4128c205cb78d0708ff6732dd862cbd2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 An Infrastructure for Agent Service Composition in Open Environments Kenichi Yoshimura 1, Lin Padgham 1, and Wei Liu 2 1 2 RMIT University The University of Western Australia
An Infrastructure for Agent Service Composition in Open Environments Kenichi Yoshimura 1, Lin Padgham 1, and Wei Liu 2 1 2 RMIT University The University of Western Australia
 Outline n n n Motivation (Semantic Web and Agentcities) Communication in an Open Environment (FIPA-JACK) Service Composition v. s. Teamwork A Service Composition Tool (ASKIT) Conclusion and future work What’s next
Outline n n n Motivation (Semantic Web and Agentcities) Communication in an Open Environment (FIPA-JACK) Service Composition v. s. Teamwork A Service Composition Tool (ASKIT) Conclusion and future work What’s next
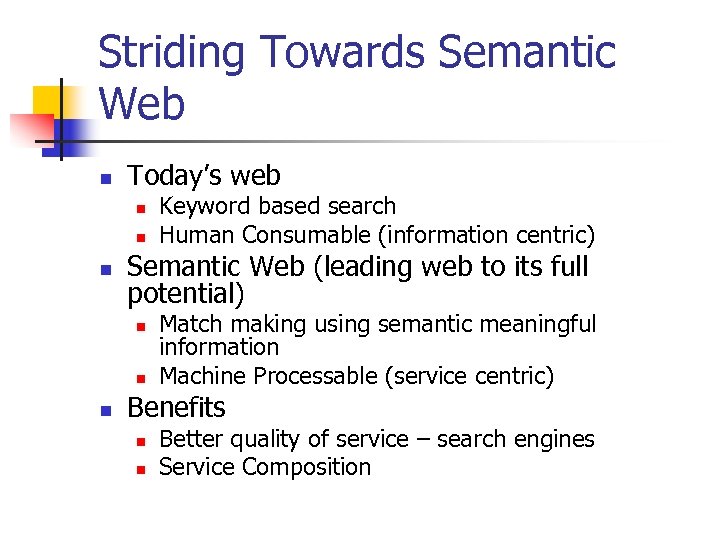 Striding Towards Semantic Web n Today’s web n n n Semantic Web (leading web to its full potential) n n n Keyword based search Human Consumable (information centric) Match making using semantic meaningful information Machine Processable (service centric) Benefits n n Better quality of service – search engines Service Composition
Striding Towards Semantic Web n Today’s web n n n Semantic Web (leading web to its full potential) n n n Keyword based search Human Consumable (information centric) Match making using semantic meaningful information Machine Processable (service centric) Benefits n n Better quality of service – search engines Service Composition
 Semantic Web: Not an easy move Content Providers – Static website owners (annotate content using ontologies) n Service Providers – Companies and Government (deploy HTML form based services into Web services) n Service Consumers (able to search and compose services) Who are going to go through all this trouble and become early Semantic Web Adopters? n
Semantic Web: Not an easy move Content Providers – Static website owners (annotate content using ontologies) n Service Providers – Companies and Government (deploy HTML form based services into Web services) n Service Consumers (able to search and compose services) Who are going to go through all this trouble and become early Semantic Web Adopters? n
 Agentcities Project n n n Agentcities is a worldwide open network of platforms hosting diverse agent based services. It is also a test-bed to help realise the commercial and research potential of agent based applications The ultimate aim is to n n www. agentcities. org and www. agentcities. net enable the dynamic, intelligent and autonomous composition of services to achieve user and business goals. A working network of agent-based services based on Foundation for Intelligent Physical Agents (FIPA) standards
