c6354a825bf29b65a746bc6bc25946a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 AN OVERVIEW OF INCOME-TAX LAW IN INDIA PRESENTED BY: SIB SANKAR BANIK, W. B. A&A. S INTERNAL AUDIT OFFICER, FINANCE (INTERNAL AUDIT)DEPARTMENT GOVERNMENT OF WEST BENGAL MOB: 8926225065 E-MAIL ID: sibsankar. banik 40@gmail. com
AN OVERVIEW OF INCOME-TAX LAW IN INDIA PRESENTED BY: SIB SANKAR BANIK, W. B. A&A. S INTERNAL AUDIT OFFICER, FINANCE (INTERNAL AUDIT)DEPARTMENT GOVERNMENT OF WEST BENGAL MOB: 8926225065 E-MAIL ID: sibsankar. banik 40@gmail. com
 BASIC COMPONENTS Income-tax is the most significant direct tax. The income-tax law in India consists of the following components: • Income Tax Act • Annual Finance Acts • Income Tax Rules • Circulars/Notifications • Legal decisions of Courts
BASIC COMPONENTS Income-tax is the most significant direct tax. The income-tax law in India consists of the following components: • Income Tax Act • Annual Finance Acts • Income Tax Rules • Circulars/Notifications • Legal decisions of Courts
 Salary Taxation www. incometa xindia. gov. in
Salary Taxation www. incometa xindia. gov. in
 D. D. O’s RESPONSIBILITY • Every person who is responsible for paying any income chargeable under the head "Salaries" shall deduct incometax on the estimated income of the assessee under the head "Salaries" for the financial year 2014 -15. The incometax is required to be calculated on the basis of the rates given in this circular, subject to the provisions related to requirement to furnish PAN as per sec 206 AA of the Act, and shall be deducted at the time of each payment. No tax, however, will be required to be deducted at source in any case unless the estimated salary income including the value of perquisites, for the financial year exceeds Rs. 2, 50, 000/or Rs. 3, 000/- as the case may be, depending upon the age of the employee.
D. D. O’s RESPONSIBILITY • Every person who is responsible for paying any income chargeable under the head "Salaries" shall deduct incometax on the estimated income of the assessee under the head "Salaries" for the financial year 2014 -15. The incometax is required to be calculated on the basis of the rates given in this circular, subject to the provisions related to requirement to furnish PAN as per sec 206 AA of the Act, and shall be deducted at the time of each payment. No tax, however, will be required to be deducted at source in any case unless the estimated salary income including the value of perquisites, for the financial year exceeds Rs. 2, 50, 000/or Rs. 3, 000/- as the case may be, depending upon the age of the employee.
 What is t. Ds • With holding tax or Tax deduction at source means, deduction of tax as and when the transaction takes place i. e, when the payment is made or payable, which ever is earlier. • Since Government needs revenue to function, it is very important to have a flow of revenue to meet the expenditure.
What is t. Ds • With holding tax or Tax deduction at source means, deduction of tax as and when the transaction takes place i. e, when the payment is made or payable, which ever is earlier. • Since Government needs revenue to function, it is very important to have a flow of revenue to meet the expenditure.
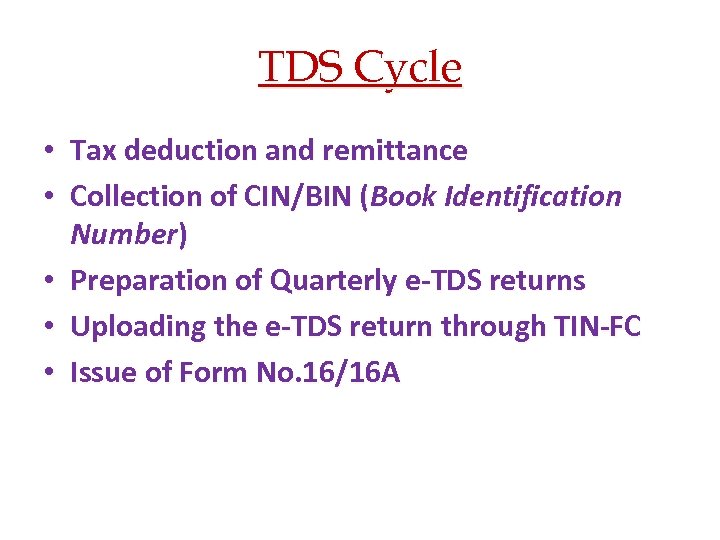 TDS Cycle • Tax deduction and remittance • Collection of CIN/BIN (Book Identification Number) • Preparation of Quarterly e-TDS returns • Uploading the e-TDS return through TIN-FC • Issue of Form No. 16/16 A
TDS Cycle • Tax deduction and remittance • Collection of CIN/BIN (Book Identification Number) • Preparation of Quarterly e-TDS returns • Uploading the e-TDS return through TIN-FC • Issue of Form No. 16/16 A
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES. 1. The levy of income tax in India is at present governed by two acts. a)The Income Tax Act, 1961 b)The Finance Act passed each year by the Parliament. 2. Income Tax is leviable annually for each Financial Year commencing on the 1 st day of April and ending on the 31 st day March following. 3. Income tax on salaries is computed on annual basis and recovered as TDS on monthly basis for the sake of our convenience.
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES. 1. The levy of income tax in India is at present governed by two acts. a)The Income Tax Act, 1961 b)The Finance Act passed each year by the Parliament. 2. Income Tax is leviable annually for each Financial Year commencing on the 1 st day of April and ending on the 31 st day March following. 3. Income tax on salaries is computed on annual basis and recovered as TDS on monthly basis for the sake of our convenience.
