group to government and consumer • Downward pressure on payments to hospital and physicians • Price competition and benefit standardization • Administrative complexity and compliance risks • Insurance price pressure and affordability problems
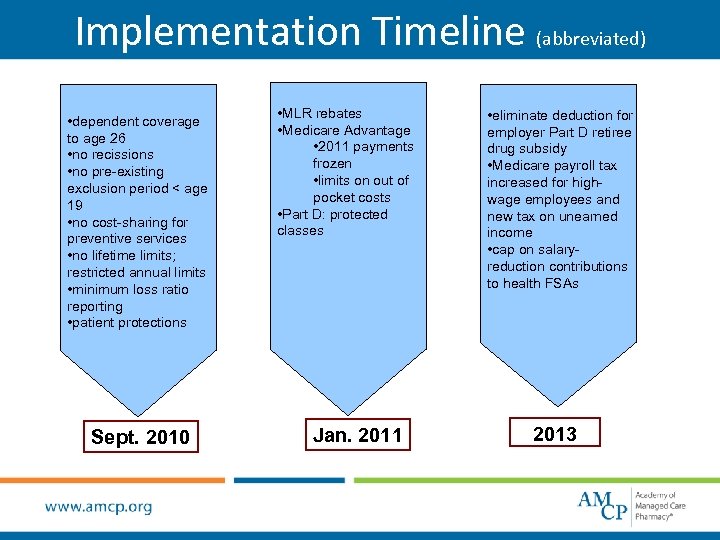 Implementation Timeline (abbreviated) • dependent coverage to age 26 • no recissions • no pre-existing exclusion period < age 19 • no cost-sharing for preventive services • no lifetime limits; restricted annual limits • minimum loss ratio reporting • patient protections Sept. 2010 • MLR rebates • Medicare Advantage • 2011 payments frozen • limits on out of pocket costs • Part D: protected classes Jan. 2011 • eliminate deduction for employer Part D retiree drug subsidy • Medicare payroll tax increased for highwage employees and new tax on unearned income • cap on salaryreduction contributions to health FSAs 2013
Implementation Timeline (abbreviated) • dependent coverage to age 26 • no recissions • no pre-existing exclusion period < age 19 • no cost-sharing for preventive services • no lifetime limits; restricted annual limits • minimum loss ratio reporting • patient protections Sept. 2010 • MLR rebates • Medicare Advantage • 2011 payments frozen • limits on out of pocket costs • Part D: protected classes Jan. 2011 • eliminate deduction for employer Part D retiree drug subsidy • Medicare payroll tax increased for highwage employees and new tax on unearned income • cap on salaryreduction contributions to health FSAs 2013
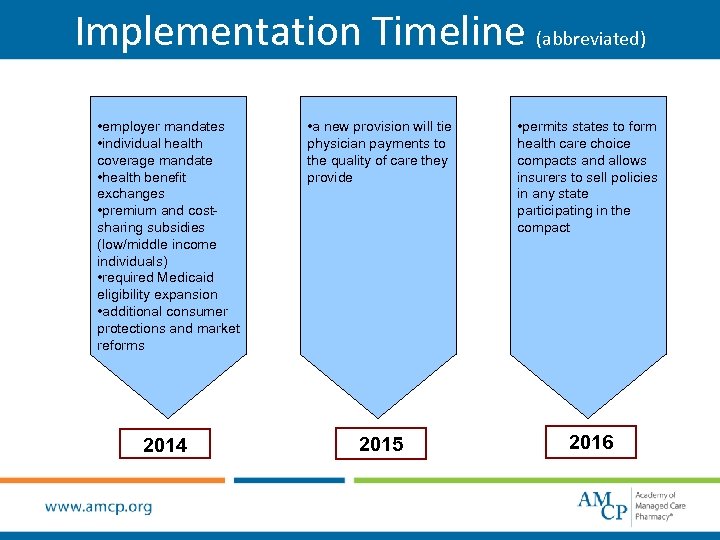 Implementation Timeline (abbreviated) • employer mandates • individual health coverage mandate • health benefit exchanges • premium and costsharing subsidies (low/middle income individuals) • required Medicaid eligibility expansion • additional consumer protections and market reforms • a new provision will tie physician payments to the quality of care they provide • permits states to form health care choice compacts and allows insurers to sell policies in any state participating in the compact 2014 2015 2016
Implementation Timeline (abbreviated) • employer mandates • individual health coverage mandate • health benefit exchanges • premium and costsharing subsidies (low/middle income individuals) • required Medicaid eligibility expansion • additional consumer protections and market reforms • a new provision will tie physician payments to the quality of care they provide • permits states to form health care choice compacts and allows insurers to sell policies in any state participating in the compact 2014 2015 2016
