e0f0f51c420b30029de0aa976b34ba70.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

An Introduction to Cards Business - A Complex Business of Many Moving Parts Pradeep Pant Cards Business Director Citibank N. A. , Taiwan March 22, 2005

Note. The data used in this presentation is indicative to explain the concepts of Card Business and may not be accurate.

“As regulation falls away & competition intensifies, management talent & insight. . . will become critical success factors. ” - The Mc. Kinsey Quarterly, 1997

What is this session about? • • Cards market in Asia Pacific Market Scenario in Taiwan market Citibank Cards business What is Cards business? – P&L Dynamics of Cards Business? • What are the Key Functions in Cards Business? – What about kind of skills & people needed in this business? • A Few Case Studies
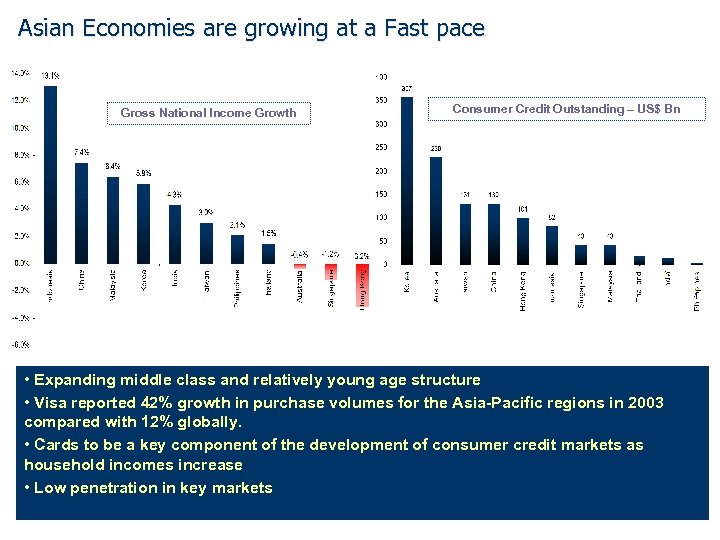
Asian Economies are growing at a Fast pace Gross National Income Growth Consumer Credit Outstanding – US$ Bn • Expanding middle class and relatively young age structure • Visa reported 42% growth in purchase volumes for the Asia-Pacific regions in 2003 compared with 12% globally. • Cards to be a key component of the development of consumer credit markets as household incomes increase • Low penetration in key markets
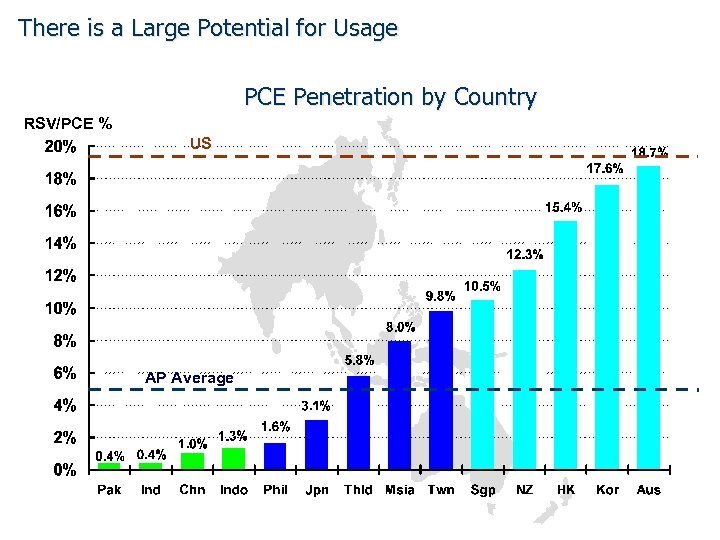
There is a Large Potential for Usage PCE Penetration by Country RSV/PCE % US AP Average
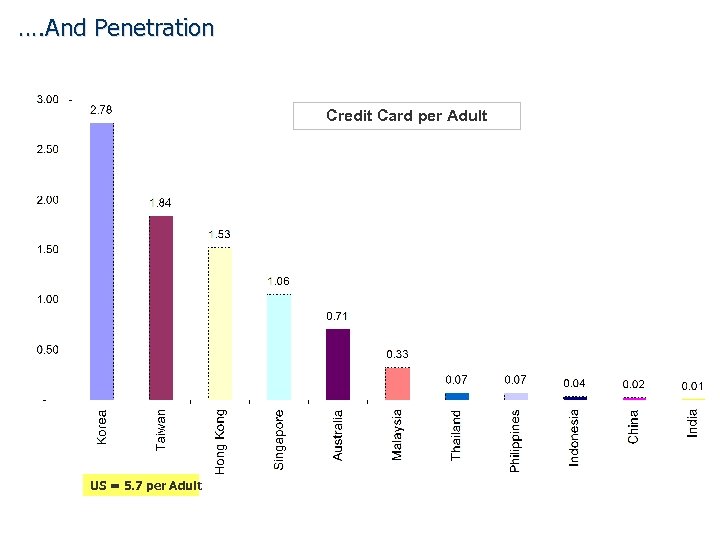
…. And Penetration Credit Card per Adult US = 5. 7 per Adult
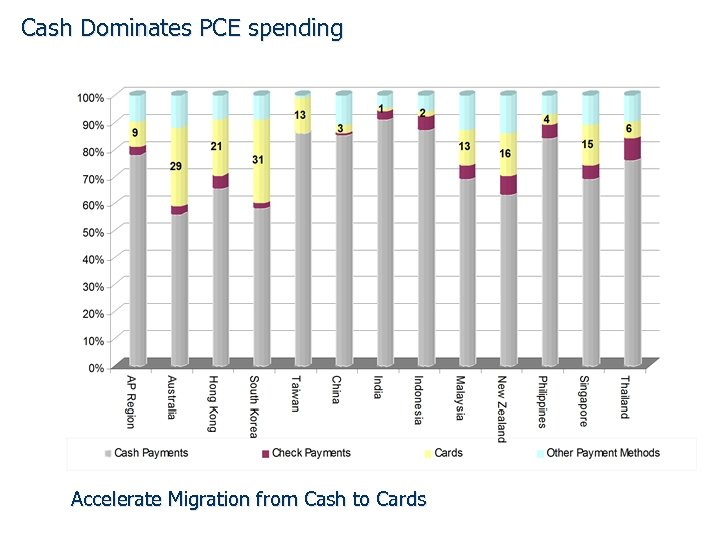
Cash Dominates PCE spending Accelerate Migration from Cash to Cards
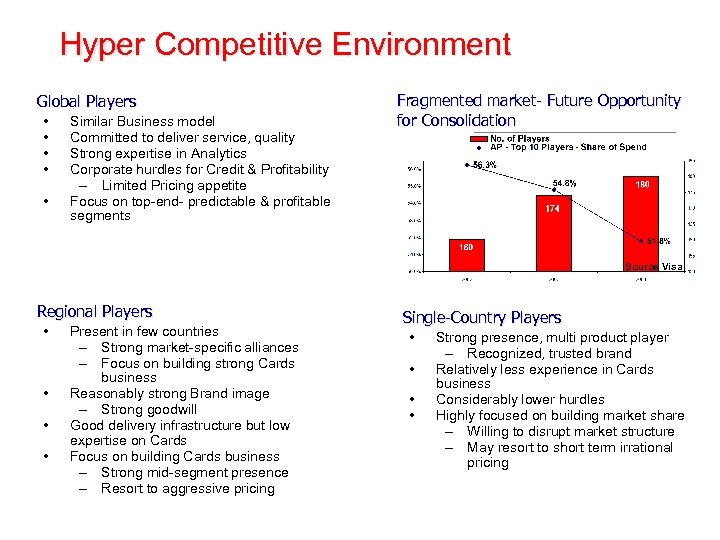
Hyper Competitive Environment Global Players • • • Similar Business model Committed to deliver service, quality Strong expertise in Analytics Corporate hurdles for Credit & Profitability – Limited Pricing appetite Focus on top-end- predictable & profitable segments Fragmented market- Future Opportunity for Consolidation Source Visa Regional Players • • Present in few countries – Strong market-specific alliances – Focus on building strong Cards business Reasonably strong Brand image – Strong goodwill Good delivery infrastructure but low expertise on Cards Focus on building Cards business – Strong mid-segment presence – Resort to aggressive pricing Single-Country Players • • Strong presence, multi product player – Recognized, trusted brand Relatively less experience in Cards business Considerably lower hurdles Highly focused on building market share – Willing to disrupt market structure – May resort to short term irrational pricing

