456a75f6b32f9e4330c1c3b3fcb69502.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79
 An Introduction to Data Warehousing Anand Deshpande Persistent Systems Pvt. Ltd. http: //www. persistent. co. in IIT DB Class
An Introduction to Data Warehousing Anand Deshpande Persistent Systems Pvt. Ltd. http: //www. persistent. co. in IIT DB Class
 Optimizing the Warehouse for Decision Support IIT DB Class
Optimizing the Warehouse for Decision Support IIT DB Class
 Data -- Heart of the Data Warehouse • • Heart of the data warehouse is the data itself! Single version of the truth Corporate memory Data is organized in a way that represents business -- subject orientation IIT DB Class 3
Data -- Heart of the Data Warehouse • • Heart of the data warehouse is the data itself! Single version of the truth Corporate memory Data is organized in a way that represents business -- subject orientation IIT DB Class 3
 Consider a Retail Sales Example • A retail chain sells products in retail stores. • We want to track the effect of promotions on retail sales. • • Product Table (60, 000 SKUs) Store Table (500 stores) Promotion (3000 promotions per week) Sales (2 Billion) IIT DB Class 4
Consider a Retail Sales Example • A retail chain sells products in retail stores. • We want to track the effect of promotions on retail sales. • • Product Table (60, 000 SKUs) Store Table (500 stores) Promotion (3000 promotions per week) Sales (2 Billion) IIT DB Class 4
 • What is the total dollar sales and the total dollar costs of all candy sold in supermarket stores on Saturdays? SELECT p. category, sum(f. dollar_sales), sum(f. dollar. cost) FROM sales_fact f, product p, time t, store s WHERE f. product_key = p. product_key and f. time_key = t. time_key and f. store_key = s. store_key and p. category = ‘Candy’ and t. day_of_week = ‘Saturday’ and s. floor_plan_type = ‘Super_Market” GROUP BY p. category IIT DB Class 5
• What is the total dollar sales and the total dollar costs of all candy sold in supermarket stores on Saturdays? SELECT p. category, sum(f. dollar_sales), sum(f. dollar. cost) FROM sales_fact f, product p, time t, store s WHERE f. product_key = p. product_key and f. time_key = t. time_key and f. store_key = s. store_key and p. category = ‘Candy’ and t. day_of_week = ‘Saturday’ and s. floor_plan_type = ‘Super_Market” GROUP BY p. category IIT DB Class 5
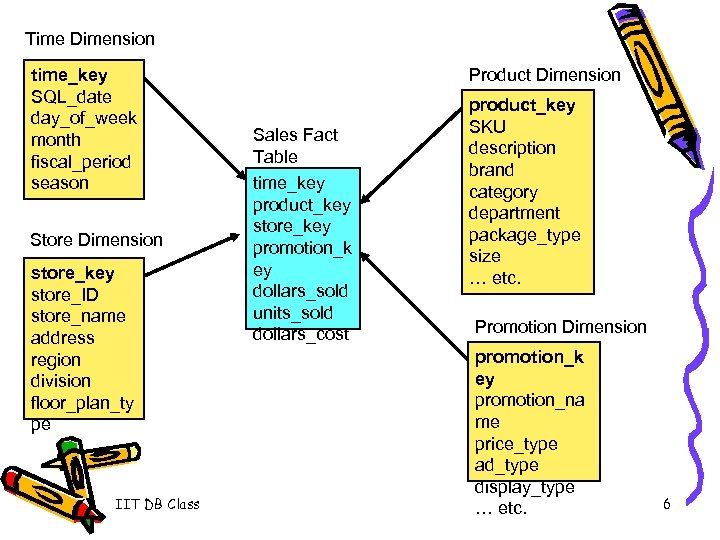 Time Dimension time_key SQL_date day_of_week month fiscal_period season Store Dimension store_key store_ID store_name address region division floor_plan_ty pe IIT DB Class Product Dimension Sales Fact Table time_key product_key store_key promotion_k ey dollars_sold units_sold dollars_cost product_key SKU description brand category department package_type size … etc. Promotion Dimension promotion_k ey promotion_na me price_type ad_type display_type … etc. 6
Time Dimension time_key SQL_date day_of_week month fiscal_period season Store Dimension store_key store_ID store_name address region division floor_plan_ty pe IIT DB Class Product Dimension Sales Fact Table time_key product_key store_key promotion_k ey dollars_sold units_sold dollars_cost product_key SKU description brand category department package_type size … etc. Promotion Dimension promotion_k ey promotion_na me price_type ad_type display_type … etc. 6
 • IIT DB Class SELECT NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 1, NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 2, SUM(AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 3) SUM(AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 4) SUM(AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 5) FROM DIMENSION TABLE 1 DIMENSION TABLE 2 DIMENSION TABLE 3 DIMENSION TABLE 4 FACT TABLE WHERE JOINCONDITION 1 JOINCONDITION 2 AND JOINCONDITION 3 AND JOINCONDITION 4 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 1 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 2 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 3 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 4 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 5 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 6 GROUP BY NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 1 NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 2 ORDER BY NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 1 NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 2 7
• IIT DB Class SELECT NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 1, NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 2, SUM(AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 3) SUM(AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 4) SUM(AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 5) FROM DIMENSION TABLE 1 DIMENSION TABLE 2 DIMENSION TABLE 3 DIMENSION TABLE 4 FACT TABLE WHERE JOINCONDITION 1 JOINCONDITION 2 AND JOINCONDITION 3 AND JOINCONDITION 4 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 1 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 2 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 3 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 4 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 5 AND DIMENSIONCONSTRAINT 6 GROUP BY NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 1 NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 2 ORDER BY NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 1 NON-AGGREGATE FIELDNAME 2 7
