08f6655828395c29efbaa731d08724ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

An Evidence-Based Approach to Transfusion of the Preterm Infant

Disclosure I am on the speakers bureau for: Ikari and Fisher Paykell
Anemia of Prematurity 1. ANEMIA q Definitions q Clinical burden and effects q Risk : benefit ratio 2. REDUCING TRANSFUSION q Placental transfusion q Minimizing iatrogenic anemia q Erythropoietin 3. WHAT HEMOGLOBIN TRIGGERS TO USE? q Randomized Trial Data

Hemoglobin and reticulocytes during first year of life Lundstrom 1977 Saarnen and Siimes 1978 Cited by: Dallman PR 1981 “Rapid developmental changes and complex interactions for oxygen delivery (prevent) developing clear cut criteria for transfusion. Consequently clinical practices vary widely. ’’
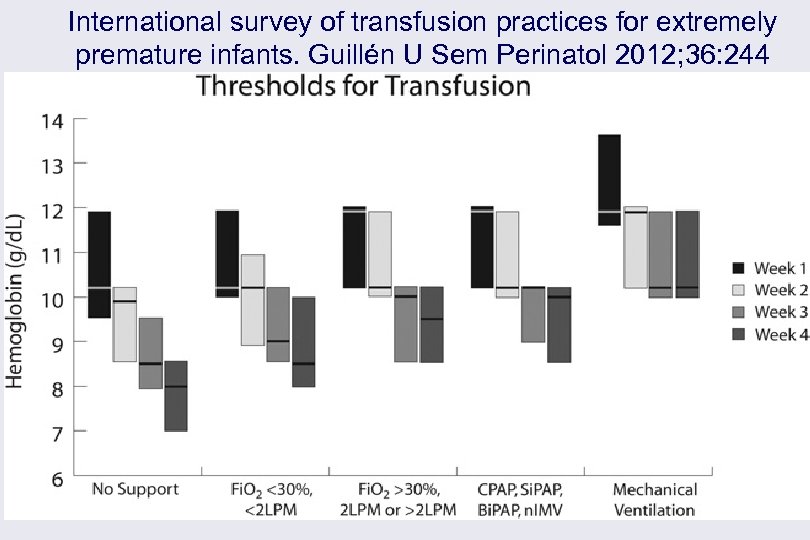
International survey of transfusion practices for extremely premature infants. Guillén U Sem Perinatol 2012; 36: 244
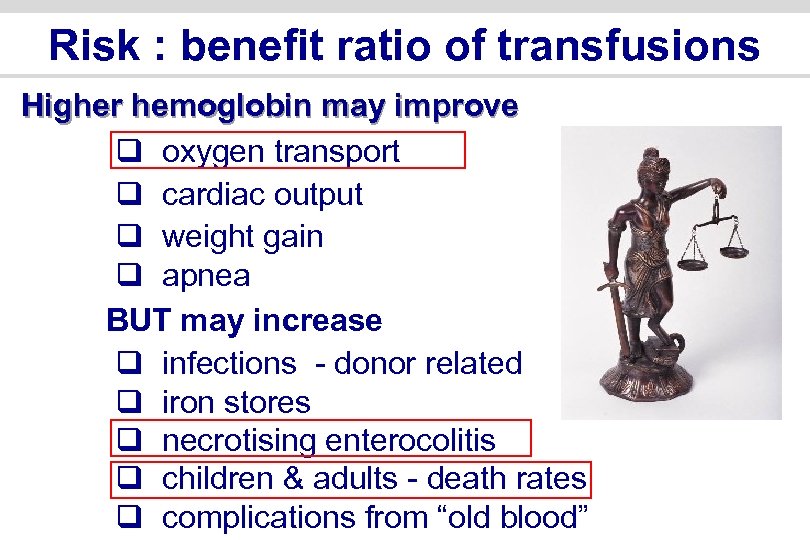
Risk : benefit ratio of transfusions Higher hemoglobin may improve q oxygen transport q cardiac output q weight gain q apnea BUT may increase q infections - donor related q iron stores q necrotising enterocolitis q children & adults - death rates q complications from “old blood”