What is this session about? • • Cards market in Asia Pacific Market Scenario in Taiwan market Citibank Cards business What is Cards business? – P&L Dynamics of Cards Business? • What are the Key Functions in Cards Business? – What about kind of skills & people needed in this business? • A Few Case Studies
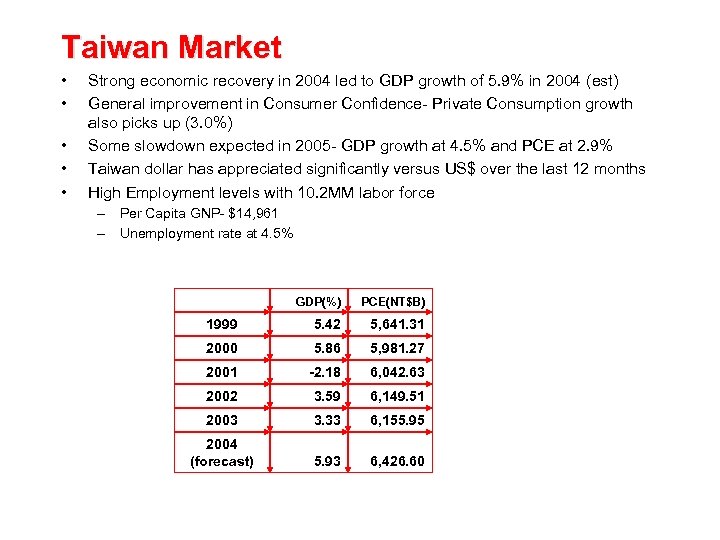
Taiwan Market • • • Strong economic recovery in 2004 led to GDP growth of 5. 9% in 2004 (est) General improvement in Consumer Confidence- Private Consumption growth also picks up (3. 0%) Some slowdown expected in 2005 - GDP growth at 4. 5% and PCE at 2. 9% Taiwan dollar has appreciated significantly versus US$ over the last 12 months High Employment levels with 10. 2 MM labor force – Per Capita GNP- $14, 961 – Unemployment rate at 4. 5% GDP(%) PCE(NT$B) 1999 5. 42 5, 641. 31 2000 5. 86 5, 981. 27 2001 -2. 18 6, 042. 63 2002 3. 59 6, 149. 51 2003 3. 33 6, 155. 95 2004 (forecast) 5. 93 6, 426. 60

Market Background- Regulatory • Regulators very active with the goals of – – Consumer protections, – Stable credit environment & – Fair competition in Cards Industry • Also Bankers’ Association plays an active self regulatory role • Card Businesses need to report independent financial statement by 3 Q 05
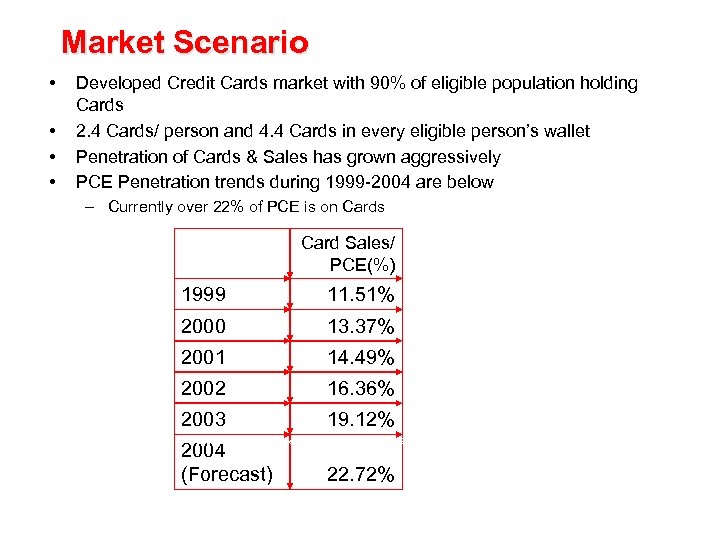
Market Scenario • • Developed Credit Cards market with 90% of eligible population holding Cards 2. 4 Cards/ person and 4. 4 Cards in every eligible person’s wallet Penetration of Cards & Sales has grown aggressively PCE Penetration trends during 1999 -2004 are below – Currently over 22% of PCE is on Cards Card Sales/ PCE(%) 1999 11. 51% 2000 13. 37% 2001 14. 49% 2002 16. 36% 2003 19. 12% Source: Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting & Statistics, Executive Yuan, FSC 2004 (Forecast) 22. 72%
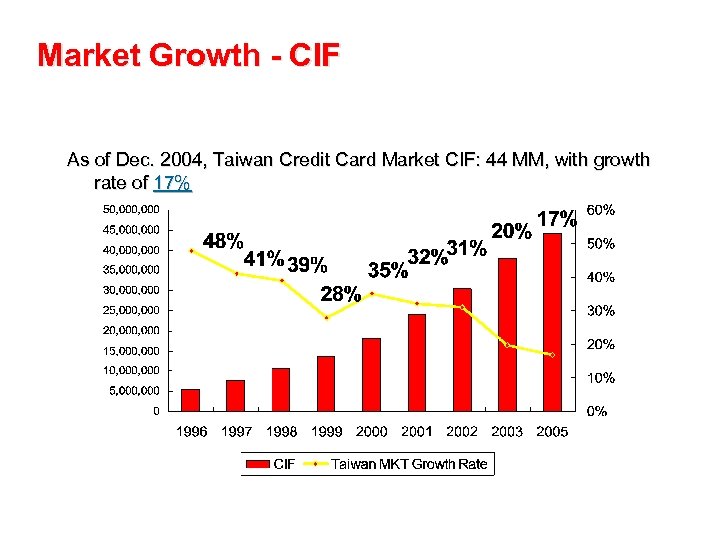
Market Growth - CIF As of Dec. 2004, Taiwan Credit Card Market CIF: 44 MM, with growth rate of 17%
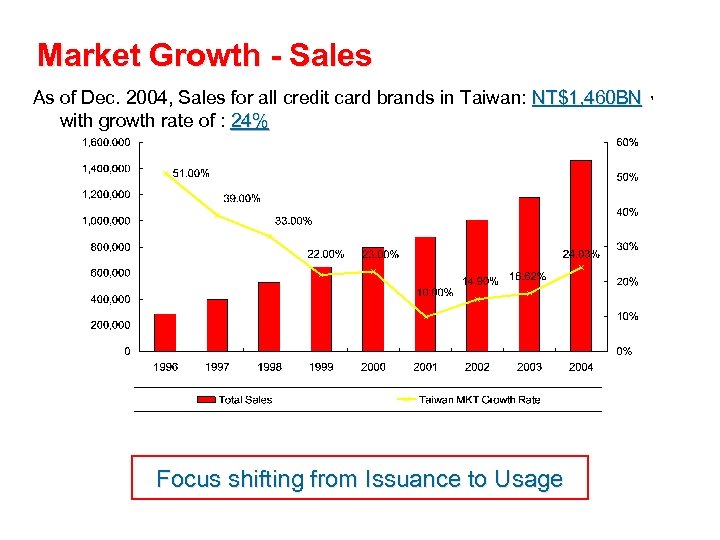
Market Growth - Sales As of Dec. 2004, Sales for all credit card brands in Taiwan: NT$1, 460 BN, 460 BN with growth rate of : 24% Focus shifting from Issuance to Usage