 A Real Data Warehouse Query IIT DB Class 8
A Real Data Warehouse Query IIT DB Class 8
 Schema Design • Database organization – – must look like business must be recognizable by business user approachable by business user Must be simple • Schema Types – Star Schema – Fact Constellation Schema – Snowflake schema IIT DB Class 9
Schema Design • Database organization – – must look like business must be recognizable by business user approachable by business user Must be simple • Schema Types – Star Schema – Fact Constellation Schema – Snowflake schema IIT DB Class 9
 Dimension Tables • Dimension tables – – – Define business in terms already familiar to users Wide rows with lots of descriptive text Small tables (about a million rows) Joined to fact table by a foreign key heavily indexed typical dimensions • time periods, geographic region (markets, cities), products, customers, salesperson, etc. IIT DB Class 10
Dimension Tables • Dimension tables – – – Define business in terms already familiar to users Wide rows with lots of descriptive text Small tables (about a million rows) Joined to fact table by a foreign key heavily indexed typical dimensions • time periods, geographic region (markets, cities), products, customers, salesperson, etc. IIT DB Class 10
 Fact Table • Central table – – mostly raw numeric items narrow rows, a few columns at most large number of rows (millions to a billion) Access via dimensions IIT DB Class 11
Fact Table • Central table – – mostly raw numeric items narrow rows, a few columns at most large number of rows (millions to a billion) Access via dimensions IIT DB Class 11
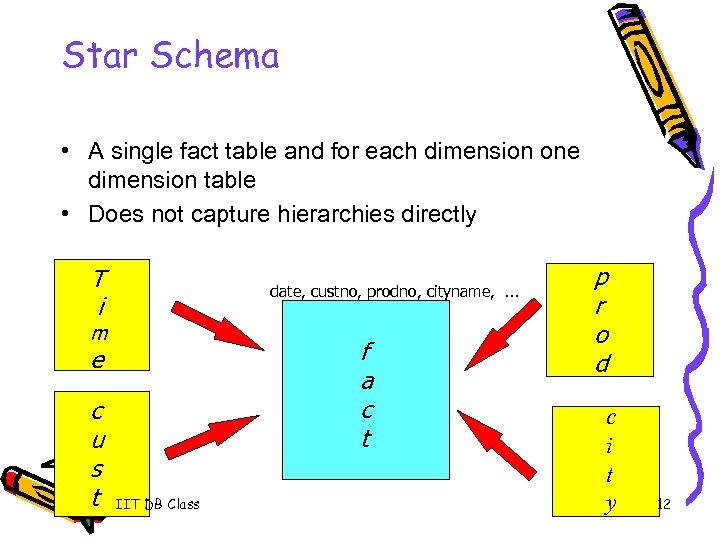 Star Schema • A single fact table and for each dimension one dimension table • Does not capture hierarchies directly T i date, custno, prodno, cityname, . . . m f a c t e c u s t IIT DB Class p r o d c i t y 12
Star Schema • A single fact table and for each dimension one dimension table • Does not capture hierarchies directly T i date, custno, prodno, cityname, . . . m f a c t e c u s t IIT DB Class p r o d c i t y 12
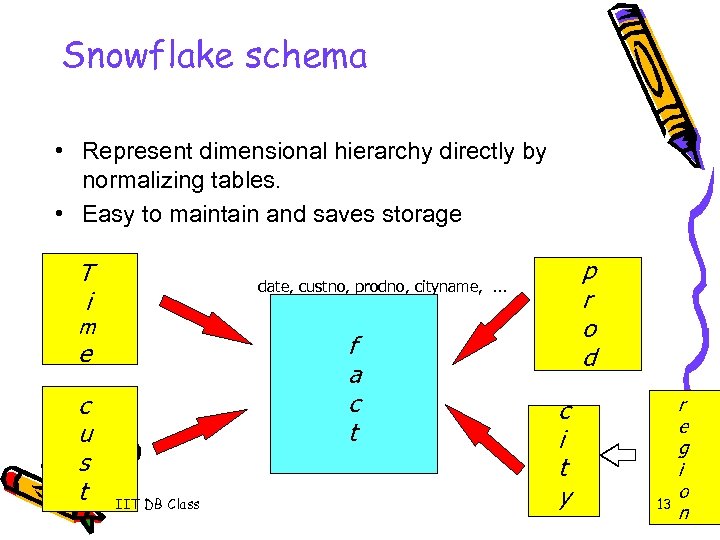 Snowflake schema • Represent dimensional hierarchy directly by normalizing tables. • Easy to maintain and saves storage T i m f a c t e c u s t p r o d date, custno, prodno, cityname, . . . IIT DB Class c i t y 13 r e g i o n
Snowflake schema • Represent dimensional hierarchy directly by normalizing tables. • Easy to maintain and saves storage T i m f a c t e c u s t p r o d date, custno, prodno, cityname, . . . IIT DB Class c i t y 13 r e g i o n
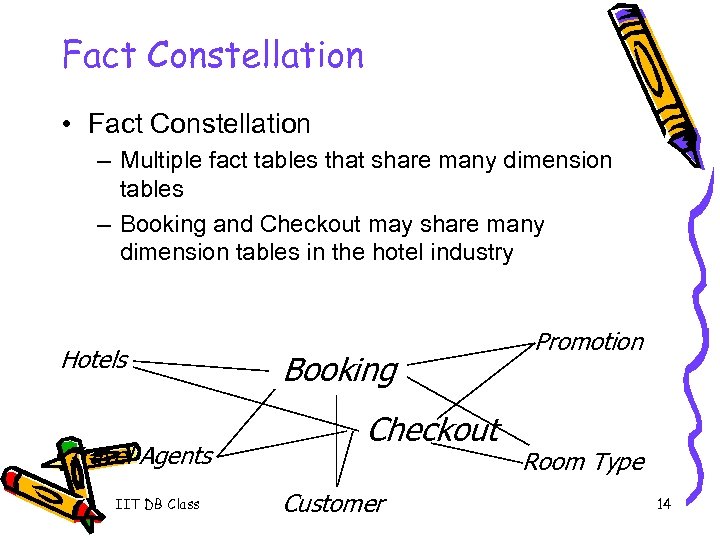 Fact Constellation • Fact Constellation – Multiple fact tables that share many dimension tables – Booking and Checkout may share many dimension tables in the hotel industry Hotels Travel Agents IIT DB Class Booking Checkout Customer Promotion Room Type 14
Fact Constellation • Fact Constellation – Multiple fact tables that share many dimension tables – Booking and Checkout may share many dimension tables in the hotel industry Hotels Travel Agents IIT DB Class Booking Checkout Customer Promotion Room Type 14
 Data Warehouse Structure • Subject Orientation -- customer, product, policy, account etc. . . A subject may be implemented as a set of related tables. E. g. , customer may be five tables IIT DB Class 15
Data Warehouse Structure • Subject Orientation -- customer, product, policy, account etc. . . A subject may be implemented as a set of related tables. E. g. , customer may be five tables IIT DB Class 15
 Data Granularity in Warehouse • Summarized data stored – reduce storage costs – reduce cpu usage – increases performance since smaller number of records to be processed – design around traditional high level reporting needs – tradeoff with volume of data to be stored and detailed usage of data IIT DB Class 16
Data Granularity in Warehouse • Summarized data stored – reduce storage costs – reduce cpu usage – increases performance since smaller number of records to be processed – design around traditional high level reporting needs – tradeoff with volume of data to be stored and detailed usage of data IIT DB Class 16
 Granularity in Warehouse • Can not answer some questions with summarized data – Did Anand call Seshadri last month? Not possible to answer if total duration of calls by Anand over a month is only maintained and individual call details are not. • Detailed data too voluminous IIT DB Class 17
Granularity in Warehouse • Can not answer some questions with summarized data – Did Anand call Seshadri last month? Not possible to answer if total duration of calls by Anand over a month is only maintained and individual call details are not. • Detailed data too voluminous IIT DB Class 17
 Granularity in Warehouse • Tradeoff is to have dual level of granularity – Store summary data on disks • 95% of DSS processing done against this data – Store detail on tapes • 5% of DSS processing against this data IIT DB Class 18