Pre Tx 97 -113 g/l Pre Tx Hgb<97 Pre Tx 113 -129 g/l
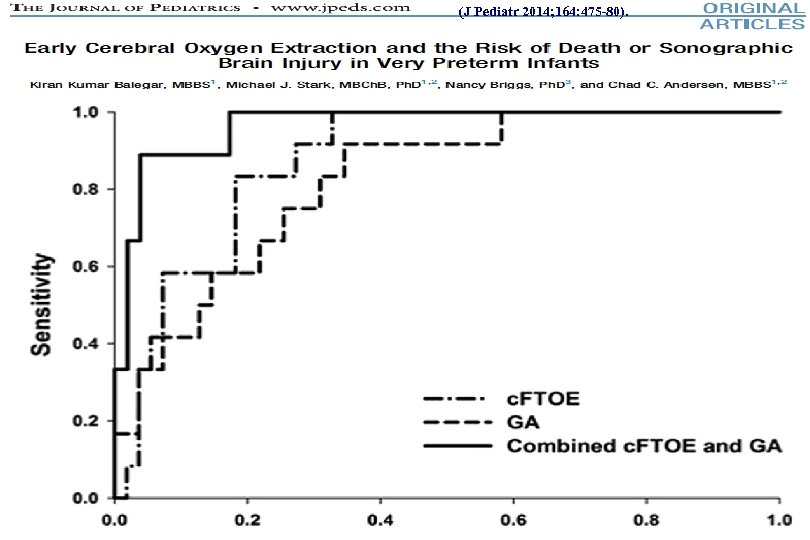
(J Pediatr 2014; 164: 475 -80).
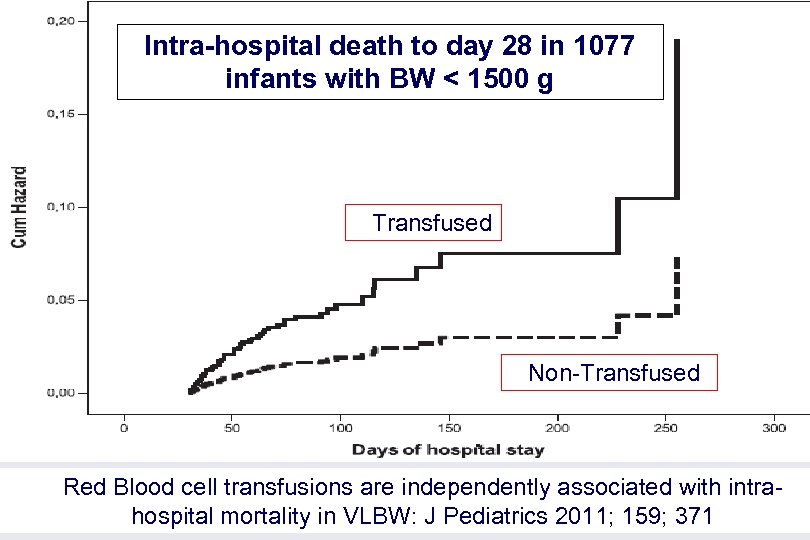
Intra-hospital death to day 28 in 1077 infants with BW < 1500 g Transfused Non-Transfused Red Blood cell transfusions are independently associated with intrahospital mortality in VLBW: J Pediatrics 2011; 159; 371
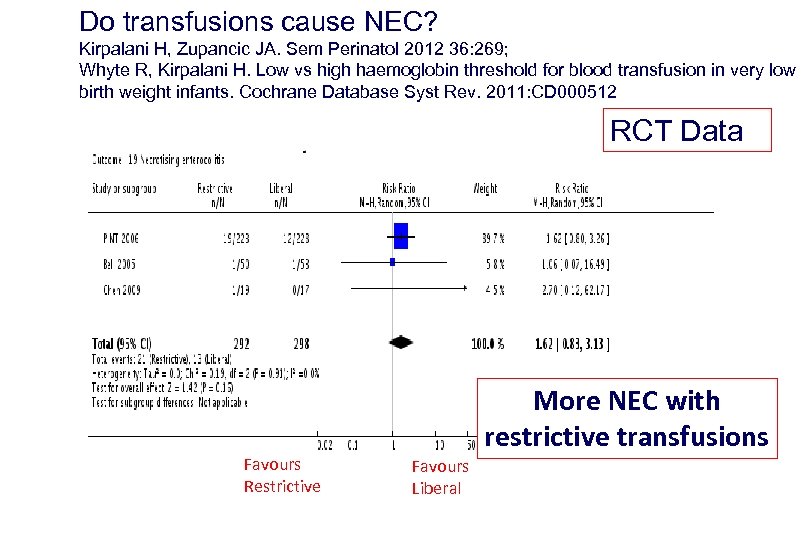
Do transfusions cause NEC? Kirpalani H, Zupancic JA. Sem Perinatol 2012 36: 269; Whyte R, Kirpalani H. Low vs high haemoglobin threshold for blood transfusion in very low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011: CD 000512 RCT Data Favours Restrictive More NEC with restrictive transfusions Favours Liberal
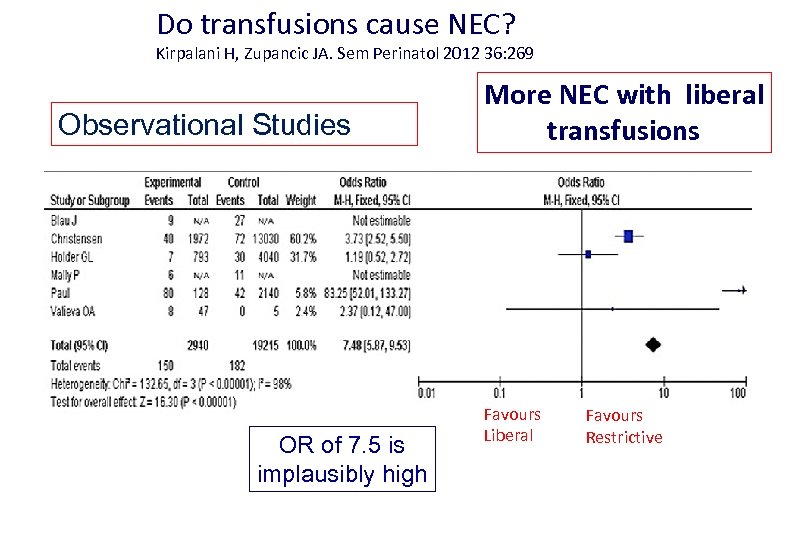
Do transfusions cause NEC? Kirpalani H, Zupancic JA. Sem Perinatol 2012 36: 269 Observational Studies OR of 7. 5 is implausibly high More NEC with liberal transfusions Favours Liberal Favours Restrictive
Anemia of Prematurity 1. ANEMIA q Definitions q Clinical burden and effects q Risk : benefit ratio 2. REDUCING TRANSFUSION q Placental transfusion q Minimizing iatrogenic anemia q Erythropoietin 3. WHAT HEMOGLOBIN TRIGGERS TO USE? q Randomized Trial Data
