779a5b2f1aa4aa4b1fa8dee8de83e29c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

An IIT Kanpur / Media Lab Asia initiative BRi. CS Build Robots Create Science BRi. CS team, IIT Kanpur Amitabha Mukerjee with Vibhanshu Abhishek, Deepak Agarwal, Deepak Arzare , Avishek Banerjee, Manish Maheswari, Manu Prakash, Gaurav Sharma, Nikhil Sinha, Sarala Verma, and about 30 other BRi. CSters worldwide

Learning through Design • Moving away from Rote Learning • Problem Solving : DESIGN • Manipulatives / Functioning Models Solar robot, Aditi Mallya School Bangalore, December 2001
MYTH: disembodied mind § The Myth: § Learning takes place in the mind § The body is the placid host § Digital Consequences § Computers are boxes containing disembodied minds § Learning in the mind by direct interaction with the computer

Philosophy § Western tradition § Rudolf Carnap’s “remembering as similar” – sensory models to language – ideas = public language. § Indian tradition § Perception as pratyak. Sha-pram. ANa § Advaita – sat as indeterminate perception, abstracted in cit as ideas § Premise – pre-linguistic perception as source of learning

Psychology § § § Child stores sensory perceptions in toto Similarity - cluster similar notions Cotemporaneous occurences – causality § Ball is round to the touch § Ball image has darker areas near the edges § Abstraction – shape from shading (3 D) § Sensory-Motor loops are the fundamental mechanism in learning (Piaget, Papert)

BRi. CS Workshops § § Anchoring on a theme § Theme: Waking up in the morning Ideation Functional Prototypes

BRi. CS Objectives § Set in the developing world context § Child’s sense of identity lost in the crush of inadequate resources § Rote-oriented educational practices inorganic growth - imported 19 th c. § Primal jolt needed to re-think practices. § Constructivist features § Use of Robots / Constructions

BRi. CS Model § Initial workshop in school § Hands-on theme-anchored Problem Solving § Draw in like-minded teachers § Further interaction in curricular contexts § Propagate through already exposed students § Future workshops with local resources § Enable local colleges / franchisees

Toys from Junk § Use of junk materials § Themes related to own lives
Robots from Junk • Straw Connectors • Ballpen refill bearings • Used sandals • Wire Gears • Paper

Robots from Kits • Fully functional • Easy to use Sensors • Programmable using visual icons • Expensive

Robots in imagination Haunted House (Vidya Devi Jindal Girls School Hissar Feb 2002)
Chakka Robots • Simple Electronics • Do-it-yourself sensors • Material Preparation, Soldering • Common components • Spring switches as sensors • Wall-hugging robot • b. o. m. cost Rs. 100
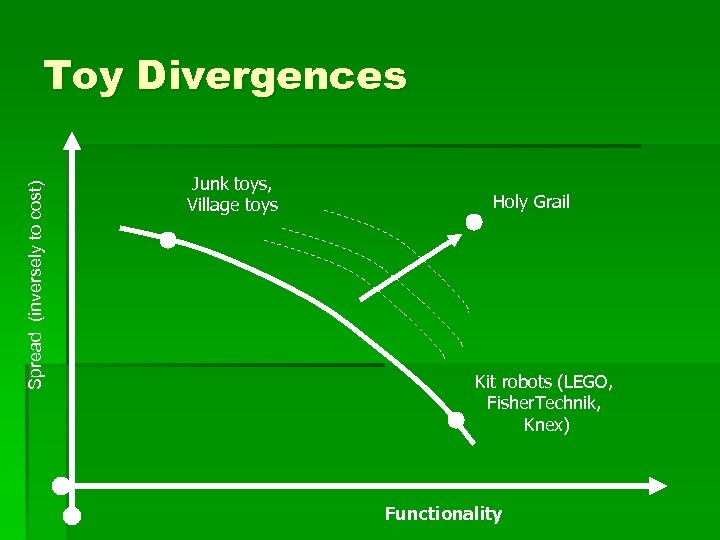
Spread (inversely to cost) Toy Divergences Junk toys, Village toys Holy Grail Kit robots (LEGO, Fisher. Technik, Knex) Functionality

