f615a6061ee658be5200d5088637cbef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
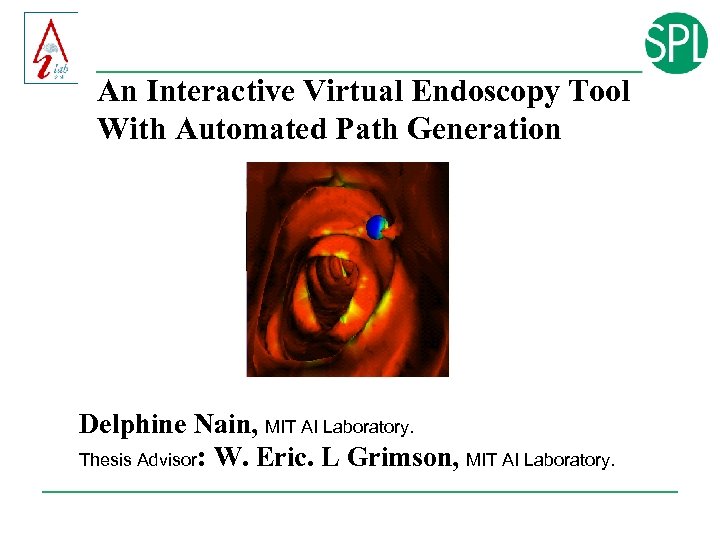 An Interactive Virtual Endoscopy Tool With Automated Path Generation Delphine Nain, MIT AI Laboratory. Thesis Advisor: W. Eric. L Grimson, MIT AI Laboratory.
An Interactive Virtual Endoscopy Tool With Automated Path Generation Delphine Nain, MIT AI Laboratory. Thesis Advisor: W. Eric. L Grimson, MIT AI Laboratory.
 Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
 Medical Motivation • Cancer is the 2 nd cause of death in the US • 43 % of people have a risk to be diagnosed with cancer – Out of those 88 % are cancer in inner organ • How can “see” inside the body to screen and cure?
Medical Motivation • Cancer is the 2 nd cause of death in the US • 43 % of people have a risk to be diagnosed with cancer – Out of those 88 % are cancer in inner organ • How can “see” inside the body to screen and cure?
