ab61c11c08e1088a3a804452932bc49a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence CE 40417 Chapter 12 – Planning and Acting in Real World Ramin Halavati (halavati@ce. sharif. edu) In which we see how more expressive representations and more interactive agent architectures lead to planners that are useful in real world.
An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence CE 40417 Chapter 12 – Planning and Acting in Real World Ramin Halavati (halavati@ce. sharif. edu) In which we see how more expressive representations and more interactive agent architectures lead to planners that are useful in real world.
 Outline • Time, Schedules, and Resources • Hierarchical Task Network Planning • Planning and Acting in Nondeterministic Domains • Multi Agent Planning
Outline • Time, Schedules, and Resources • Hierarchical Task Network Planning • Planning and Acting in Nondeterministic Domains • Multi Agent Planning
 Time, Schedules, & Resources • Basic Planning: – What to do and in which order? • Real World: – What an When to do? + Limited Resources. – JOB SHOP SCHEDULING
Time, Schedules, & Resources • Basic Planning: – What to do and in which order? • Real World: – What an When to do? + Limited Resources. – JOB SHOP SCHEDULING
 Job Shop Scheduling
Job Shop Scheduling
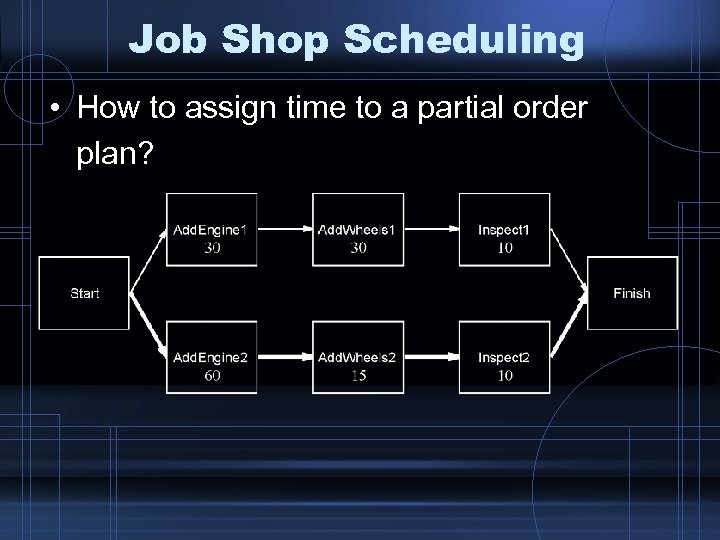 Job Shop Scheduling • How to assign time to a partial order plan?
Job Shop Scheduling • How to assign time to a partial order plan?
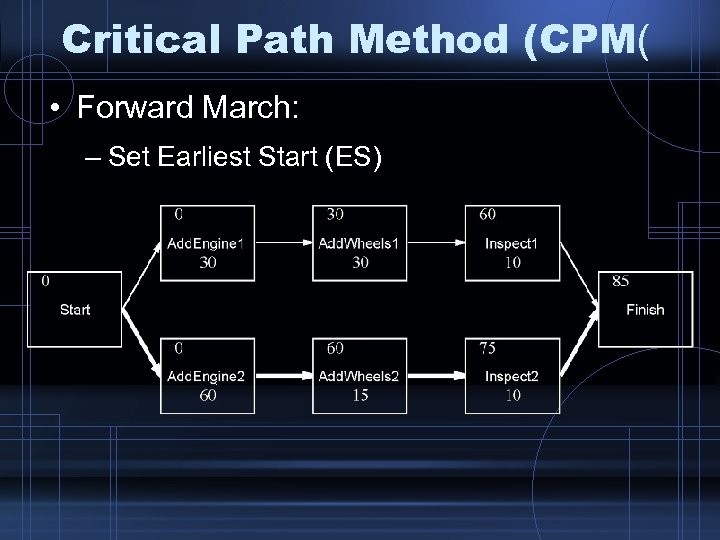 Critical Path Method (CPM( • Forward March: – Set Earliest Start (ES)
Critical Path Method (CPM( • Forward March: – Set Earliest Start (ES)
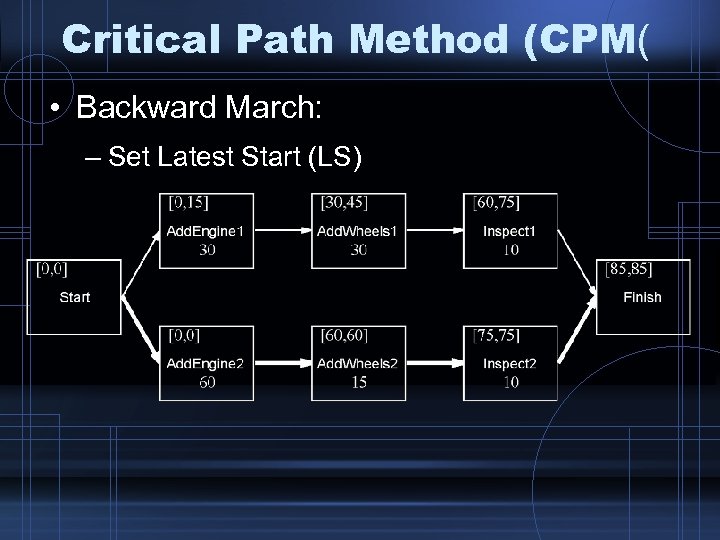 Critical Path Method (CPM( • Backward March: – Set Latest Start (LS)
Critical Path Method (CPM( • Backward March: – Set Latest Start (LS)
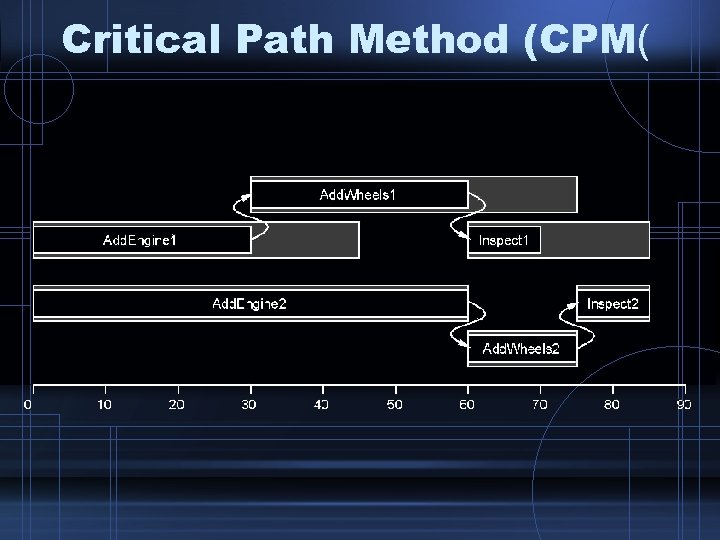 Critical Path Method (CPM(
Critical Path Method (CPM(
 Limited Resources • Resources: – Consumable vs. Reusable. • Notation: – Aggregation – Immediate Effect – Resource: R(k) • Requirement / Temporary Effect
Limited Resources • Resources: – Consumable vs. Reusable. • Notation: – Aggregation – Immediate Effect – Resource: R(k) • Requirement / Temporary Effect
 Limited Resources • No General Approach (NP-Hard) • Just Order the task so that the requirements are met. • Heuristic: – Minimum Slack Algorithm: • Give more priority to the task with least remaining slack.
Limited Resources • No General Approach (NP-Hard) • Just Order the task so that the requirements are met. • Heuristic: – Minimum Slack Algorithm: • Give more priority to the task with least remaining slack.