 ACA Implementation Delays In July of 2013, the Obama administration announced the following delays in the implementation of ACA 1) The requirement that some employer health insurance plans cap employee out of pocket cost 2) The requirement that small businesses offer either a single plan or allow employees to choose among different plans 3) The mandate that larger employers offer health insurance was postponed until 2015 4) The limit on out of pocket costs, including deductibles and co-payments, not to exceed $6, 350 for an individual and $12, 700 for a family was postponed until 2015
ACA Implementation Delays In July of 2013, the Obama administration announced the following delays in the implementation of ACA 1) The requirement that some employer health insurance plans cap employee out of pocket cost 2) The requirement that small businesses offer either a single plan or allow employees to choose among different plans 3) The mandate that larger employers offer health insurance was postponed until 2015 4) The limit on out of pocket costs, including deductibles and co-payments, not to exceed $6, 350 for an individual and $12, 700 for a family was postponed until 2015
 ACA Market Place Opens • On Oct 1, 2013, the ACA marketplace exchanges officially opened in 14 state-operated and 36 federally operated sites. • Significant computer glitches during exchanges rollout resulted in poor enrollment overall despite extended the enrollment deadline by 1 week. • In response to consumer outrage over cancelled existing individual policies which did not meet ACA requirements, the administration announced that insurers could continue to offer these existing plans into 2014. • The current infrastructure for exchange is effective from 2014 -2015, but in 2016 the system is open for changes.
ACA Market Place Opens • On Oct 1, 2013, the ACA marketplace exchanges officially opened in 14 state-operated and 36 federally operated sites. • Significant computer glitches during exchanges rollout resulted in poor enrollment overall despite extended the enrollment deadline by 1 week. • In response to consumer outrage over cancelled existing individual policies which did not meet ACA requirements, the administration announced that insurers could continue to offer these existing plans into 2014. • The current infrastructure for exchange is effective from 2014 -2015, but in 2016 the system is open for changes.
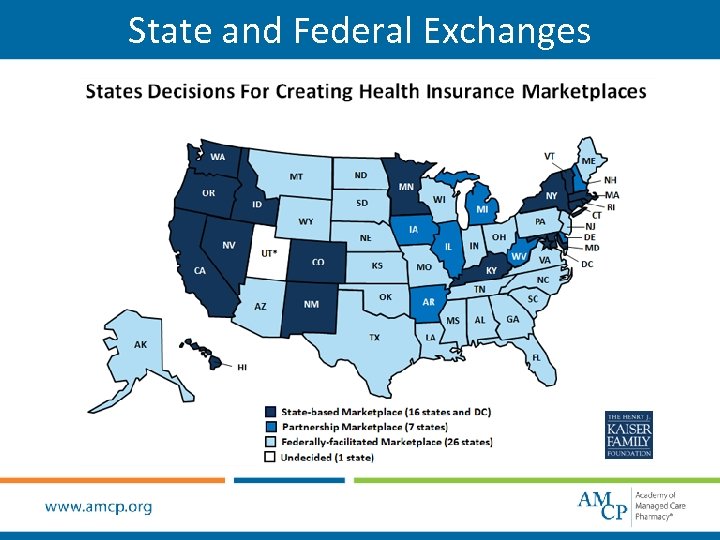 State and Federal Exchanges
State and Federal Exchanges