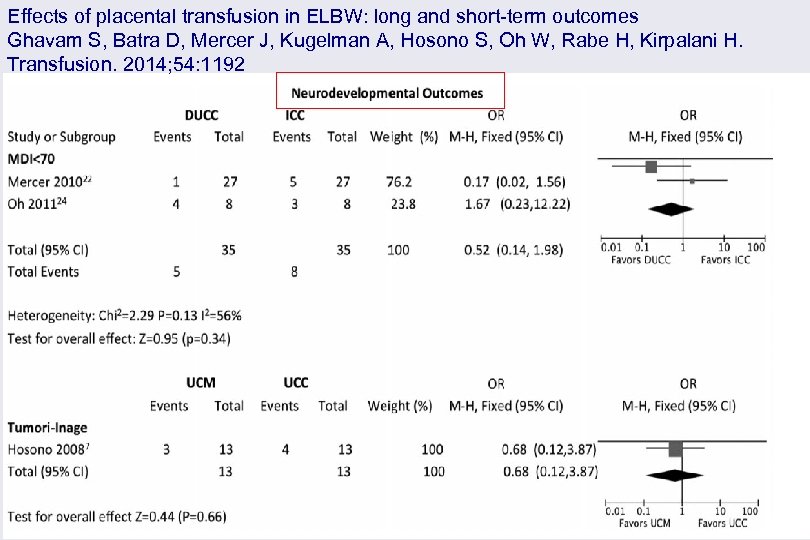
Effects of placental transfusion in ELBW: long and short-term outcomes Ghavam S, Batra D, Mercer J, Kugelman A, Hosono S, Oh W, Rabe H, Kirpalani H. Transfusion. 2014; 54: 1192
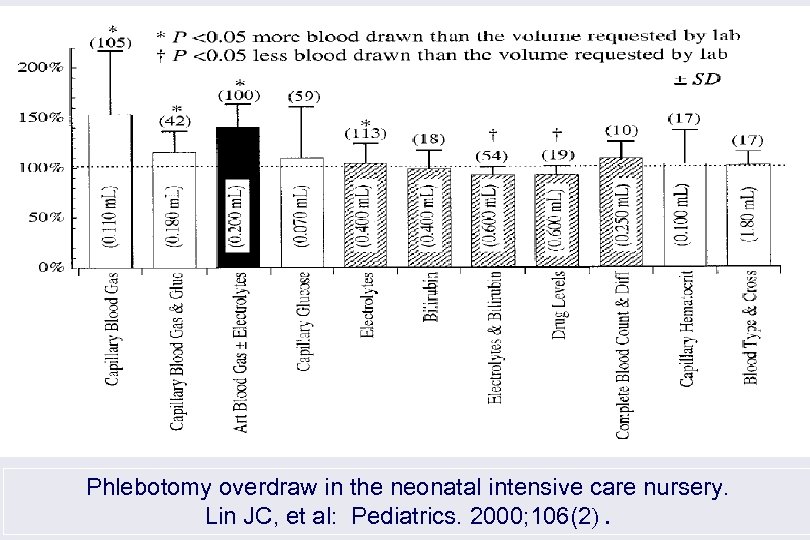
Phlebotomy overdraw in the neonatal intensive care nursery. Lin JC, et al: Pediatrics. 2000; 106(2).
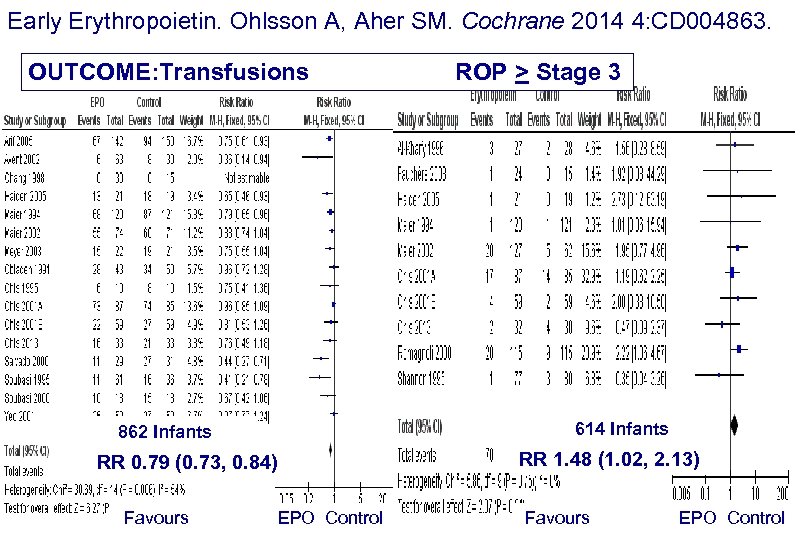
Early Erythropoietin. Ohlsson A, Aher SM. Cochrane 2014 4: CD 004863. OUTCOME: Transfusions 614 Infants 862 Infants RR 0. 79 (0. 73, 0. 84) Favours ROP > Stage 3 EPO Control RR 1. 48 (1. 02, 2. 13) Favours EPO Control
Anemia of Prematurity 1. ANEMIA - Definitions - Clinical burden and effects - Risk : benefit ratio 2. REDUCING TRANSFUSION - Placental Transfusion - Minimizing iatrogenic anemia - Erythropoietin 3. WHAT HEMOGLOBIN TRIGGERS TO USE? - Randomized Trial Data
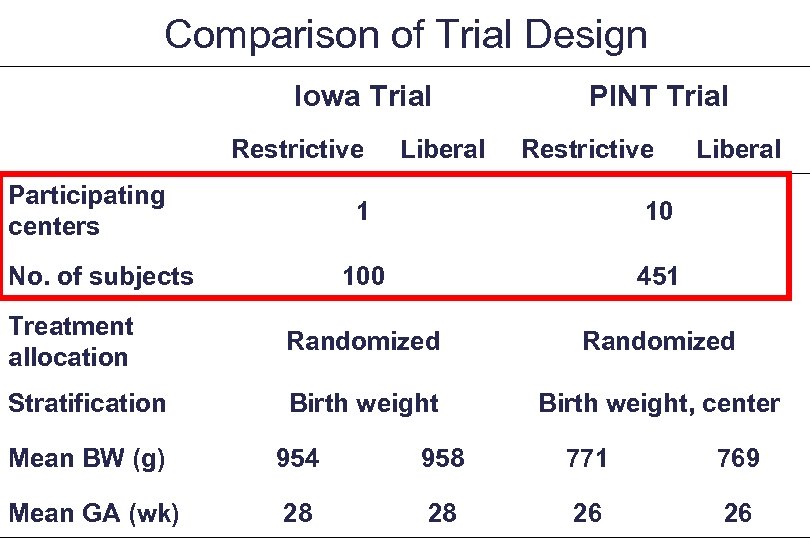
Comparison of Trial Design Iowa Trial Restrictive Participating centers Liberal PINT Trial Restrictive Liberal 1 10 100 451 Treatment allocation Randomized Stratification Birth weight, center No. of subjects Mean BW (g) 954 958 771 769 Mean GA (wk) 28 28 26 26