Competitive Environment • Over 60 Card Issuers, many may be unprofitable • “Free-for-Life Platinum” Market • Intense competition for Place-in-wallet and Share-of-wallet – High Advertising spend – Regular usage promotions – Large number of Cobrands • Citibank is #2 in Market Share Card Sales in Taiwan

What is this session about? • • Cards market in Asia Pacific Market Scenario in Taiwan market Citibank Cards business What is Cards business? – P&L Dynamics of Cards Business? • What are the Key Functions in Cards Business? – What about kind of skills & people needed in this business? • A Few Case Studies
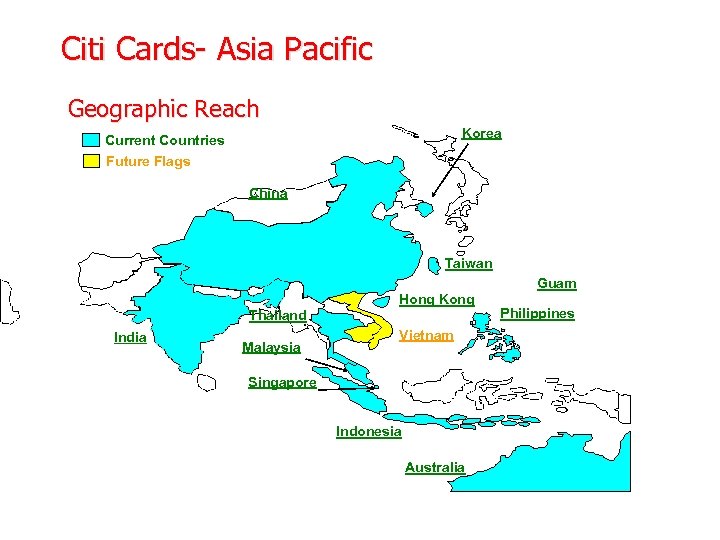
Citi Cards- Asia Pacific Geographic Reach Korea Current Countries Future Flags China Taiwan India Thailand Malaysia Hong Kong Vietnam Singapore Indonesia Australia Guam Philippines
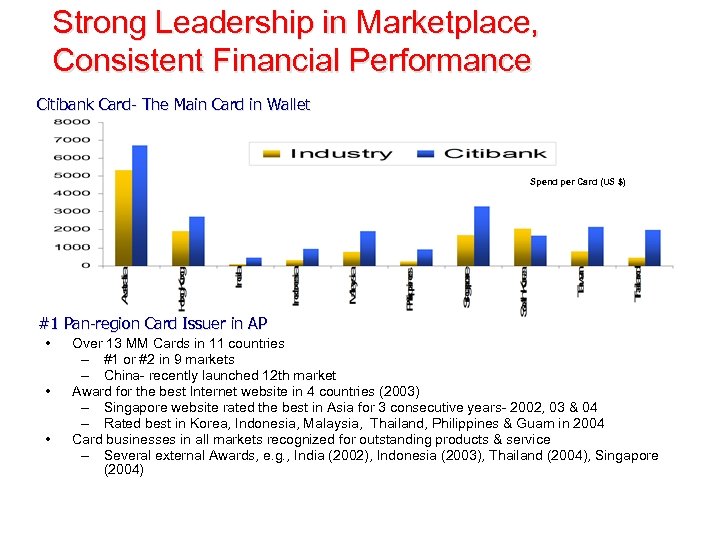
Strong Leadership in Marketplace, Consistent Financial Performance Citibank Card- The Main Card in Wallet Spend per Card (US $) #1 Pan-region Card Issuer in AP • • • Over 13 MM Cards in 11 countries – #1 or #2 in 9 markets – China- recently launched 12 th market Award for the best Internet website in 4 countries (2003) – Singapore website rated the best in Asia for 3 consecutive years- 2002, 03 & 04 – Rated best in Korea, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Philippines & Guam in 2004 Card businesses in all markets recognized for outstanding products & service – Several external Awards, e. g. , India (2002), Indonesia (2003), Thailand (2004), Singapore (2004)

Mission • Leadership in Payment Products category in Asia Pacific through– The best products, Customer Service & technology – Maximizing Risk-Reward balance by using Credit and Analytical tools • And make a significant contribution– To the bottom line of the corporation – To the customer base of the corporation