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 4. For the purpose of computing IT on salaries the term ‘salary’ includes following elements: a)Pay as defined in FR 9(21), leave salary and advance of pay. b)Bonus c) Dearness allowance d)Compensatory allowance e)House rent allowance-subject to exemption f) Value of Rent Free quarters g) Fees retainable by the employees. h) Honorarium
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 4. For the purpose of computing IT on salaries the term ‘salary’ includes following elements: a)Pay as defined in FR 9(21), leave salary and advance of pay. b)Bonus c) Dearness allowance d)Compensatory allowance e)House rent allowance-subject to exemption f) Value of Rent Free quarters g) Fees retainable by the employees. h) Honorarium
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES i)Reimbursement of tuition fees. j) Subsistence allowance k) Interim relief l) Overtime allowance m) Government Contribution to the NPS. 5. Following items are not to be taken in to account for the purpose of computing IT on salaries : a)Sumptuary allowance and uniform allowance b) Reimbursement of cost of medical treatment subject to limits
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES i)Reimbursement of tuition fees. j) Subsistence allowance k) Interim relief l) Overtime allowance m) Government Contribution to the NPS. 5. Following items are not to be taken in to account for the purpose of computing IT on salaries : a)Sumptuary allowance and uniform allowance b) Reimbursement of cost of medical treatment subject to limits
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES c) Value of LTC b) cash equivalent of leave salary received at the time of retirement. c) TA granted for tour on duty and for transfer d) Composite hill compensatory allowance e) Border area /remote area /tribal area difficult area /disturbed area allowance. f) Conveyance allowance g) CEA and hostel subsidy subject to limits h) Any allowance granted for encouraging the academic, research and other professional pursuit i) Transport allowance up to Rs. 1600/- for orthopedically handicapped persons and Rs. 800/- for others (pm) j) Any payment from GPF
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES c) Value of LTC b) cash equivalent of leave salary received at the time of retirement. c) TA granted for tour on duty and for transfer d) Composite hill compensatory allowance e) Border area /remote area /tribal area difficult area /disturbed area allowance. f) Conveyance allowance g) CEA and hostel subsidy subject to limits h) Any allowance granted for encouraging the academic, research and other professional pursuit i) Transport allowance up to Rs. 1600/- for orthopedically handicapped persons and Rs. 800/- for others (pm) j) Any payment from GPF
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 6. The salary income of a person is calculated on the total salary due to him / her as per the guidelines provided above. 7. From the total income so arrived at(gross salary) the following deductions to the extent permissible are to be allowed to get taxable salary a) HRA exemption to the extent admissible b) Accrued interest/interest paid on HBA , c) Donation to any recognized charitable trust/ fund such as Prime Minister’s National relief fund d) Professional tax paid to local bodies. e) For handicapped employees an amount of Rs. 50000 or Rs. 1, 000/- as the case may be
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 6. The salary income of a person is calculated on the total salary due to him / her as per the guidelines provided above. 7. From the total income so arrived at(gross salary) the following deductions to the extent permissible are to be allowed to get taxable salary a) HRA exemption to the extent admissible b) Accrued interest/interest paid on HBA , c) Donation to any recognized charitable trust/ fund such as Prime Minister’s National relief fund d) Professional tax paid to local bodies. e) For handicapped employees an amount of Rs. 50000 or Rs. 1, 000/- as the case may be
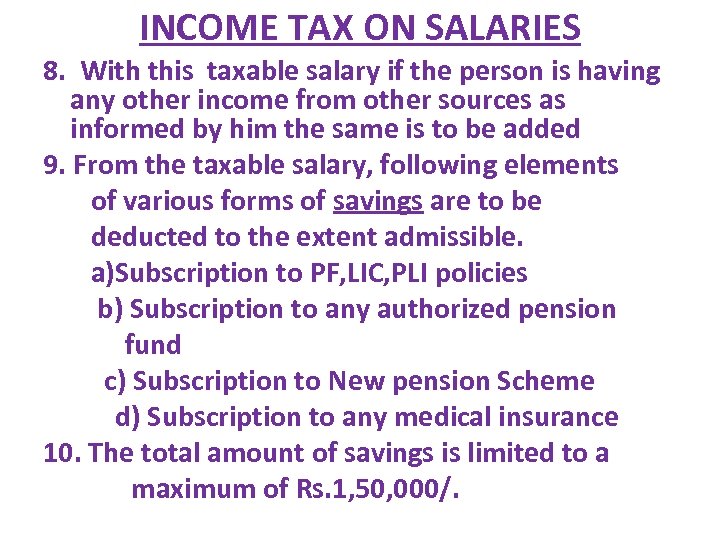 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 8. With this taxable salary if the person is having any other income from other sources as informed by him the same is to be added 9. From the taxable salary, following elements of various forms of savings are to be deducted to the extent admissible. a)Subscription to PF, LIC, PLI policies b) Subscription to any authorized pension fund c) Subscription to New pension Scheme d) Subscription to any medical insurance 10. The total amount of savings is limited to a maximum of Rs. 1, 50, 000/.
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 8. With this taxable salary if the person is having any other income from other sources as informed by him the same is to be added 9. From the taxable salary, following elements of various forms of savings are to be deducted to the extent admissible. a)Subscription to PF, LIC, PLI policies b) Subscription to any authorized pension fund c) Subscription to New pension Scheme d) Subscription to any medical insurance 10. The total amount of savings is limited to a maximum of Rs. 1, 50, 000/.
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 11. Thus the amount of taxable income is to arrived as follows. a)Total salary income -____ b)less total of exempted items( such as HRA exemption) -- ____(-) c ) Gross Taxable income -- _______ d) less savings(limited to maximum) _____(-) e) Net taxable salary ----- _____
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 11. Thus the amount of taxable income is to arrived as follows. a)Total salary income -____ b)less total of exempted items( such as HRA exemption) -- ____(-) c ) Gross Taxable income -- _______ d) less savings(limited to maximum) _____(-) e) Net taxable salary ----- _____
 Deduction on House Rent allowance House rent allowance granted to the employee is exempt u/s 10(13 A) to the following extent; Provided expenditure on rent is actually incurred, the amount of exemption granted is the least of • (1) HRA received • (2) Rent paid Less 10% of salary • (3) 40% of salary, (50% in case of Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata & Delhi). Salary includes bonus + Dearness allowance, where provided by terms of employment.
Deduction on House Rent allowance House rent allowance granted to the employee is exempt u/s 10(13 A) to the following extent; Provided expenditure on rent is actually incurred, the amount of exemption granted is the least of • (1) HRA received • (2) Rent paid Less 10% of salary • (3) 40% of salary, (50% in case of Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata & Delhi). Salary includes bonus + Dearness allowance, where provided by terms of employment.
 Section 80 CCC: Deduction in respect of Premium Paid for Annuity Plan of LIC or Other Insurer • This section provides deduction to an Individual for any amount paid or deposited in any annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer for receiving pension from a fund referred to in Section 10(23 AAB). • In case the annuity is surrendered before the date of its maturity, the surrender value is taxable in the year of receipt.
Section 80 CCC: Deduction in respect of Premium Paid for Annuity Plan of LIC or Other Insurer • This section provides deduction to an Individual for any amount paid or deposited in any annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer for receiving pension from a fund referred to in Section 10(23 AAB). • In case the annuity is surrendered before the date of its maturity, the surrender value is taxable in the year of receipt.