Granularity in Warehouse • Tradeoff is to have dual level of granularity – Store summary data on disks • 95% of DSS processing done against this data – Store detail on tapes • 5% of DSS processing against this data IIT DB Class 18
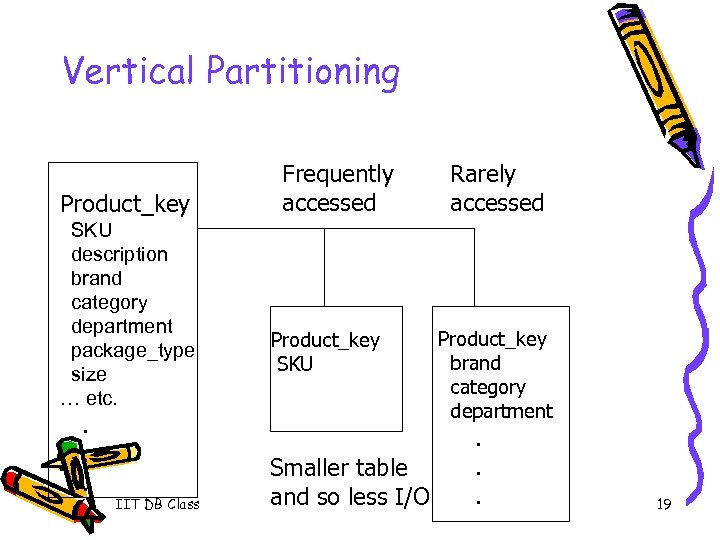 Vertical Partitioning Product_key SKU description brand category department package_type size … etc. . IIT DB Class Frequently accessed Product_key SKU Smaller table and so less I/O Rarely accessed Product_key brand category department . . . 19
Vertical Partitioning Product_key SKU description brand category department package_type size … etc. . IIT DB Class Frequently accessed Product_key SKU Smaller table and so less I/O Rarely accessed Product_key brand category department . . . 19
 Derived Data • Introduction of derived (calculated data) may often help • Have seen this in the context of dual levels of granularity • Can keep auxiliary views and indexes to speed up query processing IIT DB Class 20
Derived Data • Introduction of derived (calculated data) may often help • Have seen this in the context of dual levels of granularity • Can keep auxiliary views and indexes to speed up query processing IIT DB Class 20
 Denormalization • Normalization in a data warehouse may lead to lots of small tables • Can lead to excessive I/O’s since many tables have to be accessed • Denormalization is the answer especially since updates are rare IIT DB Class 21
Denormalization • Normalization in a data warehouse may lead to lots of small tables • Can lead to excessive I/O’s since many tables have to be accessed • Denormalization is the answer especially since updates are rare IIT DB Class 21
 Creating Arrays • Many time each occurrence of a sequence of data is in a different physical location • Beneficial to collect all occurrences together and store as an array in a single row • Makes sense only if there a stable number of occurrences which are accessed together • In a data warehouse, such situations arise naturally due to time based orientation » can create an array by month IIT DB Class 22
Creating Arrays • Many time each occurrence of a sequence of data is in a different physical location • Beneficial to collect all occurrences together and store as an array in a single row • Makes sense only if there a stable number of occurrences which are accessed together • In a data warehouse, such situations arise naturally due to time based orientation » can create an array by month IIT DB Class 22
 Selective Redundancy • Description of an item can be stored redundantly with order table -- most often item description is also accessed with order table • Updates have to be careful IIT DB Class 23
Selective Redundancy • Description of an item can be stored redundantly with order table -- most often item description is also accessed with order table • Updates have to be careful IIT DB Class 23
 Partitioning • Breaking data into several physical units that can be handled separately • Not a question of whether to do it in data warehouses but how to do it • Granularity and partitioning are key to effective implementation of a warehouse IIT DB Class 24
Partitioning • Breaking data into several physical units that can be handled separately • Not a question of whether to do it in data warehouses but how to do it • Granularity and partitioning are key to effective implementation of a warehouse IIT DB Class 24
 Why Partitioning? • Flexibility in managing data • Smaller physical units allow – – – easy restructuring free indexing sequential scans if needed easy reorganization easy recovery easy monitoring IIT DB Class 25
Why Partitioning? • Flexibility in managing data • Smaller physical units allow – – – easy restructuring free indexing sequential scans if needed easy reorganization easy recovery easy monitoring IIT DB Class 25
 Criterion for Partitioning • Typically partitioned by – – – date line of business geography organizational unit any combination of above IIT DB Class 26
Criterion for Partitioning • Typically partitioned by – – – date line of business geography organizational unit any combination of above IIT DB Class 26
 Where to Partition? • Application level or DBMS level • Makes sense to partition at application level – Allows different definition for each year • Important since warehouse spans many years and as business evolves definition changes – Allows data to be moved between processing complexes easily IIT DB Class 27
Where to Partition? • Application level or DBMS level • Makes sense to partition at application level – Allows different definition for each year • Important since warehouse spans many years and as business evolves definition changes – Allows data to be moved between processing complexes easily IIT DB Class 27
 Where to Partition? • Application level or DBMS level • Makes sense to partition at application level – Allows different definition for each year • Important since warehouse spans many years and as business evolves definition changes – Allows data to be moved between processing complexes easily IIT DB Class 28
