460a490c50a9d7159b6fa041f45d48da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 1
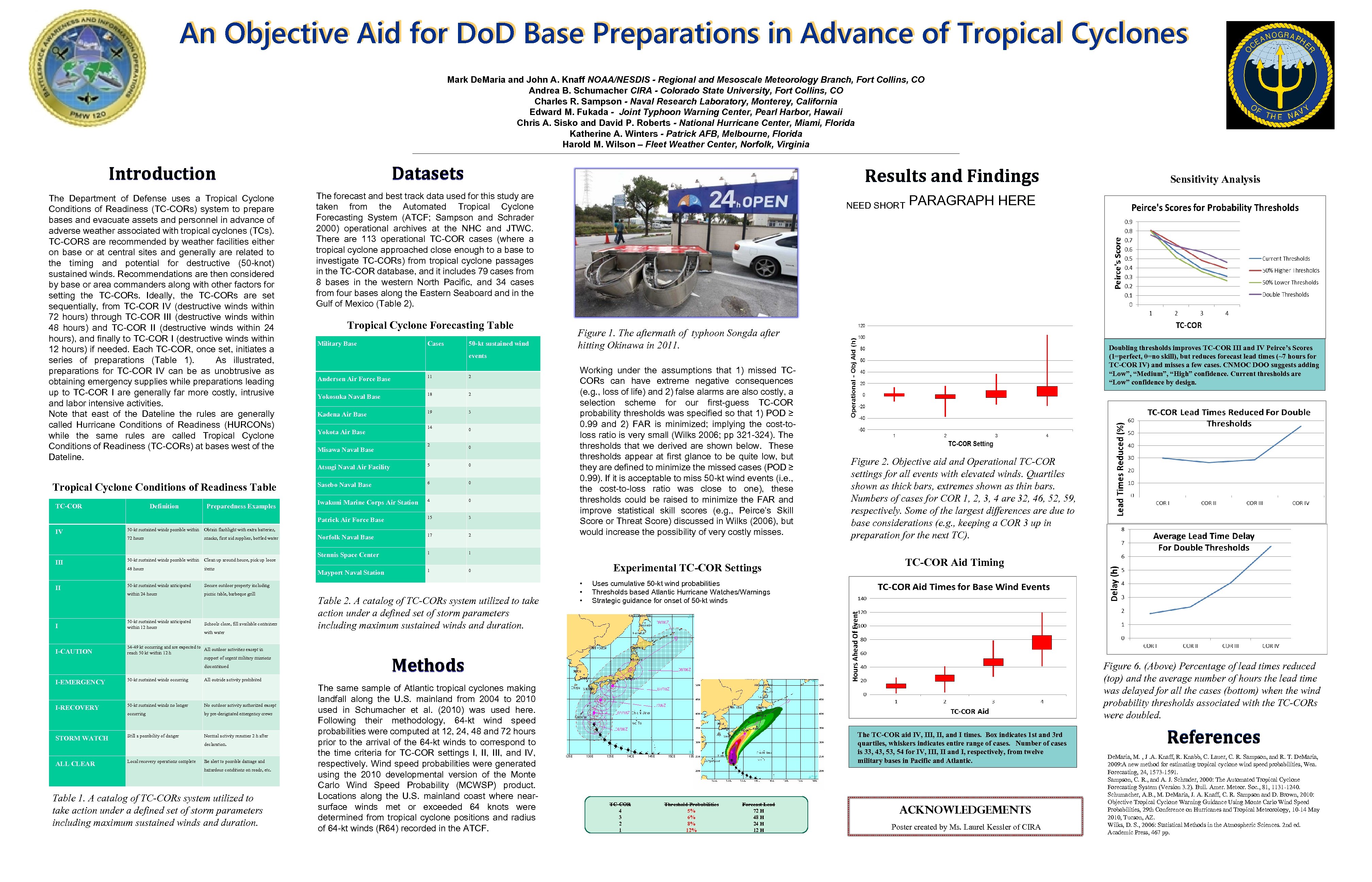
An Objective Aid for Do. D Base Preparations in Advance of Tropical Cyclones Mark De. Maria and John A. Knaff NOAA/NESDIS - Regional and Mesoscale Meteorology Branch, Fort Collins, CO Andrea B. Schumacher CIRA - Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO Charles R. Sampson - Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, California Edward M. Fukada - Joint Typhoon Warning Center, Pearl Harbor, Hawaii Chris A. Sisko and David P. Roberts - National Hurricane Center, Miami, Florida Katherine A. Winters - Patrick AFB, Melbourne, Florida Harold M. Wilson – Fleet Weather Center, Norfolk, Virginia Datasets Introduction The Department of Defense uses a Tropical Cyclone Conditions of Readiness (TC-CORs) system to prepare bases and evacuate assets and personnel in advance of adverse weather associated with tropical cyclones (TCs). TC-CORS are recommended by weather facilities either on base or at central sites and generally are related to the timing and potential for destructive (50 -knot) sustained winds. Recommendations are then considered by base or area commanders along with other factors for setting the TC-CORs. Ideally, the TC-CORs are set sequentially, from TC-COR IV (destructive winds within 72 hours) through TC-COR III (destructive winds within 48 hours) and TC-COR II (destructive winds within 24 hours), and finally to TC-COR I (destructive winds within 12 hours) if needed. Each TC-COR, once set, initiates a series of preparations (Table 1). As illustrated, preparations for TC-COR IV can be as unobtrusive as obtaining emergency supplies while preparations leading up to TC-COR I are generally far more costly, intrusive and labor intensive activities. Note that east of the Dateline the rules are generally called Hurricane Conditions of Readiness (HURCONs) while the same rules are called Tropical Cyclone Conditions of Readiness (TC-CORs) at bases west of the Dateline. Results and Findings The forecast and best track data used for this study are taken from the Automated Tropical Cyclone Forecasting System (ATCF; Sampson and Schrader 2000) operational archives at the NHC and JTWC. There are 113 operational TC-COR cases (where a tropical cyclone approached close enough to a base to investigate TC-CORs) from tropical cyclone passages in the TC-COR database, and it includes 79 cases from 8 bases in the western North Pacific, and 34 cases from four bases along the Eastern Seaboard and in the Gulf of Mexico (Table 2). Tropical Cyclone Forecasting Table Military Base Cases 50 -kt sustained wind IV Definition Preparedness Examples 50 -kt sustained winds possible within snacks, first aid