 Deductions on Section 80 C, 80 CCC & 80 CCD • Total Deduction under section 80 C, 80 CCC and 80 CCD (1) together cannot exceed Rs 1, 50, 000 for the financial year 2014 -15 (assessment year 2015 -16). The limit for financial year 2015 -16 is also Rs 1, 50, 000.
Deductions on Section 80 C, 80 CCC & 80 CCD • Total Deduction under section 80 C, 80 CCC and 80 CCD (1) together cannot exceed Rs 1, 50, 000 for the financial year 2014 -15 (assessment year 2015 -16). The limit for financial year 2015 -16 is also Rs 1, 50, 000.
 New Inclusion - 80 CCD(1 B) • A new section 80 CCD(1 B) has been introduced to provide for additional deduction for amount contributed to NPS of up to Rs. 50, 000. • Therefore for financial year 2015 -16, Total Deduction under Section 80 C, 80 CCD(1) and 80 CCD(1 B) cannot exceed Rs 2, 000. • From assessment year 2012 -13, employer's contribution under section 80 CCD(2) towards NPS is outside the monetary ceiling mentioned above.
New Inclusion - 80 CCD(1 B) • A new section 80 CCD(1 B) has been introduced to provide for additional deduction for amount contributed to NPS of up to Rs. 50, 000. • Therefore for financial year 2015 -16, Total Deduction under Section 80 C, 80 CCD(1) and 80 CCD(1 B) cannot exceed Rs 2, 000. • From assessment year 2012 -13, employer's contribution under section 80 CCD(2) towards NPS is outside the monetary ceiling mentioned above.
 Deduction from gross total income: Section 80 TTA • Deduction from gross total income with respect to any Income by way of Interest on Savings account • Deduction from gross total income of an individual or HUF, up to a maximum of Rs. 10, 000/-, in respect of interest on deposits in savings account with a bank, co-operative society or post office. Section 80 TTA deduction is not available on interest income from fixed deposits.
Deduction from gross total income: Section 80 TTA • Deduction from gross total income with respect to any Income by way of Interest on Savings account • Deduction from gross total income of an individual or HUF, up to a maximum of Rs. 10, 000/-, in respect of interest on deposits in savings account with a bank, co-operative society or post office. Section 80 TTA deduction is not available on interest income from fixed deposits.
 DEDUCTIONS FROM TOTAL INCOME (Section 80 D): For financial year 2015 -16 – Deduction is raised from Rs 15, 000 to Rs 25, 000. The deduction for senior citizens is raised from Rs 20, 000 to Rs 30, 000. For financial year 201516 – Deduction is raised from Rs 15, 000 to Rs 25, 000. The deduction for senior citizens is raised from Rs 20, 000 to Rs 30, 000.
DEDUCTIONS FROM TOTAL INCOME (Section 80 D): For financial year 2015 -16 – Deduction is raised from Rs 15, 000 to Rs 25, 000. The deduction for senior citizens is raised from Rs 20, 000 to Rs 30, 000. For financial year 201516 – Deduction is raised from Rs 15, 000 to Rs 25, 000. The deduction for senior citizens is raised from Rs 20, 000 to Rs 30, 000.
 DEDUCTIONS FROM TOTAL INCOME (Section 80 DD): • Section 80 DD: Deduction in respect of Rehabilitation of Handicapped Dependent Relative • Where disability is 40% or more but less than 80% fixed deduction of Rs 50, 000. • Where there is severe disability (disability is 80% or more) – fixed deduction of Rs 1, 000. • A certificate of disability is required from prescribed medical authority. • For financial year 2015 -16 – The deduction limit of Rs 50, 000 has been raised to Rs 75, 000 and Rs 1, 000 has been raised to Rs 1, 25, 000.
DEDUCTIONS FROM TOTAL INCOME (Section 80 DD): • Section 80 DD: Deduction in respect of Rehabilitation of Handicapped Dependent Relative • Where disability is 40% or more but less than 80% fixed deduction of Rs 50, 000. • Where there is severe disability (disability is 80% or more) – fixed deduction of Rs 1, 000. • A certificate of disability is required from prescribed medical authority. • For financial year 2015 -16 – The deduction limit of Rs 50, 000 has been raised to Rs 75, 000 and Rs 1, 000 has been raised to Rs 1, 25, 000.
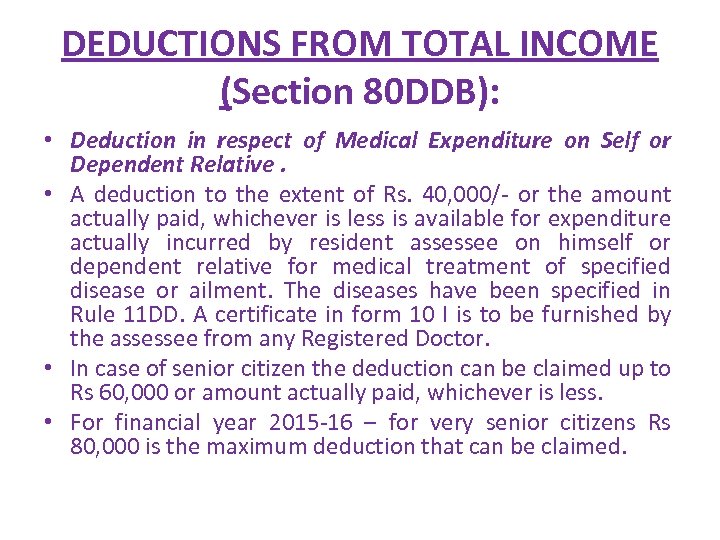 DEDUCTIONS FROM TOTAL INCOME (Section 80 DDB): • Deduction in respect of Medical Expenditure on Self or Dependent Relative. • A deduction to the extent of Rs. 40, 000/- or the amount actually paid, whichever is less is available for expenditure actually incurred by resident assessee on himself or dependent relative for medical treatment of specified disease or ailment. The diseases have been specified in Rule 11 DD. A certificate in form 10 I is to be furnished by the assessee from any Registered Doctor. • In case of senior citizen the deduction can be claimed up to Rs 60, 000 or amount actually paid, whichever is less. • For financial year 2015 -16 – for very senior citizens Rs 80, 000 is the maximum deduction that can be claimed.