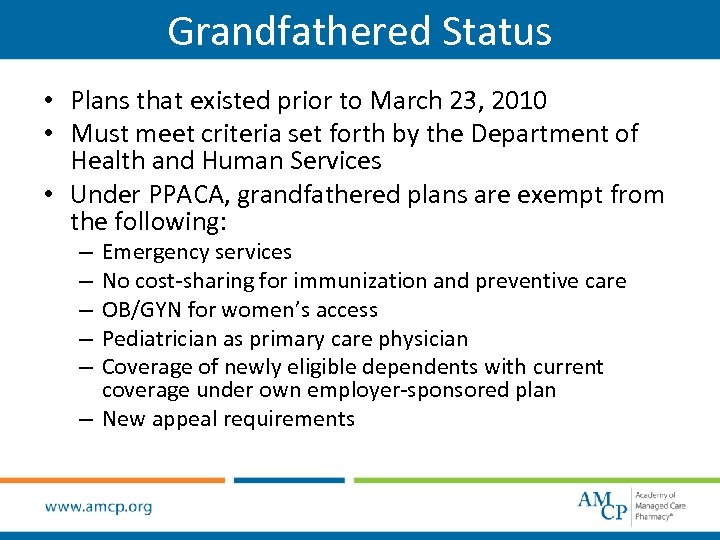 Grandfathered Status • Plans that existed prior to March 23, 2010 • Must meet criteria set forth by the Department of Health and Human Services • Under PPACA, grandfathered plans are exempt from the following: Emergency services No cost-sharing for immunization and preventive care OB/GYN for women’s access Pediatrician as primary care physician Coverage of newly eligible dependents with current coverage under own employer-sponsored plan – New appeal requirements – – –
Grandfathered Status • Plans that existed prior to March 23, 2010 • Must meet criteria set forth by the Department of Health and Human Services • Under PPACA, grandfathered plans are exempt from the following: Emergency services No cost-sharing for immunization and preventive care OB/GYN for women’s access Pediatrician as primary care physician Coverage of newly eligible dependents with current coverage under own employer-sponsored plan – New appeal requirements – – –
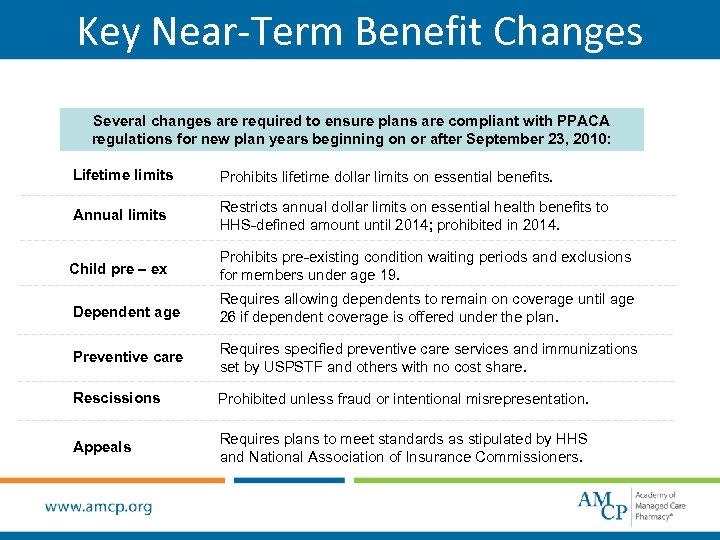 Key Near-Term Benefit Changes Several changes are required to ensure plans are compliant with PPACA regulations for new plan years beginning on or after September 23, 2010: Lifetime limits Prohibits lifetime dollar limits on essential benefits. Annual limits Restricts annual dollar limits on essential health benefits to HHS-defined amount until 2014; prohibited in 2014. Child pre – ex Prohibits pre-existing condition waiting periods and exclusions for members under age 19. Dependent age Requires allowing dependents to remain on coverage until age 26 if dependent coverage is offered under the plan. Preventive care Requires specified preventive care services and immunizations set by USPSTF and others with no cost share. Rescissions Prohibited unless fraud or intentional misrepresentation. Appeals Requires plans to meet standards as stipulated by HHS and National Association of Insurance Commissioners.
Key Near-Term Benefit Changes Several changes are required to ensure plans are compliant with PPACA regulations for new plan years beginning on or after September 23, 2010: Lifetime limits Prohibits lifetime dollar limits on essential benefits. Annual limits Restricts annual dollar limits on essential health benefits to HHS-defined amount until 2014; prohibited in 2014. Child pre – ex Prohibits pre-existing condition waiting periods and exclusions for members under age 19. Dependent age Requires allowing dependents to remain on coverage until age 26 if dependent coverage is offered under the plan. Preventive care Requires specified preventive care services and immunizations set by USPSTF and others with no cost share. Rescissions Prohibited unless fraud or intentional misrepresentation. Appeals Requires plans to meet standards as stipulated by HHS and National Association of Insurance Commissioners.