Digital Kathputli Techkriti IIT Kanpur Feb 2002
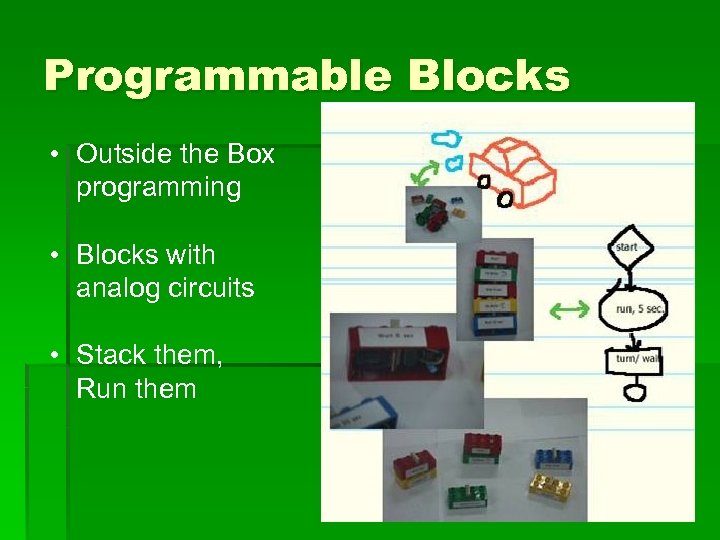
Programmable Blocks • Outside the Box programming • Blocks with analog circuits • Stack them, Run them

Programmable Blocks

Sustaining BRi. CS • BRi. CS chapters in other Colleges • BHU-IT (Varanasi) (Nov 2002) • VJTI Mumbai (planned March 2003) • Franchise / NGO Model • Calcutta (opening Jan 2003) • Pedagogic Ownership at school level – teacher exposure • School – to – school • V. V. School Delhi, August 2002

Scaling up § 2000 Indian students exposed to BRi. CS § 71 million to go: § Middle School – 43 mn § High School – 28 mn § Tighter curricular integration § Others: § Colleges – 12 mn § Primary School – 114 mn

Scaling up - Globally § Many groups working with Mechatronics for education (IEEE, Open Society Institute, ICICI) § Tasks: § Curricular emphasis § Teacher Resources and Creativity § Major Regions: § China?
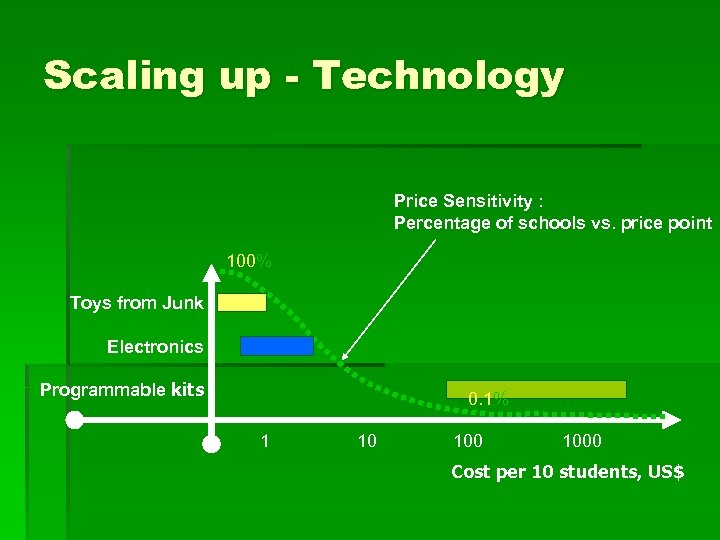
Scaling up - Technology Price Sensitivity : Percentage of schools vs. price point 100% Toys from Junk Electronics Programmable kits 0. 1% 1 10 1000 Cost per 10 students, US$
Expanding BRi. CS • Professional Design Workshops • Rapid functional prototyping • Executive Creativity Workshops • SIDBI (February 2003) • College curricula– mechatronics • Permanent BRi. CS labs – National Science Museums
Future Agenda • Learning Assessment • within curricular context • Low-cost programmable models • Deployment through mainstream educational channels • State Governments, • Other nations
779a5b2f1aa4aa4b1fa8dee8de83e29c.ppt