Agentcities Project n n n Agentcities is a worldwide open network of platforms hosting diverse agent based services. It is also a test-bed to help realise the commercial and research potential of agent based applications The ultimate aim is to n n www. agentcities. org and www. agentcities. net enable the dynamic, intelligent and autonomous composition of services to achieve user and business goals. A working network of agent-based services based on Foundation for Intelligent Physical Agents (FIPA) standards
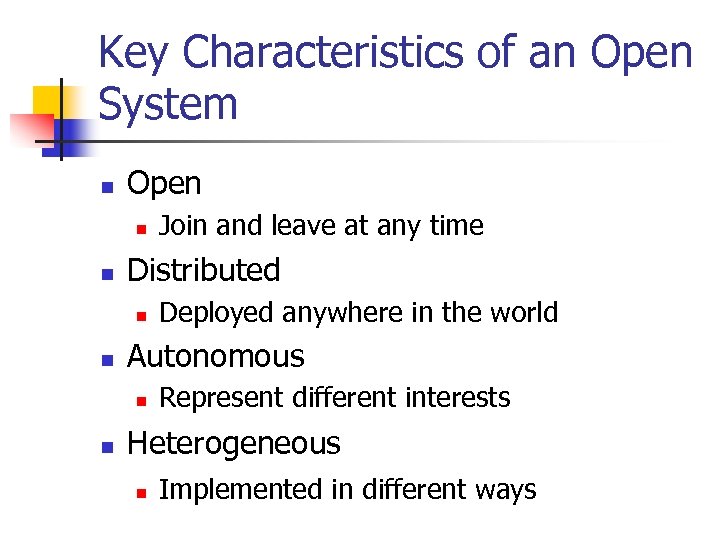 Key Characteristics of an Open System n Open n n Distributed n n Deployed anywhere in the world Autonomous n n Join and leave at any time Represent different interests Heterogeneous n Implemented in different ways
Key Characteristics of an Open System n Open n n Distributed n n Deployed anywhere in the world Autonomous n n Join and leave at any time Represent different interests Heterogeneous n Implemented in different ways
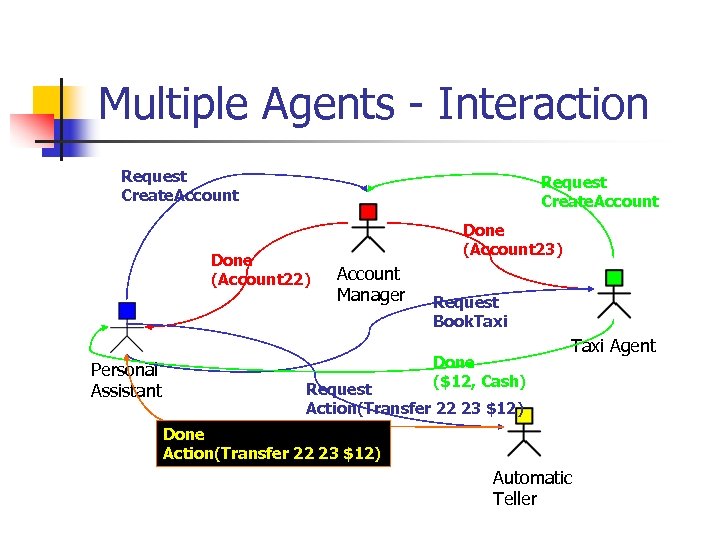 Multiple Agents - Interaction Request Create. Account Done (Account 22) Personal Assistant Done (Account 23) Account Manager Request Book. Taxi Done ($12, Cash) Taxi Agent Request Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Done Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Automatic Teller
Multiple Agents - Interaction Request Create. Account Done (Account 22) Personal Assistant Done (Account 23) Account Manager Request Book. Taxi Done ($12, Cash) Taxi Agent Request Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Done Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Automatic Teller
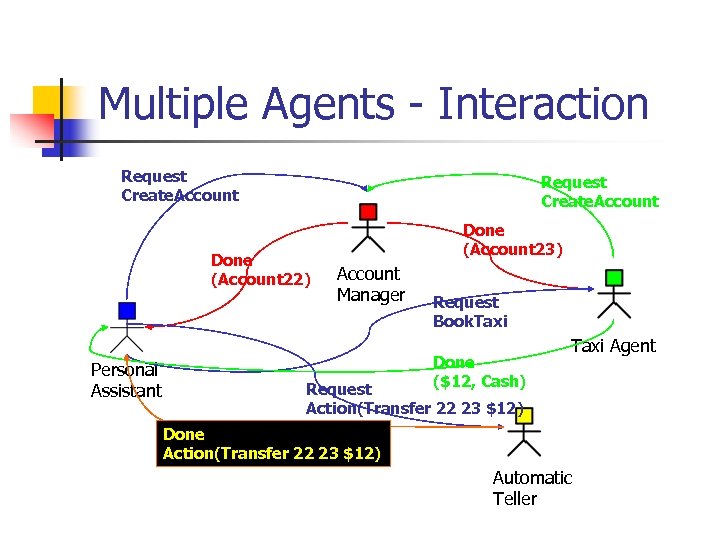 Multiple Agents - Interaction Request Create. Account Done (Account 22) Personal Assistant Done (Account 23) Account Manager Request Book. Taxi Done ($12, Cash) Taxi Agent Request Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Done Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Automatic Teller
Multiple Agents - Interaction Request Create. Account Done (Account 22) Personal Assistant Done (Account 23) Account Manager Request Book. Taxi Done ($12, Cash) Taxi Agent Request Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Done Action(Transfer 22 23 $12) Automatic Teller
 Agent Infrastructures Used by Agentcites Platforms n FIPA Compliant Agent Development Tools (Open Source) n n n JADE FIPA-OS April Agent Platform Zeus BDI Agent Development Tools n JACK (Commercial) - Made FIPA Compliant through FIPA-JACK
Agent Infrastructures Used by Agentcites Platforms n FIPA Compliant Agent Development Tools (Open Source) n n n JADE FIPA-OS April Agent Platform Zeus BDI Agent Development Tools n JACK (Commercial) - Made FIPA Compliant through FIPA-JACK