 Benefit Limits • Lifetime limits: no longer allowed for “essential health benefits” • Annual limits: restricted limits on “essential health benefits” until 2014; prohibited in 2014 – three-year phase out • $750, 000 for plan years beginning (9/23/2010 – 9/22/2011) • $1. 25 million for plan years beginning (9/23/2010 – 9/22/2012) • $2 million for plan years beginning (9/23/2012 – 12/31/2013)
Benefit Limits • Lifetime limits: no longer allowed for “essential health benefits” • Annual limits: restricted limits on “essential health benefits” until 2014; prohibited in 2014 – three-year phase out • $750, 000 for plan years beginning (9/23/2010 – 9/22/2011) • $1. 25 million for plan years beginning (9/23/2010 – 9/22/2012) • $2 million for plan years beginning (9/23/2012 – 12/31/2013)
 Preventative Care • Requires coverage of certain preventive care items or services at $0 cost share – vaccines currently recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) – evidence-based preventive services • Inclusion of preventive drugs in this mandate (e. g. smoking cessation, aspirin, folic acid, iron, fluoride) subject to interpretation. Further guidance may be needed • Grandfathered plans exempt
Preventative Care • Requires coverage of certain preventive care items or services at $0 cost share – vaccines currently recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) – evidence-based preventive services • Inclusion of preventive drugs in this mandate (e. g. smoking cessation, aspirin, folic acid, iron, fluoride) subject to interpretation. Further guidance may be needed • Grandfathered plans exempt
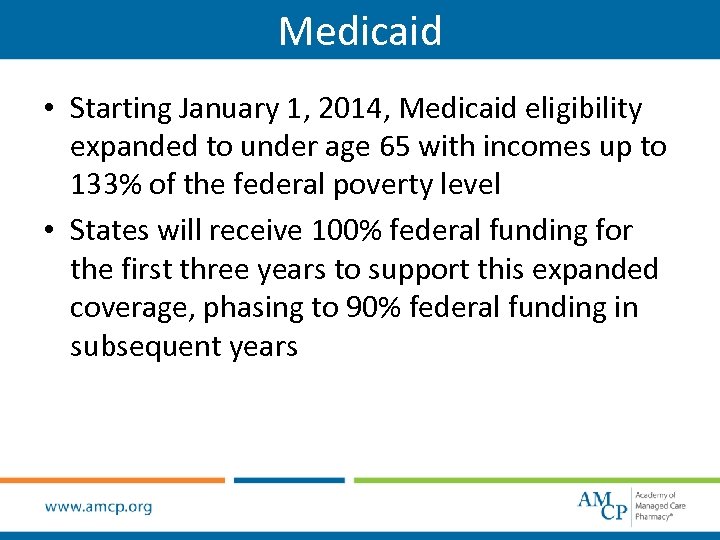 Medicaid • Starting January 1, 2014, Medicaid eligibility expanded to under age 65 with incomes up to 133% of the federal poverty level • States will receive 100% federal funding for the first three years to support this expanded coverage, phasing to 90% federal funding in subsequent years
Medicaid • Starting January 1, 2014, Medicaid eligibility expanded to under age 65 with incomes up to 133% of the federal poverty level • States will receive 100% federal funding for the first three years to support this expanded coverage, phasing to 90% federal funding in subsequent years
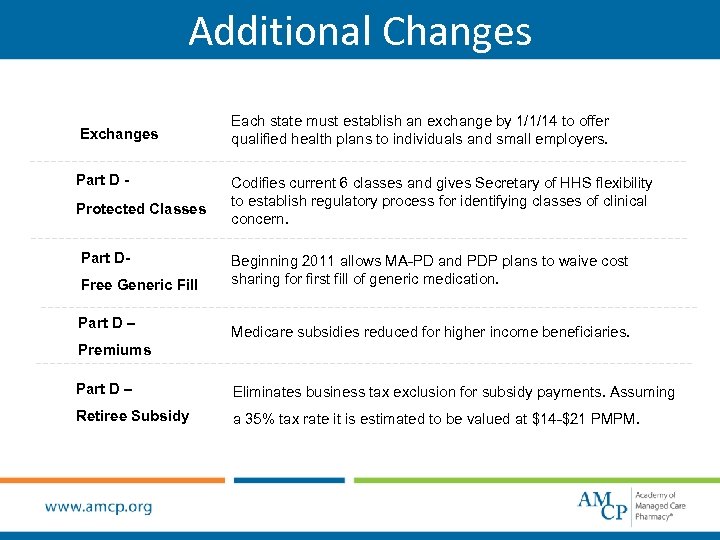 Additional Changes Exchanges Part D Protected Classes Part DFree Generic Fill Part D – Each state must establish an exchange by 1/1/14 to offer qualified health plans to individuals and small employers. Codifies current 6 classes and gives Secretary of HHS flexibility to establish regulatory process for identifying classes of clinical concern. Beginning 2011 allows MA-PD and PDP plans to waive cost sharing for first fill of generic medication. Medicare subsidies reduced for higher income beneficiaries. Premiums Part D – Eliminates business tax exclusion for subsidy payments. Assuming Retiree Subsidy a 35% tax rate it is estimated to be valued at $14 -$21 PMPM.
