8c8b915909d6cce025e2aa88b9cc6390.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 An Overview of Learning Technology Specifications and Standards Bill Olivier Director, CETIS
An Overview of Learning Technology Specifications and Standards Bill Olivier Director, CETIS
 Learning Technology Standards • • • Benefits Who is doing what globally & in the UK? What is a specification? What is its lifecycle? What stage are current specifications and standards at? De facto & De Jure standards Supporting actions
Learning Technology Standards • • • Benefits Who is doing what globally & in the UK? What is a specification? What is its lifecycle? What stage are current specifications and standards at? De facto & De Jure standards Supporting actions
 Why? • The Internet is founded on open standards • The Web is also based on the open standards that build on Internet standards • Learning Technology is creating open standards that build on Web and other Internet standards • It is now very hard to see any Internet application for widespread use that is not built on open standards • i. Learning is too big for any one company to build alone - interoperability between systems from many sources
Why? • The Internet is founded on open standards • The Web is also based on the open standards that build on Internet standards • Learning Technology is creating open standards that build on Web and other Internet standards • It is now very hard to see any Internet application for widespread use that is not built on open standards • i. Learning is too big for any one company to build alone - interoperability between systems from many sources
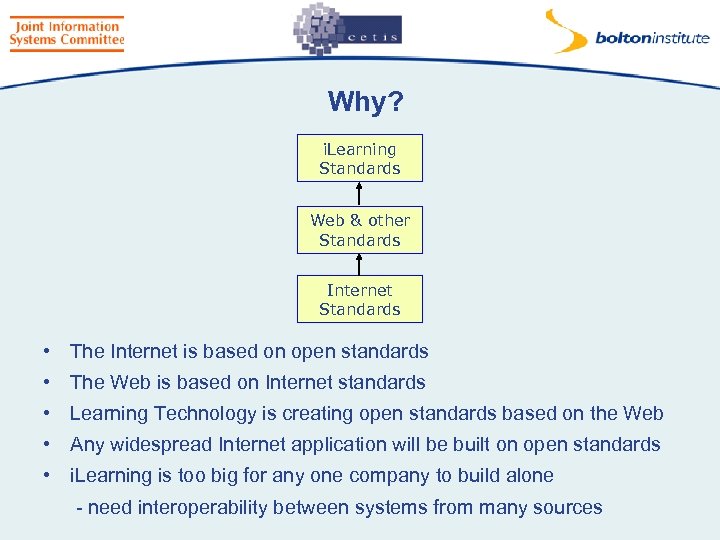 Why? i. Learning Standards Web & other Standards Internet Standards • The Internet is based on open standards • The Web is based on Internet standards • Learning Technology is creating open standards based on the Web • Any widespread Internet application will be built on open standards • i. Learning is too big for any one company to build alone - need interoperability between systems from many sources
Why? i. Learning Standards Web & other Standards Internet Standards • The Internet is based on open standards • The Web is based on Internet standards • Learning Technology is creating open standards based on the Web • Any widespread Internet application will be built on open standards • i. Learning is too big for any one company to build alone - need interoperability between systems from many sources
 What for? Front of House: CONTENT • Content Vendors want: their content to run on all platforms • Platform vendors want: all content to run on their system • End users want: their content of choice to run on their platform of choice Back of House: SYSTEMS INTEGRATION • Managed Learning Environments will have many parts • Bespoke systems integration is expensive and inflexible