 In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Use the agreed syntax Follow agreed semantic of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Use the agreed syntax Follow agreed semantic of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
 In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Use the agreed syntax Follow agreed semantic Content Language of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Use the agreed syntax Follow agreed semantic Content Language of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
 In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Use the agreed syntax Communicative Act Follow agreed semantic Content Language of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Use the agreed syntax Communicative Act Follow agreed semantic Content Language of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
 In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Protocol Use the agreed syntax Communicative Act Follow agreed semantic Content Language of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
In order to communicate n n Use same vocabulary and have the same perception of the world Protocol Use the agreed syntax Communicative Act Follow agreed semantic Content Language of communicative act Ontology Follow agreed sequence of messages
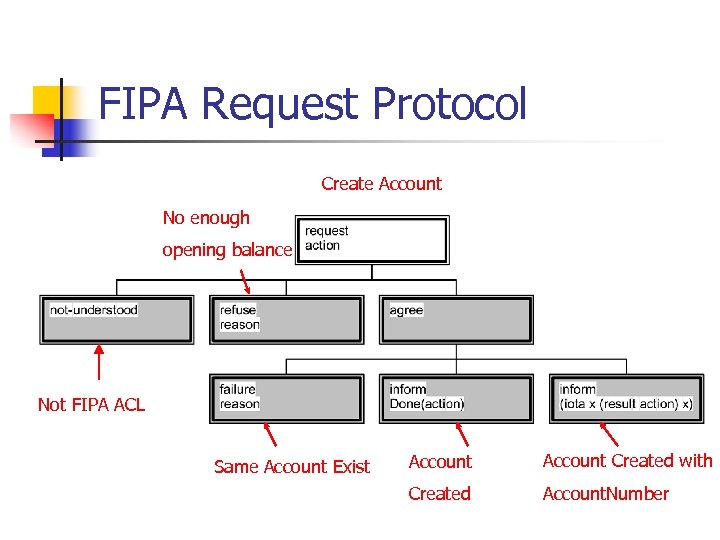 FIPA Request Protocol Create Account No enough opening balance Not FIPA ACL Same Account Exist Account Created with Created Account. Number
FIPA Request Protocol Create Account No enough opening balance Not FIPA ACL Same Account Exist Account Created with Created Account. Number
 ACL Performatives n n n Inform Request QUERY_REF Refuse Failure …… many more
ACL Performatives n n n Inform Request QUERY_REF Refuse Failure …… many more
 FIPA ACL Message (Example) Content Language: SL (request : sender (agent-identifier : name x) : receiver (set (agent-identifer : name y)) : content ( (action (agent-identifier : name y) (create. Client : personal. Info (Personal. Info : lastname Liu : agent. Id( … ) …))) : ontology urn: x-acnet: EPFL: ontology: banking: v 2. 0 : protocol fipa-request)
FIPA ACL Message (Example) Content Language: SL (request : sender (agent-identifier : name x) : receiver (set (agent-identifer : name y)) : content ( (action (agent-identifier : name y) (create. Client : personal. Info (Personal. Info : lastname Liu : agent. Id( … ) …))) : ontology urn: x-acnet: EPFL: ontology: banking: v 2. 0 : protocol fipa-request)