supplies, bottled water 2 Yokosuka Naval Base 18 2 Kadena Air Base 19 3 14 0 2 0 5 0 Sasebo Naval Base 6 0 Iwakuni Marine Corps Air Station 4 0 15 3 Norfolk Naval Base 17 2 Stennis Space Center 1 50 -kt sustained winds possible within Clean up around house, pick up loose 48 hours items 50 -kt sustained winds anticipated Mayport Naval Station 1 Misawa Naval Base Secure outdoor property including within 24 hours picnic table, barbeque grill I 50 -kt sustained winds anticipated within 12 hours Schools close, fill available containers I-CAUTION 34 -49 kt occurring and are expected to All outdoor activities except in reach 50 kt within 12 h support of urgent military missions III II with water discontinued I-EMERGENCY 50 -kt sustained winds occurring I-RECOVERY 50 -kt sustained winds no longer No outdoor activity authorized except occurring by pre-designated emergency crews STORM WATCH Still a possibility of danger Normal activity resumes 2 h after ALL CLEAR Local recovery operations complete Figure 1. The aftermath of typhoon Songda after hitting Okinawa in 2011. Doubling thresholds improves TC-COR III and IV Peirce’s Scores (1=perfect, 0=no skill), but reduces forecast lead times (~7 hours for TC-COR IV) and misses a few cases. CNMOC DOO suggests adding “Low”, “Medium”, “High” confidence. Current thresholds are “Low” confidence by design. Working under the assumptions that 1) missed TCCORs can have extreme negative consequences (e. g. , loss of life) and 2) false alarms are also costly, a selection scheme for our first-guess TC-COR probability thresholds was specified so that 1) POD ≥ 0. 99 and 2) FAR is minimized; implying the cost-toloss ratio is very small (Wilks 2006; pp 321 -324). The thresholds that we derived are shown below. These thresholds appear at first glance to be quite low, but they are defined to minimize the missed cases (POD ≥ 0. 99). If it is acceptable to miss 50 -kt wind events (i. e. , the cost-to-loss ratio was close to one), these thresholds could be raised to minimize the FAR and improve statistical skill scores (e. g. , Peirce’s Skill Score or Threat Score) discussed in Wilks (2006), but would increase the possibility of very costly misses. 1 Yokota Air Base Obtain flashlight with extra batteries, 72 hours Andersen Air Force Base 11 Patrick Air Force Base TC-COR PARAGRAPH HERE events Atsugi Naval Air Facility Tropical Cyclone Conditions of Readiness Table NEED SHORT Experimental TC-COR Settings 0 Table 2. A catalog of TC-CORs system utilized to take action under a defined set of storm parameters including maximum sustained winds and duration. • • • Figure 2. Objective aid and Operational TC-COR settings for all events with elevated winds. Quartiles shown as thick bars, extremes shown as thin