2d52c3668c8e3f6637559df86be9debf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

An On-line Document Clustering Method Based on Forgetting Factors Yoshiharu Ishikawa, Yibing Chen Hiroyuki Kitagawa University of Tsukuba, Japan Sept. 7, 2001 ECDL 2001 1

Outline n n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 2
Background n The Internet enabled on-line document delivery services n n n Important technologies (and applications) for on-line documents n n newsfeed services over the network periodically issued on-line journals information filtering document summarization, information extraction topic detection and tracking (TDT) Clustering works as a core technique for these applications 3

Our Objectives (1) n n n Development of an on-line clustering method which considers the novelty of each document Presents a snapshot of clusters in an up-to-date manner Example: articles from sports news feed Formula 1 & M. Schumacher U. S. Open Tennis Other articles Soccer World Cup time 4

Our Objectives (2) n n Development of a novelty-based clustering method for on-line documents Features: n It weights high importance on newer documents than older ones and forgets obsolete ones n n Incremental clustering processing n n introduction of a new document similarity measure that considers novelty and obsolescence of documents low processing cost to generate a new clustering result Automatic maintenance of target documents n obsolete documents are automatically deleted from the clustering target 5
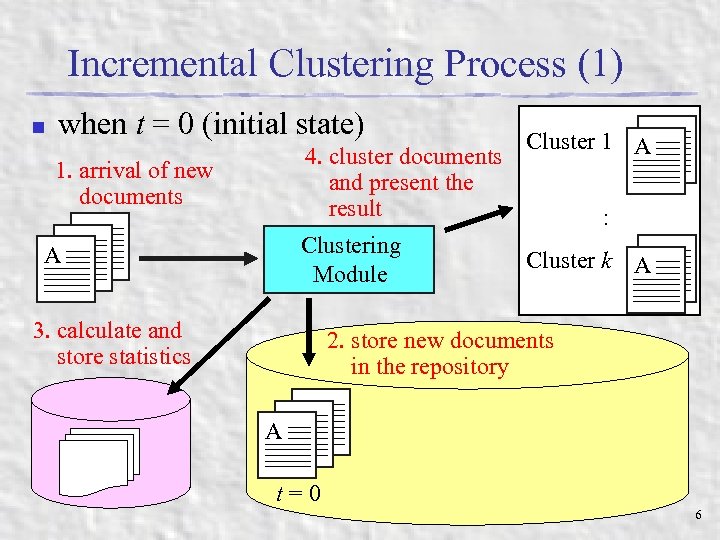
Incremental Clustering Process (1) n when t = 0 (initial state) 1. arrival of new documents AA A A Cluster 1 A 4. cluster documents and present the result : Clustering A Cluster k A Module 3. calculate and store statistics 2. store new documents in the repository AA A t=0 6
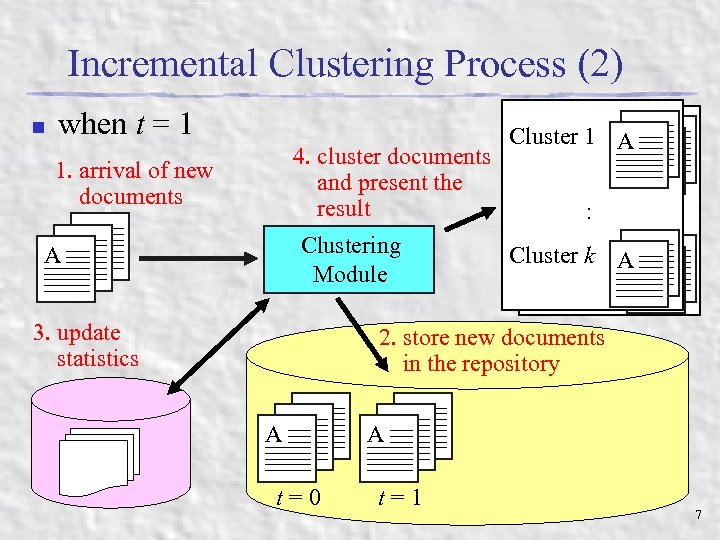
Incremental Clustering Process (2) n when t = 1 1. arrival of new documents AA A 4. cluster documents and present the result Clustering Module 3. update statistics AA Cluster 1 1 AA Cluster :: AA Cluster k k AA Cluster 2. store new documents in the repository AA A t=0 t=1 7
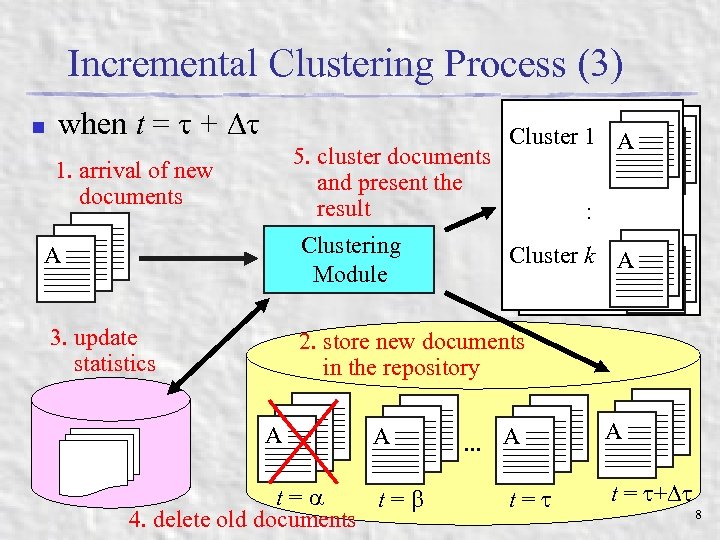
Incremental Clustering Process (3) n when t = + 1. arrival of new documents AA A 5. cluster documents and present the result Clustering Module 3. update statistics AA Cluster 1 1 AA Cluster :: AA Cluster k k AA Cluster 2. store new documents in the repository AA A AA. . . A t= t= 4. delete old documents t= AA A t = + 8