PICOT Iowa Population <32 wks GA Intervention Comparison Outcomes Time frame Liberal Hgb Tx Restrictive Hgb Tx No. of RBC Tx 36 wks PMA

PRIMARY OUTCOME IOWA Number of Transfusions Low Hgb High Hgb 3. 3 + 2. 9 5. 2 + 4. 5 p = 0. 025
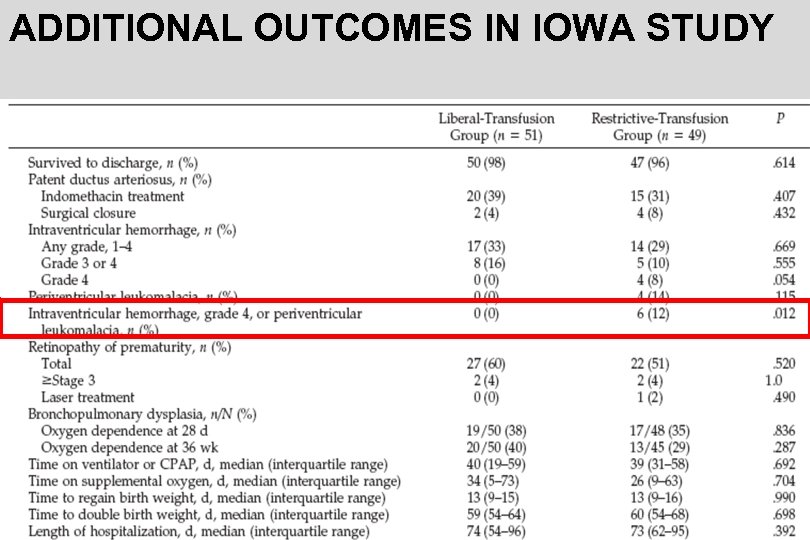
ADDITIONAL OUTCOMES IN IOWA STUDY