What for? Front of House: CONTENT • Content Vendors want: their content to run on all platforms • Platform vendors want: all content to run on their system • End users want: their content of choice to run on their platform of choice Back of House: SYSTEMS INTEGRATION • Managed Learning Environments will have many parts • Bespoke systems integration is expensive and inflexible
 What for? Open standards aim for: • Portable learning activities and content – Big savings when moving content • Reusable learning activities and content – Productions costs offset over many more uses • Plug & play modular systems – Big savings in systems integration costs – Adaptable systems that are easy to change and evolve • They also help build & maintain a bigger open market – essential in a young field like learning technology
What for? Open standards aim for: • Portable learning activities and content – Big savings when moving content • Reusable learning activities and content – Productions costs offset over many more uses • Plug & play modular systems – Big savings in systems integration costs – Adaptable systems that are easy to change and evolve • They also help build & maintain a bigger open market – essential in a young field like learning technology
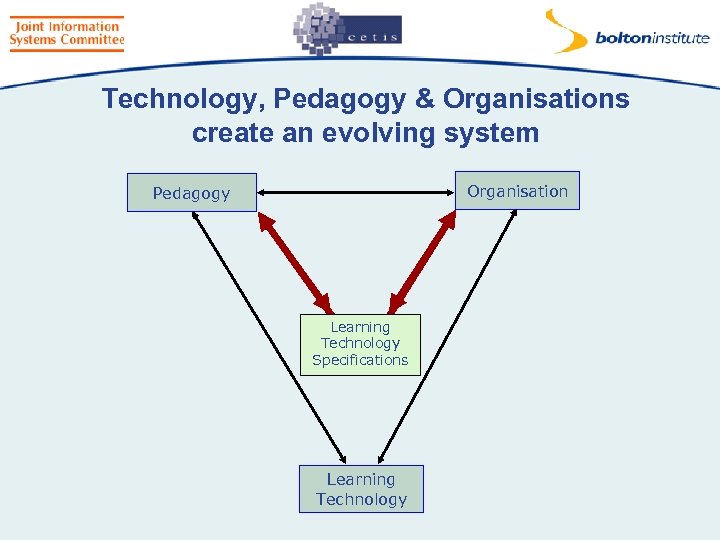 Technology, Pedagogy & Organisations create an evolving system Organisation Pedagogy Learning Technology Specifications Learning Technology
Technology, Pedagogy & Organisations create an evolving system Organisation Pedagogy Learning Technology Specifications Learning Technology
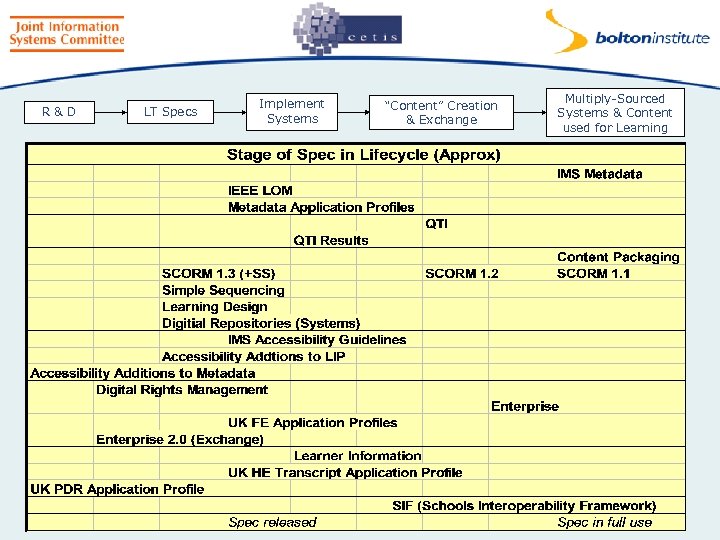
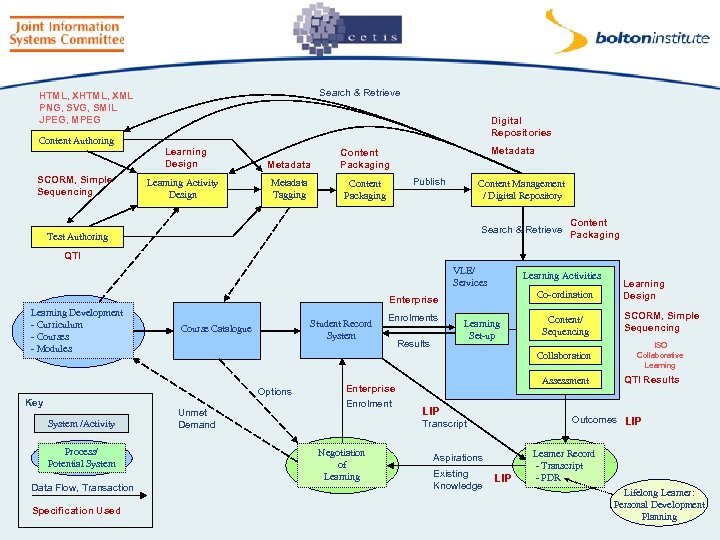 Search & Retrieve HTML, XML PNG, SVG, SMIL JPEG, MPEG Content Authoring SCORM, Simple Sequencing Digital Repositories Learning Design Learning Activity Design Metadata Tagging Content Packaging Metadata Content Packaging Publish Content Management / Digital Repository Search & Retrieve Test Authoring Content Packaging QTI VLE/ Services Learning Activities Co-ordination Enterprise Learning Development - Curriculum - Courses - Modules Course Catalogue System /Activity Process/ Potential System Data Flow, Transaction Specification Used Unmet Demand Enrolments Results Learning Set-up LIP ISO Collaborative Learning Aspirations Existing Knowledge QTI Results Outcomes LIP Transcript Negotiation of Learning SCORM, Simple Sequencing Assessment Enterprise Enrolment Content/ Sequencing Collaboration Student Record System Options Key Learning Design LIP Learner Record - Transcript - PDR Lifelong Learner: Personal Development Planning
Search & Retrieve HTML, XML PNG, SVG, SMIL JPEG, MPEG Content Authoring SCORM, Simple Sequencing Digital Repositories Learning Design Learning Activity Design Metadata Tagging Content Packaging Metadata Content Packaging Publish Content Management / Digital Repository Search & Retrieve Test Authoring Content Packaging QTI VLE/ Services Learning Activities Co-ordination Enterprise Learning Development - Curriculum - Courses - Modules Course Catalogue System /Activity Process/ Potential System Data Flow, Transaction Specification Used Unmet Demand Enrolments Results Learning Set-up LIP ISO Collaborative Learning Aspirations Existing Knowledge QTI Results Outcomes LIP Transcript Negotiation of Learning SCORM, Simple Sequencing Assessment Enterprise Enrolment Content/ Sequencing Collaboration Student Record System Options Key Learning Design LIP Learner Record - Transcript - PDR Lifelong Learner: Personal Development Planning
 Who is doing what globally? Creating Specifications • AICC (Aircraft Industry CBT Consortium) • IMS (No Longer: Instructional Management System!) • CEN/ISSS (Centre Europeen de Normalisation) Creating Standards • IEEE LTSC (Learning Technology Standards Committee) • ISO SC 36 (International Standards Organisation) (Standards Committee 36) BSI (British Standards Institution) IST 43
Who is doing what globally? Creating Specifications • AICC (Aircraft Industry CBT Consortium) • IMS (No Longer: Instructional Management System!) • CEN/ISSS (Centre Europeen de Normalisation) Creating Standards • IEEE LTSC (Learning Technology Standards Committee) • ISO SC 36 (International Standards Organisation) (Standards Committee 36) BSI (British Standards Institution) IST 43
 Who is doing what in the UK? Working with Learning technology Specifications US • ADL for the US Do. D – SCORM – (Shareable Content Object Reference Model) UK • JISC – CETIS for F/HE sectors • Uf. I • BECTa – Nl. N materials • SUf. I • UKe. U
Who is doing what in the UK? Working with Learning technology Specifications US • ADL for the US Do. D – SCORM – (Shareable Content Object Reference Model) UK • JISC – CETIS for F/HE sectors • Uf. I • BECTa – Nl. N materials • SUf. I • UKe. U
 ADL Functions (provides a model for supporting other specifications): • Gather requirements from its constituency • Provide a Reference Model for US Do. D web-based training • Reference model integrates specifications & standards • Provide an Open Source reference implementation • Support implementers, mainly via Plugfests • Feedback problems & suggest changes to spec bodies • Gather new requirements from vendors and constituency
ADL Functions (provides a model for supporting other specifications): • Gather requirements from its constituency • Provide a Reference Model for US Do. D web-based training • Reference model integrates specifications & standards • Provide an Open Source reference implementation • Support implementers, mainly via Plugfests • Feedback problems & suggest changes to spec bodies • Gather new requirements from vendors and constituency
 CETIS Acts as a 2 -way link between F/HE & standards bodies Functions: • Gather requirements from its constituency • Develop application profiles with users and vendors – VLE-MIS, ISR/ILR, Dearing Learner Record (Transcript & PDR), Metadata • Support implementers via JISC Programmes & Plugfests • Feedback problems & suggest changes to spec bodies • Support specialist users via SIGs • Support more general users via Fora • Gather new requirements from vendors and constituency