Outline n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method n n n n C 2 ICM Clustering Method F 2 ICM Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 9
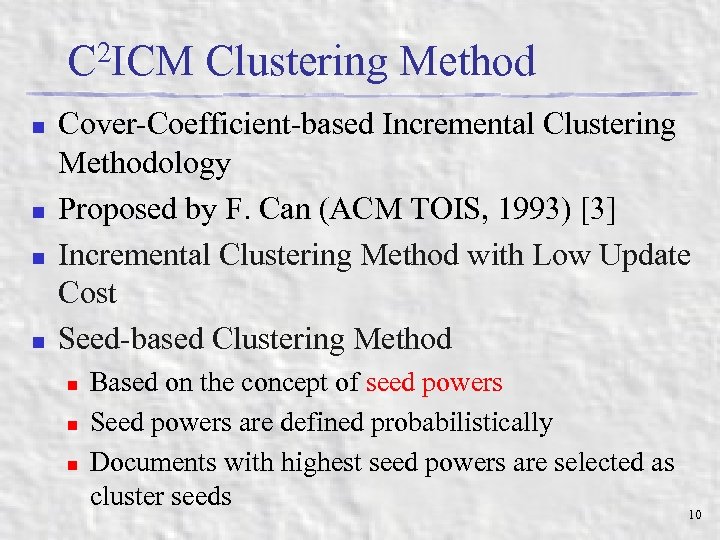
C 2 ICM Clustering Method n n Cover-Coefficient-based Incremental Clustering Methodology Proposed by F. Can (ACM TOIS, 1993) [3] Incremental Clustering Method with Low Update Cost Seed-based Clustering Method n n n Based on the concept of seed powers Seed powers are defined probabilistically Documents with highest seed powers are selected as cluster seeds 10
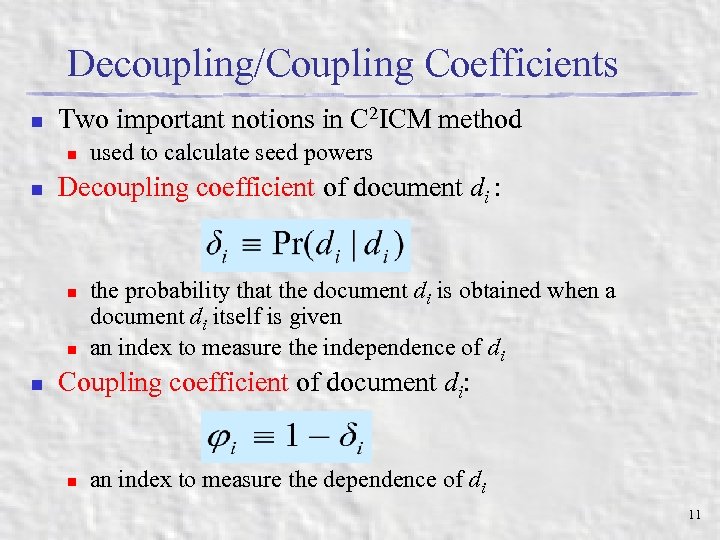
Decoupling/Coupling Coefficients n Two important notions in C 2 ICM method n n Decoupling coefficient of document di : n n n used to calculate seed powers the probability that the document di is obtained when a document di itself is given an index to measure the independence of di Coupling coefficient of document di: n an index to measure the dependence of di 11
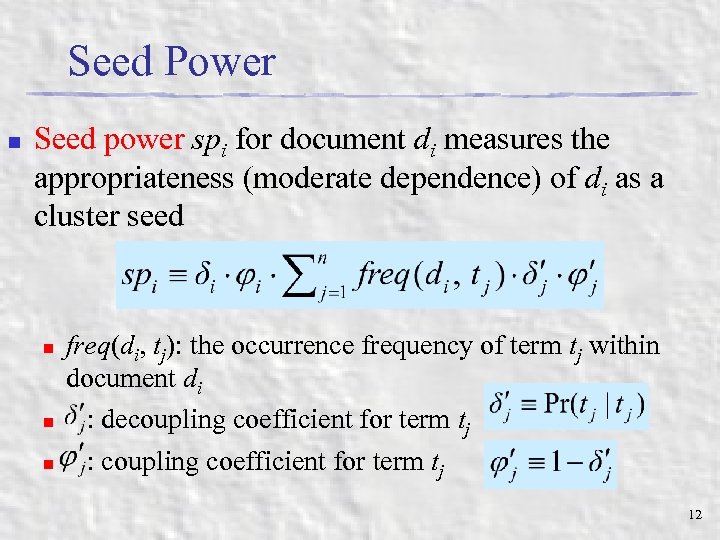
Seed Power n Seed power spi for document di measures the appropriateness (moderate dependence) of di as a cluster seed n n n freq(di, tj): the occurrence frequency of term tj within document di : decoupling coefficient for term tj : coupling coefficient for term tj 12
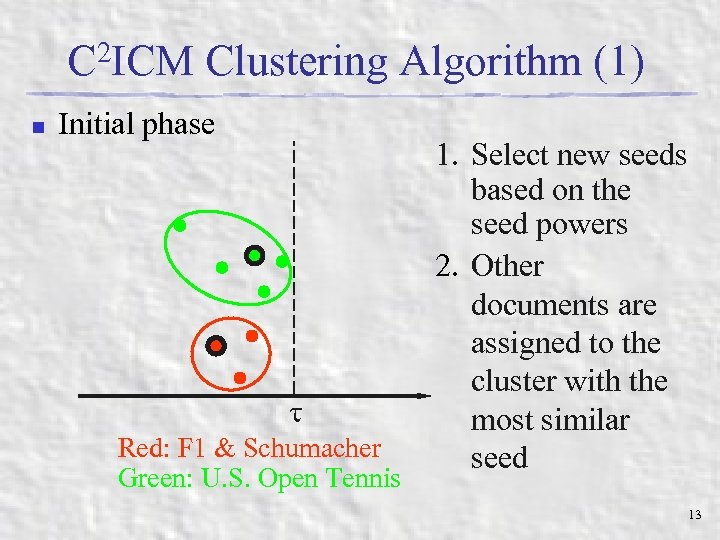
C 2 ICM Clustering Algorithm (1) n Initial phase Red: F 1 & Schumacher Green: U. S. Open Tennis 1. Select new seeds based on the seed powers 2. Other documents are assigned to the cluster with the most similar seed 13
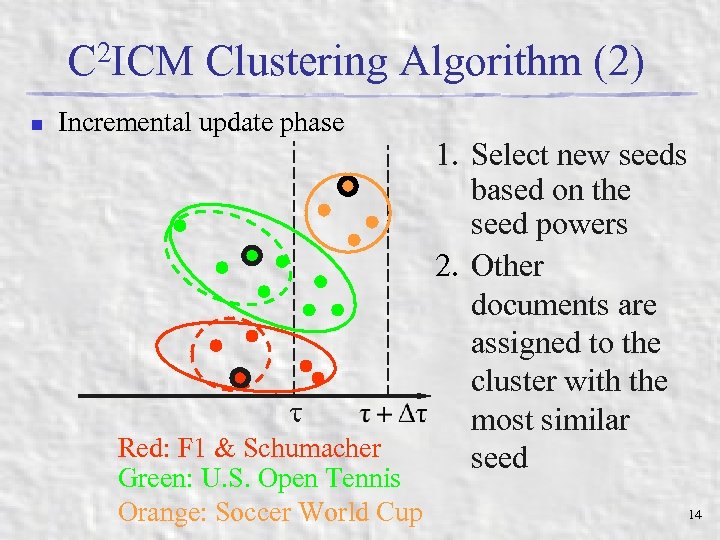
C 2 ICM Clustering Algorithm (2) n Incremental update phase Red: F 1 & Schumacher Green: U. S. Open Tennis Orange: Soccer World Cup 1. Select new seeds based on the seed powers 2. Other documents are assigned to the cluster with the most similar seed 14