Additional Changes Exchanges Part D Protected Classes Part DFree Generic Fill Part D – Each state must establish an exchange by 1/1/14 to offer qualified health plans to individuals and small employers. Codifies current 6 classes and gives Secretary of HHS flexibility to establish regulatory process for identifying classes of clinical concern. Beginning 2011 allows MA-PD and PDP plans to waive cost sharing for first fill of generic medication. Medicare subsidies reduced for higher income beneficiaries. Premiums Part D – Eliminates business tax exclusion for subsidy payments. Assuming Retiree Subsidy a 35% tax rate it is estimated to be valued at $14 -$21 PMPM.
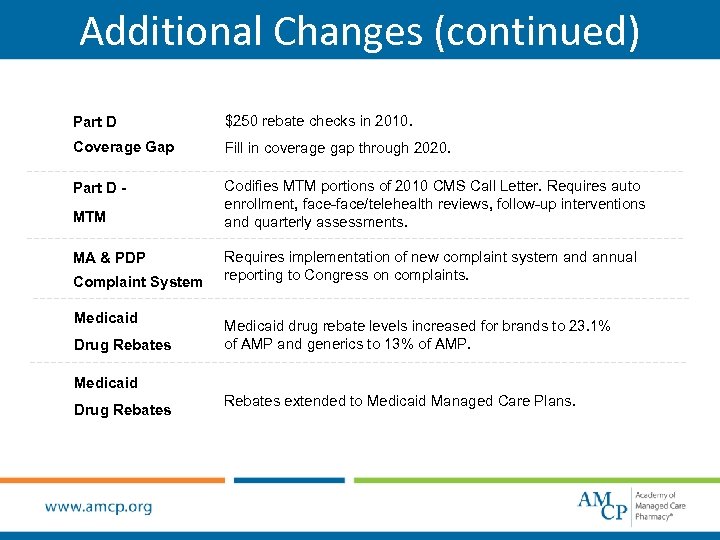 Additional Changes (continued) Part D $250 rebate checks in 2010. Coverage Gap Fill in coverage gap through 2020. Part D - Codifies MTM portions of 2010 CMS Call Letter. Requires auto enrollment, face-face/telehealth reviews, follow-up interventions and quarterly assessments. MTM MA & PDP Complaint System Medicaid Drug Rebates Requires implementation of new complaint system and annual reporting to Congress on complaints. Medicaid drug rebate levels increased for brands to 23. 1% of AMP and generics to 13% of AMP. Medicaid Drug Rebates extended to Medicaid Managed Care Plans.
Additional Changes (continued) Part D $250 rebate checks in 2010. Coverage Gap Fill in coverage gap through 2020. Part D - Codifies MTM portions of 2010 CMS Call Letter. Requires auto enrollment, face-face/telehealth reviews, follow-up interventions and quarterly assessments. MTM MA & PDP Complaint System Medicaid Drug Rebates Requires implementation of new complaint system and annual reporting to Congress on complaints. Medicaid drug rebate levels increased for brands to 23. 1% of AMP and generics to 13% of AMP. Medicaid Drug Rebates extended to Medicaid Managed Care Plans.
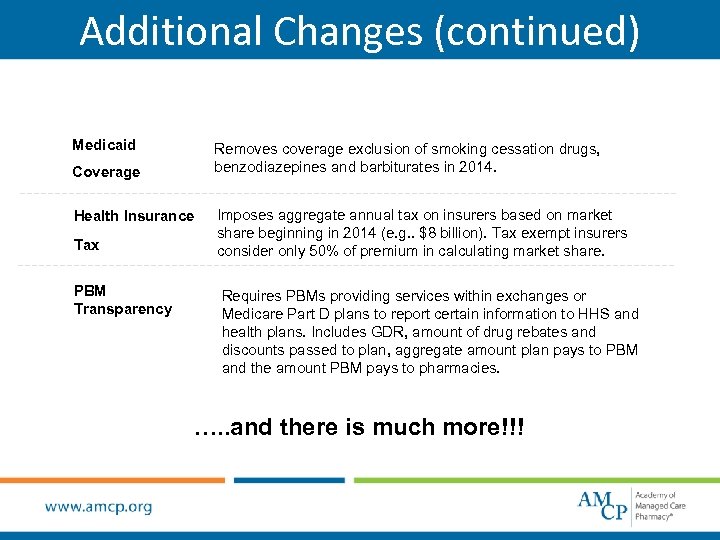 Additional Changes (continued) Medicaid Removes coverage exclusion of smoking cessation drugs, benzodiazepines and barbiturates in 2014. Coverage Health Insurance Tax PBM Transparency Imposes aggregate annual tax on insurers based on market share beginning in 2014 (e. g. . $8 billion). Tax exempt insurers consider only 50% of premium in calculating market share. Requires PBMs providing services within exchanges or Medicare Part D plans to report certain information to HHS and health plans. Includes GDR, amount of drug rebates and discounts passed to plan, aggregate amount plan pays to PBM and the amount PBM pays to pharmacies. …. . and there is much more!!!