 Job Shop Scheduling, One Last Word. • Separated / Integrated Planning and Scheduling. • Semi Automatic
Job Shop Scheduling, One Last Word. • Separated / Integrated Planning and Scheduling. • Semi Automatic
 Hierarchical Planning • Hierarchical Task Network: – At each “level, ” only a small number of individual planning actions, then descend to lower levels to “solve these” for real. – At higher levels, the planner ignores “internal effects” of decompositions. But these have to be resolved at some level…
Hierarchical Planning • Hierarchical Task Network: – At each “level, ” only a small number of individual planning actions, then descend to lower levels to “solve these” for real. – At higher levels, the planner ignores “internal effects” of decompositions. But these have to be resolved at some level…
 HTN Sample • Construction Domain: – Actions: • Buy Land: Money Land • Get Load: Good Credit Money • Get Permit: Land Permit • Hire Builder: Contract • Construction: Permit Contract House Built • Pay Builder: Money House Built House • …
HTN Sample • Construction Domain: – Actions: • Buy Land: Money Land • Get Load: Good Credit Money • Get Permit: Land Permit • Hire Builder: Contract • Construction: Permit Contract House Built • Pay Builder: Money House Built House • …
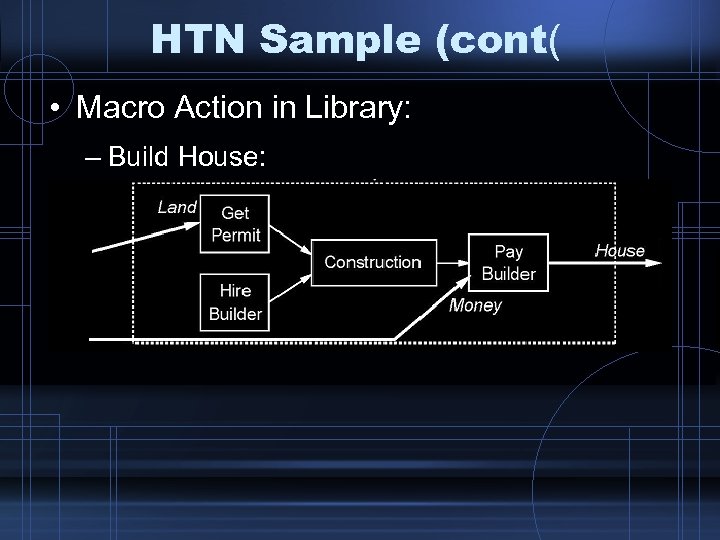 HTN Sample (cont( • Macro Action in Library: – Build House:
HTN Sample (cont( • Macro Action in Library: – Build House:
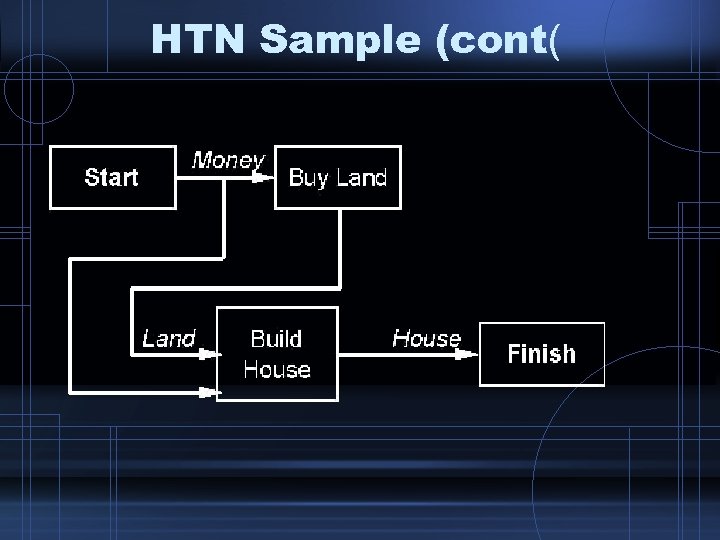 HTN Sample (cont(
HTN Sample (cont(
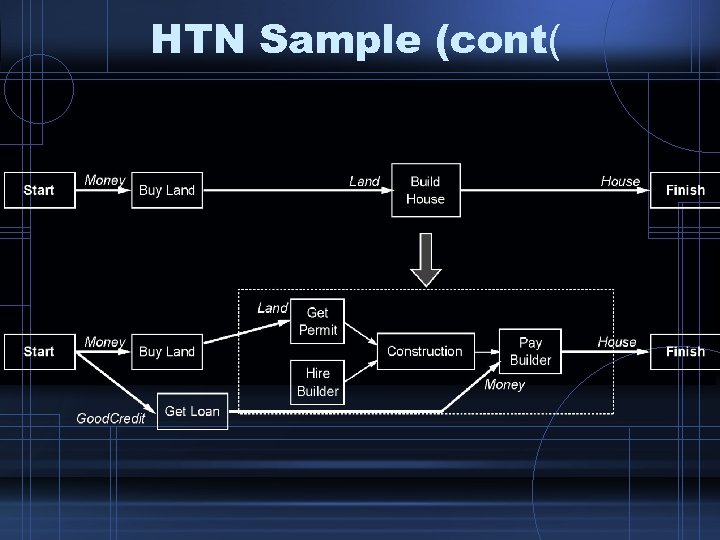 HTN Sample (cont(
HTN Sample (cont(
 HTN Cons and Pros • What’s Bad? – Recursion? – Sub Task Sharing: • Enjoy honey moon in Hawaii and raise a family. • Library: – Enjoy Honey moon in Hawaaii: Get Married , Go to Hawaii. – Raise Family: Get Married, Have two children.