 Ontology and Content FIPA Agent Mangement Ontology (request : sender (agent-identifier : name x) : receiver (set (agent-identifer : name y)) : content ( (action (agent-identifier : name y) (create. Client : personal. Info (Personal. Info : lastname Liu : agent. Id( … ) …))) : ontology urn: x-acnet: EPFL: ontology: banking: v 2. 0 Domain Ontologies : protocol fipa-request)
Ontology and Content FIPA Agent Mangement Ontology (request : sender (agent-identifier : name x) : receiver (set (agent-identifer : name y)) : content ( (action (agent-identifier : name y) (create. Client : personal. Info (Personal. Info : lastname Liu : agent. Id( … ) …))) : ontology urn: x-acnet: EPFL: ontology: banking: v 2. 0 Domain Ontologies : protocol fipa-request)
 Composite Service and Teamwork n n n Execution of composite services involves unconscious collaboration of heterogenous agents. Similar characteristics desirable such as parallel execution and synchronisation of activities. Observation of commitments between a user agent and service provider agents - however, traditional models of teamwork are typically too restrictive in open environments. (E. g. Joint Intentions, Joint Goals and mutual beliefs)
Composite Service and Teamwork n n n Execution of composite services involves unconscious collaboration of heterogenous agents. Similar characteristics desirable such as parallel execution and synchronisation of activities. Observation of commitments between a user agent and service provider agents - however, traditional models of teamwork are typically too restrictive in open environments. (E. g. Joint Intentions, Joint Goals and mutual beliefs)
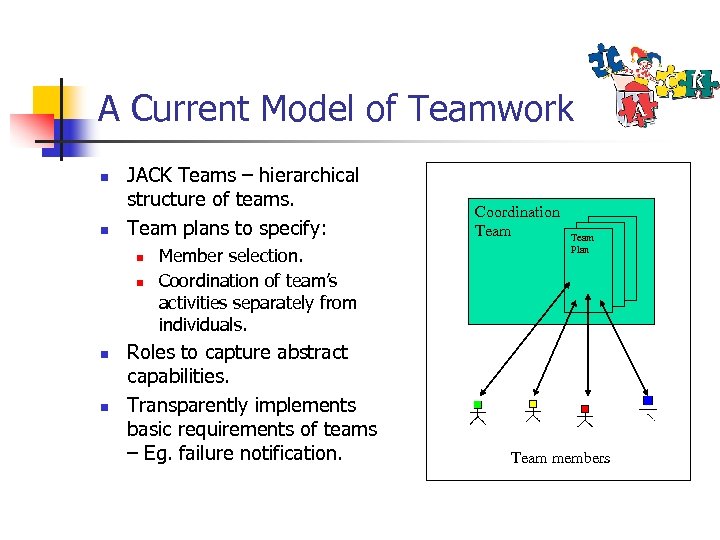 A Current Model of Teamwork n n JACK Teams – hierarchical structure of teams. Team plans to specify: n n Member selection. Coordination of team’s activities separately from individuals. Roles to capture abstract capabilities. Transparently implements basic requirements of teams – Eg. failure notification. Coordination Team Plan Team members
A Current Model of Teamwork n n JACK Teams – hierarchical structure of teams. Team plans to specify: n n Member selection. Coordination of team’s activities separately from individuals. Roles to capture abstract capabilities. Transparently implements basic requirements of teams – Eg. failure notification. Coordination Team Plan Team members
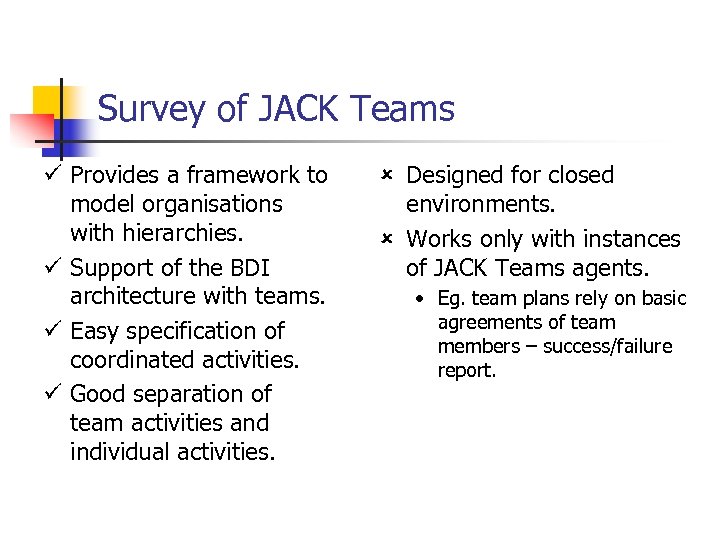 Survey of JACK Teams ü Provides a framework to model organisations with hierarchies. ü Support of the BDI architecture with teams. ü Easy specification of coordinated activities. ü Good separation of team activities and individual activities. û Designed for closed environments. û Works only with instances of JACK Teams agents. • Eg. team plans rely on basic agreements of team members – success/failure report.