Additional Changes (continued) Medicaid Removes coverage exclusion of smoking cessation drugs, benzodiazepines and barbiturates in 2014. Coverage Health Insurance Tax PBM Transparency Imposes aggregate annual tax on insurers based on market share beginning in 2014 (e. g. . $8 billion). Tax exempt insurers consider only 50% of premium in calculating market share. Requires PBMs providing services within exchanges or Medicare Part D plans to report certain information to HHS and health plans. Includes GDR, amount of drug rebates and discounts passed to plan, aggregate amount plan pays to PBM and the amount PBM pays to pharmacies. …. . and there is much more!!!
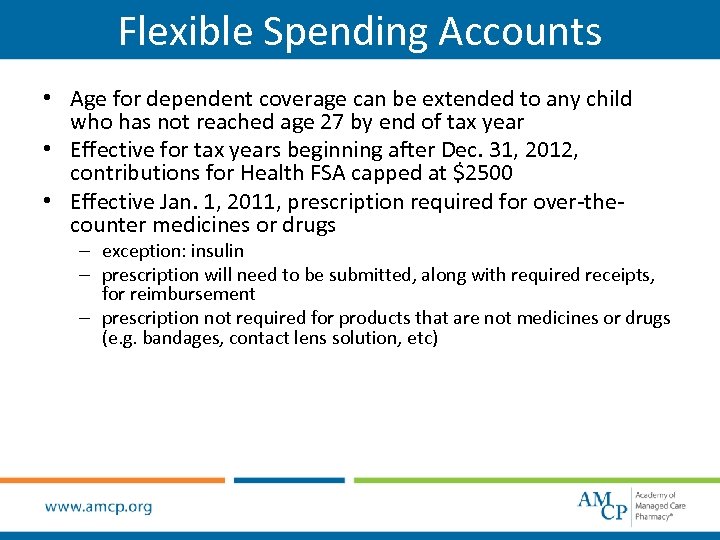 Flexible Spending Accounts • Age for dependent coverage can be extended to any child who has not reached age 27 by end of tax year • Effective for tax years beginning after Dec. 31, 2012, contributions for Health FSA capped at $2500 • Effective Jan. 1, 2011, prescription required for over-thecounter medicines or drugs – exception: insulin – prescription will need to be submitted, along with required receipts, for reimbursement – prescription not required for products that are not medicines or drugs (e. g. bandages, contact lens solution, etc)
Flexible Spending Accounts • Age for dependent coverage can be extended to any child who has not reached age 27 by end of tax year • Effective for tax years beginning after Dec. 31, 2012, contributions for Health FSA capped at $2500 • Effective Jan. 1, 2011, prescription required for over-thecounter medicines or drugs – exception: insulin – prescription will need to be submitted, along with required receipts, for reimbursement – prescription not required for products that are not medicines or drugs (e. g. bandages, contact lens solution, etc)
 Enhanced Appeals Process • Members entitled to an external review (when internal appeals have been exhausted) – plans must contract with at least three Independent Review Organizations (IRO) – claim assignments must be rotated • Denial notices provided in culturally and linguistically appropriate manner • Requirements for denial language – claim details – diagnostic codes • Coverage must continue pending outcome of appeal • Shortened time limits (not later than 24 hours)
Enhanced Appeals Process • Members entitled to an external review (when internal appeals have been exhausted) – plans must contract with at least three Independent Review Organizations (IRO) – claim assignments must be rotated • Denial notices provided in culturally and linguistically appropriate manner • Requirements for denial language – claim details – diagnostic codes • Coverage must continue pending outcome of appeal • Shortened time limits (not later than 24 hours)
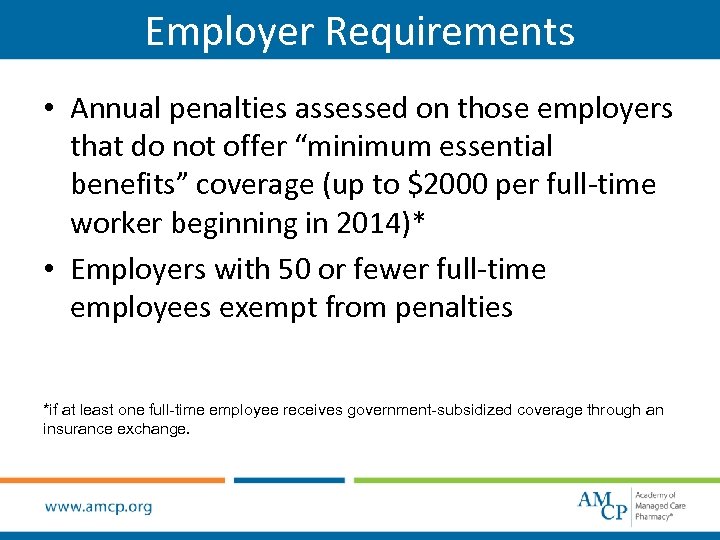 Employer Requirements • Annual penalties assessed on those employers that do not offer “minimum essential benefits” coverage (up to $2000 per full-time worker beginning in 2014)* • Employers with 50 or fewer full-time employees exempt from penalties *if at least one full-time employee receives government-subsidized coverage through an insurance exchange.