DEDUCTIONS FROM TOTAL INCOME (Section 80 DDB): • Deduction in respect of Medical Expenditure on Self or Dependent Relative. • A deduction to the extent of Rs. 40, 000/- or the amount actually paid, whichever is less is available for expenditure actually incurred by resident assessee on himself or dependent relative for medical treatment of specified disease or ailment. The diseases have been specified in Rule 11 DD. A certificate in form 10 I is to be furnished by the assessee from any Registered Doctor. • In case of senior citizen the deduction can be claimed up to Rs 60, 000 or amount actually paid, whichever is less. • For financial year 2015 -16 – for very senior citizens Rs 80, 000 is the maximum deduction that can be claimed.
 Section 80 E: Deduction with respect to Interest on Loan for Higher Studies • Deduction in respect of interest on loan taken for pursuing higher education. This loan is taken for higher education for the assessee, spouse or children or for a student for whom the assessee is a legal guardian.
Section 80 E: Deduction with respect to Interest on Loan for Higher Studies • Deduction in respect of interest on loan taken for pursuing higher education. This loan is taken for higher education for the assessee, spouse or children or for a student for whom the assessee is a legal guardian.
 Deduction for First Time Home Owners (Section 80 EE): This section provided deduction on the Home Loan Interest paid and is valid for financial years 2014 -15 (Assessment year 2015 -16) only. The deduction under this section is available only to Individuals for first house purchased where the value of the house is Rs 40 lakhs or less and loan taken for the house is Rs 25 lakhs or less. And the Loan has been sanctioned between 01. 04. 2013 to 31. 03. 2014. The total deduction allowed under this section is Rs 1, 000.
Deduction for First Time Home Owners (Section 80 EE): This section provided deduction on the Home Loan Interest paid and is valid for financial years 2014 -15 (Assessment year 2015 -16) only. The deduction under this section is available only to Individuals for first house purchased where the value of the house is Rs 40 lakhs or less and loan taken for the house is Rs 25 lakhs or less. And the Loan has been sanctioned between 01. 04. 2013 to 31. 03. 2014. The total deduction allowed under this section is Rs 1, 000.
 Section 80 U: Deduction with respect to Person suffering from Physical Disability • Deduction of Rs. 50, 000/- to an individual who suffers from a physical disability (including blindness) or mental retardation. Further, if the individual is a person with severe disability, deduction of Rs. 100, 000/- shall be available u/s 80 U. Certificate should be obtained from a Govt. Doctor. The relevant rule is Rule 11 D. • For financial year 2015 -16 – The deduction limit of Rs 50, 000 has been raised to Rs 75, 000 and Rs 1, 000 has been raised to Rs 1, 25, 000.
Section 80 U: Deduction with respect to Person suffering from Physical Disability • Deduction of Rs. 50, 000/- to an individual who suffers from a physical disability (including blindness) or mental retardation. Further, if the individual is a person with severe disability, deduction of Rs. 100, 000/- shall be available u/s 80 U. Certificate should be obtained from a Govt. Doctor. The relevant rule is Rule 11 D. • For financial year 2015 -16 – The deduction limit of Rs 50, 000 has been raised to Rs 75, 000 and Rs 1, 000 has been raised to Rs 1, 25, 000.
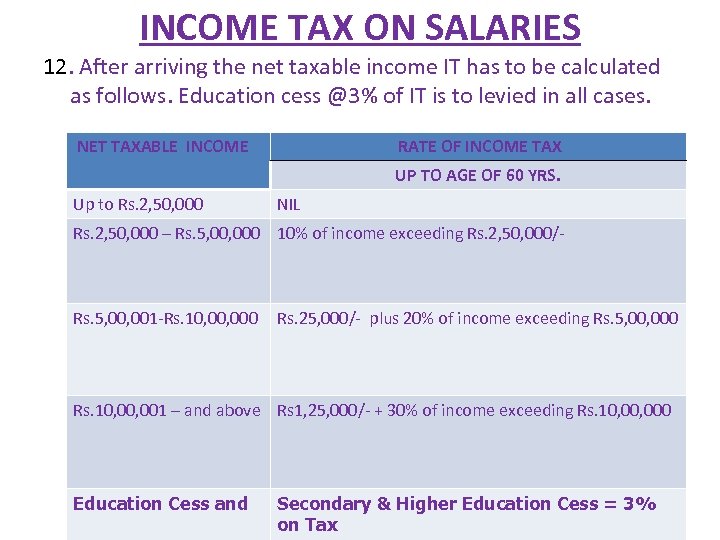 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 12. After arriving the net taxable income IT has to be calculated as follows. Education cess @3% of IT is to levied in all cases. NET TAXABLE INCOME RATE OF INCOME TAX UP TO AGE OF 60 YRS. Up to Rs. 2, 50, 000 NIL Rs. 2, 50, 000 – Rs. 5, 000 10% of income exceeding Rs. 2, 50, 000/- Rs. 5, 001 -Rs. 10, 000 Rs. 25, 000/- plus 20% of income exceeding Rs. 5, 000 Rs. 10, 001 – and above Rs 1, 25, 000/- + 30% of income exceeding Rs. 10, 000 Education Cess and Secondary & Higher Education Cess = 3% on Tax
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 12. After arriving the net taxable income IT has to be calculated as follows. Education cess @3% of IT is to levied in all cases. NET TAXABLE INCOME RATE OF INCOME TAX UP TO AGE OF 60 YRS. Up to Rs. 2, 50, 000 NIL Rs. 2, 50, 000 – Rs. 5, 000 10% of income exceeding Rs. 2, 50, 000/- Rs. 5, 001 -Rs. 10, 000 Rs. 25, 000/- plus 20% of income exceeding Rs. 5, 000 Rs. 10, 001 – and above Rs 1, 25, 000/- + 30% of income exceeding Rs. 10, 000 Education Cess and Secondary & Higher Education Cess = 3% on Tax
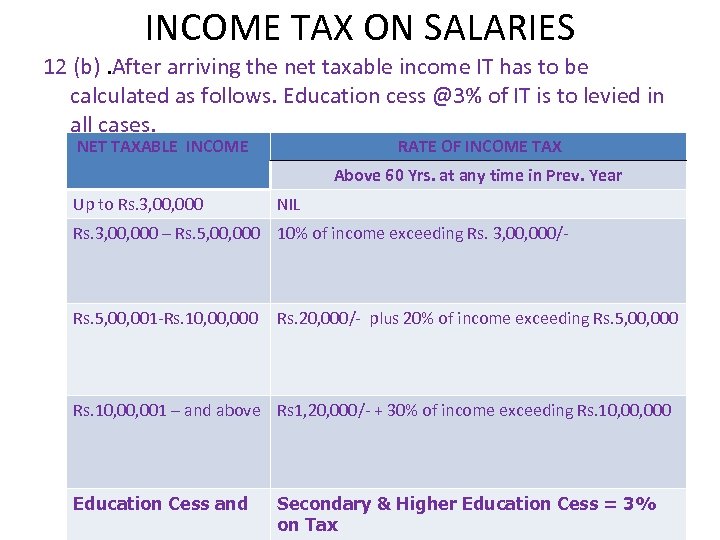 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 12 (b). After arriving the net taxable income IT has to be calculated as follows. Education cess @3% of IT is to levied in all cases. NET TAXABLE INCOME RATE OF INCOME TAX Above 60 Yrs. at any time in Prev. Year Up to Rs. 3, 000 NIL Rs. 3, 000 – Rs. 5, 000 10% of income exceeding Rs. 3, 000/- Rs. 5, 001 -Rs. 10, 000 Rs. 20, 000/- plus 20% of income exceeding Rs. 5, 000 Rs. 10, 001 – and above Rs 1, 20, 000/- + 30% of income exceeding Rs. 10, 000 Education Cess and Secondary & Higher Education Cess = 3% on Tax