HTN Cons and Pros • What’s Bad? – Recursion? – Sub Task Sharing: • Enjoy honey moon in Hawaii and raise a family. • Library: – Enjoy Honey moon in Hawaaii: Get Married , Go to Hawaii. – Raise Family: Get Married, Have two children.
 HTN Cons and Pros • What’s Good: – Almost all real applications are HTN + some thing else. – It’s a heuristic to decrease the branching factor by a great level.
HTN Cons and Pros • What’s Good: – Almost all real applications are HTN + some thing else. – It’s a heuristic to decrease the branching factor by a great level.
 Non. Deterministic Domains • What if we don’t know all about situations and effects. • E. g. – Init: A table and a chair of unknown colors. – Goal: A table and a chair of the same colors. – Condition: Painting may have flaws.
Non. Deterministic Domains • What if we don’t know all about situations and effects. • E. g. – Init: A table and a chair of unknown colors. – Goal: A table and a chair of the same colors. – Condition: Painting may have flaws.
 Sensorless Planning • We don’t know all beforehand we can’t find it out, even when it is done. – Plan so that to reach the goal state, regardless of everything. (Coercion) – Not always possible.
Sensorless Planning • We don’t know all beforehand we can’t find it out, even when it is done. – Plan so that to reach the goal state, regardless of everything. (Coercion) – Not always possible.
 Conditional Planning • We can check the state ahead, then perform the pre-planned program. – Sense Actions – Conditional Branches
Conditional Planning • We can check the state ahead, then perform the pre-planned program. – Sense Actions – Conditional Branches
 Conditional Planning in Fully Observable Domains • Vacuum World: – Left: At. Right At. Left At. Right – Left: At. Right (At. Left At. Right) ( At. Left At. Right) – Suck: when At. Left Clean. Left when At. Right Clean. Right – Left: when At. Left Clean. Left when At. Right At. Left At. Right
Conditional Planning in Fully Observable Domains • Vacuum World: – Left: At. Right At. Left At. Right – Left: At. Right (At. Left At. Right) ( At. Left At. Right) – Suck: when At. Left Clean. Left when At. Right Clean. Right – Left: when At. Left Clean. Left when At. Right At. Left At. Right
 Notation Expantion: • Expanding Plan Notation: – If (state) Then (…) else (…) – If (At. Left Clean. Right) Then {} else Suck.
Notation Expantion: • Expanding Plan Notation: – If (state) Then (…) else (…) – If (At. Left Clean. Right) Then {} else Suck.