Outline n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method n n n n C 2 ICM Clustering Method F 2 ICM Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 15
F 2 ICM Clustering Method n n Extension of C 2 ICM method Main differences n n n Introduction of a new document similarity measure based on the notion of the forgetting factor: it weights high importance on newer documents to generate clusters Incremental maintenance of statistics Automatic deletion of obsolete old documents 16

Outline n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor n n n Document forgetting model Derivation of document similarity measure Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 17
Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor n New Document Similarity Measure Based on Document Forgetting Model n n Assumption: each delivered document gradually loses its value (weight) as time passes Derivation of document similarity measure based on the assumption n n put high weights on new documents and low weights on old ones old documents have low effects on clustering Using the derived document similarity measure, we can achieve a novelty-based clustering 18
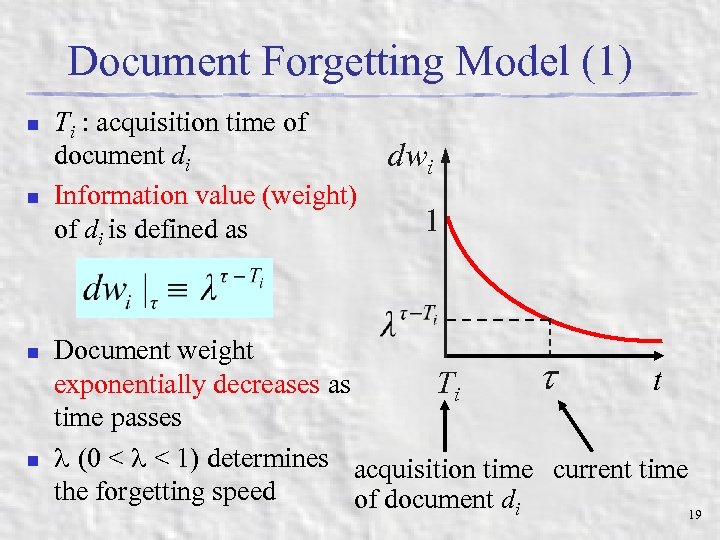
Document Forgetting Model (1) n n Ti : acquisition time of document di Information value (weight) of di is defined as dwi 1 Document weight t t exponentially decreases as Ti time passes (0 < < 1) determines acquisition time current time the forgetting speed of document di 19
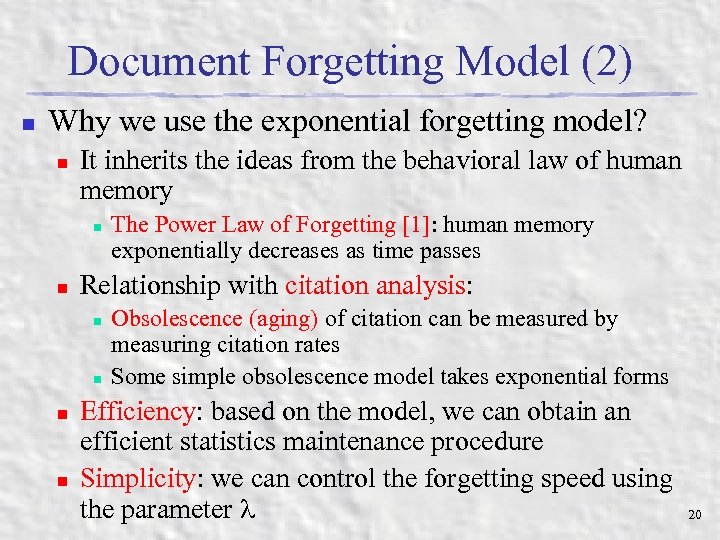
Document Forgetting Model (2) n Why we use the exponential forgetting model? n It inherits the ideas from the behavioral law of human memory n n Relationship with citation analysis: n n The Power Law of Forgetting [1]: human memory exponentially decreases as time passes Obsolescence (aging) of citation can be measured by measuring citation rates Some simple obsolescence model takes exponential forms Efficiency: based on the model, we can obtain an efficient statistics maintenance procedure Simplicity: we can control the forgetting speed using the parameter 20