CETIS Acts as a 2 -way link between F/HE & standards bodies Functions: • Gather requirements from its constituency • Develop application profiles with users and vendors – VLE-MIS, ISR/ILR, Dearing Learner Record (Transcript & PDR), Metadata • Support implementers via JISC Programmes & Plugfests • Feedback problems & suggest changes to spec bodies • Support specialist users via SIGs • Support more general users via Fora • Gather new requirements from vendors and constituency
 CETIS SIGs Special Interest Groups • Main Link with F/HE community • Disseminate information re existing and forthcoming specs • Gather requirements expert views and opinions • Learn from experience of implementing and using specs • Mutual support & problem solving • Develop and share good practice 5 SIGs and 3 Fora • Accessibility, Assessment , Educational Content, Learner Information and Profiles, Metadata • FE Focus Group, Pedagogy, MLE (Managed Learning Environment)
CETIS SIGs Special Interest Groups • Main Link with F/HE community • Disseminate information re existing and forthcoming specs • Gather requirements expert views and opinions • Learn from experience of implementing and using specs • Mutual support & problem solving • Develop and share good practice 5 SIGs and 3 Fora • Accessibility, Assessment , Educational Content, Learner Information and Profiles, Metadata • FE Focus Group, Pedagogy, MLE (Managed Learning Environment)
 Two Questions • What is the lifecycle of a specification? • Which stage have particular specifications reached? • The answers to these are critical to the issue of Government mandation or recommendation of specifications
Two Questions • What is the lifecycle of a specification? • Which stage have particular specifications reached? • The answers to these are critical to the issue of Government mandation or recommendation of specifications
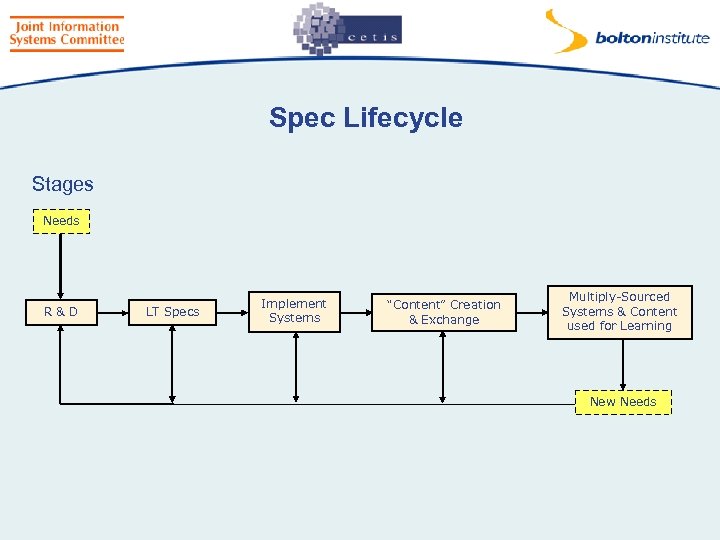 Spec Lifecycle Stages Needs R&D LT Specs Implement Systems “Content” Creation & Exchange Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
Spec Lifecycle Stages Needs R&D LT Specs Implement Systems “Content” Creation & Exchange Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
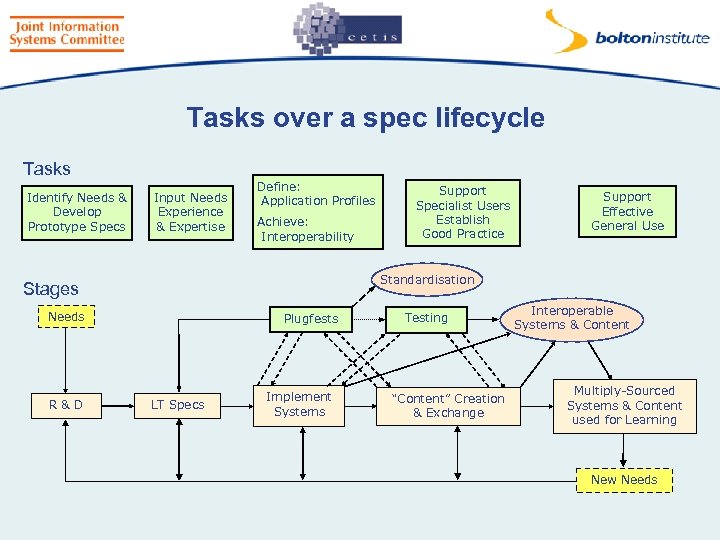 Tasks over a spec lifecycle Tasks Identify Needs & Develop Prototype Specs Input Needs Experience & Expertise Define: Application Profiles Achieve: Interoperability Support Effective General Use Standardisation Stages Needs R&D Support Specialist Users Establish Good Practice Plugfests LT Specs Implement Systems Testing “Content” Creation & Exchange Interoperable Systems & Content Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