What is this session about? • • Cards market in Asia Pacific Market Scenario in Taiwan market Citibank Cards business What is Cards business? – P&L Dynamics of Cards Business? • What are the Key Functions in Cards Business? – What about kind of skills & people needed in this business? • A Few Case Studies
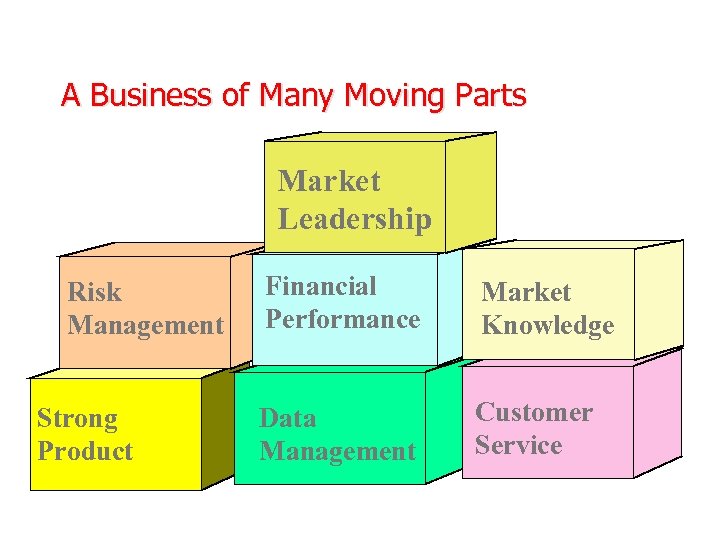
A Business of Many Moving Parts Market Leadership Risk Management Strong Product Financial Performance Market Knowledge Data Management Customer Service
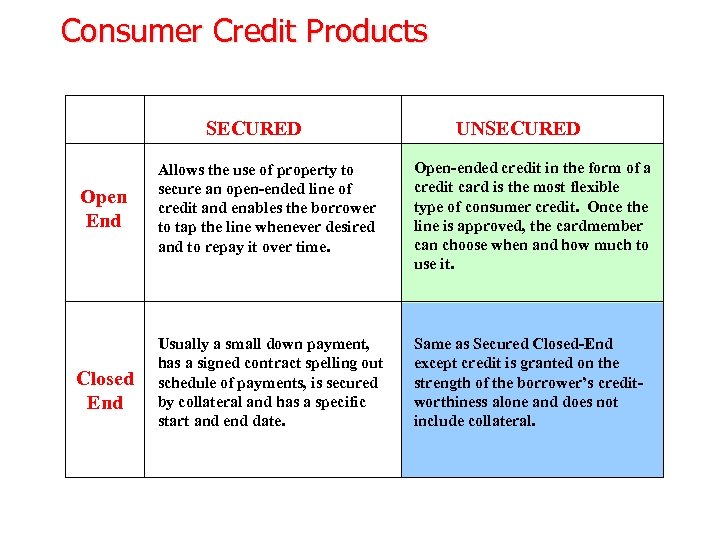
Consumer Credit Products SECURED UNSECURED Open End Allows the use of property to secure an open-ended line of credit and enables the borrower to tap the line whenever desired and to repay it over time. Open-ended credit in the form of a credit card is the most flexible type of consumer credit. Once the line is approved, the cardmember can choose when and how much to use it. Closed End Usually a small down payment, has a signed contract spelling out schedule of payments, is secured by collateral and has a specific start and end date. Same as Secured Closed-End except credit is granted on the strength of the borrower’s creditworthiness alone and does not include collateral.