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 12 (b). After arriving the net taxable income IT has to be calculated as follows. Education cess @3% of IT is to levied in all cases. NET TAXABLE INCOME RATE OF INCOME TAX Above 60 Yrs. at any time in Prev. Year Up to Rs. 3, 000 NIL Rs. 3, 000 – Rs. 5, 000 10% of income exceeding Rs. 3, 000/- Rs. 5, 001 -Rs. 10, 000 Rs. 20, 000/- plus 20% of income exceeding Rs. 5, 000 Rs. 10, 001 – and above Rs 1, 20, 000/- + 30% of income exceeding Rs. 10, 000 Education Cess and Secondary & Higher Education Cess = 3% on Tax
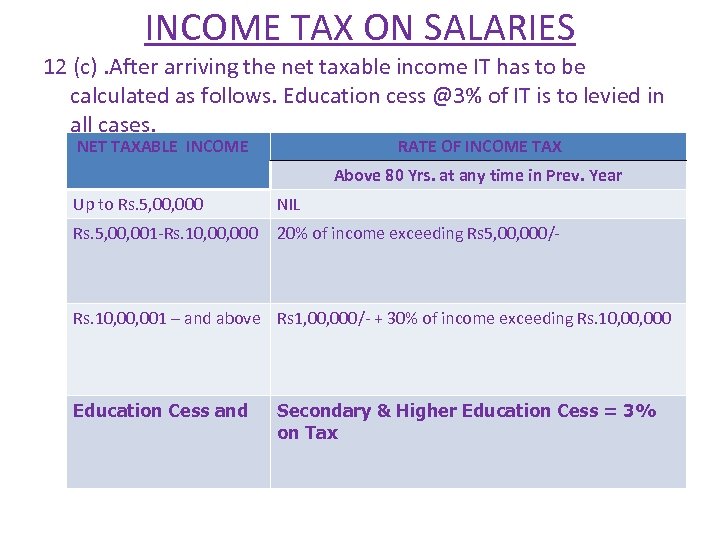 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 12 (c). After arriving the net taxable income IT has to be calculated as follows. Education cess @3% of IT is to levied in all cases. NET TAXABLE INCOME RATE OF INCOME TAX Above 80 Yrs. at any time in Prev. Year Up to Rs. 5, 000 NIL Rs. 5, 001 -Rs. 10, 000 20% of income exceeding Rs 5, 000/- Rs. 10, 001 – and above Rs 1, 000/- + 30% of income exceeding Rs. 10, 000 Education Cess and Secondary & Higher Education Cess = 3% on Tax
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 12 (c). After arriving the net taxable income IT has to be calculated as follows. Education cess @3% of IT is to levied in all cases. NET TAXABLE INCOME RATE OF INCOME TAX Above 80 Yrs. at any time in Prev. Year Up to Rs. 5, 000 NIL Rs. 5, 001 -Rs. 10, 000 20% of income exceeding Rs 5, 000/- Rs. 10, 001 – and above Rs 1, 000/- + 30% of income exceeding Rs. 10, 000 Education Cess and Secondary & Higher Education Cess = 3% on Tax
 INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 13. The IT and education cess so arrived at is to be dived by 12 and the same is to be recovered on monthly basis.
INCOME TAX ON SALARIES 13. The IT and education cess so arrived at is to be dived by 12 and the same is to be recovered on monthly basis.
 Average rate of deduction The statute enjoins the employer to compute the tax liability of the employee on the basis of the rates in force and to deduct the tax at the average rate computed on the basis of the same. Thus, the employer is required to compute at the beginning of the financial year, the total salary income payable to an employee during the financial year. Further, the employer should also take into account any other income as reported by the employee. After considering the incomes exempt, deductions and relief, the tax liability of the employee should be determined on the basis of the rates in force for the financial year. Every month, 1/12 of this net tax liability as computed above is required to be deducted.
Average rate of deduction The statute enjoins the employer to compute the tax liability of the employee on the basis of the rates in force and to deduct the tax at the average rate computed on the basis of the same. Thus, the employer is required to compute at the beginning of the financial year, the total salary income payable to an employee during the financial year. Further, the employer should also take into account any other income as reported by the employee. After considering the incomes exempt, deductions and relief, the tax liability of the employee should be determined on the basis of the rates in force for the financial year. Every month, 1/12 of this net tax liability as computed above is required to be deducted.
 Tax deduction and remittance • It is the duty of the deductor (who is responsible of signing the bills or the paying authority) to deduct income tax at the time of payment as per the prevailing rates and make sure correctness of the details of PAN which is submitted by the deductee/payee. • Remittance: • 1. By Challan (No. 281, for the TDS payments) • 2. By Book-adjustment (through Treasury or PAO) • Time Limit: • 1. If the tax is to be paid by challan – 7 th of the following month • 2. If the tax adjusted through Book-adjustment – same day
Tax deduction and remittance • It is the duty of the deductor (who is responsible of signing the bills or the paying authority) to deduct income tax at the time of payment as per the prevailing rates and make sure correctness of the details of PAN which is submitted by the deductee/payee. • Remittance: • 1. By Challan (No. 281, for the TDS payments) • 2. By Book-adjustment (through Treasury or PAO) • Time Limit: • 1. If the tax is to be paid by challan – 7 th of the following month • 2. If the tax adjusted through Book-adjustment – same day
 Mode of Payment of TDS • Compulsory filing of Statement by PAO, Treasury Officer, etc in case of payment of TDS by Book Entry. * Office of the State Government, where tax has been paid to the credit of the Central Government without the production of a challan [Book Entry], the Pay and Accounts Officer or the Treasury Officer submit a statement in Form No. 24 G within ten days from the end of the month to M/s National Securities Depository Ltd in respect of tax deducted by the deductors intimate the number (Book Identification Number or BIN) generated by the agency.