Tasks over a spec lifecycle Tasks Identify Needs & Develop Prototype Specs Input Needs Experience & Expertise Define: Application Profiles Achieve: Interoperability Support Effective General Use Standardisation Stages Needs R&D Support Specialist Users Establish Good Practice Plugfests LT Specs Implement Systems Testing “Content” Creation & Exchange Interoperable Systems & Content Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
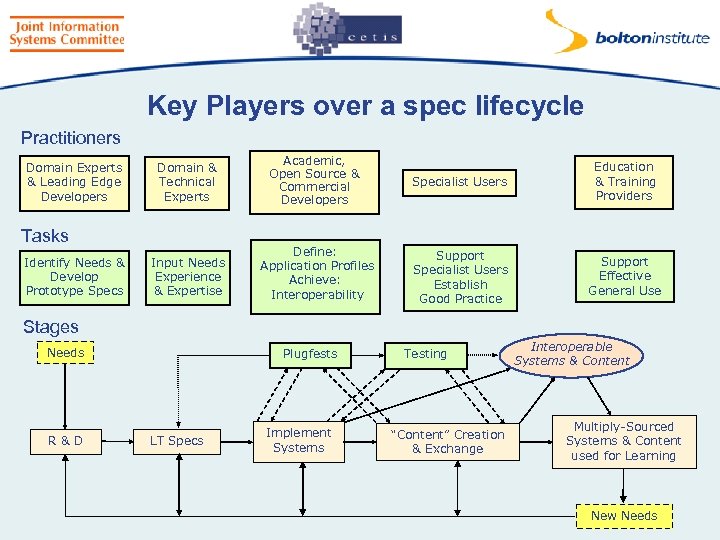 Key Players over a spec lifecycle Practitioners Domain Experts & Leading Edge Developers Domain & Technical Experts Academic, Open Source & Commercial Developers Specialist Users Education & Training Providers Input Needs Experience & Expertise Define: Application Profiles Achieve: Interoperability Support Specialist Users Establish Good Practice Support Effective General Use Tasks Identify Needs & Develop Prototype Specs Stages Needs R&D Plugfests LT Specs Implement Systems Testing “Content” Creation & Exchange Interoperable Systems & Content Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
Key Players over a spec lifecycle Practitioners Domain Experts & Leading Edge Developers Domain & Technical Experts Academic, Open Source & Commercial Developers Specialist Users Education & Training Providers Input Needs Experience & Expertise Define: Application Profiles Achieve: Interoperability Support Specialist Users Establish Good Practice Support Effective General Use Tasks Identify Needs & Develop Prototype Specs Stages Needs R&D Plugfests LT Specs Implement Systems Testing “Content” Creation & Exchange Interoperable Systems & Content Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
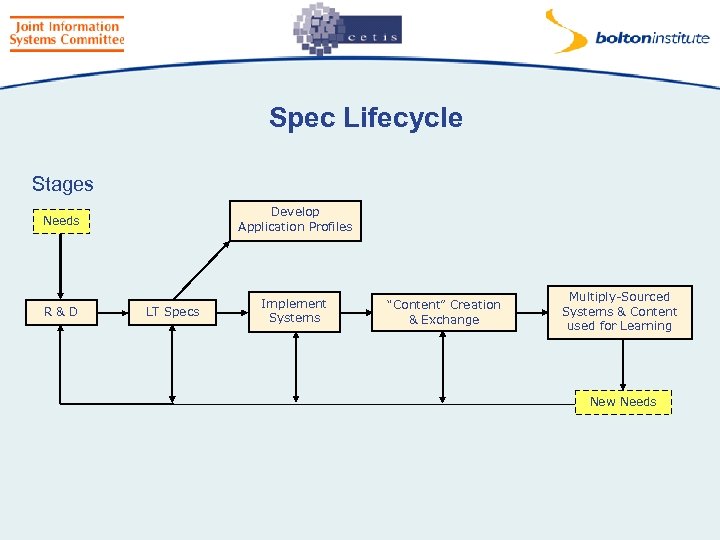 Spec Lifecycle Stages Develop Application Profiles Needs R&D LT Specs Implement Systems “Content” Creation & Exchange Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
Spec Lifecycle Stages Develop Application Profiles Needs R&D LT Specs Implement Systems “Content” Creation & Exchange Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning New Needs
 Application Profiles • A variant of a specification • Adapted to meet particular needs – of a (large) organisation, sector, country, the EU, etc. • Needs have to be identified & requirements specified • Types – – Proper subset – simplified as not all needed More optional fields made mandatory – increases interoperability Some mandatory fields made optional Extended: some new fields added • First two still compliant with original specification • Last two can produce content that is not compliant with original specification
Application Profiles • A variant of a specification • Adapted to meet particular needs – of a (large) organisation, sector, country, the EU, etc. • Needs have to be identified & requirements specified • Types – – Proper subset – simplified as not all needed More optional fields made mandatory – increases interoperability Some mandatory fields made optional Extended: some new fields added • First two still compliant with original specification • Last two can produce content that is not compliant with original specification