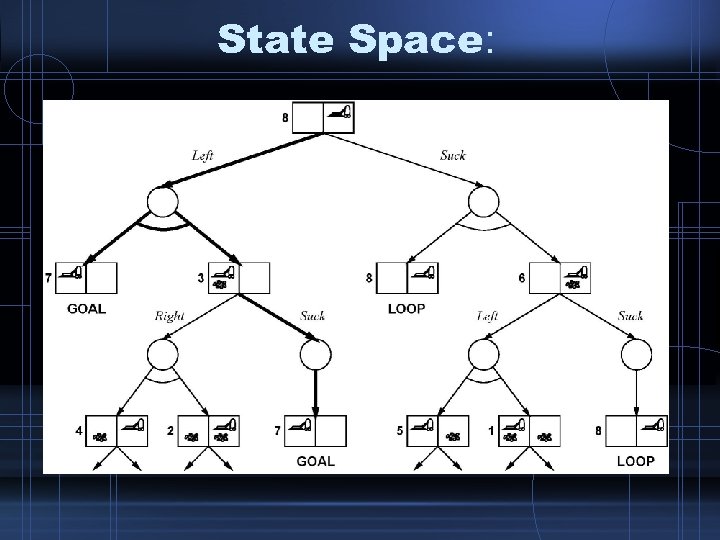 State Space:
State Space:
 Conditional Planner:
Conditional Planner:
 Unavoidable Loops in Conditional Planner • New Notation: – Instead of just Left : while (At. Right) Left
Unavoidable Loops in Conditional Planner • New Notation: – Instead of just Left : while (At. Right) Left
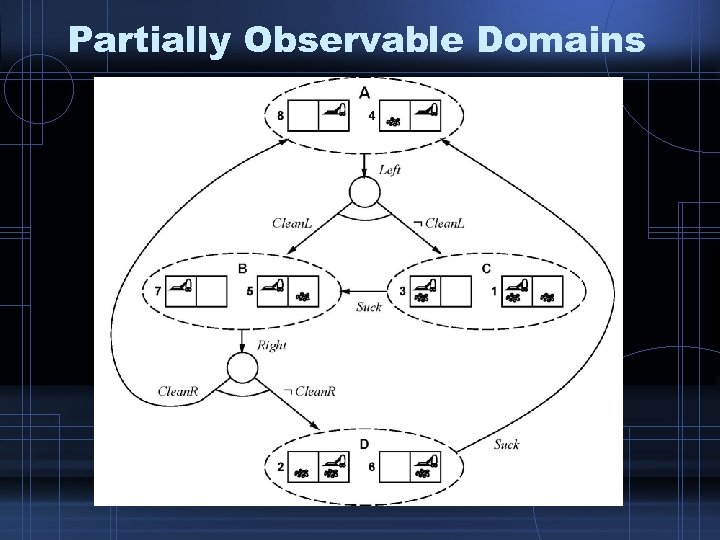 Partially Observable Domains
Partially Observable Domains
 Partially Observable Domains • Easiest Approach: – Assume set of current states and the next state sets are created, quite similar to nondeterministic actions case.
Partially Observable Domains • Easiest Approach: – Assume set of current states and the next state sets are created, quite similar to nondeterministic actions case.
 Execution Monitoring and Replanning • Check if the plan is going on is predecided? If not, replan based on current situation.
Execution Monitoring and Replanning • Check if the plan is going on is predecided? If not, replan based on current situation.
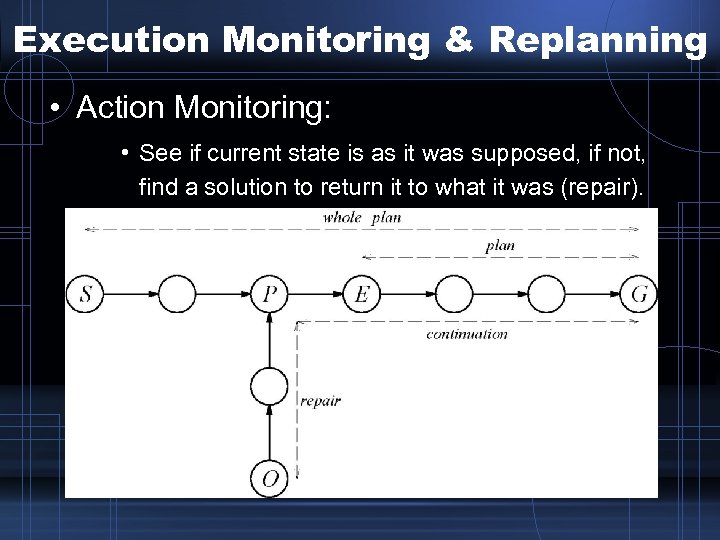 Execution Monitoring & Replanning • Action Monitoring: • See if current state is as it was supposed, if not, find a solution to return it to what it was (repair).