Employer Requirements • Annual penalties assessed on those employers that do not offer “minimum essential benefits” coverage (up to $2000 per full-time worker beginning in 2014)* • Employers with 50 or fewer full-time employees exempt from penalties *if at least one full-time employee receives government-subsidized coverage through an insurance exchange.
 Individual Mandate • Beginning in 2014, individuals will be required to have health insurance • Mandate spreads costs among whole population • Starting 2016, annual penalty for those without coverage: greater of $695 (up to $2085 per family) or 2. 5% of household income – lower penalties apply during phase-in period in 2014 and 2015 • Exemptions for certain groups
Individual Mandate • Beginning in 2014, individuals will be required to have health insurance • Mandate spreads costs among whole population • Starting 2016, annual penalty for those without coverage: greater of $695 (up to $2085 per family) or 2. 5% of household income – lower penalties apply during phase-in period in 2014 and 2015 • Exemptions for certain groups
 Health Insurance Exchange or Marketplace • State run clearinghouse to facilitate buying, selling and administration of health coverage • Beginning in 2014, individuals and small employer (average of 100 or fewer employees) may participate • Beginning in 2017, large employers (> 101 employees) may participate
Health Insurance Exchange or Marketplace • State run clearinghouse to facilitate buying, selling and administration of health coverage • Beginning in 2014, individuals and small employer (average of 100 or fewer employees) may participate • Beginning in 2017, large employers (> 101 employees) may participate
 ACA Adoption in the Market Place • ACCESS – Historic decrease in uninsured (down 10 million in 2014) – Medicaid expansion has resulted in 17% ↑ in membership – Previously insured have more generous, preventive coverage • CONSUMER AFFORDABILITY – Premiums are holding stable for 8 in 10 consumers who got insured for $100 or less after tax credits – 87% of 2015 Open Enrollees got financial assistance to help lower their premiums • QUALITY – – A Gallup study found that 7 or 10 who signed up in 2014 say quality is excellent/good. – Morbidity/Mortality due to hospital-aquired conditions are down 17% since 2010 with an estimated $12 Billion in savings. – Hospital Readmission rates for Medicare patients were down between 2012 and 2013.
ACA Adoption in the Market Place • ACCESS – Historic decrease in uninsured (down 10 million in 2014) – Medicaid expansion has resulted in 17% ↑ in membership – Previously insured have more generous, preventive coverage • CONSUMER AFFORDABILITY – Premiums are holding stable for 8 in 10 consumers who got insured for $100 or less after tax credits – 87% of 2015 Open Enrollees got financial assistance to help lower their premiums • QUALITY – – A Gallup study found that 7 or 10 who signed up in 2014 say quality is excellent/good. – Morbidity/Mortality due to hospital-aquired conditions are down 17% since 2010 with an estimated $12 Billion in savings. – Hospital Readmission rates for Medicare patients were down between 2012 and 2013.