Outline n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor n n n Document forgetting model Derivation of document similarity measure Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 21
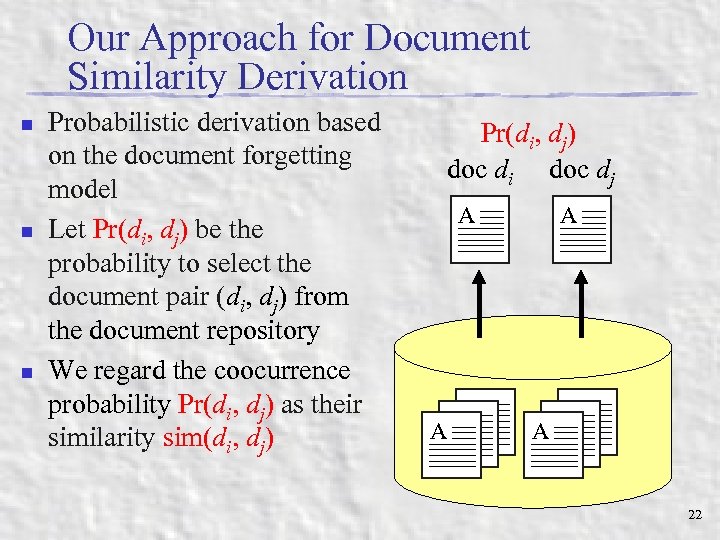
Our Approach for Document Similarity Derivation n Probabilistic derivation based on the document forgetting model Let Pr(di, dj) be the probability to select the document pair (di, dj) from the document repository We regard the coocurrence probability Pr(di, dj) as their similarity sim(di, dj) Pr(di, dj) doc di doc dj A A AA A 22
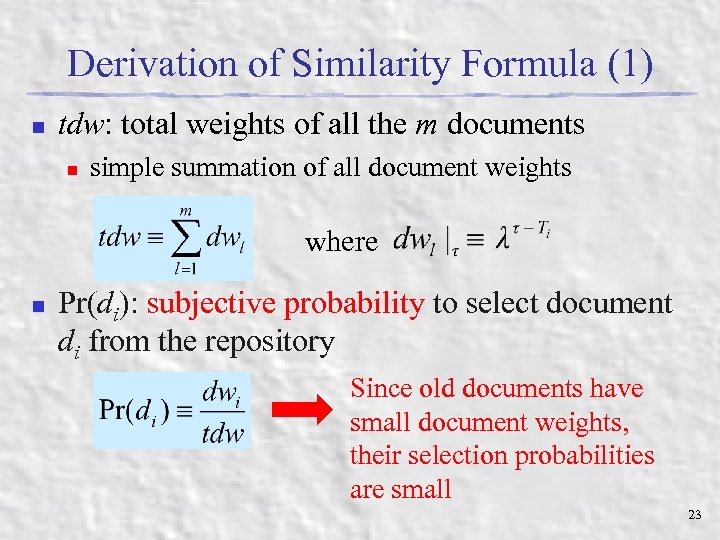
Derivation of Similarity Formula (1) n tdw: total weights of all the m documents n simple summation of all document weights where n Pr(di): subjective probability to select document di from the repository Since old documents have small document weights, their selection probabilities are small 23
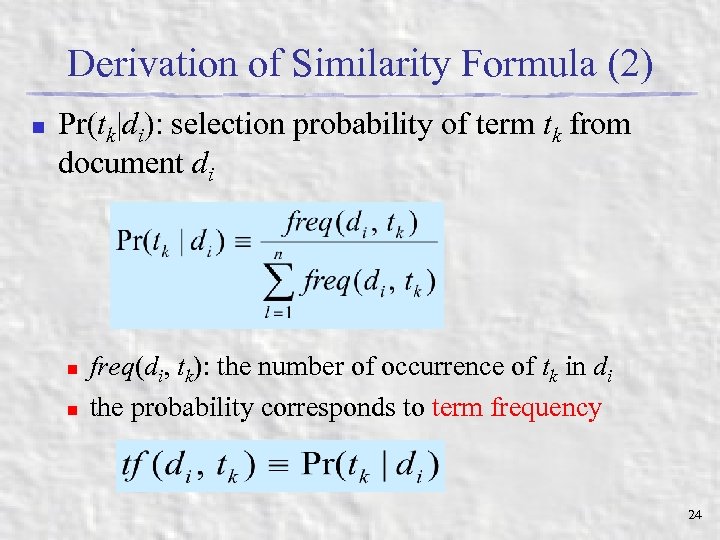
Derivation of Similarity Formula (2) n Pr(tk|di): selection probability of term tk from document di n n freq(di, tk): the number of occurrence of tk in di the probability corresponds to term frequency 24
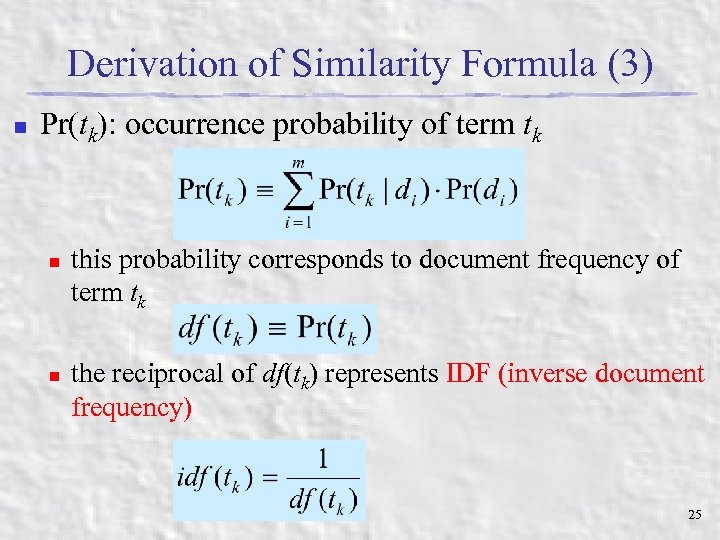
Derivation of Similarity Formula (3) n Pr(tk): occurrence probability of term tk n n this probability corresponds to document frequency of term tk the reciprocal of df(tk) represents IDF (inverse document frequency) 25
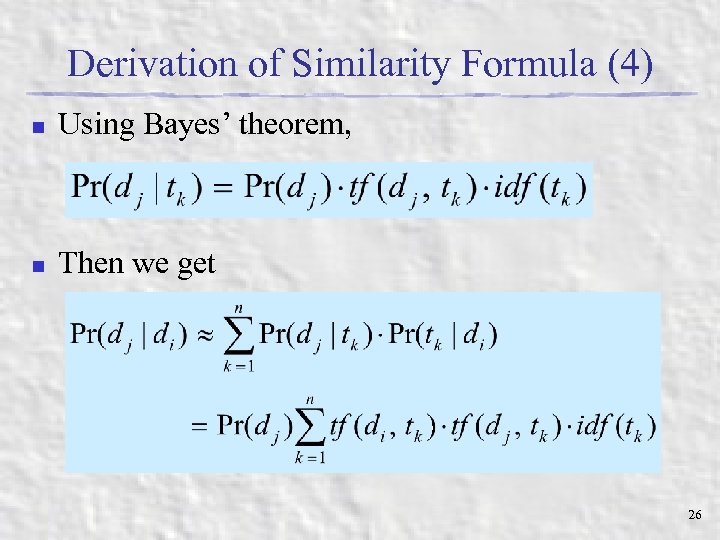
Derivation of Similarity Formula (4) n Using Bayes’ theorem, n Then we get 26
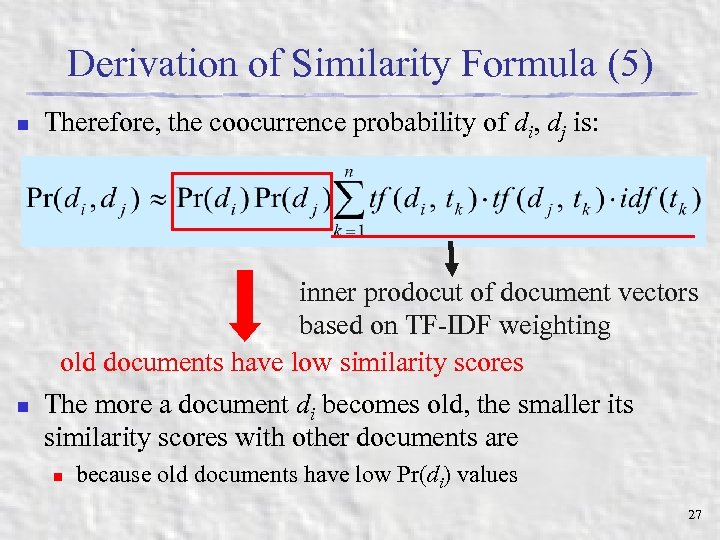
Derivation of Similarity Formula (5) n Therefore, the coocurrence probability of di, dj is: inner prodocut of document vectors based on TF-IDF weighting old documents have low similarity scores n The more a document di becomes old, the smaller its similarity scores with other documents are n because old documents have low Pr(di) values 27