Survey of JACK Teams ü Provides a framework to model organisations with hierarchies. ü Support of the BDI architecture with teams. ü Easy specification of coordinated activities. ü Good separation of team activities and individual activities. û Designed for closed environments. û Works only with instances of JACK Teams agents. • Eg. team plans rely on basic agreements of team members – success/failure report.
 Mapping Teams to Services n Roles and service types n n Represent a composite service as a team plan. n n n Both captures abstract capabilities of an entity. Reuse existing facilities such as parallel execution and synchronisation. Abstractly describe requirements by roles (i. e. service types). Additional layer (proxy agents) encapsulating service agents into JACK Team entities: n n Making unreliable services consistent from the team’s view – a selected services being unavailable, failures in interactions, and monitoring time-out for network related failures. Managing interaction protocols and content languages.
Mapping Teams to Services n Roles and service types n n Represent a composite service as a team plan. n n n Both captures abstract capabilities of an entity. Reuse existing facilities such as parallel execution and synchronisation. Abstractly describe requirements by roles (i. e. service types). Additional layer (proxy agents) encapsulating service agents into JACK Team entities: n n Making unreliable services consistent from the team’s view – a selected services being unavailable, failures in interactions, and monitoring time-out for network related failures. Managing interaction protocols and content languages.
 Extending Team Plans n n BDI architectures enable recovery from failures by selecting different plans that achieves the same goal. Establish() method allows dynamic sub-teams selection from a list of potential agents (role containers). JACK team plans have strong notions of failure. When a team plan fails, why not re-execute with a different combination of agents? n Potentially avoids computational redundancies. n Additional level of backtracking.
Extending Team Plans n n BDI architectures enable recovery from failures by selecting different plans that achieves the same goal. Establish() method allows dynamic sub-teams selection from a list of potential agents (role containers). JACK team plans have strong notions of failure. When a team plan fails, why not re-execute with a different combination of agents? n Potentially avoids computational redundancies. n Additional level of backtracking.
