2eb27ddc5d35bb6982917a52cf98525d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

An Empirical Examination of Current High-Availability Clustering Solutions’ Performance Jeffrey Absher De. Paul University Research Symposium Presentation November 2003 See actual paper for bibliographical, procedural info, and appropriate academic reference information

HA and Related Technology Distributed OS l Load Balancing l Disaster Recovery l Fault Tolerance l HA clustering l

HA’s defining traits l l l SPOF avoided by using redundancy Single image to the outside world using a single virtual IP address and hostname Automated fault management and recovery Multiple access paths from each cluster node to each resource group (set of HA services) Simple abstraction for applications and administrators Undisrupted (or minimal disrupted) services during failover. “If a computer breaks down, the functions performed by that computer will be handled by some other computer in the cluster. ”
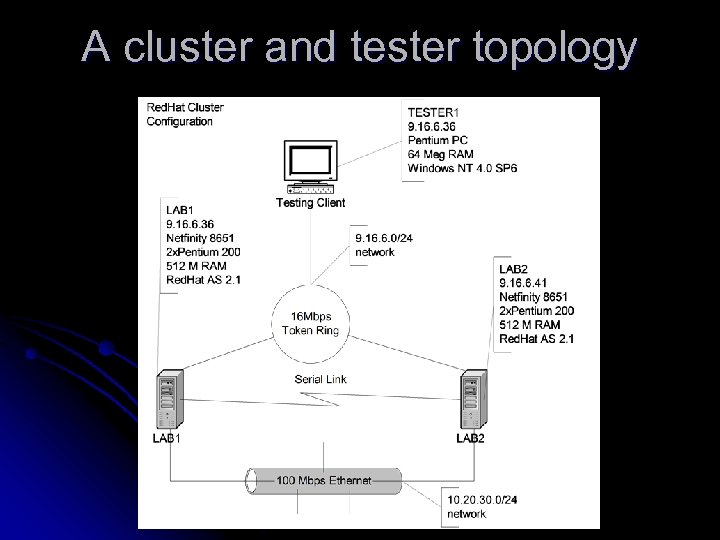
A cluster and tester topology
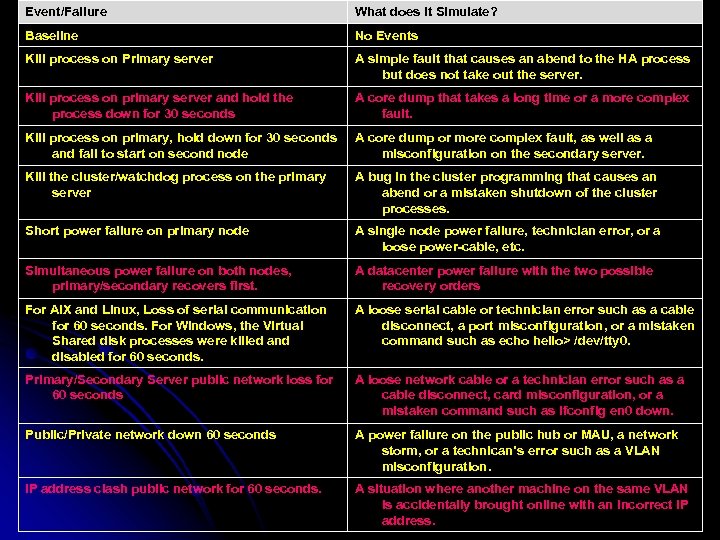
Event/Failure What does it Simulate? Baseline No Events Kill process on Primary server A simple fault that causes an abend to the HA process but does not take out the server. Kill process on primary server and hold the process down for 30 seconds A core dump that takes a long time or a more complex fault. Kill process on primary, hold down for 30 seconds and fail to start on second node A core dump or more complex fault, as well as a misconfiguration on the secondary server. Kill the cluster/watchdog process on the primary server A bug in the cluster programming that causes an abend or a mistaken shutdown of the cluster processes. Short power failure on primary node A single node power failure, technician error, or a loose power-cable, etc. Simultaneous power failure on both nodes, primary/secondary recovers first. A datacenter power failure with the two possible recovery orders For AIX and Linux, Loss of serial communication for 60 seconds. For Windows, the Virtual Shared disk processes were killed and disabled for 60 seconds. A loose serial cable or technician error such as a cable disconnect, a port misconfiguration, or a mistaken command such as echo hello> /dev/tty 0. Primary/Secondary Server public network loss for 60 seconds A loose network cable or a technician error such as a cable disconnect, card misconfiguration, or a mistaken command such as ifconfig en 0 down. Public/Private network down 60 seconds A power failure on the public hub or MAU, a network storm, or a technican’s error such as a VLAN misconfiguration. IP address clash public network for 60 seconds. A situation where another machine on the same VLAN is accidentally brought online with an incorrect IP address.