Outline n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor n n n Document forgetting model Derivation of document similarity measure Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 28
Updating Statistics and Probabilities n when t = + 1. arrival of new documents AA A AA Cluster 1 1 AA Cluster 5. present new clustering result Clustering Module 3. update statistics :: AA Cluster k k AA Cluster 2. store new documents in the repository AA A t= 4. delete old documents AA A AA. . . A t= AA A t = + 29
Approach to Update Processing (1) n In every incremental clustering step, we have to calculate document similarities n n To compute similarities, we need to calculate document statistics and probabilities beforehand It is inefficient to compute statistics every time from scratch Incremental Update Processing n Store the calculated statistics and probabilities and utilize them for later computation 30
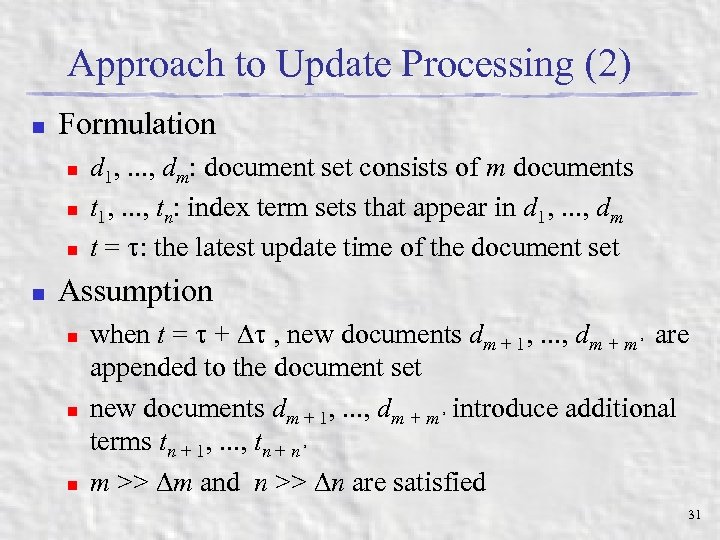
Approach to Update Processing (2) n Formulation n n d 1, . . . , dm: document set consists of m documents t 1, . . . , tn: index term sets that appear in d 1, . . . , dm t = : the latest update time of the document set Assumption n when t = + , new documents dm + 1, . . . , dm + m’ are appended to the document set new documents dm + 1, . . . , dm + m’ introduce additional terms tn + 1, . . . , tn + n’ m >> m and n >> n are satisfied 31
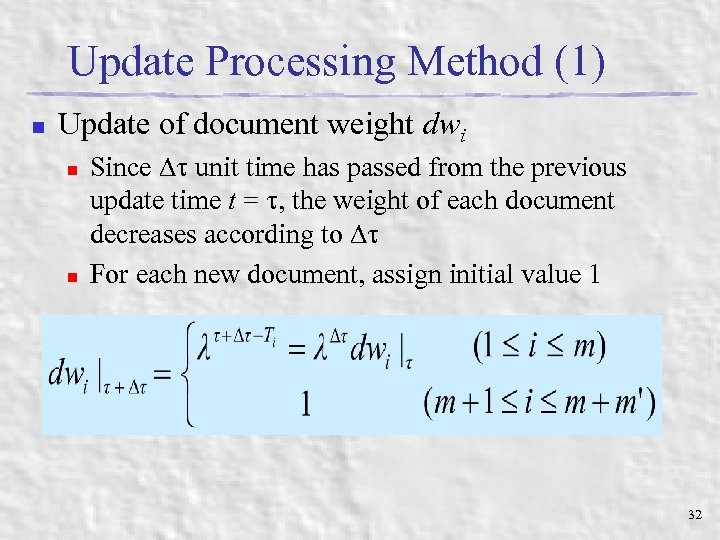
Update Processing Method (1) n Update of document weight dwi n n Since unit time has passed from the previous update time t = , the weight of each document decreases according to For each new document, assign initial value 1 32
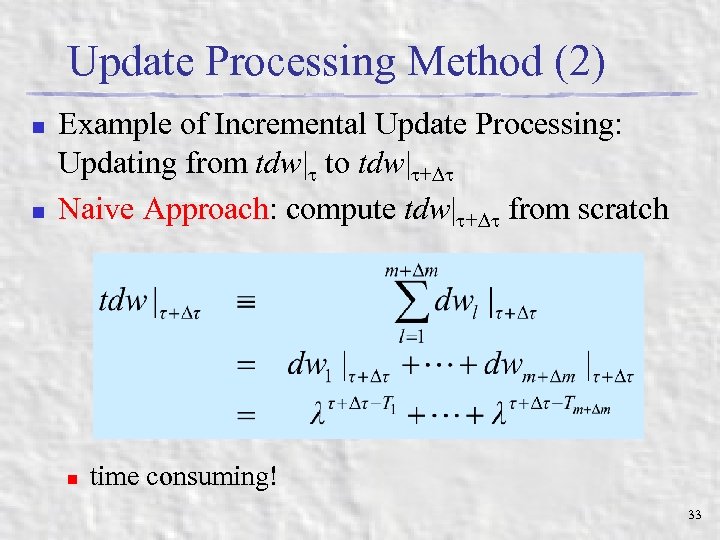
Update Processing Method (2) n n Example of Incremental Update Processing: Updating from tdw| to tdw| + Naive Approach: compute tdw| + from scratch n time consuming! 33
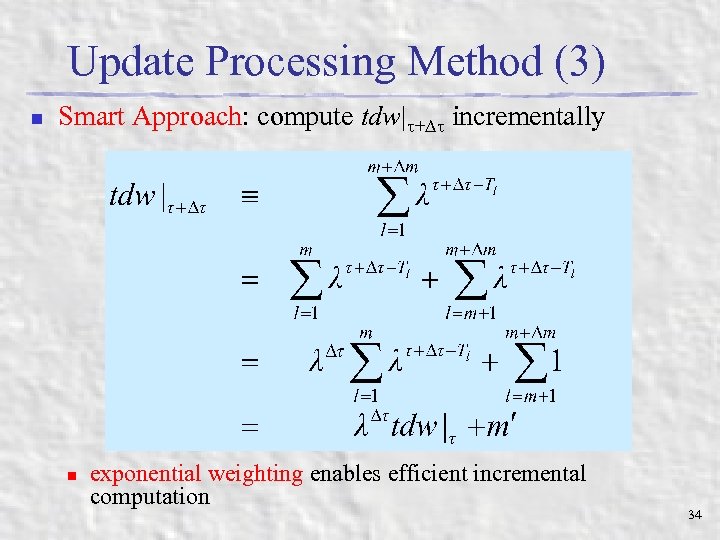
Update Processing Method (3) n Smart Approach: compute tdw| + incrementally n exponential weighting enables efficient incremental computation 34
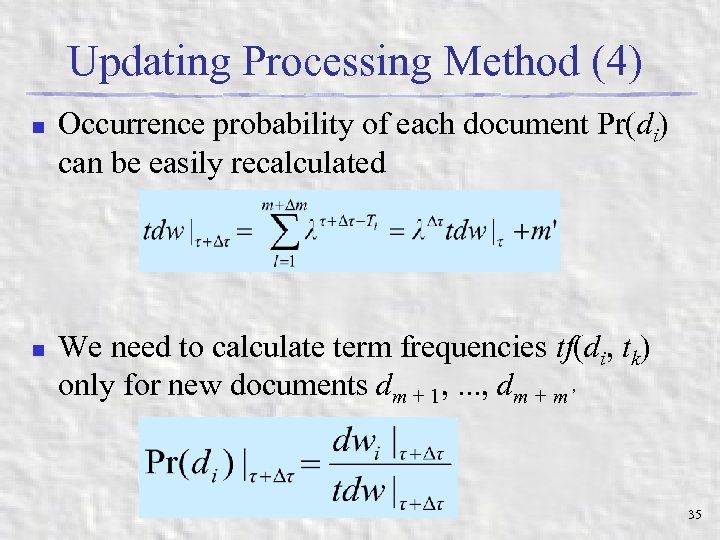
Updating Processing Method (4) n n Occurrence probability of each document Pr(di) can be easily recalculated We need to calculate term frequencies tf(di, tk) only for new documents dm + 1, . . . , dm + m’ 35
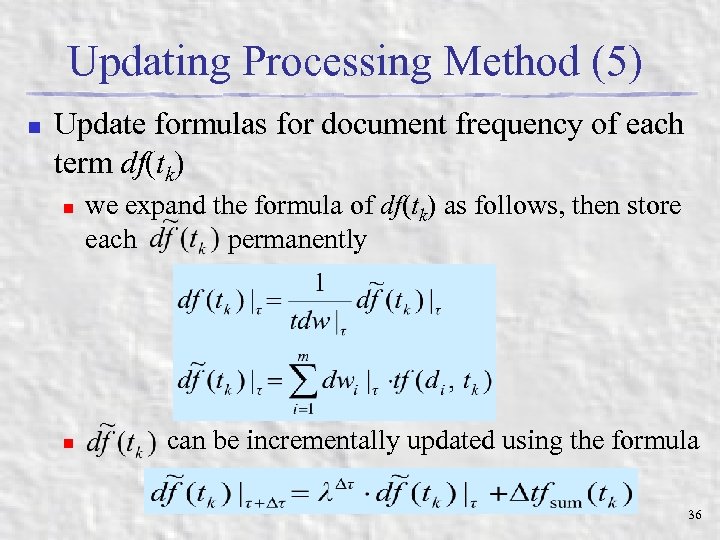
Updating Processing Method (5) n Update formulas for document frequency of each term df(tk) n n we expand the formula of df(tk) as follows, then store each permanently can be incrementally updated using the formula 36
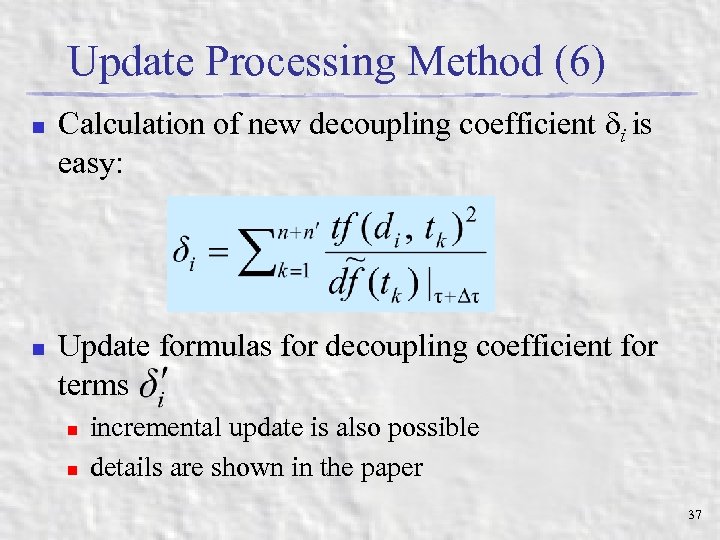
Update Processing Method (6) n n Calculation of new decoupling coefficient i is easy: Update formulas for decoupling coefficient for terms n n incremental update is also possible details are shown in the paper 37
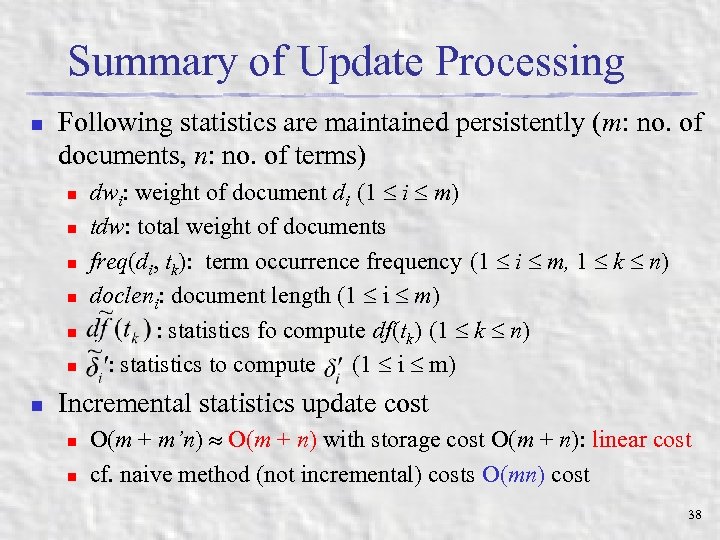
Summary of Update Processing n Following statistics are maintained persistently (m: no. of documents, n: no. of terms) n n n n dwi: weight of document di (1 i m) tdw: total weight of documents freq(di, tk): term occurrence frequency (1 i m, 1 k n) docleni: document length (1 i m) : statistics fo compute df(tk) (1 k n) : statistics to compute (1 i m) Incremental statistics update cost n n O(m + m’n) O(m + n) with storage cost O(m + n): linear cost cf. naive method (not incremental) costs O(mn) cost 38