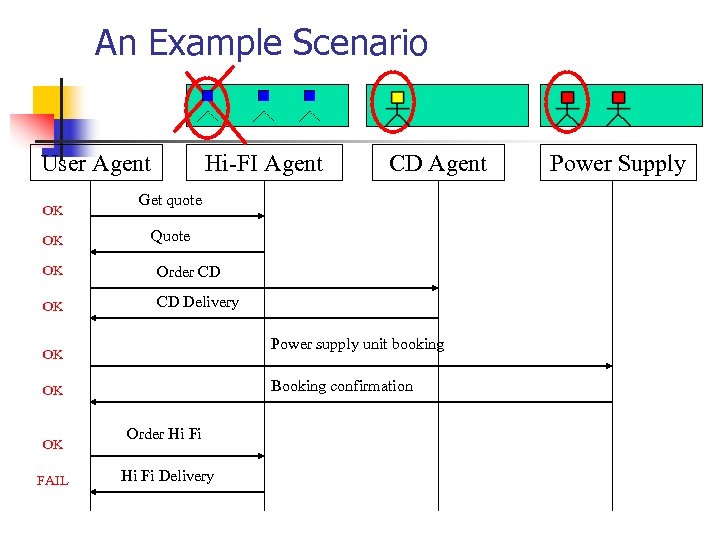 An Example Scenario User Agent OK OK Hi-FI Agent CD Agent Get quote Quote OK Order CD OK CD Delivery Power supply unit booking OK Booking confirmation OK OK FAIL Order Hi Fi Delivery Power Supply
An Example Scenario User Agent OK OK Hi-FI Agent CD Agent Get quote Quote OK Order CD OK CD Delivery Power supply unit booking OK Booking confirmation OK OK FAIL Order Hi Fi Delivery Power Supply
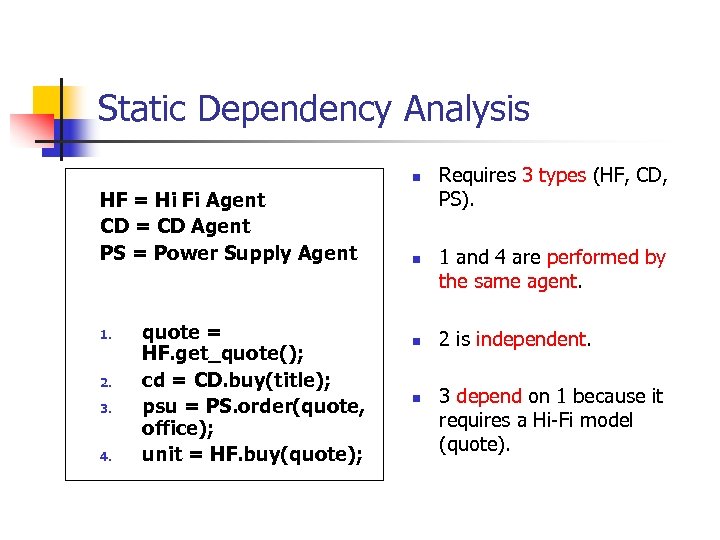 Static Dependency Analysis n HF = Hi Fi Agent CD = CD Agent PS = Power Supply Agent 1. 2. 3. 4. quote = HF. get_quote(); cd = CD. buy(title); psu = PS. order(quote, office); unit = HF. buy(quote); n n n Requires 3 types (HF, CD, PS). 1 and 4 are performed by the same agent. 2 is independent. 3 depend on 1 because it requires a Hi-Fi model (quote).
Static Dependency Analysis n HF = Hi Fi Agent CD = CD Agent PS = Power Supply Agent 1. 2. 3. 4. quote = HF. get_quote(); cd = CD. buy(title); psu = PS. order(quote, office); unit = HF. buy(quote); n n n Requires 3 types (HF, CD, PS). 1 and 4 are performed by the same agent. 2 is independent. 3 depend on 1 because it requires a Hi-Fi model (quote).
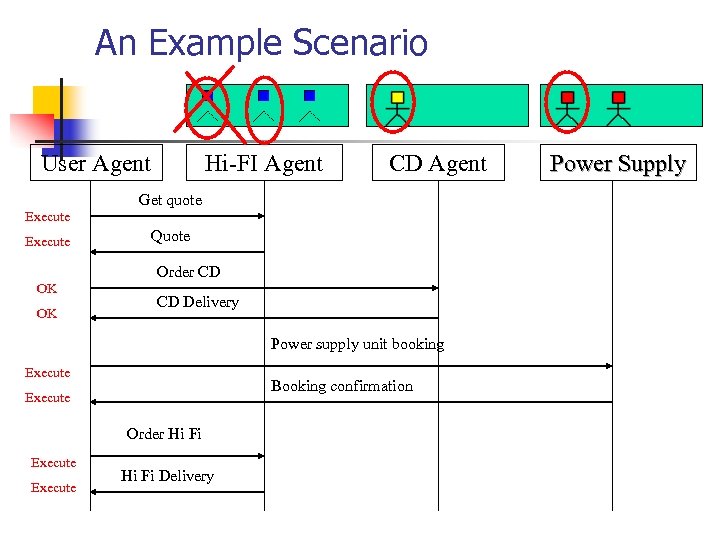 An Example Scenario User Agent Hi-FI Agent CD Agent Get quote Execute Quote Order CD OK OK CD Delivery Power supply unit booking Execute Booking confirmation Execute Order Hi Fi Execute Hi Fi Delivery Power Supply
An Example Scenario User Agent Hi-FI Agent CD Agent Get quote Execute Quote Order CD OK OK CD Delivery Power supply unit booking Execute Booking confirmation Execute Order Hi Fi Execute Hi Fi Delivery Power Supply
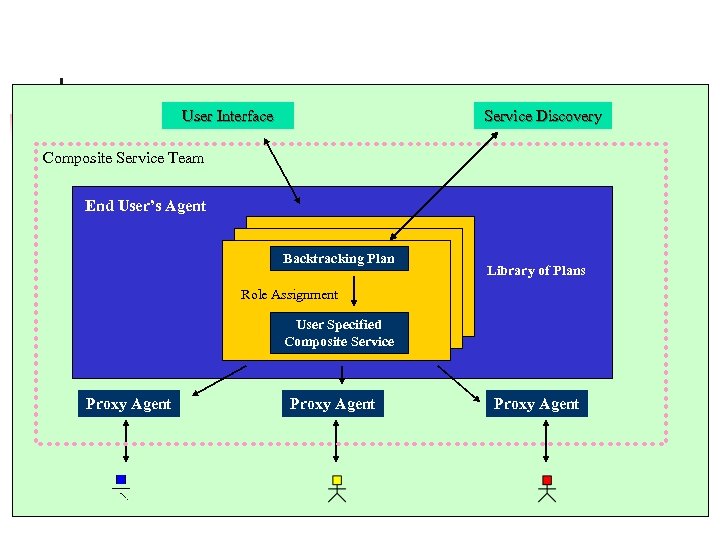 Putting Interface. Together. . . User All Service Discovery Composite Service Team End User’s Agent Backtracking Plan Library of Plans Role Assignment User Specified Composite Service Proxy Agent
Putting Interface. Together. . . User All Service Discovery Composite Service Team End User’s Agent Backtracking Plan Library of Plans Role Assignment User Specified Composite Service Proxy Agent
 What’s ASKIT? (Agent Service Komposition Interface Tool) (RMIT) n n n A demonstration system. Demonstrate service composition – reuse existing services. A tool that enables people with limited programming experience compose customised services as easy as browsing information on the Internet. No knowledge of open environments required. Viewing a composite service as a loose form of teamwork. The use of a goal directed BDI framework and study suitability of an existing model of teamwork for open environments.