Where to Partition? • Application level or DBMS level • Makes sense to partition at application level – Allows different definition for each year • Important since warehouse spans many years and as business evolves definition changes – Allows data to be moved between processing complexes easily IIT DB Class 28
 Indexing Techniques • Bitmap index: – A collection of bitmaps -- one for each distinct value of the column – Each bitmap has N bits where N is the number of rows in the table – A bit corresponding to a value v for a row r is set if and only if r has the value for the indexed attribute IIT DB Class 29
Indexing Techniques • Bitmap index: – A collection of bitmaps -- one for each distinct value of the column – Each bitmap has N bits where N is the number of rows in the table – A bit corresponding to a value v for a row r is set if and only if r has the value for the indexed attribute IIT DB Class 29
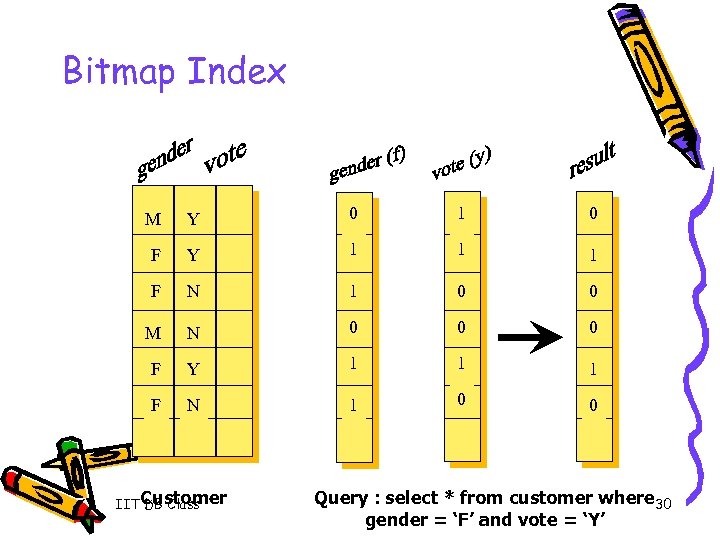 Bitmap Index M Y 0 1 0 F Y 1 1 1 F N 1 0 0 M N 0 0 0 F Y 1 1 1 F N 1 0 0 IITCustomer DB Class Query : select * from customer where 30 gender = ‘F’ and vote = ‘Y’
Bitmap Index M Y 0 1 0 F Y 1 1 1 F N 1 0 0 M N 0 0 0 F Y 1 1 1 F N 1 0 0 IITCustomer DB Class Query : select * from customer where 30 gender = ‘F’ and vote = ‘Y’
 Join Indexes • Pre-computed joins • A join index between a fact table and a dimension table correlates a dimension tuple with the fact tuples that have the same value on the common dimensional attribute – e. g. , a join index on city dimension of calls fact table – correlates for each city the calls (in the calls table) that originated from that city IIT DB Class 31
Join Indexes • Pre-computed joins • A join index between a fact table and a dimension table correlates a dimension tuple with the fact tuples that have the same value on the common dimensional attribute – e. g. , a join index on city dimension of calls fact table – correlates for each city the calls (in the calls table) that originated from that city IIT DB Class 31
 Join Indexes • Join indexes can also span multiple dimension tables – e. g. , a join index on city and time dimension of calls fact table IIT DB Class 32
Join Indexes • Join indexes can also span multiple dimension tables – e. g. , a join index on city and time dimension of calls fact table IIT DB Class 32
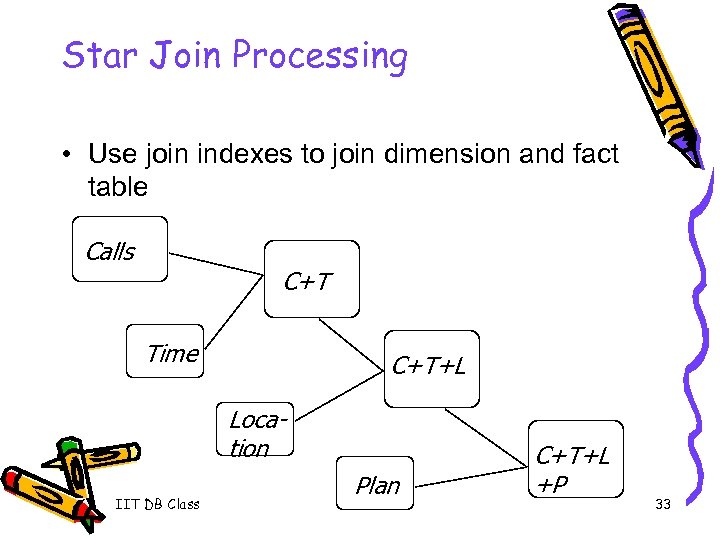 Star Join Processing • Use join indexes to join dimension and fact table Calls C+T Time C+T+L Location IIT DB Class Plan C+T+L +P 33
Star Join Processing • Use join indexes to join dimension and fact table Calls C+T Time C+T+L Location IIT DB Class Plan C+T+L +P 33
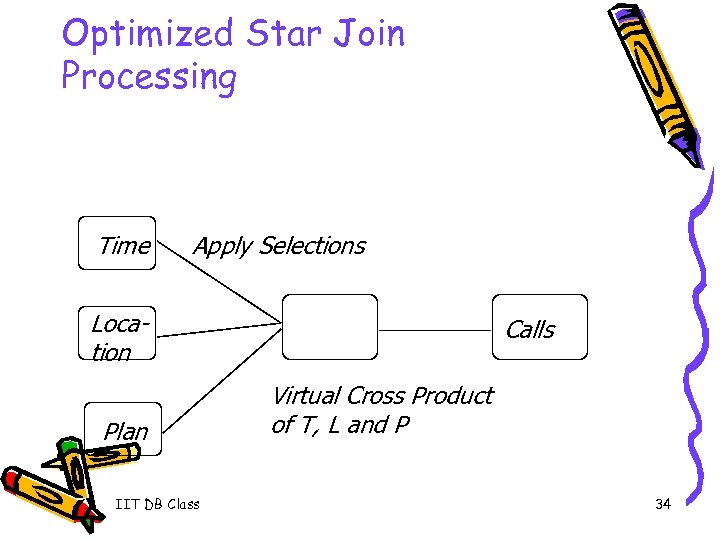 Optimized Star Join Processing Time Apply Selections Location Plan IIT DB Class Calls Virtual Cross Product of T, L and P 34
Optimized Star Join Processing Time Apply Selections Location Plan IIT DB Class Calls Virtual Cross Product of T, L and P 34
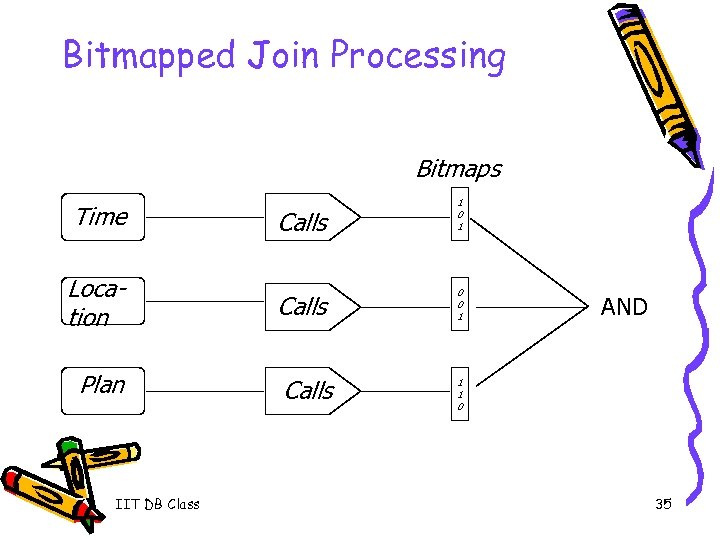 Bitmapped Join Processing Bitmaps Calls 1 0 1 Location Calls 0 0 1 Plan Calls Time IIT DB Class AND 1 1 0 35
Bitmapped Join Processing Bitmaps Calls 1 0 1 Location Calls 0 0 1 Plan Calls Time IIT DB Class AND 1 1 0 35
 Intelligent Scan • Piggyback multiple scans of a relation (Redbrick) – piggybacking also done if second scan starts a little while after the first scan IIT DB Class 36
Intelligent Scan • Piggyback multiple scans of a relation (Redbrick) – piggybacking also done if second scan starts a little while after the first scan IIT DB Class 36
 Parallel Query Processing • Three forms of parallelism – Independent – Pipelined – Partitioned and “partition and replicate” • Deterrents to parallelism – startup – communication IIT DB Class 37
Parallel Query Processing • Three forms of parallelism – Independent – Pipelined – Partitioned and “partition and replicate” • Deterrents to parallelism – startup – communication IIT DB Class 37
 Parallel Query Processing • Partitioned Data – Parallel scans – Yields I/O parallelism • Parallel algorithms for relational operators – Joins, Aggregates, Sort • Parallel Utilities – Load, Archive, Update, Parse, Checkpoint, Recovery • Parallel Query Optimization IIT DB Class 38
Parallel Query Processing • Partitioned Data – Parallel scans – Yields I/O parallelism • Parallel algorithms for relational operators – Joins, Aggregates, Sort • Parallel Utilities – Load, Archive, Update, Parse, Checkpoint, Recovery • Parallel Query Optimization IIT DB Class 38
 Pre-computed Aggregates • Keep aggregated data for efficiency (precomputed queries) • Questions – Which aggregates to compute? – How to update aggregates? – How to use pre-computed aggregates in queries? IIT DB Class 39
Pre-computed Aggregates • Keep aggregated data for efficiency (precomputed queries) • Questions – Which aggregates to compute? – How to update aggregates? – How to use pre-computed aggregates in queries? IIT DB Class 39
 Pre-computed Aggregates • Aggregated table can be maintained by the – warehouse server – middle tier – client applications • Pre-computed aggregates -- special case of materialized views -- same questions and issues remain IIT DB Class 40