 Application Profiles Still needs the same processes as a Specification • Identification of needs & specification of requirements • Changes to be made then have to be agreed between: – The user community (who, why, what, when, where) – The software developers / vendors (how) • Documentation produced • Implementation in systems • Plugfests and other tasks to establish interoperability • Development of test suites • Testing Service • Adoption and development of best practice
Application Profiles Still needs the same processes as a Specification • Identification of needs & specification of requirements • Changes to be made then have to be agreed between: – The user community (who, why, what, when, where) – The software developers / vendors (how) • Documentation produced • Implementation in systems • Plugfests and other tasks to establish interoperability • Development of test suites • Testing Service • Adoption and development of best practice
 R&D LT Specs Implement Systems “Content” Creation & Exchange Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning
R&D LT Specs Implement Systems “Content” Creation & Exchange Multiply-Sourced Systems & Content used for Learning
 What does an LT specification look like? IMS specifications have usually had three parts: 1. Information Model 2. Binding – so far all have been XML bindings 3. Best Practice Guide (Implementation) Increasingly will also see: 4. Behavioural Model 5. Service Interface / Transactions / Protocols + bindings XML-based
What does an LT specification look like? IMS specifications have usually had three parts: 1. Information Model 2. Binding – so far all have been XML bindings 3. Best Practice Guide (Implementation) Increasingly will also see: 4. Behavioural Model 5. Service Interface / Transactions / Protocols + bindings XML-based
 De facto & de jure: must work, provide benefits & evolve • De facto standards are those adopted by the market – May be proprietary – set by the market ‘gorilla’ – Internet: usually set by an open body with many participants • De jure are those set by a (large) purchaser e. g. Government / Govt. Department / large corporation • Conditions for setting a de jure standard: – MUST provide interoperability in practice – MUST enable the exchanges needed to carry out wor – MUST be able to evolve and respond to: • Changing world • Changing technology • Better ways of doing things
De facto & de jure: must work, provide benefits & evolve • De facto standards are those adopted by the market – May be proprietary – set by the market ‘gorilla’ – Internet: usually set by an open body with many participants • De jure are those set by a (large) purchaser e. g. Government / Govt. Department / large corporation • Conditions for setting a de jure standard: – MUST provide interoperability in practice – MUST enable the exchanges needed to carry out wor – MUST be able to evolve and respond to: • Changing world • Changing technology • Better ways of doing things