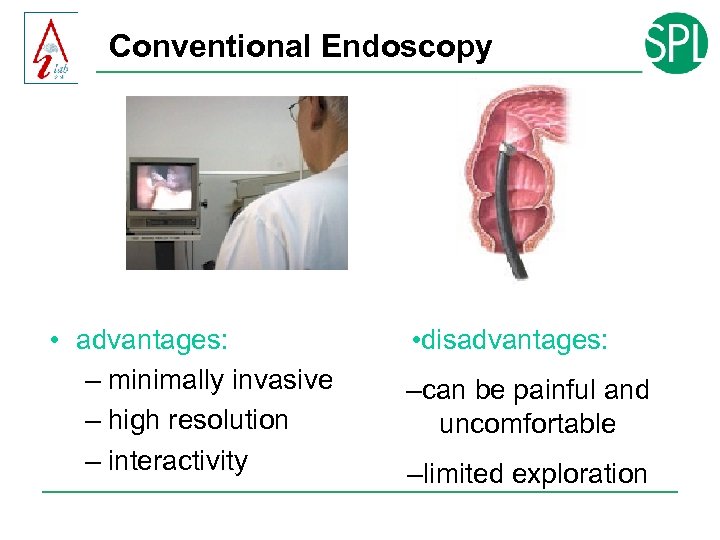 Conventional Endoscopy • advantages: – minimally invasive – high resolution – interactivity • disadvantages: –can be painful and uncomfortable –limited exploration
Conventional Endoscopy • advantages: – minimally invasive – high resolution – interactivity • disadvantages: –can be painful and uncomfortable –limited exploration
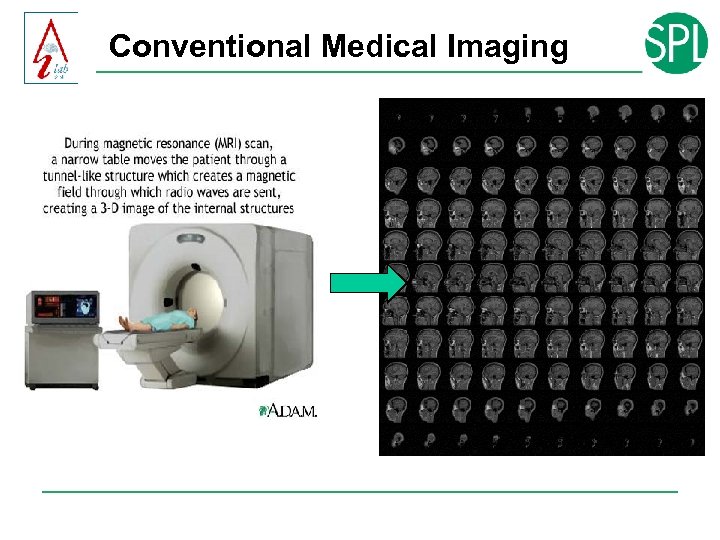 Conventional Medical Imaging
Conventional Medical Imaging
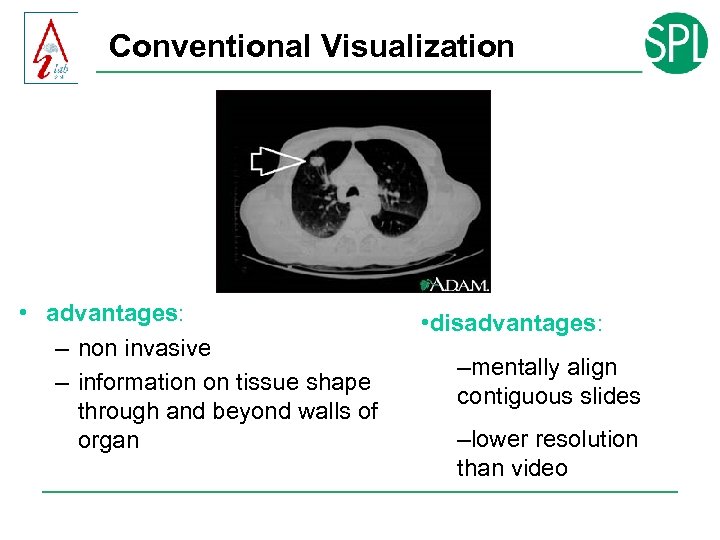 Conventional Visualization • advantages: – non invasive – information on tissue shape through and beyond walls of organ • disadvantages: –mentally align contiguous slides –lower resolution than video
Conventional Visualization • advantages: – non invasive – information on tissue shape through and beyond walls of organ • disadvantages: –mentally align contiguous slides –lower resolution than video