Key Players • • Issuers: Financial institutions who issue credit cards Consumers: Individuals who use the cards Merchants: Points of sales where the cards are used Acquirers: Financial institutions who process (acquire) transactions performed at the merchant sites • Associations: Organizations that provide networks to facilitate transactions between Acquirers and Issuers (Visa, Master. Card & Diners) • Others: Regulatory bodies, consumer right groups, third party service providers, credit agencies, etc.
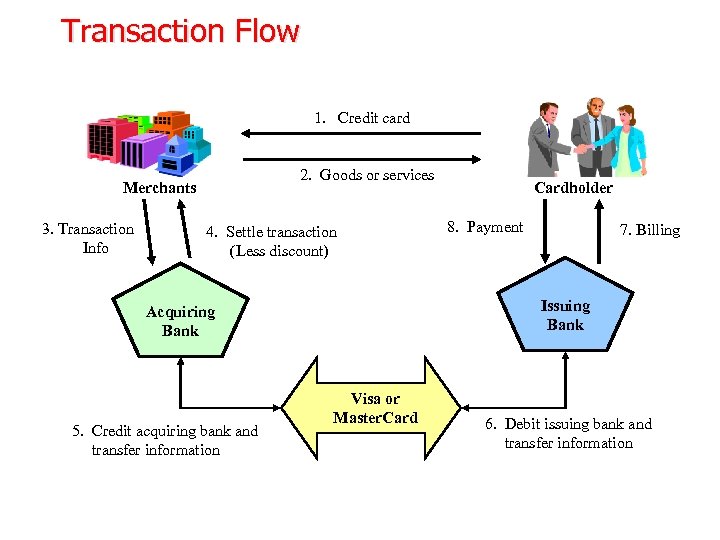
Transaction Flow 1. Credit card 2. Goods or services Merchants 3. Transaction Info 4. Settle transaction (Less discount) 8. Payment 7. Billing Issuing Bank Acquiring Bank 5. Credit acquiring bank and transfer information Cardholder Visa or Master. Card 6. Debit issuing bank and transfer information
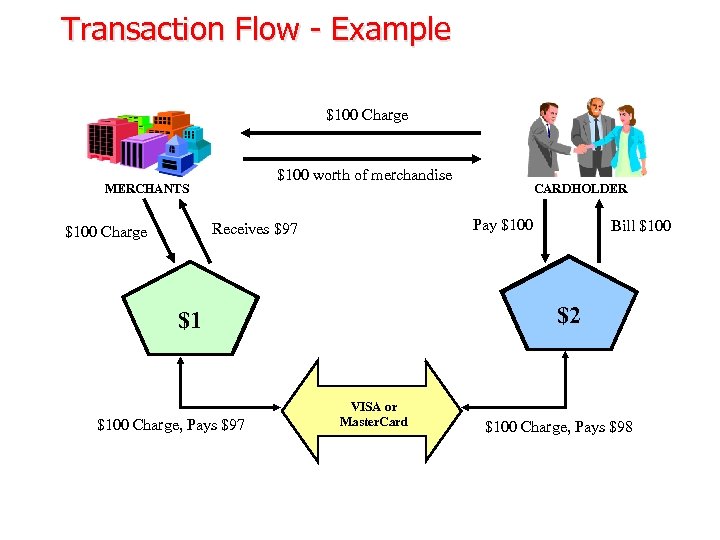
Transaction Flow - Example $100 Charge $100 worth of merchandise MERCHANTS Pay $100 Receives $97 $100 Charge Bill $100 ISSUING BANK $2 ACQUIRING BANK $1 $100 Charge, Pays $97 CARDHOLDER VISA or Master. Card $100 Charge, Pays $98
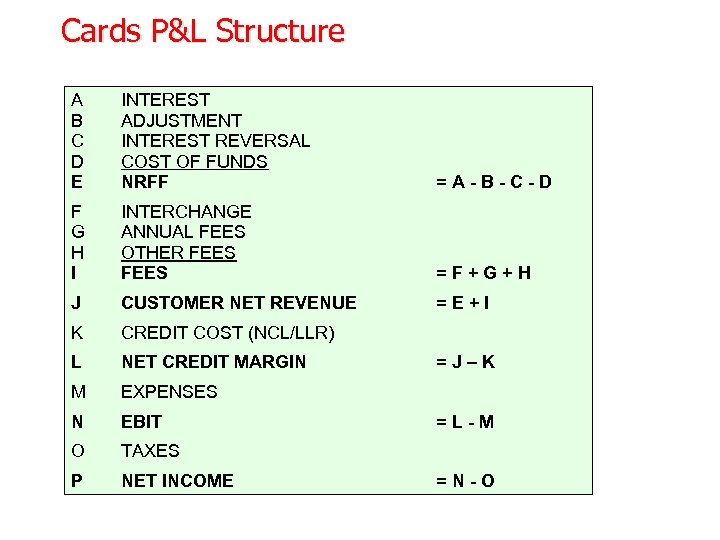
Cards P&L Structure A B C D E INTEREST ADJUSTMENT INTEREST REVERSAL COST OF FUNDS NRFF = A - B - C - D F G H I INTERCHANGE ANNUAL FEES OTHER FEES = F + G + H J CUSTOMER NET REVENUE = E + I K CREDIT COST (NCL/LLR) L NET CREDIT MARGIN = J – K M EXPENSES N EBIT O = L - M TAXES P NET INCOME = N - O
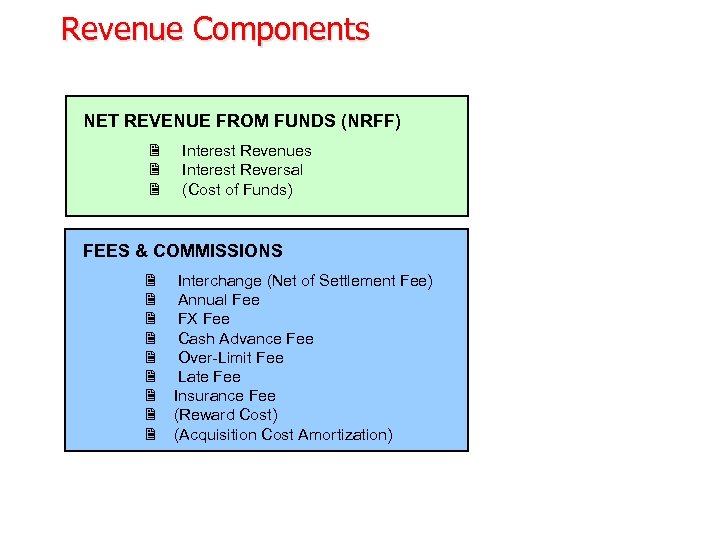
Revenue Components NET REVENUE FROM FUNDS (NRFF) 2 2 2 Interest Revenues Interest Reversal (Cost of Funds) FEES & COMMISSIONS 2 Interchange (Net of Settlement Fee) 2 Annual Fee 2 FX Fee 2 Cash Advance Fee 2 Over-Limit Fee 2 Late Fee 2 Insurance Fee 2 (Reward Cost) 2 (Acquisition Cost Amortization)
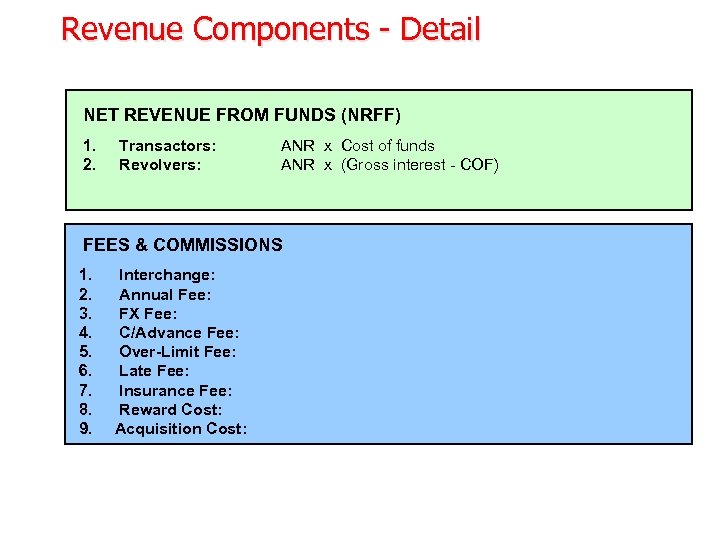
Revenue Components - Detail NET REVENUE FROM FUNDS (NRFF) 1. 2. Transactors: Revolvers: ANR x Cost of funds ANR x (Gross interest - COF) FEES & COMMISSIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Interchange: Annual Fee: FX Fee: C/Advance Fee: Over-Limit Fee: Late Fee: Insurance Fee: Reward Cost: Acquisition Cost:
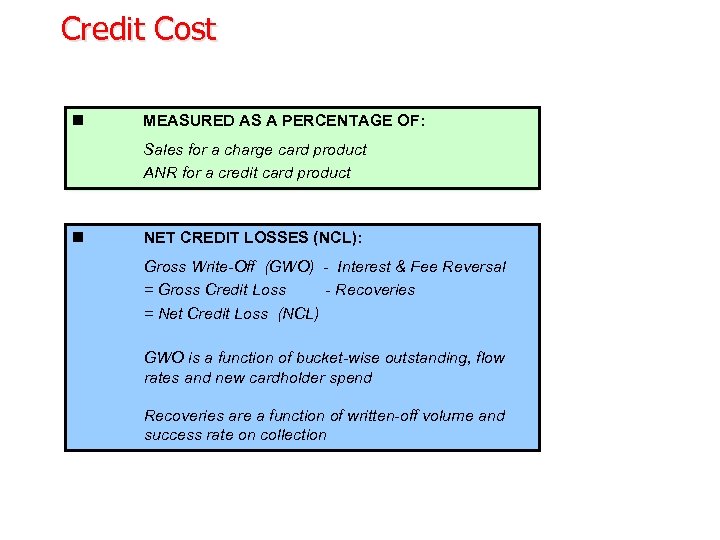
Credit Cost n MEASURED AS A PERCENTAGE OF: Sales for a charge card product ANR for a credit card product n NET CREDIT LOSSES (NCL): Gross Write-Off (GWO) - Interest & Fee Reversal = Gross Credit Loss - Recoveries = Net Credit Loss (NCL) GWO is a function of bucket-wise outstanding, flow rates and new cardholder spend Recoveries are a function of written-off volume and success rate on collection