Outline n n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 39
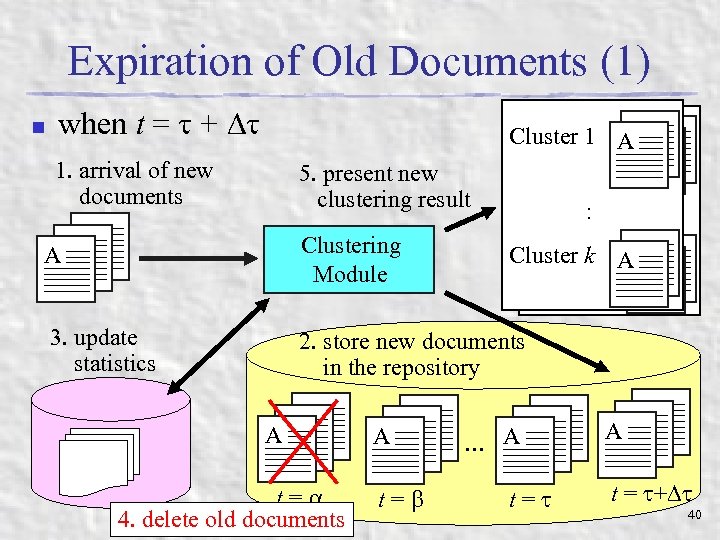
Expiration of Old Documents (1) n when t = + 1. arrival of new documents AA A AA Cluster 1 1 AA Cluster 5. present new clustering result Clustering Module 3. update statistics :: AA Cluster k k AA Cluster 2. store new documents in the repository AA A t= 4. delete old documents AA A AA. . . A t= AA A t = + 40