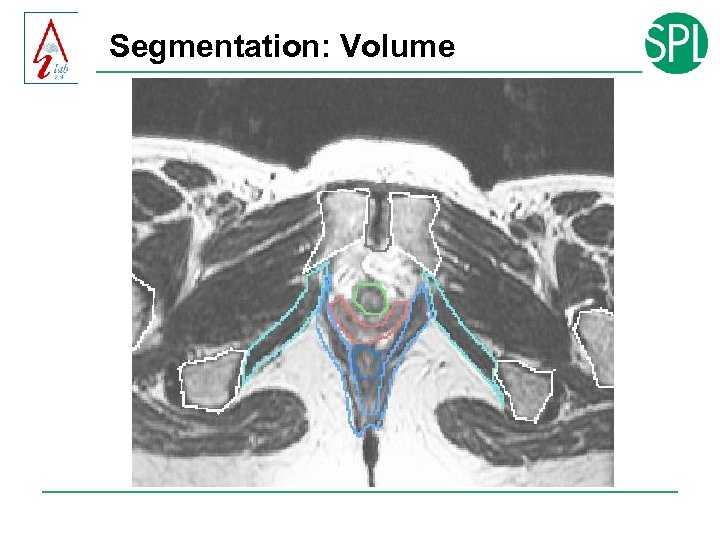 Segmentation: Volume
Segmentation: Volume
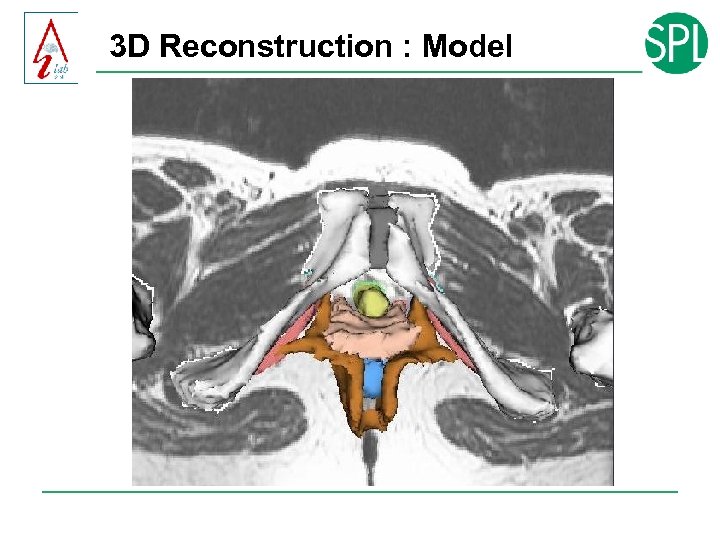 3 D Reconstruction : Model
3 D Reconstruction : Model
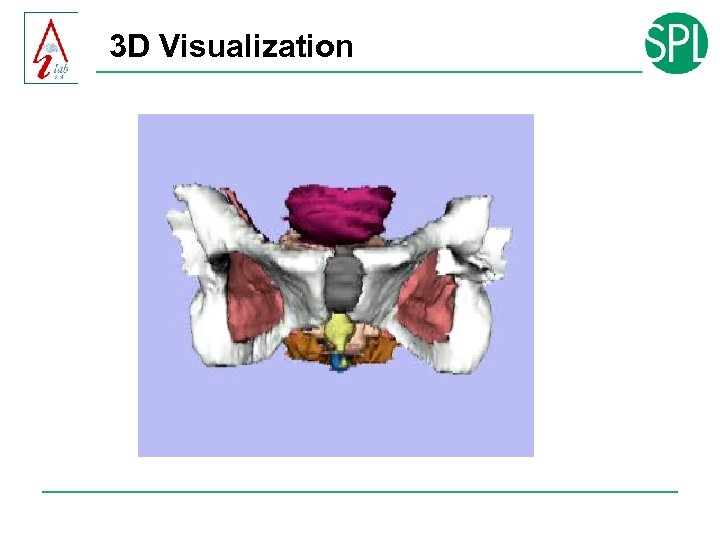
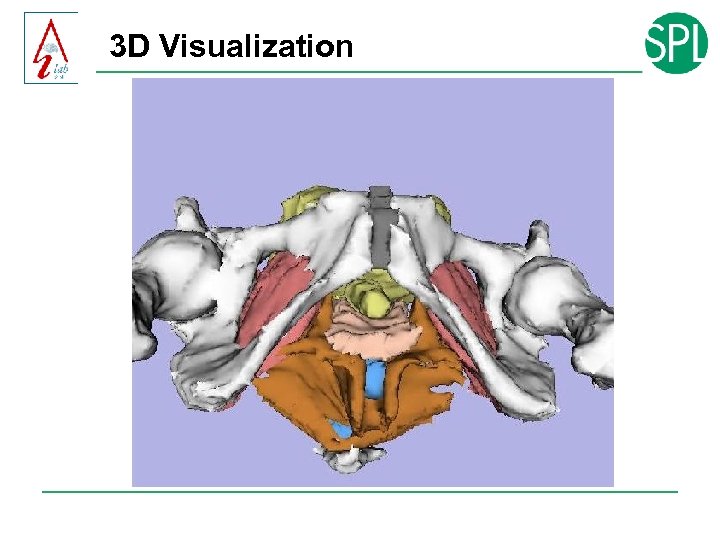 3 D Visualization
3 D Visualization
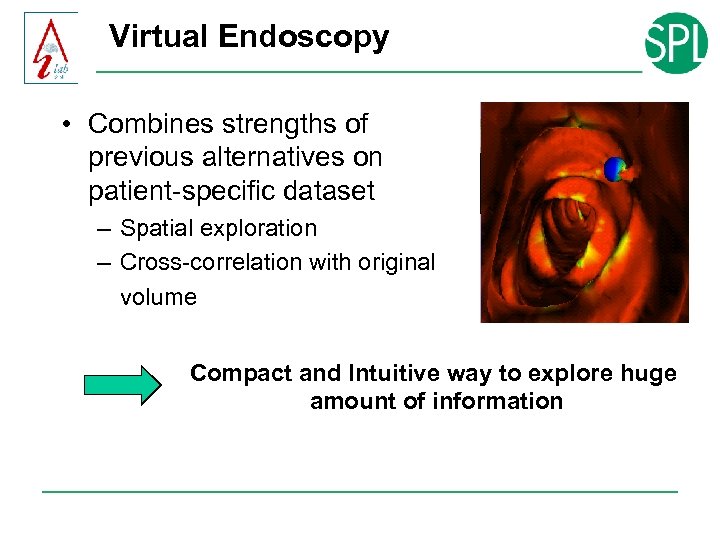 Virtual Endoscopy • Combines strengths of previous alternatives on patient-specific dataset – Spatial exploration – Cross-correlation with original volume Compact and Intuitive way to explore huge amount of information
Virtual Endoscopy • Combines strengths of previous alternatives on patient-specific dataset – Spatial exploration – Cross-correlation with original volume Compact and Intuitive way to explore huge amount of information