Pre-computed Aggregates • Aggregated table can be maintained by the – warehouse server – middle tier – client applications • Pre-computed aggregates -- special case of materialized views -- same questions and issues remain IIT DB Class 40
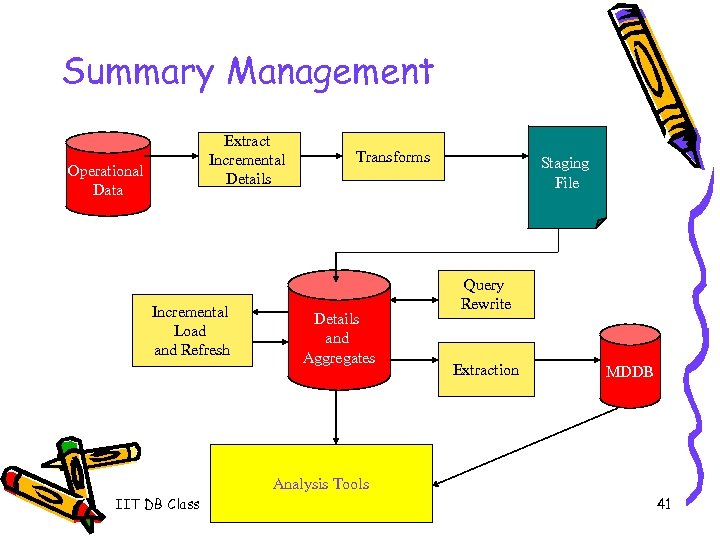 Summary Management Extract Incremental Details Operational Data Incremental Load and Refresh Transforms Details and Aggregates Staging File Query Rewrite Extraction MDDB Analysis Tools IIT DB Class 41
Summary Management Extract Incremental Details Operational Data Incremental Load and Refresh Transforms Details and Aggregates Staging File Query Rewrite Extraction MDDB Analysis Tools IIT DB Class 41
 SQL Extensions • Extended family of aggregate functions – – rank (top 10 customers) percentile (top 30% of customers) median, mode Object Relational Systems allow addition of new aggregate functions IIT DB Class 42
SQL Extensions • Extended family of aggregate functions – – rank (top 10 customers) percentile (top 30% of customers) median, mode Object Relational Systems allow addition of new aggregate functions IIT DB Class 42
 SQL Extensions • Reporting features – running total, cumulative totals • Cube operator – group by on all subsets of a set of attributes (month, city) – redundant scan and sorting of data can be avoided IIT DB Class 43
SQL Extensions • Reporting features – running total, cumulative totals • Cube operator – group by on all subsets of a set of attributes (month, city) – redundant scan and sorting of data can be avoided IIT DB Class 43
 Server Scalability • Scalability is the #1 IT requirement for Data Warehousing • Hardware Platform options – SMP – Clusters (shared disk) – MPP • Loosely coupled (shared nothing) • Hybrid IIT DB Class 44
Server Scalability • Scalability is the #1 IT requirement for Data Warehousing • Hardware Platform options – SMP – Clusters (shared disk) – MPP • Loosely coupled (shared nothing) • Hybrid IIT DB Class 44
 SMP Characteristics • SMP -- Symmetric multi processing -- shared everything • Multiple CPUs share same memory • Workload is balanced across CPUs by OS • Scalability is limited to bandwidth of internal bus and OS architecture • Not tolerant to failure in processing node • Architecture is mostly invisible to applications IIT DB Class 45
SMP Characteristics • SMP -- Symmetric multi processing -- shared everything • Multiple CPUs share same memory • Workload is balanced across CPUs by OS • Scalability is limited to bandwidth of internal bus and OS architecture • Not tolerant to failure in processing node • Architecture is mostly invisible to applications IIT DB Class 45
 SMP Benefits • Lower entry point -- can start with SMP • Mature technology IIT DB Class 46
SMP Benefits • Lower entry point -- can start with SMP • Mature technology IIT DB Class 46
 MPP Characteristics • Each node owns a portion of the database • Nodes are connected via an interconnection network • Each node can be a single CPU or SMP • Load balancing done by application • High scalability due to local processing isolation IIT DB Class 47
MPP Characteristics • Each node owns a portion of the database • Nodes are connected via an interconnection network • Each node can be a single CPU or SMP • Load balancing done by application • High scalability due to local processing isolation IIT DB Class 47
 MPP benefits • High availability • High scalability IIT DB Class 48
MPP benefits • High availability • High scalability IIT DB Class 48
 Viewing the Data with OLAP Making Decision Support Possible IIT DB Class
Viewing the Data with OLAP Making Decision Support Possible IIT DB Class
 Limitations of SQL “A Freshman in Business needs a Ph. D. in SQL” -- Ralph Kimball IIT DB Class 50
Limitations of SQL “A Freshman in Business needs a Ph. D. in SQL” -- Ralph Kimball IIT DB Class 50
 Typical OLAP Queries • Write a multi-table join to compare sales for each product line YTD this year vs. last year. • Repeat the above process to find the top 5 product contributors to margin. • Repeat the above process to find the sales of a product line to new vs. existing customers. • Repeat the above process to find the customers that have had negative sales growth. IIT DB Class 51
Typical OLAP Queries • Write a multi-table join to compare sales for each product line YTD this year vs. last year. • Repeat the above process to find the top 5 product contributors to margin. • Repeat the above process to find the sales of a product line to new vs. existing customers. • Repeat the above process to find the customers that have had negative sales growth. IIT DB Class 51
 What Is OLAP? • • • Online Analytical Processing - coined by EF Codd in 1994 paper contracted by Arbor Software* Generally synonymous with earlier terms such as Decisions Support, Business Intelligence, Executive Information System OLAP = Multidimensional Database MOLAP: Multidimensional OLAP (Arbor Essbase, Oracle Express) ROLAP: Relational OLAP (Informix Meta. Cube, Microstrategy DSS Agent) * Reference: http: //www. arborsoft. com/essbase/wht_ppr/codd. TOC. html IIT DB Class 52