Expiration of Old Documents (2) n Two reasons to delete old documents: n n n reduction of storage area old documents have only tiny effects on the resulting clustering structure Our approach: n n If dwi < ( is a small parameter constant) is satisfied, delete document di When we delete di, related statistics values are deleted n n e. g. , freq(di, tk) details are in the proceedings and [6] 41
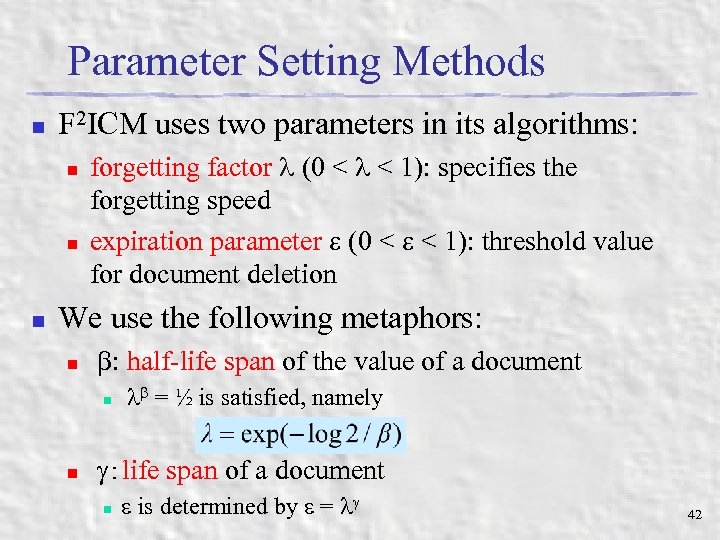
Parameter Setting Methods n F 2 ICM uses two parameters in its algorithms: n n n forgetting factor (0 < < 1): specifies the forgetting speed expiration parameter (0 < < 1): threshold value for document deletion We use the following metaphors: n : half-life span of the value of a document n n = ½ is satisfied, namely :life span of a document n is determined by = 42