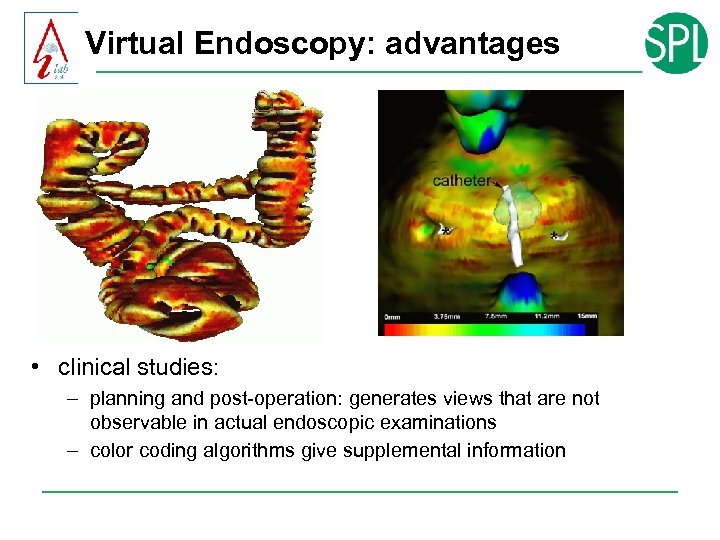 Virtual Endoscopy: advantages • clinical studies: – planning and post-operation: generates views that are not observable in actual endoscopic examinations – color coding algorithms give supplemental information
Virtual Endoscopy: advantages • clinical studies: – planning and post-operation: generates views that are not observable in actual endoscopic examinations – color coding algorithms give supplemental information
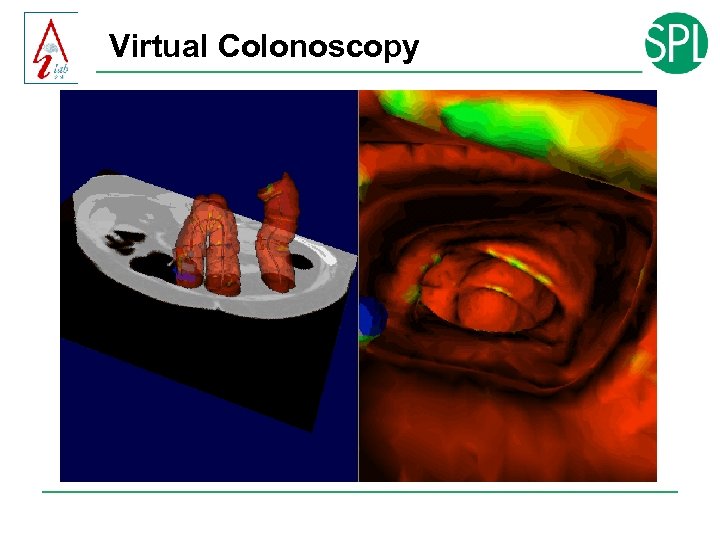 Virtual Colonoscopy
Virtual Colonoscopy
 System Requirements • Combination of Interactivity and Automation is key • Cross Reference between 3 D models and grayscale volumes
System Requirements • Combination of Interactivity and Automation is key • Cross Reference between 3 D models and grayscale volumes
 Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
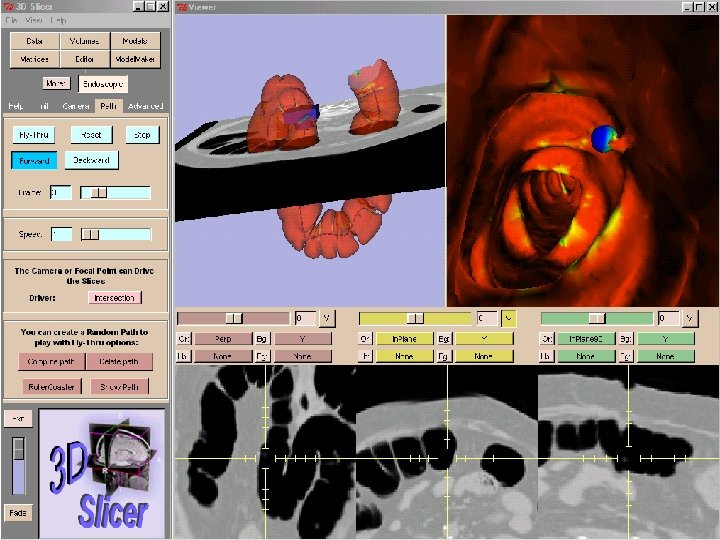 Display
Display
 Navigation Interface
Navigation Interface
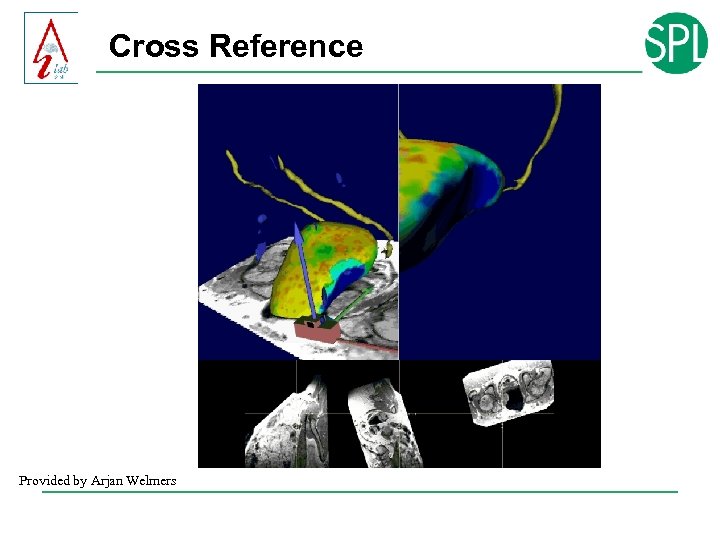 Cross Reference Provided by Arjan Welmers