What Is OLAP? • • • Online Analytical Processing - coined by EF Codd in 1994 paper contracted by Arbor Software* Generally synonymous with earlier terms such as Decisions Support, Business Intelligence, Executive Information System OLAP = Multidimensional Database MOLAP: Multidimensional OLAP (Arbor Essbase, Oracle Express) ROLAP: Relational OLAP (Informix Meta. Cube, Microstrategy DSS Agent) * Reference: http: //www. arborsoft. com/essbase/wht_ppr/codd. TOC. html IIT DB Class 52
 Strengths of OLAP • It is a powerful visualization paradigm • It provides fast, interactive response times • It is good for analyzing time series • It can be useful to find some clusters and outliners • Many vendors offer OLAP tools IIT DB Class 53
Strengths of OLAP • It is a powerful visualization paradigm • It provides fast, interactive response times • It is good for analyzing time series • It can be useful to find some clusters and outliners • Many vendors offer OLAP tools IIT DB Class 53
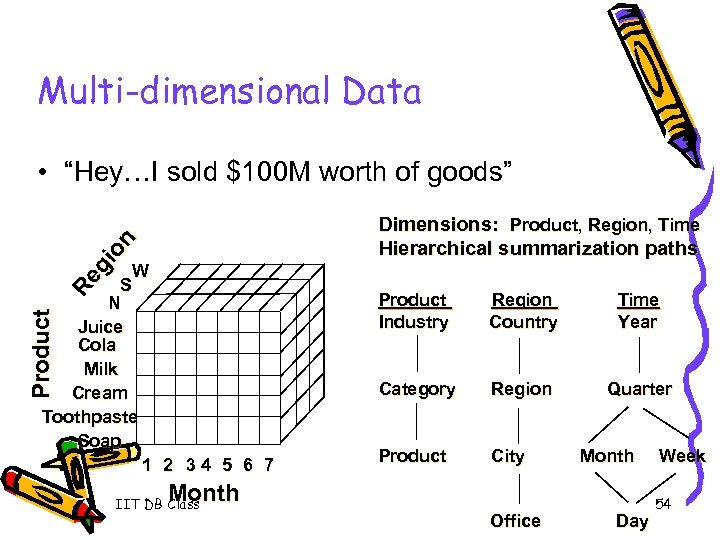 Multi-dimensional Data • “Hey…I sold $100 M worth of goods” Re gi on Dimensions: Product, Region, Time Hierarchical summarization paths Product W S N Juice Cola Milk Cream Toothpaste Soap 1 2 34 5 6 7 Product Industry Region Country Time Year Category Region Quarter Product City Month IIT DB Class Office Day Week 54
Multi-dimensional Data • “Hey…I sold $100 M worth of goods” Re gi on Dimensions: Product, Region, Time Hierarchical summarization paths Product W S N Juice Cola Milk Cream Toothpaste Soap 1 2 34 5 6 7 Product Industry Region Country Time Year Category Region Quarter Product City Month IIT DB Class Office Day Week 54
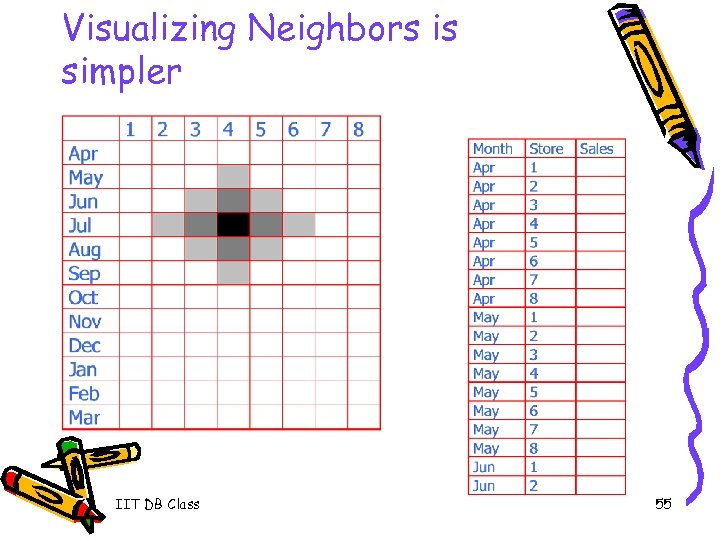 Visualizing Neighbors is simpler IIT DB Class 55
Visualizing Neighbors is simpler IIT DB Class 55
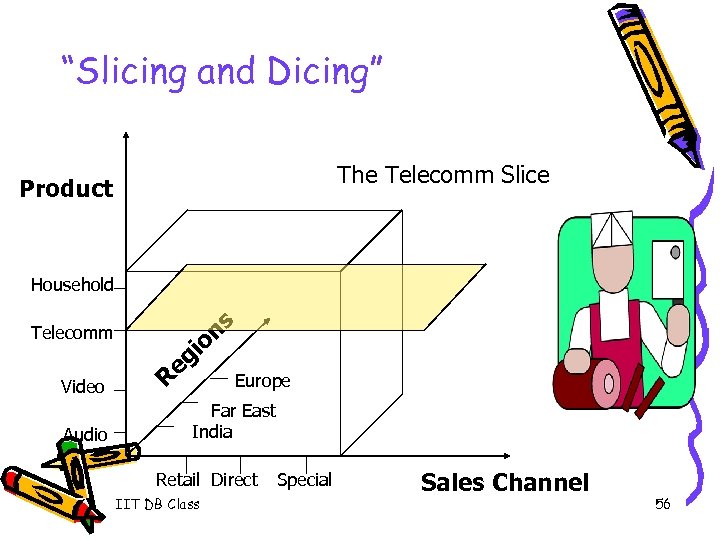 “Slicing and Dicing” The Telecomm Slice Product Household Telecomm Video Audio R gi e ns o Europe Far East India Retail Direct IIT DB Class Special Sales Channel 56
“Slicing and Dicing” The Telecomm Slice Product Household Telecomm Video Audio R gi e ns o Europe Far East India Retail Direct IIT DB Class Special Sales Channel 56
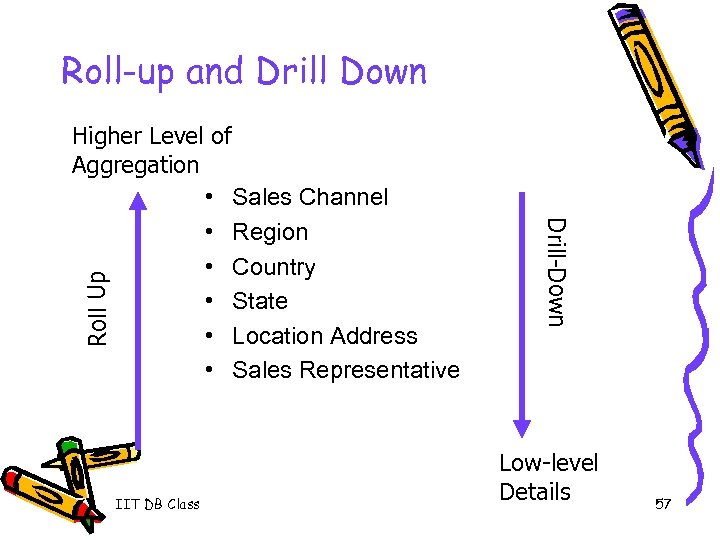 Roll-up and Drill Down Roll Up IIT DB Class Drill-Down Higher Level of Aggregation • Sales Channel • Region • Country • State • Location Address • Sales Representative Low-level Details 57
Roll-up and Drill Down Roll Up IIT DB Class Drill-Down Higher Level of Aggregation • Sales Channel • Region • Country • State • Location Address • Sales Representative Low-level Details 57
 Nature of OLAP Analysis • Aggregation -- (total sales, percentto-total) • Comparison -- Budget vs. Expenses • Ranking -- Top 10, quartile analysis • Access to detailed and aggregate data • Complex criteria specification • Visualization IIT DB Class 58
Nature of OLAP Analysis • Aggregation -- (total sales, percentto-total) • Comparison -- Budget vs. Expenses • Ranking -- Top 10, quartile analysis • Access to detailed and aggregate data • Complex criteria specification • Visualization IIT DB Class 58
 Organizationally Structured Data • Different Departments look at the same detailed data in different ways. Without the detailed, organizationally structured data as a foundation, there is no reconcilability of data marketing sales finance IIT DB Class manufacturing 59
Organizationally Structured Data • Different Departments look at the same detailed data in different ways. Without the detailed, organizationally structured data as a foundation, there is no reconcilability of data marketing sales finance IIT DB Class manufacturing 59
 Multidimensional Spreadsheets • Analysts need spreadsheets that support – – – pivot tables (cross-tabs) drill-down and roll-up slice and dice sort selections derived attributes • Popular in retail domain IIT DB Class 60
Multidimensional Spreadsheets • Analysts need spreadsheets that support – – – pivot tables (cross-tabs) drill-down and roll-up slice and dice sort selections derived attributes • Popular in retail domain IIT DB Class 60
 SQL Extensions • Front-end tools require – Extended Family of Aggregate Functions • rank, median, mode – Reporting Features • running totals, cumulative totals – Results of multiple group by • total sales by month and total sales by product – Data Cube IIT DB Class 61
SQL Extensions • Front-end tools require – Extended Family of Aggregate Functions • rank, median, mode – Reporting Features • running totals, cumulative totals – Results of multiple group by • total sales by month and total sales by product – Data Cube IIT DB Class 61
 Red Brick Formation™ Extraction, Transformation, and Data Loading IIT DB Class
Red Brick Formation™ Extraction, Transformation, and Data Loading IIT DB Class
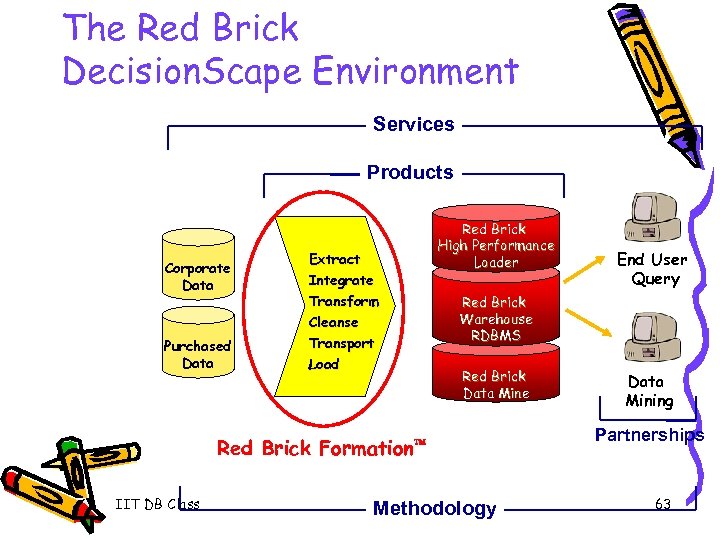 The Red Brick Decision. Scape Environment Services Products Corporate Data Purchased Data Extract Integrate Transform Cleanse Transport Load Red Brick High Performance Loader Red Brick Warehouse RDBMS Red Brick Data Mine Red Brick Formation IIT DB Class End User Query Methodology Data Mining Partnerships 63
The Red Brick Decision. Scape Environment Services Products Corporate Data Purchased Data Extract Integrate Transform Cleanse Transport Load Red Brick High Performance Loader Red Brick Warehouse RDBMS Red Brick Data Mine Red Brick Formation IIT DB Class End User Query Methodology Data Mining Partnerships 63