Execution Monitoring & Replanning • Action Monitoring: • See if current state is as it was supposed, if not, find a solution to return it to what it was (repair).
 Execution Monitoring & Replanning • Plan Monitoring: – See if the previous plan is still wise? – Serendipity! – A precondition of future actions has failed and can not be recovered.
Execution Monitoring & Replanning • Plan Monitoring: – See if the previous plan is still wise? – Serendipity! – A precondition of future actions has failed and can not be recovered.
 Execution Monitoring in Partially Observable Domains • Things may fail and we don’t know. • Sensing actions may be required – And they may need extra-planning. • We may stuck in futile attempts: – The electronic key is incorrect, but we think it might be due to incorrect pushing in.
Execution Monitoring in Partially Observable Domains • Things may fail and we don’t know. • Sensing actions may be required – And they may need extra-planning. • We may stuck in futile attempts: – The electronic key is incorrect, but we think it might be due to incorrect pushing in.
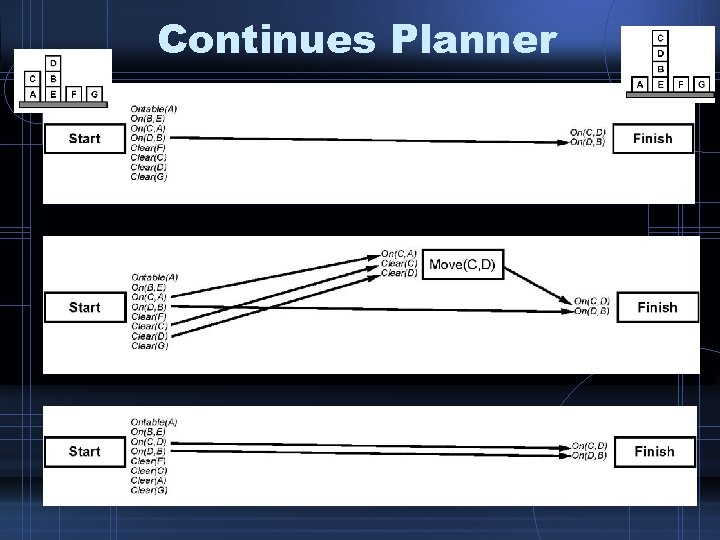
 Continues Planner • Keep planning, sensing and executing… – Which is not unlikely, such as maintenance planning, auto-pilot, plant control, …
Continues Planner • Keep planning, sensing and executing… – Which is not unlikely, such as maintenance planning, auto-pilot, plant control, …
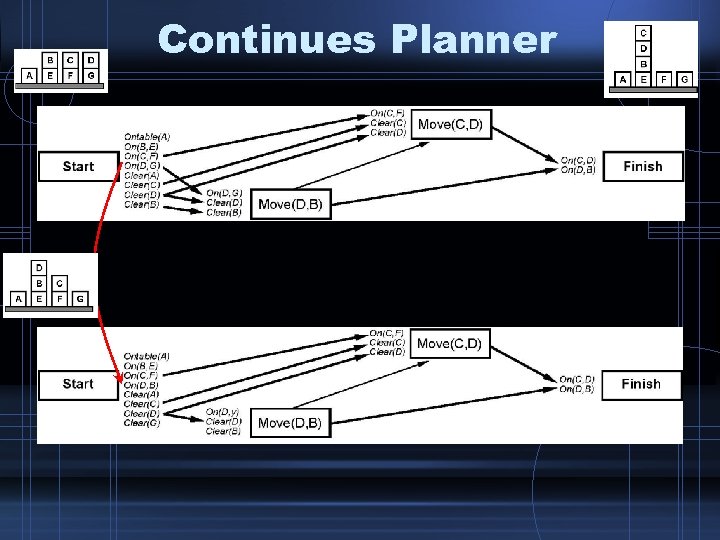 Continues Planner
Continues Planner
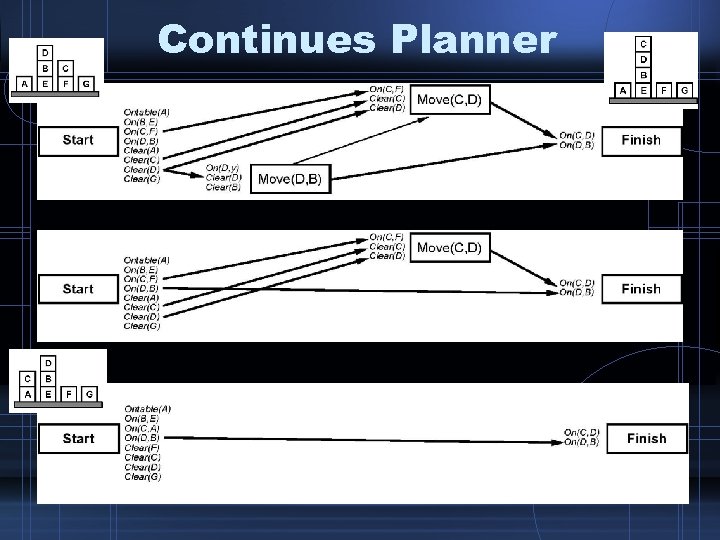 Continues Planner
Continues Planner
 Continues Planner
Continues Planner
 Continuous Planner • POP + … – Missing Goal: • A new goal has erupted. Just add it. – Open precondition: • An action has lost its support links. Add a new causal link. – Causal Conflicts: • A causal link is suddenly threatened. Choose an appropriate ordering.
Continuous Planner • POP + … – Missing Goal: • A new goal has erupted. Just add it. – Open precondition: • An action has lost its support links. Add a new causal link. – Causal Conflicts: • A causal link is suddenly threatened. Choose an appropriate ordering.
 Continuous Planner • POP + … – Unsupported Link: • A link from start to something has suddenly last its true value. Remove it. – Redundant Action: • An action no more produces something needed. Remove it.