J Pediatr 2006: 149; 301

PICOT PINT Population Intervention Comparison Outcomes Time frame <1000 g BW Liberal Hgb Tx Restrictive Hgb Tx Intact Survival 36 wks PMA

Inclusions § < 1000 g BW § < 48 hours age § < 31 wks GA

TRANSFUSION THRESHOLDS Respiratory support Yes No Age High Low Week one 135 115 120 100 Week two 120 100 85 ≥ Week three 100 85 75 85
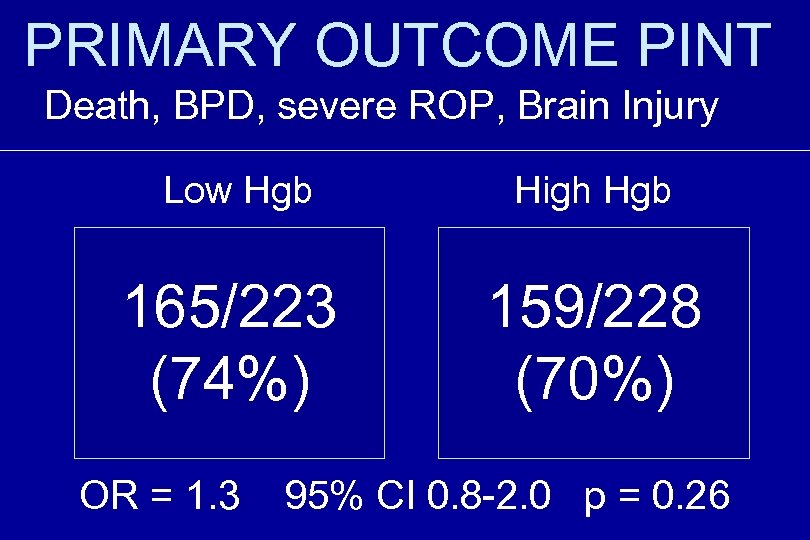
PRIMARY OUTCOME PINT Death, BPD, severe ROP, Brain Injury Low Hgb High Hgb 165/223 (74%) 159/228 (70%) OR = 1. 3 95% CI 0. 8 -2. 0 p = 0. 26