bars. Numbers of cases for COR 1, 2, 3, 4 are 32, 46, 52, 59, respectively. Some of the largest differences are due to base considerations (e. g. , keeping a COR 3 up in preparation for the next TC). TC-COR Aid Timing Uses cumulative 50 -kt wind probabilities Thresholds based Atlantic Hurricane Watches/Warnings Strategic guidance for onset of 50 -kt winds Methods Figure 6. (Above) Percentage of lead times reduced (top) and the average number of hours the lead time was delayed for all the cases (bottom) when the wind probability thresholds associated with the TC-CORs were doubled. All outside activity prohibited declaration. Be alert to possible damage and hazardous conditions on roads, etc. Table 1. A catalog of TC-CORs system utilized to take action under a defined set of storm parameters including maximum sustained winds and duration. Sensitivity Analysis The sample of Atlantic tropical cyclones making landfall along the U. S. mainland from 2004 to 2010 used in Schumacher et al. (2010) was used here. Following their methodology, 64 -kt wind speed probabilities were computed at 12, 24, 48 and 72 hours prior to the arrival of the 64 -kt winds to correspond to the time criteria for TC-COR settings I, III, and IV, respectively. Wind speed probabilities were generated using the 2010 developmental version of the Monte Carlo Wind Speed Probability (MCWSP) product. Locations along the U. S. mainland coast where nearsurface winds met or exceeded 64 knots were determined from tropical cyclone positions and radius of 64 -kt winds (R 64) recorded in the ATCF. The TC-COR aid IV, III, and I times. Box indicates 1 st and 3 rd quartiles, whiskers indicates entire range of cases. Number of cases is 33, 43, 54 for IV, III, II and I, respectively, from twelve military bases in Pacific and Atlantic. TC-COR 4 3 2 1 Threshold Probabilities 5% 6% 8% 12% Forecast Lead 72 H 48 H 24 H 12 H Acknowledgements Poster created by Ms. Laurel Kessler of CIRA References De. Maria, M. , J. A. Knaff, R. Knabb, C. Lauer, C. R. Sampson, and R. T. De. Maria, 2009: A new method for estimating tropical cyclone wind speed probabilities, Wea. Forecasting, 24, 1573 -1591. Sampson, C. R. , and A. J. Schrader, 2000: The Automated Tropical Cyclone Forecasting System (Version 3. 2). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. , 81, 1131 -1240. Schumacher, A. B. , M. De. Maria, J. A. Knaff, C. R. Sampson and D. Brown, 2010: Objective Tropical Cyclone Warning Guidance Using Monte Carlo Wind Speed Probabilities, 29 th Conference on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, 10 -14 May 2010, Tucson, AZ. Wilks, D. S. , 2006: Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences. 2 nd ed. Academic Press, 467 pp.
460a490c50a9d7159b6fa041f45d48da.ppt