Cross Reference Provided by Arjan Welmers
 Path: Update
Path: Update
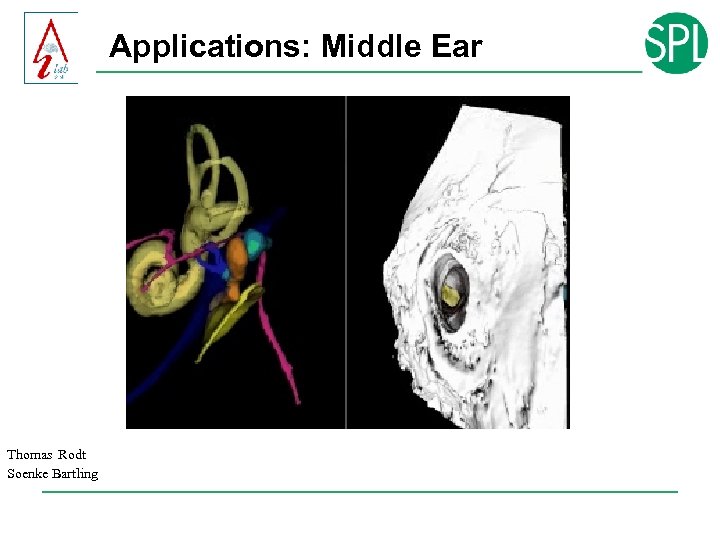 Applications: Middle Ear Thomas Rodt Soenke Bartling
Applications: Middle Ear Thomas Rodt Soenke Bartling
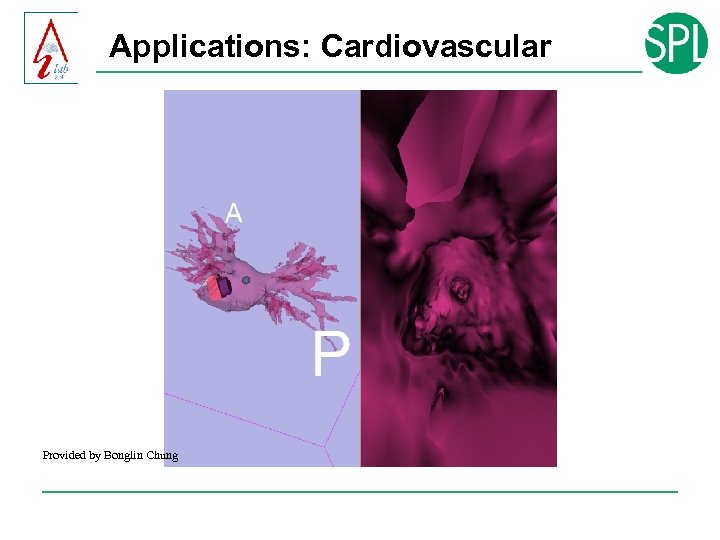 Applications: Cardiovascular Provided by Bonglin Chung
Applications: Cardiovascular Provided by Bonglin Chung
 Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
 Automated Path Planning • Goal: provide a “create path” button that produces a centerline inside a 3 D model of any topology
Automated Path Planning • Goal: provide a “create path” button that produces a centerline inside a 3 D model of any topology
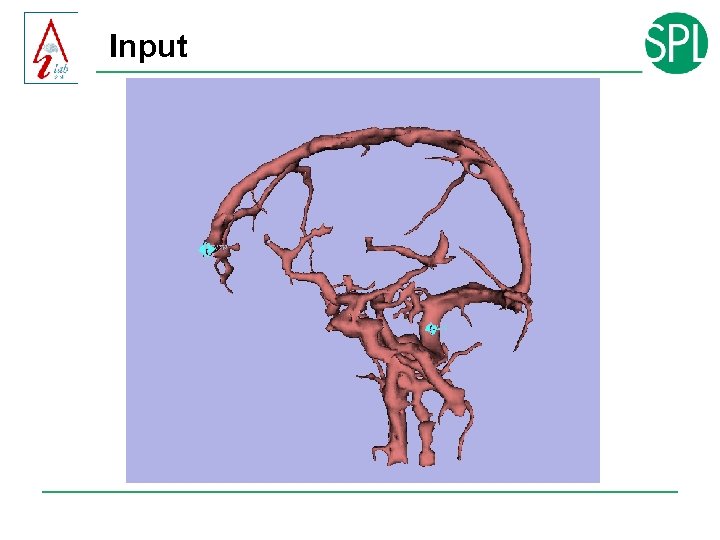 Input
Input
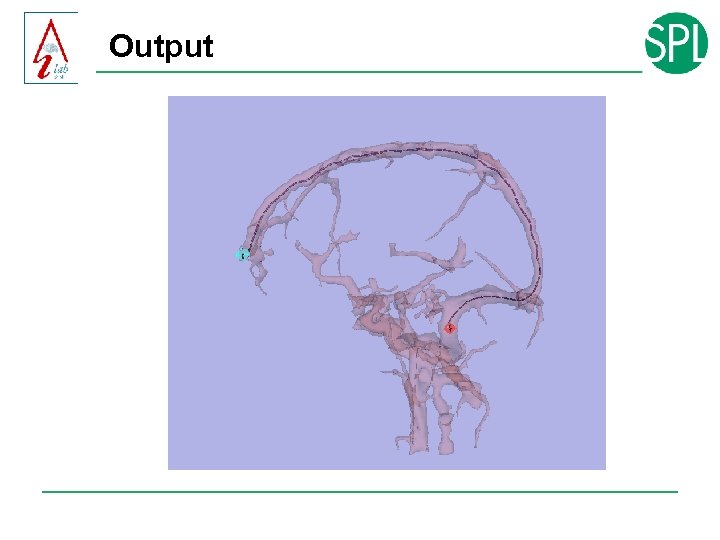 Output
Output
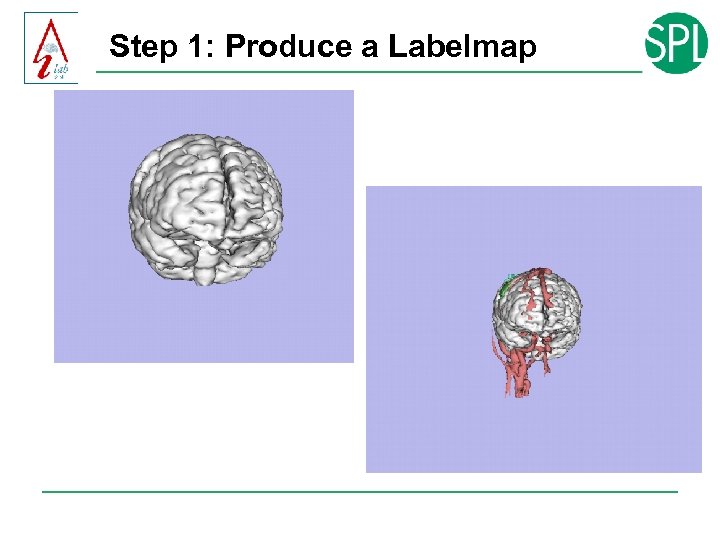 Step 1: Produce a Labelmap
Step 1: Produce a Labelmap