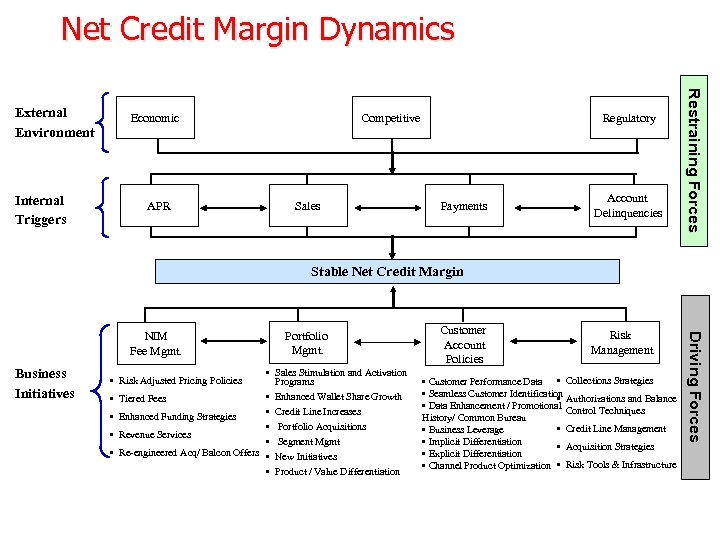
Net Credit Margin Dynamics Economic Internal Triggers APR Competitive Sales Regulatory Payments Account Delinquencies Restraining Forces External Environment Stable Net Credit Margin Business Initiatives • Sales Stimulation and Activation Programs • Enhanced Wallet Share Growth Tiered Fees • Credit Line Increases Enhanced Funding Strategies • Portfolio Acquisitions Revenue Services • Segment Mgmt Re-engineered Acq/ Balcon Offers • New Initiatives • Product / Value Differentiation • Risk Adjusted Pricing Policies • • Portfolio Mgmt. Customer Account Policies Risk Management • Customer Performance Data • Collections Strategies • Seamless Customer Identification Authorizations and Balance • • Data Enhancement / Promotional Control Techniques History/ Common Bureau • Credit Line Management • Business Leverage • Implicit Differentiation • Acquisition Strategies • Explicit Differentiation • Channel Product Optimization • Risk Tools & Infrastructure Driving Forces NIM Fee Mgmt.
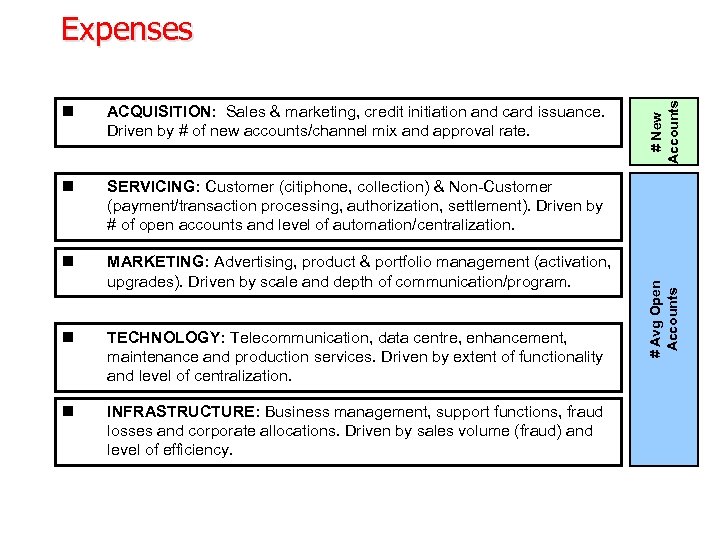
ACQUISITION: Sales & marketing, credit initiation and card issuance. Driven by # of new accounts/channel mix and approval rate. n SERVICING: Customer (citiphone, collection) & Non-Customer (payment/transaction processing, authorization, settlement). Driven by # of open accounts and level of automation/centralization. n MARKETING: Advertising, product & portfolio management (activation, upgrades). Driven by scale and depth of communication/program. n TECHNOLOGY: Telecommunication, data centre, enhancement, maintenance and production services. Driven by extent of functionality and level of centralization. n INFRASTRUCTURE: Business management, support functions, fraud losses and corporate allocations. Driven by sales volume (fraud) and level of efficiency. # Avg Open Accounts n # New Accounts Expenses
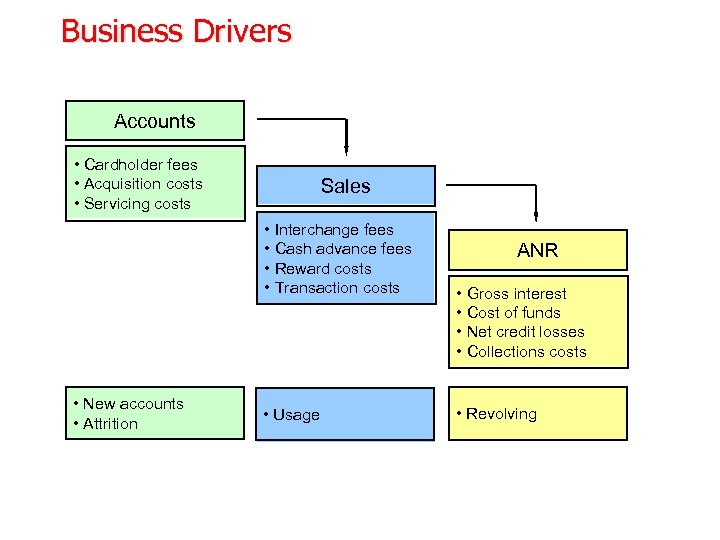
Business Drivers Accounts • Cardholder fees • Acquisition costs • Servicing costs Sales • Interchange fees • Cash advance fees • Reward costs • Transaction costs • New accounts • Attrition • Usage ANR • Gross interest • Cost of funds • Net credit losses • Collections costs • Revolving
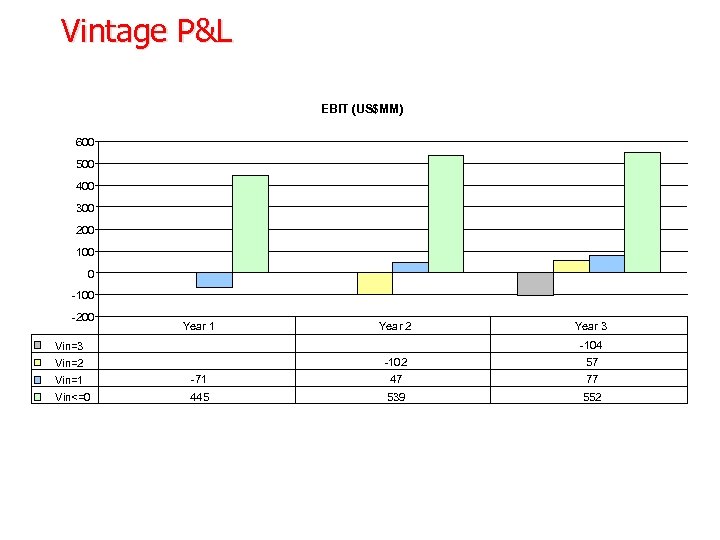
Vintage P&L EBIT (US$MM) 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 -100 -200 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 -104 Vin=3 -102 Vin=2 57 Vin=1 -71 47 77 Vin<=0 445 539 552