 Loading the Data Warehouse • Data extraction Data transformation Data loading is… – 40% of total cost – 80% of total time and effort IIT DB Class 64
Loading the Data Warehouse • Data extraction Data transformation Data loading is… – 40% of total cost – 80% of total time and effort IIT DB Class 64
 It’s All About Data Transformation • Extensive Data Manipulation: – – – – Integrating data from dissimilar sources Cleansing source data Creating and storing aggregates & summaries Deriving new data Modifying existing data Adapting to change in the business Capturing and storing metadata (documentation) IIT DB Class 65
It’s All About Data Transformation • Extensive Data Manipulation: – – – – Integrating data from dissimilar sources Cleansing source data Creating and storing aggregates & summaries Deriving new data Modifying existing data Adapting to change in the business Capturing and storing metadata (documentation) IIT DB Class 65
 Traditional “Solutions” • What are they? – 3 GL (COBOL, BASIC, PL 1, C, etc) – 4 GL (SAS, FOCUS, EASYTRIEVE, etc) • Why use them? – Availability of programming staff – Known technology – “I can do it better” attitude of in-house staff • Why you shouldn’t use them: – Little to no metadata – Expensive to develop and maintain in an iterative development environment • The Better Choice … A Data Extraction/Transformation Tool IIT DB Class 66
Traditional “Solutions” • What are they? – 3 GL (COBOL, BASIC, PL 1, C, etc) – 4 GL (SAS, FOCUS, EASYTRIEVE, etc) • Why use them? – Availability of programming staff – Known technology – “I can do it better” attitude of in-house staff • Why you shouldn’t use them: – Little to no metadata – Expensive to develop and maintain in an iterative development environment • The Better Choice … A Data Extraction/Transformation Tool IIT DB Class 66
 Red Brick Formation: A Better Choice • Model-driven transformation results in: • Development productivity: – 2 x more productive than hand-coding. – Less experience required to create jobs. • Maintenance productivity: – 8 -10 x more productive than hand-coding. – Extensive code re-use – Self-documenting at every step. IIT DB Class 67
Red Brick Formation: A Better Choice • Model-driven transformation results in: • Development productivity: – 2 x more productive than hand-coding. – Less experience required to create jobs. • Maintenance productivity: – 8 -10 x more productive than hand-coding. – Extensive code re-use – Self-documenting at every step. IIT DB Class 67
 Red Brick Formation Key Product Highlights • Flexible and Easy to Use – Visual data flow diagramming with optimized, pre-built operators • Scalability & Performance – – Generates standard C++ code Runs on Windows NT and UNIX Single pass handles multiple sources and targets Intelligent parallelization and synchronization • Extensibility & ROI – 3 rd-party integration – Productive use of people resource • Added Bonus – Integration with Red Brick Warehouse IIT DB Class 68
Red Brick Formation Key Product Highlights • Flexible and Easy to Use – Visual data flow diagramming with optimized, pre-built operators • Scalability & Performance – – Generates standard C++ code Runs on Windows NT and UNIX Single pass handles multiple sources and targets Intelligent parallelization and synchronization • Extensibility & ROI – 3 rd-party integration – Productive use of people resource • Added Bonus – Integration with Red Brick Warehouse IIT DB Class 68
 Red Brick Formation Key Product Features/Benefits • Visual, Process-Oriented Model • for Designing & Maintaining Jobs • Extensive Pre-built, Optimized Operators & Functions • • Single Pass Processing of • Multiple, Heterogeneous Sources & Targets • Scalable Client/Server Architecture IIT DB Class • Formation’s unique coding of transformation rules via Visual Snippets -- makes development & maintenance easy Job performance is enhanced and job development more standardized by utilizing pre-built operators and functions Single pass processing means that less steps and less I/O overhead leading to more efficient processing of data Scalable architecture means jobs designed for pilot or prototype will also work within “assigned windows” to process production volume of data 69
Red Brick Formation Key Product Features/Benefits • Visual, Process-Oriented Model • for Designing & Maintaining Jobs • Extensive Pre-built, Optimized Operators & Functions • • Single Pass Processing of • Multiple, Heterogeneous Sources & Targets • Scalable Client/Server Architecture IIT DB Class • Formation’s unique coding of transformation rules via Visual Snippets -- makes development & maintenance easy Job performance is enhanced and job development more standardized by utilizing pre-built operators and functions Single pass processing means that less steps and less I/O overhead leading to more efficient processing of data Scalable architecture means jobs designed for pilot or prototype will also work within “assigned windows” to process production volume of data 69