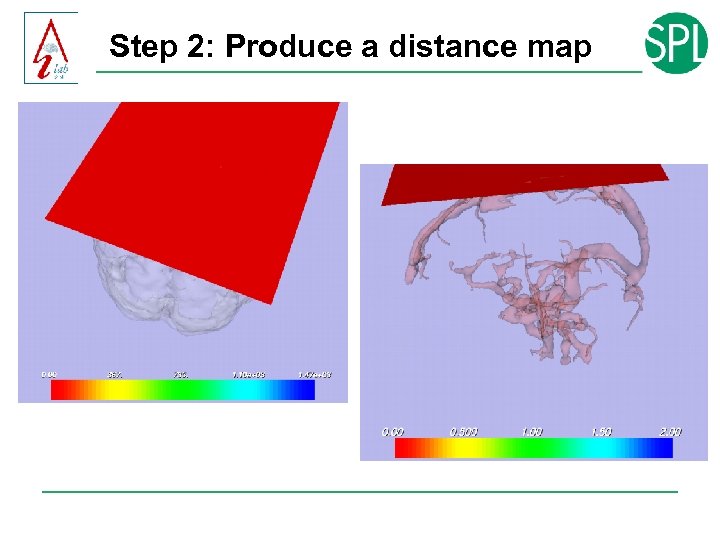 Step 2: Produce a distance map
Step 2: Produce a distance map
 Step 3: Create a Graph description of the Distance Map • Nodes are voxels inside the model • Edge weight are 1/(distance)2 from the wall of the organ
Step 3: Create a Graph description of the Distance Map • Nodes are voxels inside the model • Edge weight are 1/(distance)2 from the wall of the organ
 Step 4: Run modified Dijkstra algorithm is a single source shortest path algorithm • We use a binary heap • An optimization: keep an evolving front, stop when reach the end node
Step 4: Run modified Dijkstra algorithm is a single source shortest path algorithm • We use a binary heap • An optimization: keep an evolving front, stop when reach the end node
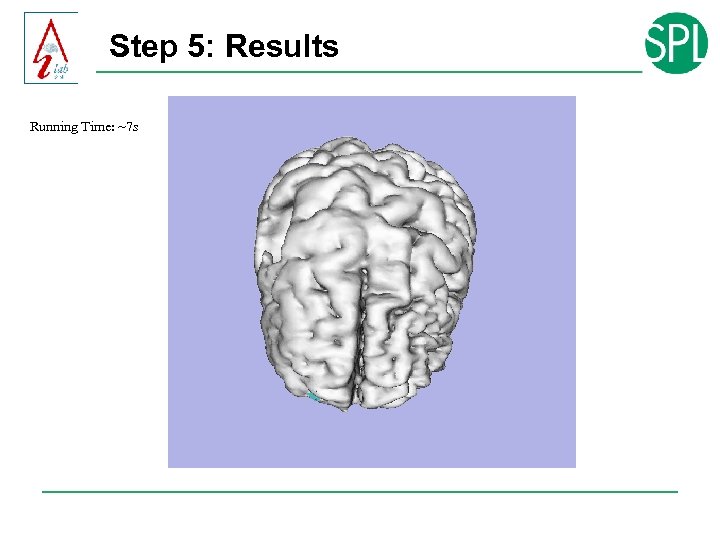 Step 5: Results Running Time: ~7 s
Step 5: Results Running Time: ~7 s
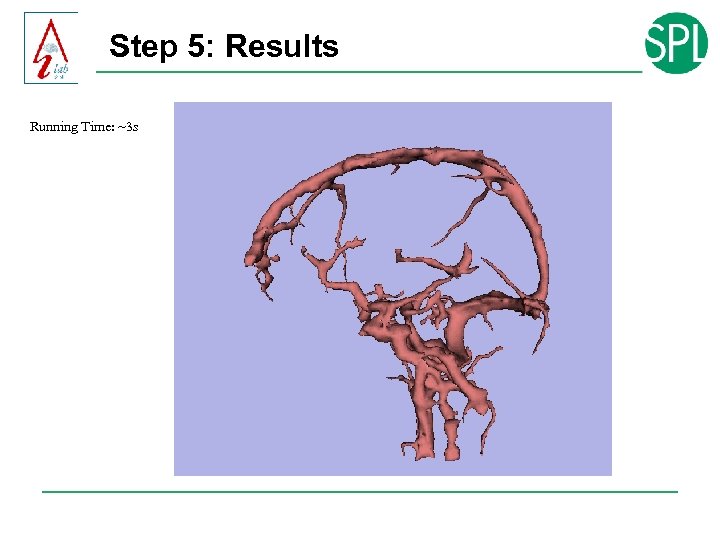 Step 5: Results Running Time: ~3 s