What’s ASKIT? (Agent Service Komposition Interface Tool) (RMIT) n n n A demonstration system. Demonstrate service composition – reuse existing services. A tool that enables people with limited programming experience compose customised services as easy as browsing information on the Internet. No knowledge of open environments required. Viewing a composite service as a loose form of teamwork. The use of a goal directed BDI framework and study suitability of an existing model of teamwork for open environments.
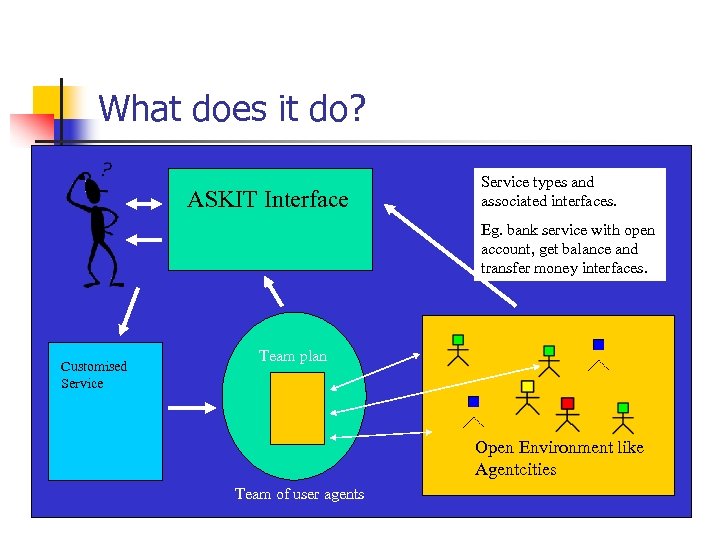 What does it do? ASKIT Interface Service types and associated interfaces. Eg. bank service with open account, get balance and transfer money interfaces. Customised Service Team plan Open Environment like Agentcities Team of user agents
What does it do? ASKIT Interface Service types and associated interfaces. Eg. bank service with open account, get balance and transfer money interfaces. Customised Service Team plan Open Environment like Agentcities Team of user agents
 Implementation issues: n n n Failure management (eg. request being rejected) Interaction with unreliable services (eg. services disappearing) Service discovery Interaction protocols and content languages Message delivery and failure recovery
Implementation issues: n n n Failure management (eg. request being rejected) Interaction with unreliable services (eg. services disappearing) Service discovery Interaction protocols and content languages Message delivery and failure recovery
 Conclusion n An infrastructure n n n Enables user-friendly service composition Implements service composition successfully using simple hierarchical teamworks Focus on flexibility in the control flow of services and robustness in an open environment
Conclusion n An infrastructure n n n Enables user-friendly service composition Implements service composition successfully using simple hierarchical teamworks Focus on flexibility in the control flow of services and robustness in an open environment
 Issues and Future Work n Service Description and Dynamic Discovery n n n Represent services so that we can automate the proxy agents generation Analysis of preconditions and postconditions of services What’s the right level of commitments of team members in open environments?