Mode of Payment of TDS • Compulsory filing of Statement by PAO, Treasury Officer, etc in case of payment of TDS by Book Entry. * Office of the State Government, where tax has been paid to the credit of the Central Government without the production of a challan [Book Entry], the Pay and Accounts Officer or the Treasury Officer submit a statement in Form No. 24 G within ten days from the end of the month to M/s National Securities Depository Ltd in respect of tax deducted by the deductors intimate the number (Book Identification Number or BIN) generated by the agency.
 Mode of Payment of TDS The deposition of TDS may be made through challan No. ITNS 281. The deductor must ensure that the details like employer’s name and address, PAN, TAN, the Assessing Officer having jurisdiction, the amount of tax and surcharge and cess, the date of payment, the salary from which TDS has been done and the tax which is being paid, are correctly filled.
Mode of Payment of TDS The deposition of TDS may be made through challan No. ITNS 281. The deductor must ensure that the details like employer’s name and address, PAN, TAN, the Assessing Officer having jurisdiction, the amount of tax and surcharge and cess, the date of payment, the salary from which TDS has been done and the tax which is being paid, are correctly filled.
 Interest, Penalty & Prosecution for Failure to Deposit Tax Deducted. • Interest at the rate of 1. 5% p. m, or part of the month, from the date of deduction to the date of actual payment, u/s 201(1 A) of IT Act, 1961. • if fail to deduct TDS, interest at the rate of 1% p. m or part of the month, from the date on which tax deductable to the date of actual payment u/s 201(1) of the IT Act, 1961.
Interest, Penalty & Prosecution for Failure to Deposit Tax Deducted. • Interest at the rate of 1. 5% p. m, or part of the month, from the date of deduction to the date of actual payment, u/s 201(1 A) of IT Act, 1961. • if fail to deduct TDS, interest at the rate of 1% p. m or part of the month, from the date on which tax deductable to the date of actual payment u/s 201(1) of the IT Act, 1961.
 Failure to pay tax deducted at source prosecution u/s 276 B fo IT Act, 1961 • Punishable with fine and rigorous imprisonment – minimum 03 months, maximum 07 years.
Failure to pay tax deducted at source prosecution u/s 276 B fo IT Act, 1961 • Punishable with fine and rigorous imprisonment – minimum 03 months, maximum 07 years.
 Furnishing of Certificate for Tax Deducted • Section 203 requires the DDO to furnish to the employee a certificate in Form 16 detailing the amount of TDS and certain other particulars : • Valid permanent account number (PAN) of the deductee; • Valid tax deduction and collection account number (TAN) of the deductor; • Book identification number or numbers (BIN)
Furnishing of Certificate for Tax Deducted • Section 203 requires the DDO to furnish to the employee a certificate in Form 16 detailing the amount of TDS and certain other particulars : • Valid permanent account number (PAN) of the deductee; • Valid tax deduction and collection account number (TAN) of the deductor; • Book identification number or numbers (BIN)
 TRACES • TRACES is a web-based application of the Income - tax Department that provides an interface to all stakeholders associated with TDS administration. It enables viewing of challan status, downloading of NSDL File, Justification Report and Form 16 / 16 A as well as viewing of annual tax credit statements (Form 26 AS). Each deductor is required to Register in the Traces portal. Form 16/16 A issued to deductees should mandatorily be generated and downloaded from the TRACES portal.
TRACES • TRACES is a web-based application of the Income - tax Department that provides an interface to all stakeholders associated with TDS administration. It enables viewing of challan status, downloading of NSDL File, Justification Report and Form 16 / 16 A as well as viewing of annual tax credit statements (Form 26 AS). Each deductor is required to Register in the Traces portal. Form 16/16 A issued to deductees should mandatorily be generated and downloaded from the TRACES portal.
 POINTS TO BE REMEMBERED. . • An assessee, being an individual resident in India, whose total income does not exceed five hundred thousand Rs. 5 lakh shall be entitled to a deduction, from the amount of income-tax (as computed before allowing the deductions under this Chapter) on his / her total income with which he/she is chargeable for any assessment year, of an amount equal to hundred per cent of such income-tax or an amount of two thousand rupees (2000/-), whichever is less.
POINTS TO BE REMEMBERED. . • An assessee, being an individual resident in India, whose total income does not exceed five hundred thousand Rs. 5 lakh shall be entitled to a deduction, from the amount of income-tax (as computed before allowing the deductions under this Chapter) on his / her total income with which he/she is chargeable for any assessment year, of an amount equal to hundred per cent of such income-tax or an amount of two thousand rupees (2000/-), whichever is less.
 POINTS TO BE REMEMBERED • E-filing of income tax return is must for assessee with annual income above Rs. 5 lakh. • Tax payers with salary income of up to Rs. 5 lakh and interest from savings bank accounts up to `10, 000 is required to file income tax returns in either mode manually or through Efiling.
POINTS TO BE REMEMBERED • E-filing of income tax return is must for assessee with annual income above Rs. 5 lakh. • Tax payers with salary income of up to Rs. 5 lakh and interest from savings bank accounts up to `10, 000 is required to file income tax returns in either mode manually or through Efiling.
 Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. *Person responsible for paying any sum for carrying any work to any resident contractor should deduct tax at source. * Tax should be deducted at source only if the contract is between the contractor and the following specified persons:
Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. *Person responsible for paying any sum for carrying any work to any resident contractor should deduct tax at source. * Tax should be deducted at source only if the contract is between the contractor and the following specified persons:
 Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C . 1. The Central Government or any State Government. 2. Any local authority. 3. Any corporation established by or under a Central, State or Provincial Act 4. A company 5. Any Co-operative Society. 6. Any authority, constituted in India by or under any law, engaged either for the purpose of dealing with and satisfying the need for housing accommodation or for the purpose of planning development or improvement of cities, towns and villages, . 7. Any Society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1960 or any law corresponding to that Act in any part of India. 8. Any Trust. 9. Any University established by or under any Central, State or Provincial Act or any institution declared to be a University under the University Grants Commission Act.
Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C . 1. The Central Government or any State Government. 2. Any local authority. 3. Any corporation established by or under a Central, State or Provincial Act 4. A company 5. Any Co-operative Society. 6. Any authority, constituted in India by or under any law, engaged either for the purpose of dealing with and satisfying the need for housing accommodation or for the purpose of planning development or improvement of cities, towns and villages, . 7. Any Society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1960 or any law corresponding to that Act in any part of India. 8. Any Trust. 9. Any University established by or under any Central, State or Provincial Act or any institution declared to be a University under the University Grants Commission Act.
 Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. 10. Any firm. 11. Any individual or Hindu Undivided Family whose books are required to be audited under section 44 AB during the immediately preceding financial year. [The turnover from business/professional exceeds the limits specified u/s 44 AB during the immediately preceding financial year]. 12. Association of persons or Body of Individuals, whether incorporated or not, whose books are required to be audited under section 44 AB during the immediately preceding financial year. Income Tax should be deducted at the time of payment or credit to the account of the contractor whichever is earlier. Income Tax is to be deducted at source @ 1% if the contractor/sub contractor payee is an individual or HUF. Payment of amounts to person other than Individual/HUF would attract TDS rate of 2%.
Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. 10. Any firm. 11. Any individual or Hindu Undivided Family whose books are required to be audited under section 44 AB during the immediately preceding financial year. [The turnover from business/professional exceeds the limits specified u/s 44 AB during the immediately preceding financial year]. 12. Association of persons or Body of Individuals, whether incorporated or not, whose books are required to be audited under section 44 AB during the immediately preceding financial year. Income Tax should be deducted at the time of payment or credit to the account of the contractor whichever is earlier. Income Tax is to be deducted at source @ 1% if the contractor/sub contractor payee is an individual or HUF. Payment of amounts to person other than Individual/HUF would attract TDS rate of 2%.
 Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. • Provisions of Section 194 C are applicable only where the contract is either a “contract for carrying out any work” or a “contract for supply of labour for works contract”. Hence, these provisions are not applicable for payments made under the contract of sale of goods. • For the purpose of this section, the following contracts are also included in the scope of “Work”: • 1. Advertising. • 2. Broadcasting and telecasting including production of programs for • broadcasting and telecasting. • 3. Carriage of goods and passengers by any mode of transport other than • Railways. • 4. Catering.
Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. • Provisions of Section 194 C are applicable only where the contract is either a “contract for carrying out any work” or a “contract for supply of labour for works contract”. Hence, these provisions are not applicable for payments made under the contract of sale of goods. • For the purpose of this section, the following contracts are also included in the scope of “Work”: • 1. Advertising. • 2. Broadcasting and telecasting including production of programs for • broadcasting and telecasting. • 3. Carriage of goods and passengers by any mode of transport other than • Railways. • 4. Catering.
 Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. • No deduction of tax at source shall be made under this section in the following circumstances: If the amount paid/payable or credited/likely to be credited to the contractor/sub-contractor does not exceed Rs. 30, 000/- in a single instance. However, the total of amounts paid or credited during the financial year should not exceed Rs. 75, 000/-. If the said amount exceeds Rs. 75, 000/-, then, the liability for payment arises on the whole of amount paid or credited and not on the amount in excess of Rs. 75, 000/-. • In a case where advance payments are made in pursuance of contract be adjusted against work to be done, tax has to be deducted at the time of the advance payments.
Deduction at Source from payments to Contractors and Subcontractors under section 194 C. • No deduction of tax at source shall be made under this section in the following circumstances: If the amount paid/payable or credited/likely to be credited to the contractor/sub-contractor does not exceed Rs. 30, 000/- in a single instance. However, the total of amounts paid or credited during the financial year should not exceed Rs. 75, 000/-. If the said amount exceeds Rs. 75, 000/-, then, the liability for payment arises on the whole of amount paid or credited and not on the amount in excess of Rs. 75, 000/-. • In a case where advance payments are made in pursuance of contract be adjusted against work to be done, tax has to be deducted at the time of the advance payments.
 RATE OF T. D. S • 194 C (1) - 1% (for Payment individual) & 2% (for Payment others) - on Rs. 30000/- for single payment / on Rs. 75000/- for aggregate payment during Financial Year. • 194 C (2) - Payment to Sub-Contractors / for Advertisements (as per rate above). • 194 I - Rent of Land, Building or Furniture - Rs. 180000/- (annually) -10%
RATE OF T. D. S • 194 C (1) - 1% (for Payment individual) & 2% (for Payment others) - on Rs. 30000/- for single payment / on Rs. 75000/- for aggregate payment during Financial Year. • 194 C (2) - Payment to Sub-Contractors / for Advertisements (as per rate above). • 194 I - Rent of Land, Building or Furniture - Rs. 180000/- (annually) -10%
 Filing of Income Tax.
Filing of Income Tax.
 TDS/ Filing of Annual Information and Return to Income Tax Authority
TDS/ Filing of Annual Information and Return to Income Tax Authority
 Who can file? Compulsory for all Deductors to file electronically.
Who can file? Compulsory for all Deductors to file electronically.
 • IMPORTANT ISSUES TAN : - TAN or Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number is a 10 digit alpha numeric number required to be obtained by all persons who are responsible for deducting or collecting tax. It is compulsory to quote TAN in TDS/TCS return (including any e-TDS/TCS return), any TDS/TCS payment challan and TDS/TCS certificates. Example : CALP 02845 D
• IMPORTANT ISSUES TAN : - TAN or Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number is a 10 digit alpha numeric number required to be obtained by all persons who are responsible for deducting or collecting tax. It is compulsory to quote TAN in TDS/TCS return (including any e-TDS/TCS return), any TDS/TCS payment challan and TDS/TCS certificates. Example : CALP 02845 D
 IMPORTANT ISSUES • Why is it necessary to have TAN ? TAN is required to be quoted in all TDS/TCS returns, all TDS/TCS payment challans and all TDS/TCS certificates to be issued. TDS/TCS returns will not be received if TAN is not quoted and challans for TDS/TCS payments will not be accepted by banks. Failure to apply for TAN or not quoting the same in the specified documents attracts a penalty of Rs. 10, 000/-.