Step 5: Results Running Time: ~3 s
 Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
Presentation Overview • Background and Motivation • Interactive System • Central Path Planning Algorithm • Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy • Conclusion
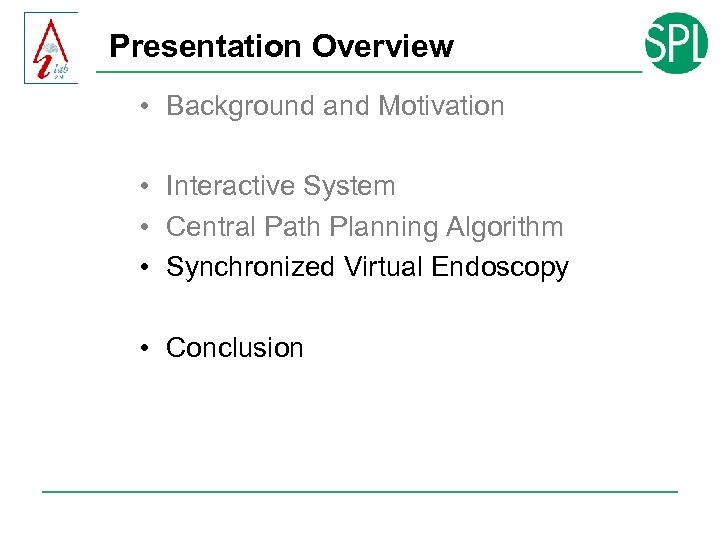
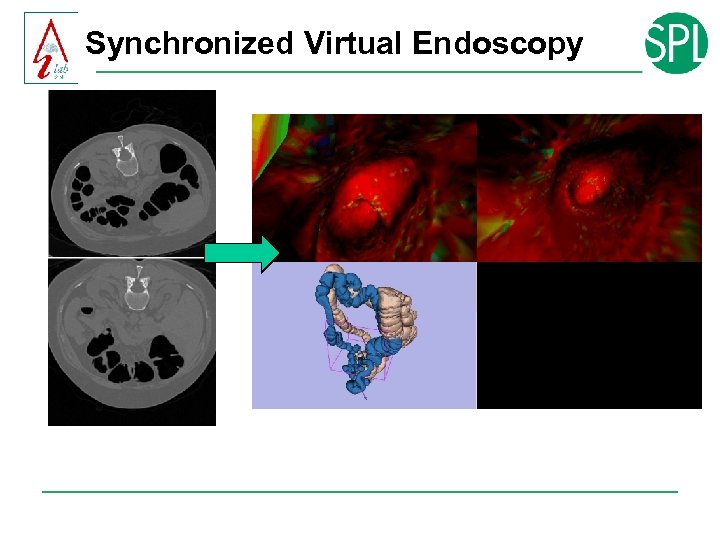
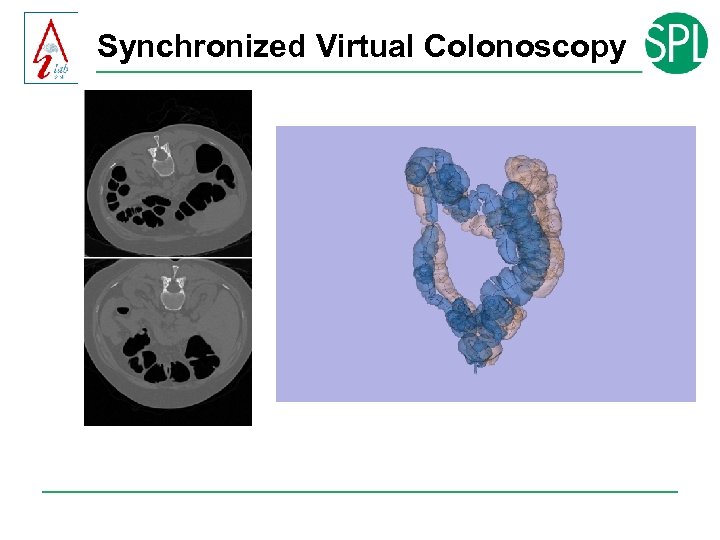 Synchronized Virtual Colonoscopy
Synchronized Virtual Colonoscopy
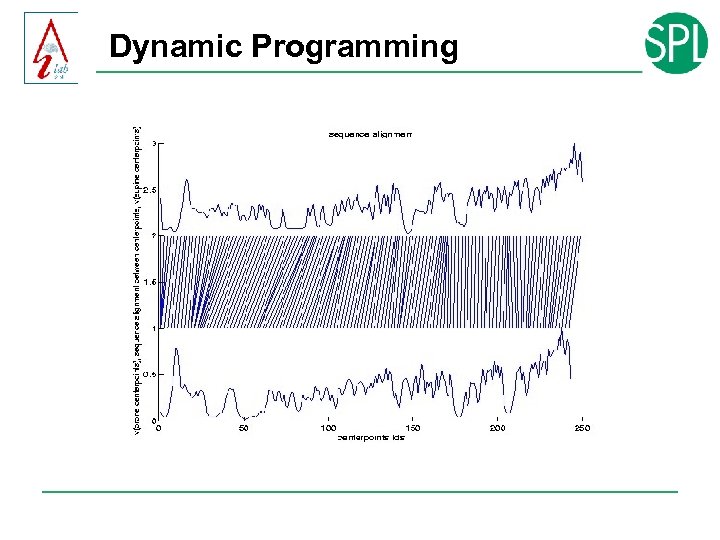 Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming
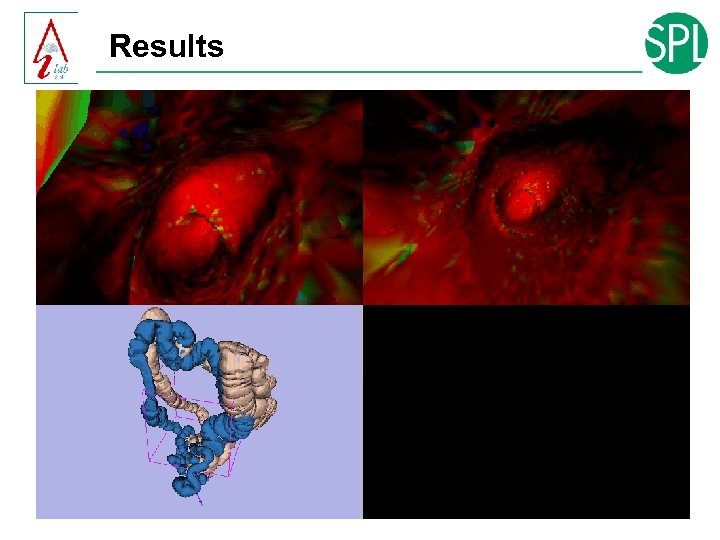 Results
Results
 Conclusion • Combination of Automation and Interactivity is key • Cross Reference is important • Synchronized Fly-Throughs is novel contribution Publication: D. Nain, S. Haker, E. Grimson, R. Kikinis “An Interactive Virtual Endoscopy Tool”, IMIVA workshop, MICCAI 2001.