Issues and Future Work n Service Description and Dynamic Discovery n n n Represent services so that we can automate the proxy agents generation Analysis of preconditions and postconditions of services What’s the right level of commitments of team members in open environments?
 Agentcities Project www. agentcities. org and www. agentcities. net n Agentcities funding finishes in Oct 2003. n What happened to Agentcities network support? n Open. Net initiative is to keep the network alive. n More support on Web Services standard, SOAP, WSDL, UDDI.
Agentcities Project www. agentcities. org and www. agentcities. net n Agentcities funding finishes in Oct 2003. n What happened to Agentcities network support? n Open. Net initiative is to keep the network alive. n More support on Web Services standard, SOAP, WSDL, UDDI.
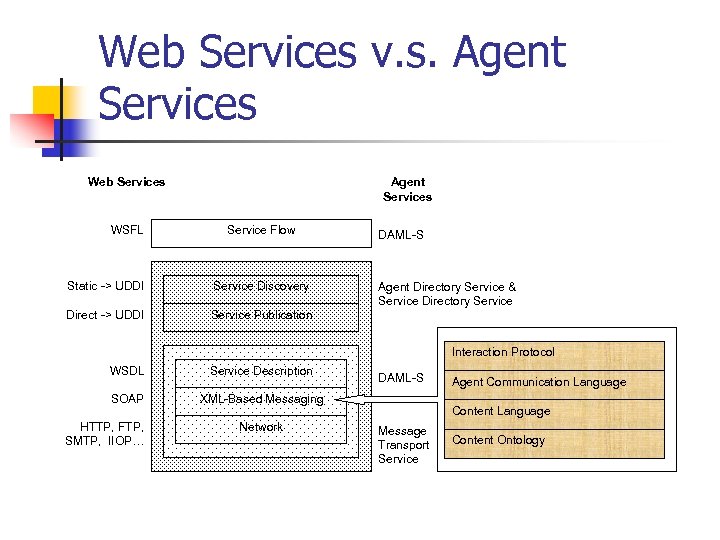 Web Services v. s. Agent Services Web Services WSFL Agent Services Service Flow Static -> UDDI Service Discovery Direct -> UDDI Service Publication DAML-S Agent Directory Service & Service Directory Service Interaction Protocol WSDL Service Description SOAP XML-Based Messaging HTTP, FTP, SMTP, IIOP… Network DAML-S Agent Communication Language Content Language Message Transport Service Content Ontology
Web Services v. s. Agent Services Web Services WSFL Agent Services Service Flow Static -> UDDI Service Discovery Direct -> UDDI Service Publication DAML-S Agent Directory Service & Service Directory Service Interaction Protocol WSDL Service Description SOAP XML-Based Messaging HTTP, FTP, SMTP, IIOP… Network DAML-S Agent Communication Language Content Language Message Transport Service Content Ontology
 Resources n ASKIT is unreliably available at http: //agentcities. cs. rmit. edu. au/agentcities: 7198: lo gin. jsp n FIPA JACK – a plug-in for JACK Intelligent Agents for FIPA standard compliancy http: //www. cs. rmit. edu. au/agents/protocols
Resources n ASKIT is unreliably available at http: //agentcities. cs. rmit. edu. au/agentcities: 7198: lo gin. jsp n FIPA JACK – a plug-in for JACK Intelligent Agents for FIPA standard compliancy http: //www. cs. rmit. edu. au/agents/protocols
 Acknowledgement n n n ASKIT project associates: Antony Iorio, Richard Jones, David Shepherdson, Andrew Lucas, Ralph Rönnquist and Jeff Schultz. Thanks to James Harland, Michael Winikoff, and Ian Mathieson for useful discussion and feedbacks! Thanks to Kenichi for the ASKIT slides!
Acknowledgement n n n ASKIT project associates: Antony Iorio, Richard Jones, David Shepherdson, Andrew Lucas, Ralph Rönnquist and Jeff Schultz. Thanks to James Harland, Michael Winikoff, and Ian Mathieson for useful discussion and feedbacks! Thanks to Kenichi for the ASKIT slides!
 Questions
Questions