IMPORTANT ISSUES • Why is it necessary to have TAN ? TAN is required to be quoted in all TDS/TCS returns, all TDS/TCS payment challans and all TDS/TCS certificates to be issued. TDS/TCS returns will not be received if TAN is not quoted and challans for TDS/TCS payments will not be accepted by banks. Failure to apply for TAN or not quoting the same in the specified documents attracts a penalty of Rs. 10, 000/-.
 Other points If any employee does not furnish his PAN to the employer, tax will be deducted (with effect from April 1, 2010) either at the normal rates or at the rate of 20%, whichever is higher. PAN of the employee should be mentioned on any correspondence and document which is exchanged between the employer and the employee.
Other points If any employee does not furnish his PAN to the employer, tax will be deducted (with effect from April 1, 2010) either at the normal rates or at the rate of 20%, whichever is higher. PAN of the employee should be mentioned on any correspondence and document which is exchanged between the employer and the employee.
 Types of e-Filing • There are three ways to file returns electronically • Option 1: Use digital signature in which case no paper return is required to be submitted • Option 2: File without digital signature in which case ITR-V form is to filed with the department. This is a single page receipt cum verification form. • Option 3: File through an e-return intermediary who would do e-Filing and also assist the Assessee file the ITR V Form.
Types of e-Filing • There are three ways to file returns electronically • Option 1: Use digital signature in which case no paper return is required to be submitted • Option 2: File without digital signature in which case ITR-V form is to filed with the department. This is a single page receipt cum verification form. • Option 3: File through an e-return intermediary who would do e-Filing and also assist the Assessee file the ITR V Form.
 forms for e-filing • Form 24 Q- All tax deductors are required to file the TDS statements in Form No. 24 Q (for tax deducted from salaries). Tax deductors are, therefore, advised to procure and quote correct PAN details of all deductees in the TDS statements for salaries in Form 24 Q. Taxpayers are also liable to furnish their correct PAN to their deductors. • Form 26 Q
forms for e-filing • Form 24 Q- All tax deductors are required to file the TDS statements in Form No. 24 Q (for tax deducted from salaries). Tax deductors are, therefore, advised to procure and quote correct PAN details of all deductees in the TDS statements for salaries in Form 24 Q. Taxpayers are also liable to furnish their correct PAN to their deductors. • Form 26 Q
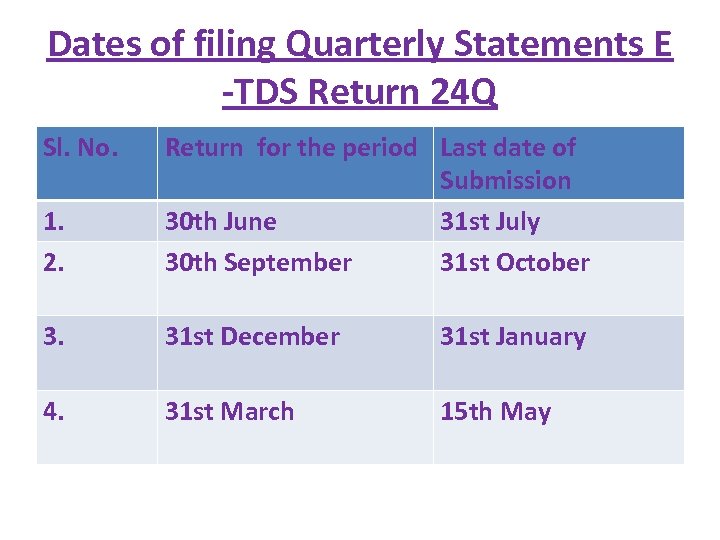 Dates of filing Quarterly Statements E -TDS Return 24 Q Sl. No. 1. 2. Return for the period Last date of Submission 30 th June 31 st July 30 th September 31 st October 3. 31 st December 31 st January 4. 31 st March 15 th May
Dates of filing Quarterly Statements E -TDS Return 24 Q Sl. No. 1. 2. Return for the period Last date of Submission 30 th June 31 st July 30 th September 31 st October 3. 31 st December 31 st January 4. 31 st March 15 th May
 Fee for default in furnishing 24 Q statements • If a person fails to deliver a 24 Q statement within the time prescribed in section 200(3) in respect of tax deducted at source he shall be liable to pay, by way of fee a sum of Rs. 200 for every day during which the failure continues. However, the amount of such fee shall not exceed the amount of tax which was deductible at source. This fee is mandatory in nature and to be paid before furnishing of such statement. • A DDO can also file a correction statement for rectification of any mistake or to add, delete or update the information furnished in the statement delivered earlier.
Fee for default in furnishing 24 Q statements • If a person fails to deliver a 24 Q statement within the time prescribed in section 200(3) in respect of tax deducted at source he shall be liable to pay, by way of fee a sum of Rs. 200 for every day during which the failure continues. However, the amount of such fee shall not exceed the amount of tax which was deductible at source. This fee is mandatory in nature and to be paid before furnishing of such statement. • A DDO can also file a correction statement for rectification of any mistake or to add, delete or update the information furnished in the statement delivered earlier.
 D. D. O. SHOULD TO SATISFY THEMSELVES ABOUT THE GENUINENESS OF CLAIM • The Drawing and Disbursing Officers should satisfy themselves about the actual deposits/ subscriptions / payments made by the employees, by calling for such particulars/ information as they deem necessary before allowing the aforesaid deductions. In case the DDO is not satisfied about the genuineness of the employee's claim regarding any deposit/ subscription/ payment made by the employee, he should not allow the same, and the employee would be free to claim the deduction/ rebate on such amount by filing his return of income and furnishing the necessary proof etc. , therewith, to the satisfaction of the Assessing Officer.
D. D. O. SHOULD TO SATISFY THEMSELVES ABOUT THE GENUINENESS OF CLAIM • The Drawing and Disbursing Officers should satisfy themselves about the actual deposits/ subscriptions / payments made by the employees, by calling for such particulars/ information as they deem necessary before allowing the aforesaid deductions. In case the DDO is not satisfied about the genuineness of the employee's claim regarding any deposit/ subscription/ payment made by the employee, he should not allow the same, and the employee would be free to claim the deduction/ rebate on such amount by filing his return of income and furnishing the necessary proof etc. , therewith, to the satisfaction of the Assessing Officer.
 Relief U/S 89(1) • Relief is available when Salary is available in arrears or advance. Benefit is available through application of form 10 (E).
Relief U/S 89(1) • Relief is available when Salary is available in arrears or advance. Benefit is available through application of form 10 (E).
 Thank you
Thank you