Outline n n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 43

Dataset and Parameter Settings n Dataset: Mainich Daily Newspaper articles n Each article consists of the following information: n n The articles we used in the experiment: n n n issue date subject area (e. g. , economy, sports) keyword list (50 150 words in Japanese) issue date: January 1994 to February 1994 subject area: international affairs Parameter Settings n nc (no. of clusters) = 10 (half-life span) = 7: the value of an article reduces to ½ in one week (life span) = 30: every document will be deleted after 30 days 44
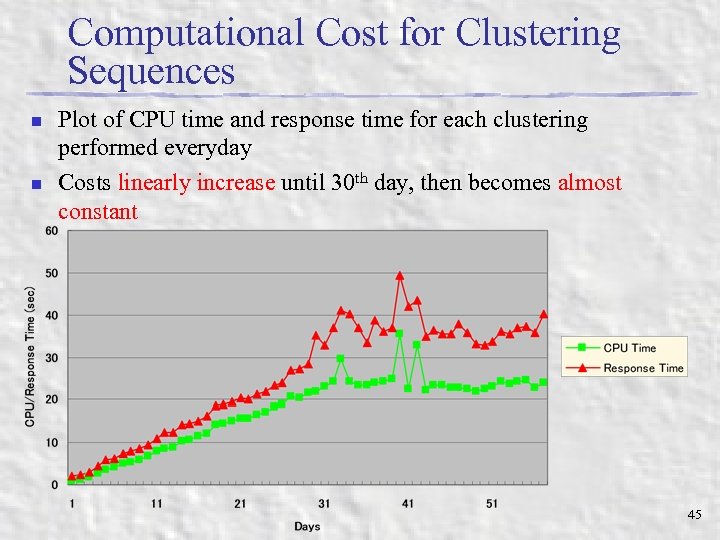
Computational Cost for Clustering Sequences n n Plot of CPU time and response time for each clustering performed everyday Costs linearly increase until 30 th day, then becomes almost constant 45
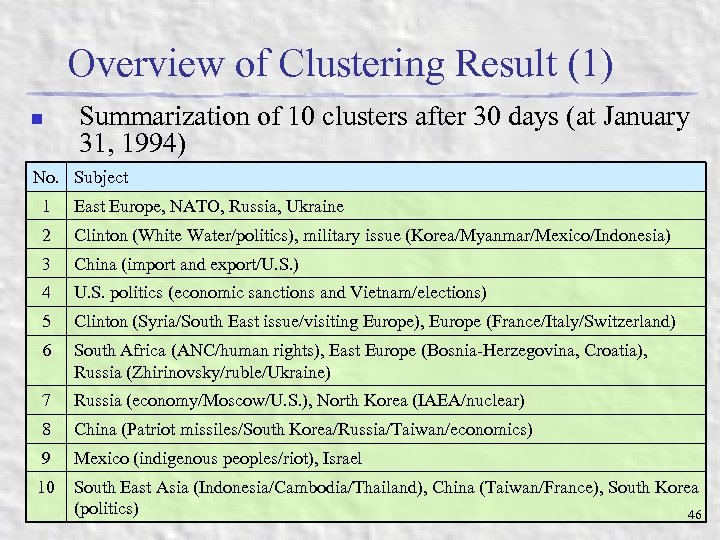
Overview of Clustering Result (1) n Summarization of 10 clusters after 30 days (at January 31, 1994) No. Subject 1 East Europe, NATO, Russia, Ukraine 2 Clinton (White Water/politics), military issue (Korea/Myanmar/Mexico/Indonesia) 3 China (import and export/U. S. ) 4 U. S. politics (economic sanctions and Vietnam/elections) 5 Clinton (Syria/South East issue/visiting Europe), Europe (France/Italy/Switzerland) 6 South Africa (ANC/human rights), East Europe (Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia), Russia (Zhirinovsky/ruble/Ukraine) 7 Russia (economy/Moscow/U. S. ), North Korea (IAEA/nuclear) 8 China (Patriot missiles/South Korea/Russia/Taiwan/economics) 9 Mexico (indigenous peoples/riot), Israel 10 South East Asia (Indonesia/Cambodia/Thailand), China (Taiwan/France), South Korea (politics) 46
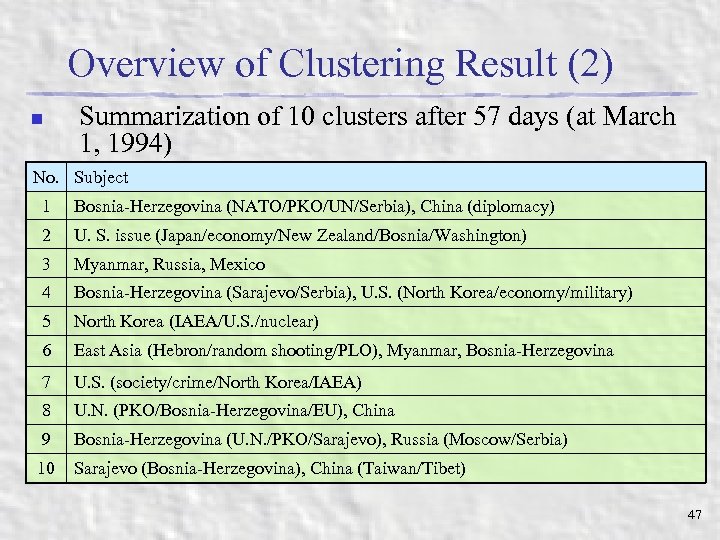
Overview of Clustering Result (2) n Summarization of 10 clusters after 57 days (at March 1, 1994) No. Subject 1 Bosnia-Herzegovina (NATO/PKO/UN/Serbia), China (diplomacy) 2 U. S. issue (Japan/economy/New Zealand/Bosnia/Washington) 3 Myanmar, Russia, Mexico 4 Bosnia-Herzegovina (Sarajevo/Serbia), U. S. (North Korea/economy/military) 5 North Korea (IAEA/U. S. /nuclear) 6 East Asia (Hebron/random shooting/PLO), Myanmar, Bosnia-Herzegovina 7 U. S. (society/crime/North Korea/IAEA) 8 U. N. (PKO/Bosnia-Herzegovina/EU), China 9 Bosnia-Herzegovina (U. N. /PKO/Sarajevo), Russia (Moscow/Serbia) 10 Sarajevo (Bosnia-Herzegovina), China (Taiwan/Tibet) 47

Summary of the Experiment n Brief observations n n n F 2 ICM groups similar articles into a cluster as far as an appropriate seed is selected But a cluster obtained by the experiment usually contains multiple topics, and different clusters contain similar topics: clusters are not well separated Reasons of the observed phenomena: n n Selected seeds are not well separated in topics: more sophisticated selection method is required The number of keywords for an articles is rather small (50 150 words) 48

Outline n n n n Background and Objectives F 2 ICM Incremental Document Clustering Method Document Similarity Based on Forgetting Factor Updating Statistics and Probabilities Document Expiration and Parameter Setting Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work 49
Conclusions and Future Work n Conclusions n Development of an on-line clustering method which considers the novelty of documents n n n Introduction of document forgetting model F 2 ICM: Forgetting Factor-based Incremental Clustering Method Incremental statistics update method (linear update cost) Automatic document expiration and parameter setting methods Preliminary report of the experiments Current and Future Work n n n Revision of the clustering algorithms based on Scatter/Gather approach [4] More detailed experiments and their evaluation Development of automatic parameter tuning methods 50
2d52c3668c8e3f6637559df86be9debf.ppt