PINT-Outcome Study (PINT-OS) Primary Outcome & a-priori components 0. 1 1 Composite 10 100 p=0. 09 OR 1. 45 (0. 94, 2. 21) 1. 18 (0. 72, 1. 93) Death 1. 32 (0. 53, 3. 27) Cerebral Palsy Cognitive Delay <70 p=0. 06 1. 74 (0. 98, 3. 11) Blindness 2. 16 (0. 19, 24. 1) Deafness 1. 45 (0. 32, 6. 58) Favors Low Favors High
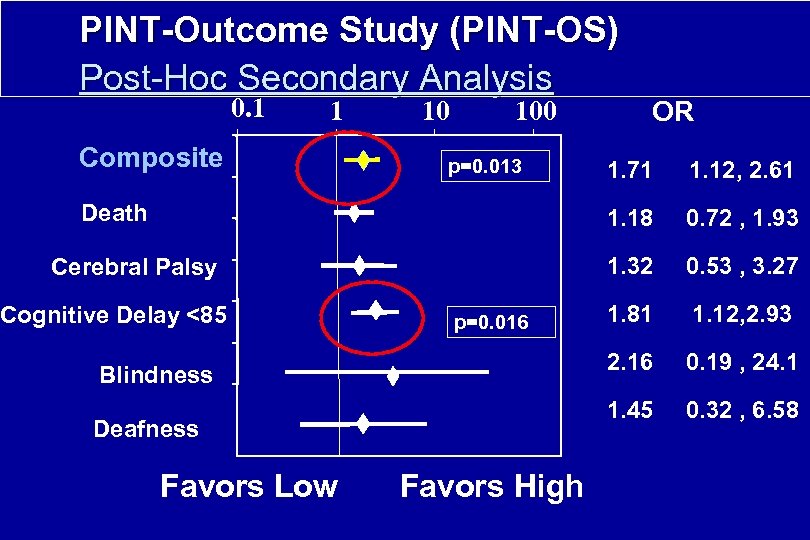
PINT-Outcome Study (PINT-OS) Post-Hoc Secondary Analysis 0. 1 1 Composite 10 100 p=0. 013 OR Cognitive Delay <85 Deafness Favors Low Favors High 1. 81 1. 12, 2. 93 0. 19 , 24. 1 1. 45 Blindness 0. 53 , 3. 27 2. 16 p=0. 016 0. 72 , 1. 93 1. 32 Cerebral Palsy 1. 12, 2. 61 1. 18 Death 1. 71 0. 32 , 6. 58
RCT era: Risk : benefit ratio of transfusions Higher hemoglobin may improve q oxygen transport q cardiac output q weight gain - Not true q apnea - Not true q NEC ? q Neurocognitive outcomes ? BUT may increase or unknown q Infections - donor related q iron stores q death rates - unlikely

WHEN SHOULD WE TRANSFUSE?

NICHD – NEONATAL RESEARCH NETWORK Transfusions For Prematures (TOP) Does a Liberal Red Blood Cell Transfusion Strategy Improve Neurologically-Intact Survival of ELBW Infants as Compared to a Restrictive Strategy? Clinicaltrials. gov NCT 01702805

CONCLUSIONS 1. Low thresholds of PINT and Iowa studies were comparable 2. It is reasonable to maintain infants above these lower thresholds 3. The high threshold was higher in Iowa than in PINT 4. The benefit of higher thresholds remains uncertain 16 th Century dissection
08f6655828395c29efbaa731d08724ba.ppt