Continuous Planner • POP + … – Unsupported Link: • A link from start to something has suddenly last its true value. Remove it. – Redundant Action: • An action no more produces something needed. Remove it.
 Uncertainty is Over.
Uncertainty is Over.
 Multi Agent Planning • When there is more than one agent in the scene. – Competitive – Cooperative • Coordination – Communication
Multi Agent Planning • When there is more than one agent in the scene. – Competitive – Cooperative • Coordination – Communication
 Cooperation • Multi Body Planning – One is in charge of all decisions… • Having the agent as one of parameters: – Go(R 2 D 3, Right) ^ Go(C 3 PO, Left). • Synchronization and Timing…
Cooperation • Multi Body Planning – One is in charge of all decisions… • Having the agent as one of parameters: – Go(R 2 D 3, Right) ^ Go(C 3 PO, Left). • Synchronization and Timing…
 Cooperation – Multi Body • Joint Planning: – Planning using action pairs: • Exponentially Many Actions: Actions Agents – Having Concurrent Actions List • Which actions happen together and which not, such as orders in POP.
Cooperation – Multi Body • Joint Planning: – Planning using action pairs: • Exponentially Many Actions: Actions Agents – Having Concurrent Actions List • Which actions happen together and which not, such as orders in POP.
 Cooperation - Coordination • Accepting a prior Convention. – Everyone drive on his/her right side of the road. – Domain Independent: • Choosing the first feasible action. • Producing all possible feasible actions and choosing the one which stands first in alphabetic order!
Cooperation - Coordination • Accepting a prior Convention. – Everyone drive on his/her right side of the road. – Domain Independent: • Choosing the first feasible action. • Producing all possible feasible actions and choosing the one which stands first in alphabetic order!
 Cooperation – Emergence • Evolutionary Emergent Behavior – Birds Flocking: • Separation • Cohesion • Alignment – Ants.
Cooperation – Emergence • Evolutionary Emergent Behavior – Birds Flocking: • Separation • Cohesion • Alignment – Ants.
 Coop. - Communication • A short message expressing – the plan / next step. • A message expressing the next step. • Plan Recognition!
Coop. - Communication • A short message expressing – the plan / next step. • A message expressing the next step. • Plan Recognition!
 Competition • Minimax + Conditional Planning
Competition • Minimax + Conditional Planning
 Essey & Project Proposals • To Do.
Essey & Project Proposals • To Do.