What is this session about? • • Cards market in Asia Pacific Market Scenario in Taiwan market Citibank Cards business What is Cards business? – P&L Dynamics of Cards Business? • What are the Key Functions in Cards Business? – What about kind of skills & people needed in this business? • A Few Case Studies

Operational Framework Marketing Risk Management • Cardholder Acquisition • Portfolio Management • Branding & Advertising • New Product Dev. & Partner Mgmt • Research & Planning • MIS • Credit / Risk Management • Risk Policies • Collections • Fraud Security Operations Technology • Credit Initiation/ Appl. Processing • Authorization • Transaction Service • Front End Collections • Customer Service • Front end distribution System • Host System • System development & maintenance Others • Financial Control, Human Resources, Legal/Compliance, Treasury
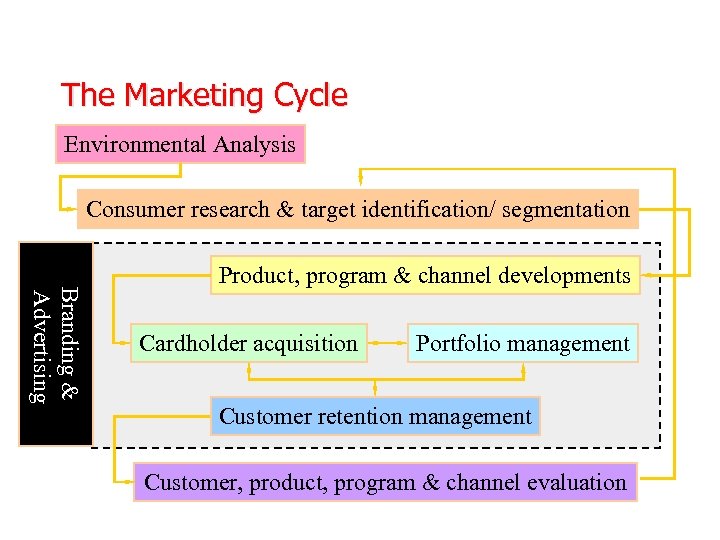
The Marketing Cycle Environmental Analysis Consumer research & target identification/ segmentation Branding & Advertising Product, program & channel developments Cardholder acquisition Portfolio management Customer retention management Customer, product, program & channel evaluation

Understanding Customers- What are characteristics of Taiwan society? • Highly Competitive • Fast Moving & Dynamic • Entrepreneurial & Achievement / Goal Oriented • Flexible to Changing Situations
Understanding Customers- Major Consumer Segments 1. Identity Builders 2. Career Builders 3. Family Builders 4. New Life Builders Target Groups ! !
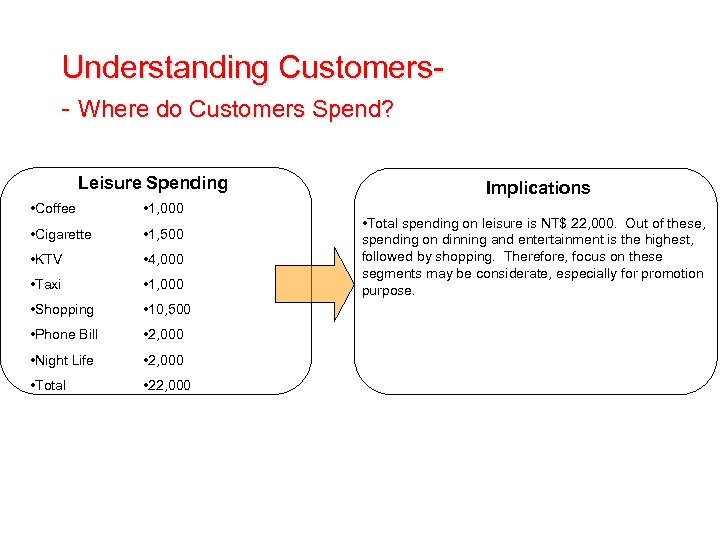
Understanding Customers- Where do Customers Spend? Leisure Spending • Coffee • 1, 000 • Cigarette • 1, 500 • KTV • 4, 000 • Taxi • 1, 000 • Shopping • 10, 500 • Phone Bill • 2, 000 • Night Life • 2, 000 • Total • 22, 000 Implications • Total spending on leisure is NT$ 22, 000. Out of these, spending on dinning and entertainment is the highest, followed by shopping. Therefore, focus on these segments may be considerate, especially for promotion purpose.
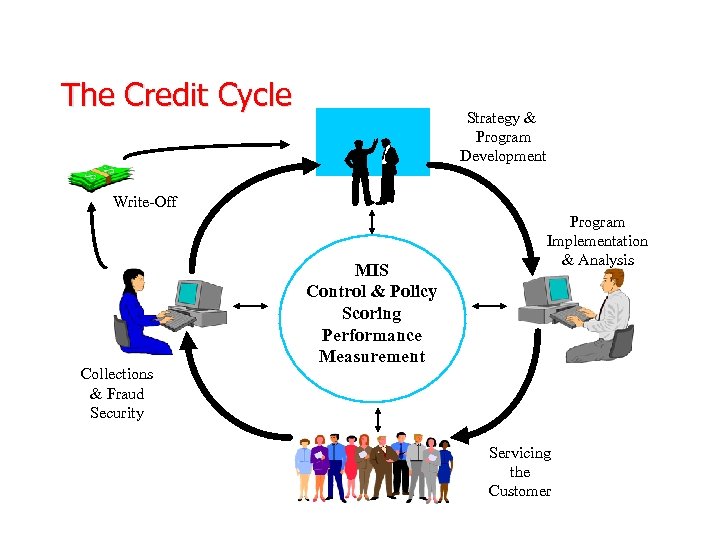
The Credit Cycle Strategy & Program Development Write-Off Collections & Fraud Security MIS Control & Policy Scoring Performance Measurement Program Implementation & Analysis Servicing the Customer

Application Processing • Receive & process applications & credit-line increase requests, and related offers in a timely and costefficient manner. • Develop & maintain a rational, automated, consistent methodology for scoring the information. • Review declines cases to determine if consolidation, credit-line reduction or “Down-Sell” will address the needs of the applicant.
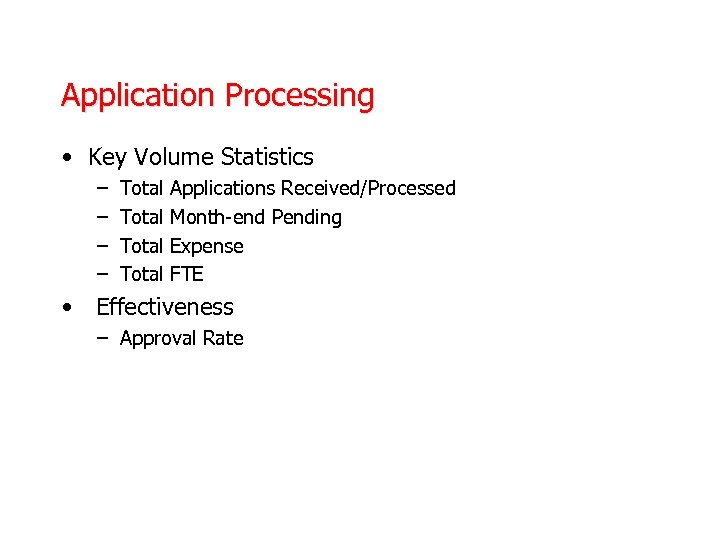
Application Processing • Key Volume Statistics – – Total Applications Received/Processed Month-end Pending Expense FTE • Effectiveness – Approval Rate
Application Processing • Efficiency – Deviation rates – Incomplete Apps • Quality – Data Entry – Verification – Credit Decision

