819710cf37882fbac34880b9bb3cdc0d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12


An Intervention To Improve Antibiotic Prescribing Habits of Doctors in a Teaching Hospital Ofei F, Forson A, Tetteh R, Ofori-Adjei D University of Ghana Medical School, Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital and Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research, Accra, Ghana.

Summary of the study aims and results § Objectives § Establish the magnitude of inappropriate prescribing for treatment of community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) § Implement a managerial and educational intervention selected by hospital consultants § Assess the effect of the intervention on the antibiotic prescribing habits of house officers for LRTI § Results § No change in behaviour observed
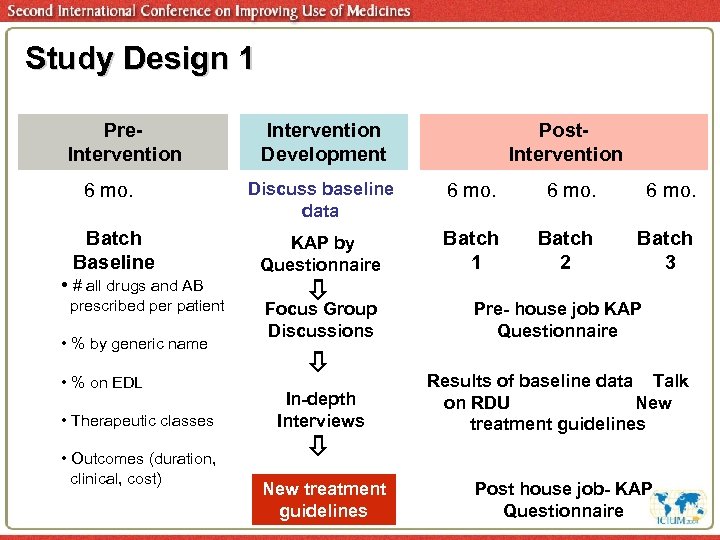
Study Design 1 Pre. Intervention 6 mo. Batch Baseline • # all drugs and AB prescribed per patient • % by generic name • % on EDL • Therapeutic classes • Outcomes (duration, clinical, cost) Intervention Development Post. Intervention Discuss baseline data 6 mo. KAP by Questionnaire Batch 1 Batch 2 Batch 3 Focus Group Discussions In-depth Interviews New treatment guidelines Pre- house job KAP Questionnaire Results of baseline data Talk on RDU New treatment guidelines Post house job- KAP Questionnaire

Study Design 2 § Intervention directed at § Specific prescriber - house officer § First contact with patients § Least experienced § Specific problem – community acquired LRTI § common § ‘easy to diagnose’ § requiring antibiotics § Intervention § selected, accepted and supervised by their consultants § documented decision making by category of prescriber
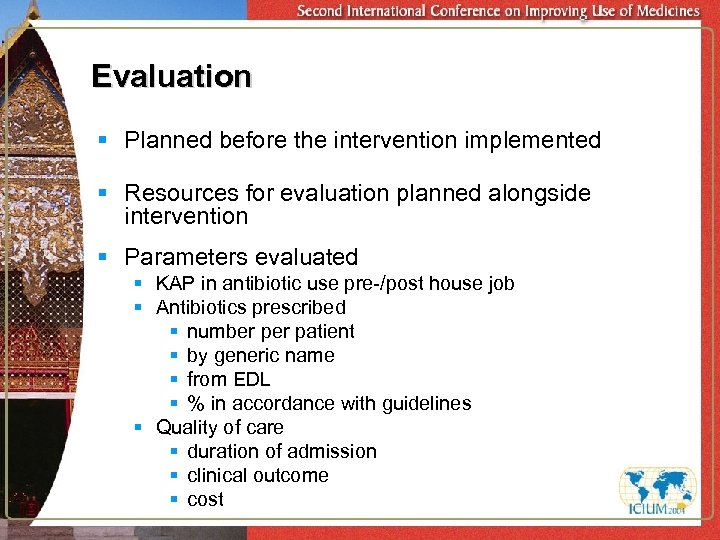
Evaluation § Planned before the intervention implemented § Resources for evaluation planned alongside intervention § Parameters evaluated § KAP in antibiotic use pre-/post house job § Antibiotics prescribed § number patient § by generic name § from EDL § % in accordance with guidelines § Quality of care § duration of admission § clinical outcome § cost

Challenging methodological issues § Regular change of house officers (and residents) § § Study cost vs. study duration § § Unable to properly assess long-term improvement Some groups were ‘freshmen’ others on a 2 nd rotation Prescribing experiences may be different Shorter duration would not allow proper assessment of sustainability of the intervention Use of control group at separate hospital with ? different managerial and regulatory systems and other possible influences § § The chances of “contamination” would be high if the study and control group were in the same hospital. Better compromise

Strengths of this design § Prospective § Time series § better assesses sustainability of intervention in view of inevitable change of HO § ‘Double’ Control § Baseline data § Control site data § Allowed identification of problems intrinsic to the health facility

Weaknesses of this design § ‘Hawthorne’ effect cannot be fully excluded § Retrospective study not feasible § Pre-intervention data inadequate § Short pre-intervention data collection

Lessons learnt § Implement and evaluate on a § longer pre-intervention phase § ? varying experiences of 1 st and 2 nd rotation house officers § larger scale in different settings of similar standards § Establish on-going evaluation published as ‘league table’ § WHO/INRUD indicators per ward or consultant § Adherence to guidelines § ? more effective feedback

Questions for future research § Assessment of factors other than physician knowledge on prescribing § § Influence of sales representatives on all categories of prescriber Influence of national and hospital regulatory controls on prescribing Patient access to unrestricted range of medicines Patient pressure

Conclusion § There is no ‘gold standard’ § The multiple influences on prescribing require multiple interventional approaches and evaluations
819710cf37882fbac34880b9bb3cdc0d.ppt