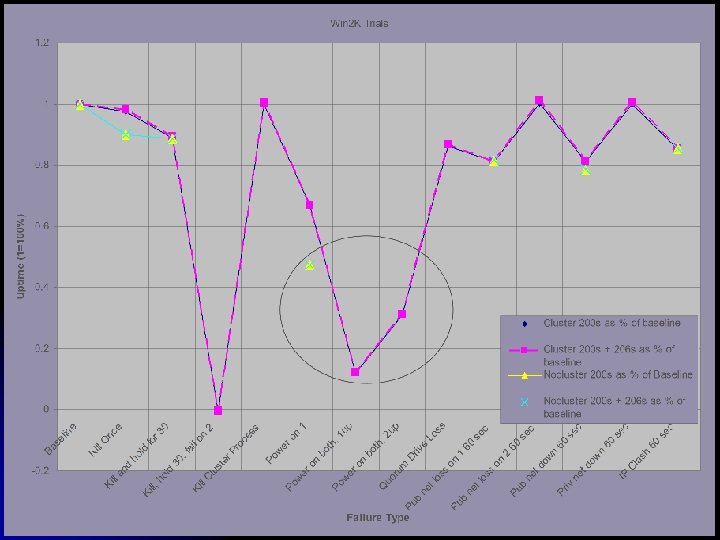
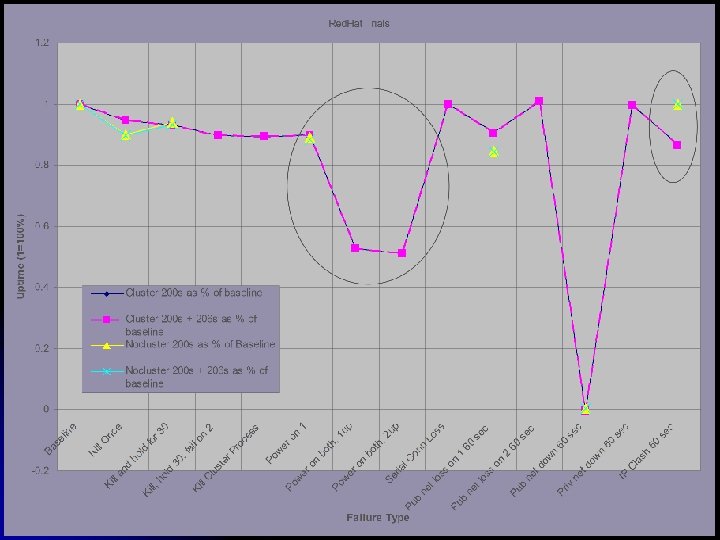
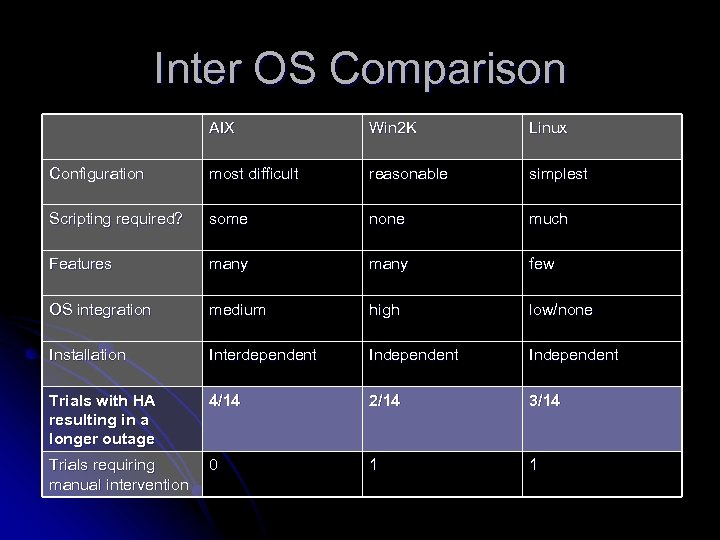
Inter OS Comparison AIX Win 2 K Linux Configuration most difficult reasonable simplest Scripting required? some none much Features many few OS integration medium high low/none Installation Interdependent Independent Trials with HA resulting in a longer outage 4/14 2/14 3/14 Trials requiring manual intervention 0 1 1

Subjective Observations l HA clustering is difficult to configure properly and the available documentation is lacking l l Multiple machines must be configured simultaneously, often packages and software must be installed and configured in a specific order. For what should be a loosely-coupled system, there are many interdependencies. Youn et al suggest that the design of “administration of clusters…needs improvement, ” – I agree Vogels et al state, “Users find it difficult to configure clusters with the desired management … properties. It is difficult to configure applications to be automatically launched in an appropriate order. Lacking solutions to these problems, clusters will remain awkward and time-consuming tools. ” - I agree

Objective Conclusions Based on Empirical Evidence l l HA is not a perfect solution for every environment, and may be a bad solution for some, depending on the expected faults. High failover time for some systems contributes to a lower-thanexpected performance of HA systems when compared to non-HA systems. l l l Failover times need to be significantly smaller than the time required for a reboot or even a restart of a slow-to-start process. Primary-node negotiation time at boot contributes to poor performance during power outages. There were cases where clustering is shown to actually decrease the uptime of a service or site.

Q&A
2eb27ddc5d35bb6982917a52cf98525d.ppt