Authorization • Crucial process in controlling delinquency and fraud while providing exceptional service and increasing sales • Good authorization process can – Prevent further credit exposure – Prevent use of lost or stolen cards – Provide opportunity to confiscate cards being used fraudulently – Detect patterns of card usage suggesting fraudulent use – Establish validity of the transaction – Managing portfolio through appropriate authorization policy

Authorization • Criteria – – – Outstanding Balance / Available Limit Delinquency Length and Depth of relationship Type of purchase Validation of purchase Behavior Score

Collections • Collection is a Balancing act – Cost vs. Return – Customer relationship (retention) vs. Asset Protection • Customer contact is important – “If you don’t make contact, you don’t collect” • People – Training & performance coaching & monitoring – Collection agency • Process & System – Technology – Performance MIS
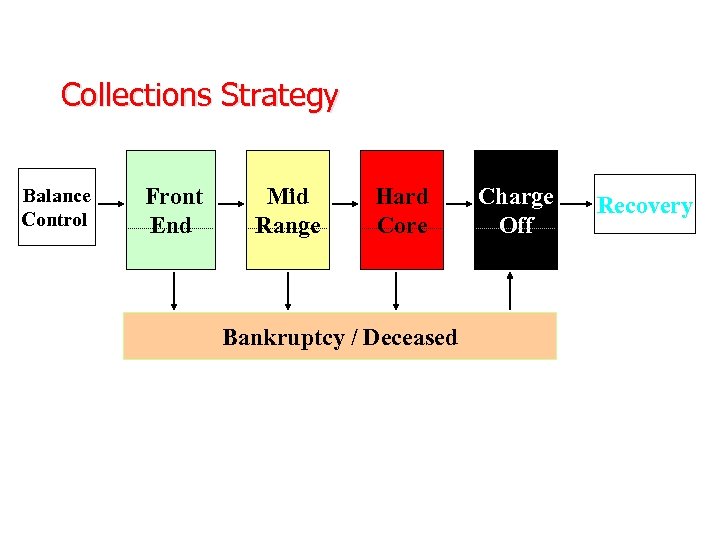
Collections Strategy Balance Control Front End Mid Range Hard Core Bankruptcy / Deceased Charge Off Recovery

Fraud - Mission • Protect the franchise against fraudulent activities while maintaining customer convenience & service

Fraud - Types • Traditional Types – – – Lost / Stolen Never Receive Issuance (NRI) Fraudulent Application Mail / Telephone Order (MOTO) Account Take Over (ATO) • Emerging Types – – Manual Counterfeit (White Plastic, Altered, etc) Electronic Counterfeit (Skimming) Merchant Fraud Internet / E-Commerce

What is this session about? • • Cards market in Asia Pacific Market Scenario in Taiwan market Citibank Cards business What is Cards business? – P&L Dynamics of Cards Business? • What are the Key Functions in Cards Business? – What about kind of skills & people needed in this business? • A Few Case Studies

Case Study #1 - Leveraging Citibank’s Global Presence
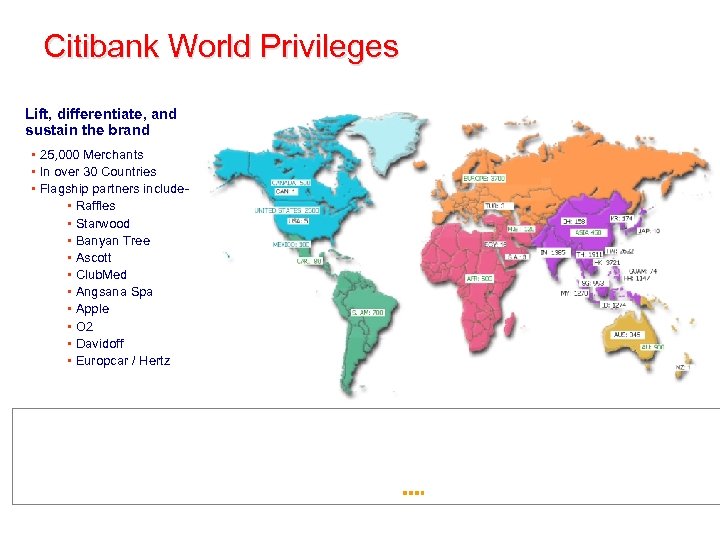
Citibank World Privileges Lift, differentiate, and sustain the brand • 25, 000 Merchants • In over 30 Countries • Flagship partners include • Raffles • Starwood • Banyan Tree • Ascott • Club. Med • Angsana Spa • Apple • O 2 • Davidoff • Europcar / Hertz

Case Study #2 - Building “Premium”
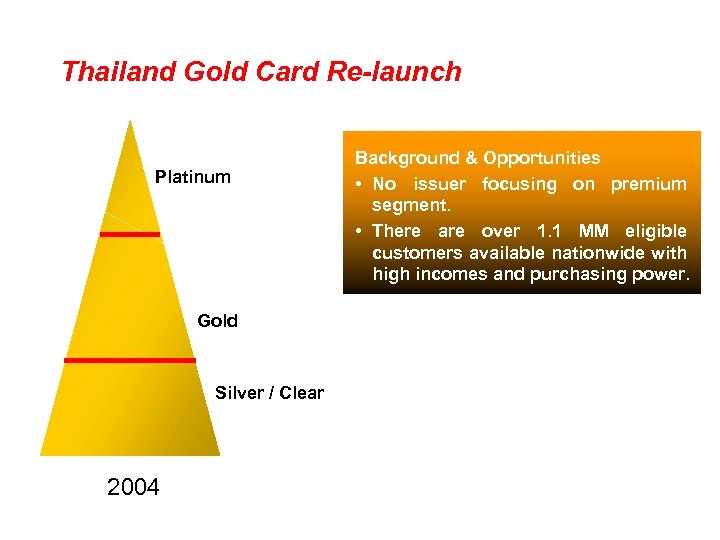
Thailand Gold Card Re-launch Platinum Gold Silver / Clear 2004 Background & Opportunities • No issuer focusing on premium segment. • There are over 1. 1 MM eligible customers available nationwide with high incomes and purchasing power.

Gold Card Re-launch - Own the Segment • • • Launched with strong new benefits Expanded market by qualifying more customers- reduce income criteria Strong Advertising support

Case Study #3 - Creating Value for Money “Cash for Customers”

Cash Back Card Objectives Own a strong ‘Value’ proposition from card users stand point Strategy Cash-back to be positioned as stronger value versus Rewards Annual fee- should be higher than Vanilla (metals) cards.

Summary • Cards is a universal product with mass appeal • Industry continuous to grow- both due to economic growth and cash-tocard shift; specially in Asia • Effective marketing requires understanding different segment dynamics and support with right product/channel strategy • Cards is a complex business requiring significant local/ international infrastructure, and good understanding of risk management, analytics, and profitability dynamics. • It’s a fun & challenging business to work in…

“As regulation falls away & competition intensifies, management talent & insight. . . will become critical success factors. ” - The Mc. Kinsey Quarterly, 1997

Questions? Thank you

e0f0f51c420b30029de0aa976b34ba70.ppt