 2015 Health Coverage Reported to IRS As part of the health coverage mandate, 2015 marks the first year that tax filers are required to report their 2014 Health Coverage by indicating one of three categories of coverage: – Minimum Essential Coverage via Non-marketplace insurance for all of 2014 (nearly 75% of Americans) • Traditional Employer Sponsored coverage • Medicare Part A or Part C • Medicaid • Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) • Under 26 years of age and covered on Parent Plan – Marketplace covered individuals and families will fill out FORM 1095 -A • This form requires that the beneficiary consider whether your estimated income was different from actual income as this can impact the tax credit received. • If your income or household size changed over the year, tax credits may be adjusted. – Individuals NOT covered by any health insurance in 2014 • While those who can afford health coverage but chose not to buy it may have to pay a fee, individuals who could not afford coverage or met other conditions can receive an exemption. • If you qualify, receiving an exemption is simple and easy, and means you won’t have to pay a fee. Reasons for exemptions include coverage was too expensive (>8% of your income), uninsured for a brief period of time, or financial hardship due to extenuating circumstances as outlined by the IRS.
2015 Health Coverage Reported to IRS As part of the health coverage mandate, 2015 marks the first year that tax filers are required to report their 2014 Health Coverage by indicating one of three categories of coverage: – Minimum Essential Coverage via Non-marketplace insurance for all of 2014 (nearly 75% of Americans) • Traditional Employer Sponsored coverage • Medicare Part A or Part C • Medicaid • Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) • Under 26 years of age and covered on Parent Plan – Marketplace covered individuals and families will fill out FORM 1095 -A • This form requires that the beneficiary consider whether your estimated income was different from actual income as this can impact the tax credit received. • If your income or household size changed over the year, tax credits may be adjusted. – Individuals NOT covered by any health insurance in 2014 • While those who can afford health coverage but chose not to buy it may have to pay a fee, individuals who could not afford coverage or met other conditions can receive an exemption. • If you qualify, receiving an exemption is simple and easy, and means you won’t have to pay a fee. Reasons for exemptions include coverage was too expensive (>8% of your income), uninsured for a brief period of time, or financial hardship due to extenuating circumstances as outlined by the IRS.
 Future of Health Reform • Impact of changes – implementation challenges – guidance and federal oversight needed – policy and political changes • Opportunities – more coverage of the uninsured – transform delivery and payment systems – shift health care focus to prevention and primary care
Future of Health Reform • Impact of changes – implementation challenges – guidance and federal oversight needed – policy and political changes • Opportunities – more coverage of the uninsured – transform delivery and payment systems – shift health care focus to prevention and primary care
 Resources • Kaiser Family Foundation: http: //healthreform. kff. org/ • DHHS consumer website: http: //healthcare. gov/ • Alliance for Health Reform: http: //www. allhealth. org/ • National Association of Insurance Commissioners: http: //www. naic. org • National Governors Association: http: //www. nga. org adapted from Kaiser. EDU: Tutorial An Overview of Health Reform
Resources • Kaiser Family Foundation: http: //healthreform. kff. org/ • DHHS consumer website: http: //healthcare. gov/ • Alliance for Health Reform: http: //www. allhealth. org/ • National Association of Insurance Commissioners: http: //www. naic. org • National Governors Association: http: //www. nga. org adapted from Kaiser. EDU: Tutorial An Overview of Health Reform
 Disclaimer The information in this document is based on preliminary review of the national health care reform legislation and is not intended to be all-inclusive or impart legal advice. Interpretations of the reform legislation vary and an effort has been made to present accurate information. This overview is intended as an educational tool only and does not replace a more rigorous review of the law’s applicability to individual circumstances and should not be relied upon as legal or compliance advice. Analysis is ongoing and additional guidance is also anticipated from the Department of Health and Human Services
Disclaimer The information in this document is based on preliminary review of the national health care reform legislation and is not intended to be all-inclusive or impart legal advice. Interpretations of the reform legislation vary and an effort has been made to present accurate information. This overview is intended as an educational tool only and does not replace a more rigorous review of the law’s applicability to individual circumstances and should not be relied upon as legal or compliance advice. Analysis is ongoing and additional guidance is also anticipated from the Department of Health and Human Services
 Thank you to AMCP member Anna Purdum for updating this presentation for 2015
Thank you to AMCP member Anna Purdum for updating this presentation for 2015