Conclusion • Combination of Automation and Interactivity is key • Cross Reference is important • Synchronized Fly-Throughs is novel contribution Publication: D. Nain, S. Haker, E. Grimson, R. Kikinis “An Interactive Virtual Endoscopy Tool”, IMIVA workshop, MICCAI 2001.
 Acknowledgements • • • • Ron Kikinis Steve Haker Lauren O’Donnell David Gering Carl-Fredrik Westin Peter Everett Sandy Wells Eric Cosman Polina Golland Soenke Bartling John Fisher Mike Halle Ferenc Jolesz
Acknowledgements • • • • Ron Kikinis Steve Haker Lauren O’Donnell David Gering Carl-Fredrik Westin Peter Everett Sandy Wells Eric Cosman Polina Golland Soenke Bartling John Fisher Mike Halle Ferenc Jolesz
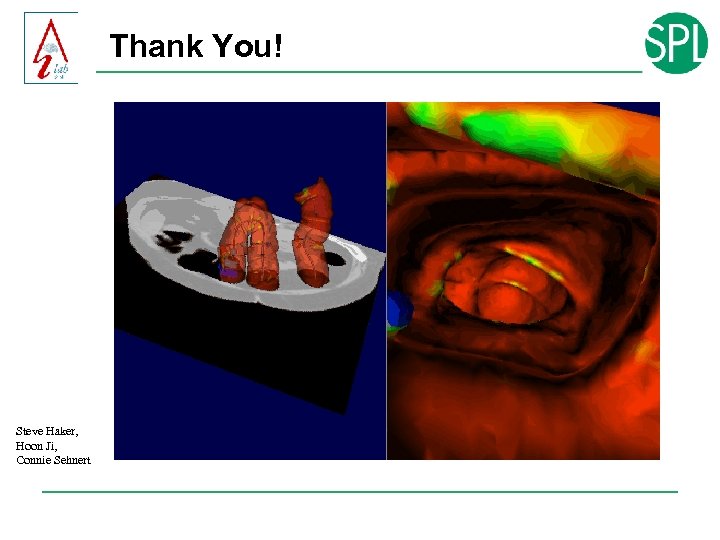 Thank You! Steve Haker, Hoon Ji, Connie Sehnert
Thank You! Steve Haker, Hoon Ji, Connie Sehnert
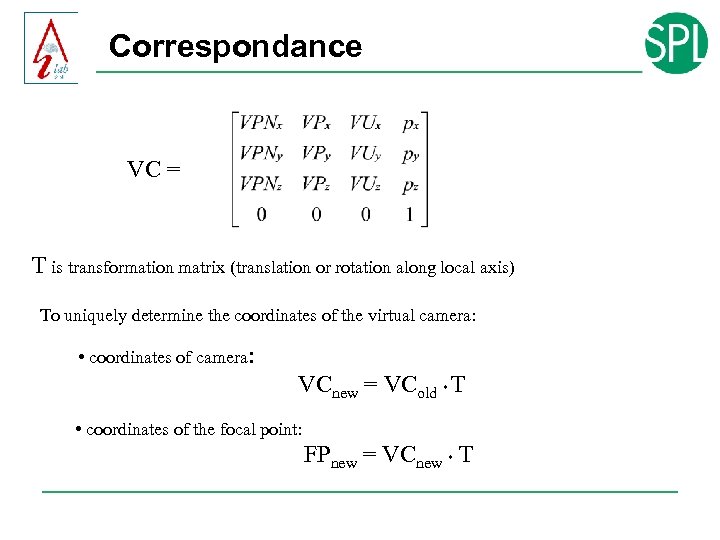 Correspondance VC = T is transformation matrix (translation or rotation along local axis) To uniquely determine the coordinates of the virtual camera: • coordinates of camera: VCnew = VCold * T • coordinates of the focal point: FPnew = VCnew * T
Correspondance VC = T is transformation matrix (translation or rotation along local axis) To uniquely determine the coordinates of the virtual camera: • coordinates of camera: VCnew = VCold * T • coordinates of the focal point: FPnew = VCnew * T
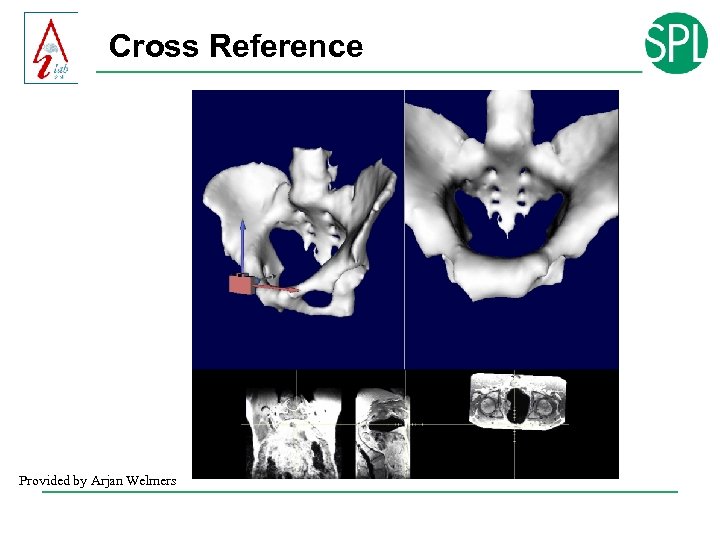 Cross Reference Provided by Arjan Welmers
Cross Reference Provided by Arjan Welmers
 3 D Visualization
3 D Visualization
 Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy
Synchronized Virtual Endoscopy