 Needs, Processes, Use cases, Specifications & Application Profiles • Specifications must meet interoperability needs • What trying to do? – What human-level purposes? – How is task divided between humans and technology? – What do users want the ICT systems to do? (Use Cases) • What systems are involved? – What needs to be exchanged between them? – How are they to communicate this information? • Globally applicable = LT Specifications & Standards • Locally applicable = Application Profiles
Needs, Processes, Use cases, Specifications & Application Profiles • Specifications must meet interoperability needs • What trying to do? – What human-level purposes? – How is task divided between humans and technology? – What do users want the ICT systems to do? (Use Cases) • What systems are involved? – What needs to be exchanged between them? – How are they to communicate this information? • Globally applicable = LT Specifications & Standards • Locally applicable = Application Profiles
 Supporting Actions • Gathering interoperability requirements • Translation into Specifications & Application Profiles • Open Source Reference Implementations • Developer support • Working to achieve interoperability – Access to ‘gold’ examples, plugfests, agreed interpretations, Spec revisions, implementation notes • Development of Test Suites and Testing service • e. Learning strategist, manager and specialist users support
Supporting Actions • Gathering interoperability requirements • Translation into Specifications & Application Profiles • Open Source Reference Implementations • Developer support • Working to achieve interoperability – Access to ‘gold’ examples, plugfests, agreed interpretations, Spec revisions, implementation notes • Development of Test Suites and Testing service • e. Learning strategist, manager and specialist users support
 Creation, implementation and effective use of specifications • social not just a technical or even a domain issue • need agreements at each level • linked set of communities of practice • Co. Ps complement specification and standards bodies (standards bodies a cross between Co. Ps & work teams)
Creation, implementation and effective use of specifications • social not just a technical or even a domain issue • need agreements at each level • linked set of communities of practice • Co. Ps complement specification and standards bodies (standards bodies a cross between Co. Ps & work teams)
 More Information CETIS web site: • Introductory and background material • Information on who does what • News and forthcoming events • Features • Links to sites others involved and to other sources • SIG pages: extensive information on particular specifications http: //www. cetis. ac. uk
More Information CETIS web site: • Introductory and background material • Information on who does what • News and forthcoming events • Features • Links to sites others involved and to other sources • SIG pages: extensive information on particular specifications http: //www. cetis. ac. uk