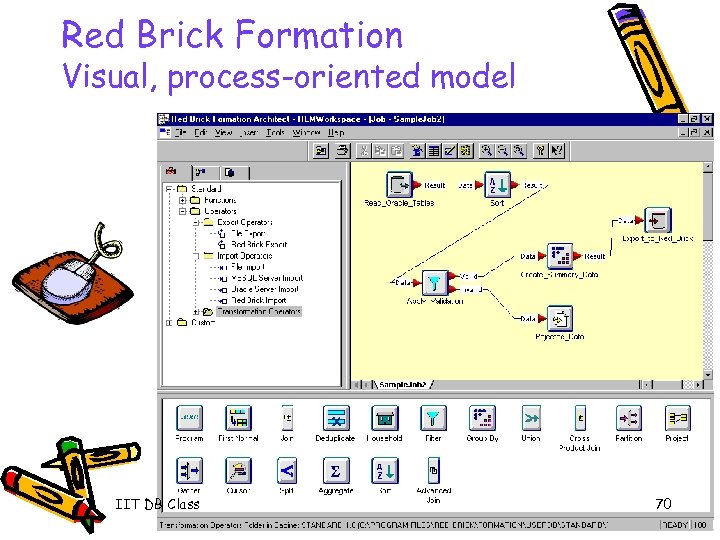 Red Brick Formation Visual, process-oriented model IIT DB Class 70
Red Brick Formation Visual, process-oriented model IIT DB Class 70
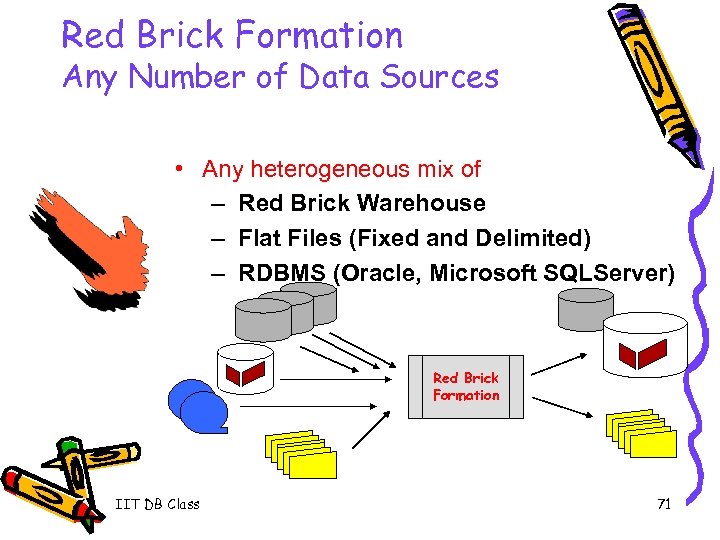 Red Brick Formation Any Number of Data Sources • Any heterogeneous mix of – Red Brick Warehouse – Flat Files (Fixed and Delimited) – RDBMS (Oracle, Microsoft SQLServer) Red Brick Formation IIT DB Class 71
Red Brick Formation Any Number of Data Sources • Any heterogeneous mix of – Red Brick Warehouse – Flat Files (Fixed and Delimited) – RDBMS (Oracle, Microsoft SQLServer) Red Brick Formation IIT DB Class 71
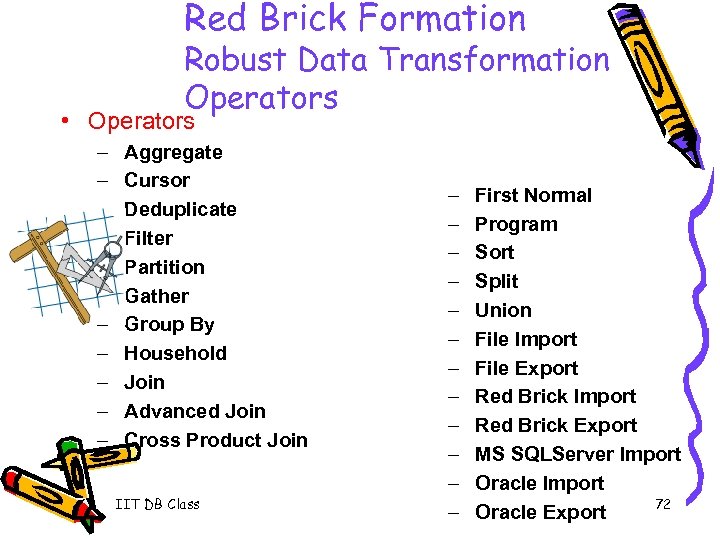 Red Brick Formation Robust Data Transformation Operators • Operators – – – Aggregate Cursor Deduplicate Filter Partition Gather Group By Household Join Advanced Join Cross Product Join IIT DB Class – – – First Normal Program Sort Split Union File Import File Export Red Brick Import Red Brick Export MS SQLServer Import Oracle Import 72 Oracle Export
Red Brick Formation Robust Data Transformation Operators • Operators – – – Aggregate Cursor Deduplicate Filter Partition Gather Group By Household Join Advanced Join Cross Product Join IIT DB Class – – – First Normal Program Sort Split Union File Import File Export Red Brick Import Red Brick Export MS SQLServer Import Oracle Import 72 Oracle Export
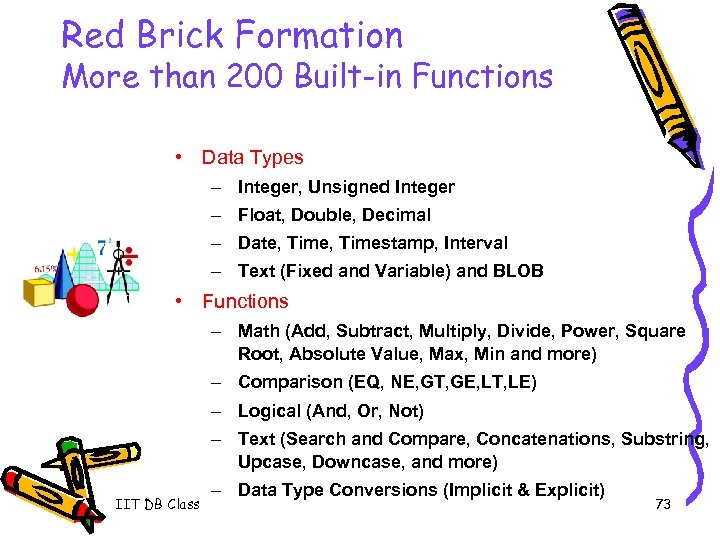 Red Brick Formation More than 200 Built-in Functions • Data Types – Integer, Unsigned Integer – Float, Double, Decimal – Date, Timestamp, Interval – Text (Fixed and Variable) and BLOB • Functions – Math (Add, Subtract, Multiply, Divide, Power, Square Root, Absolute Value, Max, Min and more) – Comparison (EQ, NE, GT, GE, LT, LE) – Logical (And, Or, Not) – Text (Search and Compare, Concatenations, Substring, Upcase, Downcase, and more) IIT DB Class – Data Type Conversions (Implicit & Explicit) 73
Red Brick Formation More than 200 Built-in Functions • Data Types – Integer, Unsigned Integer – Float, Double, Decimal – Date, Timestamp, Interval – Text (Fixed and Variable) and BLOB • Functions – Math (Add, Subtract, Multiply, Divide, Power, Square Root, Absolute Value, Max, Min and more) – Comparison (EQ, NE, GT, GE, LT, LE) – Logical (And, Or, Not) – Text (Search and Compare, Concatenations, Substring, Upcase, Downcase, and more) IIT DB Class – Data Type Conversions (Implicit & Explicit) 73
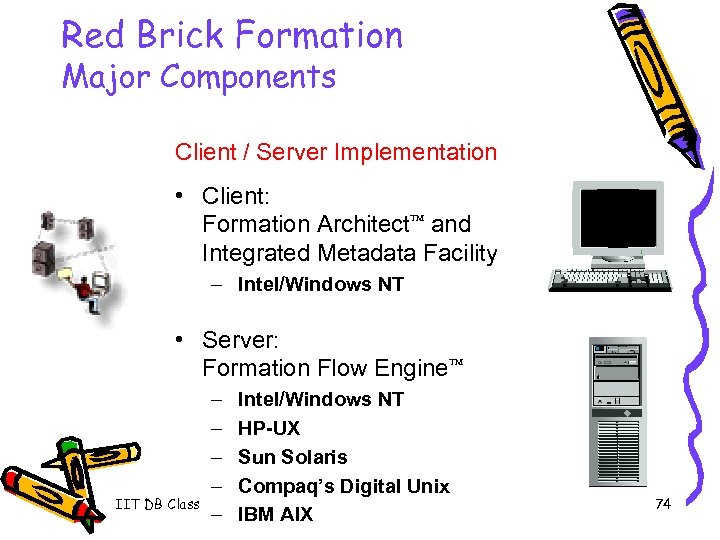 Red Brick Formation Major Components Client / Server Implementation • Client: Formation Architect and Integrated Metadata Facility – Intel/Windows NT • Server: Formation Flow Engine IIT DB Class – – – Intel/Windows NT HP-UX Sun Solaris Compaq’s Digital Unix IBM AIX 74
Red Brick Formation Major Components Client / Server Implementation • Client: Formation Architect and Integrated Metadata Facility – Intel/Windows NT • Server: Formation Flow Engine IIT DB Class – – – Intel/Windows NT HP-UX Sun Solaris Compaq’s Digital Unix IBM AIX 74
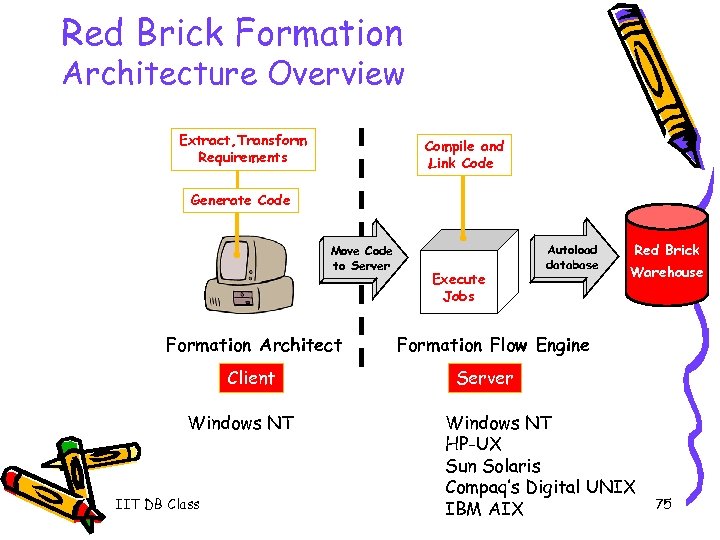 Red Brick Formation Architecture Overview Extract, Transform Requirements Compile and Link Code Generate Code Move Code to Server Formation Architect Client Windows NT IIT DB Class Execute Jobs Autoload database Red Brick Warehouse Formation Flow Engine Server Windows NT HP-UX Sun Solaris Compaq’s Digital UNIX IBM AIX 75
Red Brick Formation Architecture Overview Extract, Transform Requirements Compile and Link Code Generate Code Move Code to Server Formation Architect Client Windows NT IIT DB Class Execute Jobs Autoload database Red Brick Warehouse Formation Flow Engine Server Windows NT HP-UX Sun Solaris Compaq’s Digital UNIX IBM AIX 75
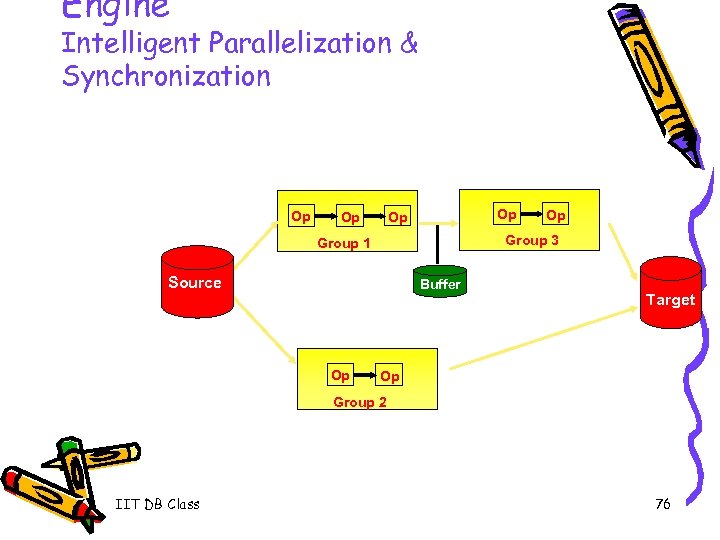 Engine Intelligent Parallelization & Synchronization Op Op Group 3 Group 1 Source Buffer Op Op Target Op Group 2 IIT DB Class 76
Engine Intelligent Parallelization & Synchronization Op Op Group 3 Group 1 Source Buffer Op Op Target Op Group 2 IIT DB Class 76
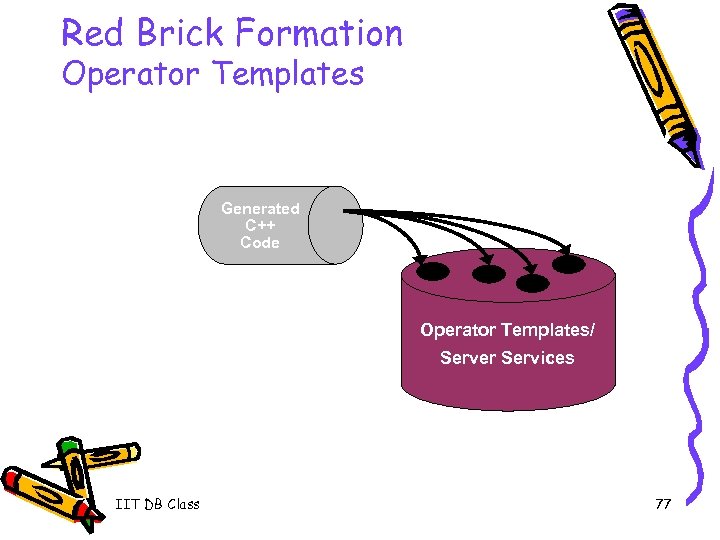 Red Brick Formation Operator Templates Generated C++ Code Operator Templates/ Server Services IIT DB Class 77
Red Brick Formation Operator Templates Generated C++ Code Operator Templates/ Server Services IIT DB Class 77
 Red Brick Formation Demonstration The Problem ? • An input file contains last night’s sales orders. • Want to select items ordered that were sold at list price, not discounted. The Solution ? • Red Brick Formation IIT DB Class 78
Red Brick Formation Demonstration The Problem ? • An input file contains last night’s sales orders. • Want to select items ordered that were sold at list price, not discounted. The Solution ? • Red Brick Formation IIT DB Class 78
 Red Brick Formation Summary of Benefits Red Brick Formation automates the process of data warehouse generation and maintenance. Designed for: • Simplicity & Flexibility • Scalability & Performance • Changing as your business changes IIT DB Class 79
Red Brick Formation Summary of Benefits Red Brick Formation automates the process of data warehouse generation and maintenance. Designed for: • Simplicity & Flexibility • Scalability & Performance • Changing as your business changes IIT DB Class 79


