af04b9d0913d0479ffdebb60d4c66812.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

An efficient Supply Chain to meet new global challenges René Colin SPACE Operating Manager Supply Chain Progress towards Aeronautical Community Excellence www. space-aero. org

Agenda q SPACE organization q SPACE operation and activities q SPACE projects and results q CONCLUSION 1 Mai 09

Organization 2 Mai 09

Why? We are only as strong as the weakest link… Aircraft manufacturers EMS Sub system integrator Machining, Surface treatment Raw materiel … in our supply chain SPACE helps small companies Mai 09
Who? Supply Chain Progress towards Aeronautical Community Excellence www. space-aero. org
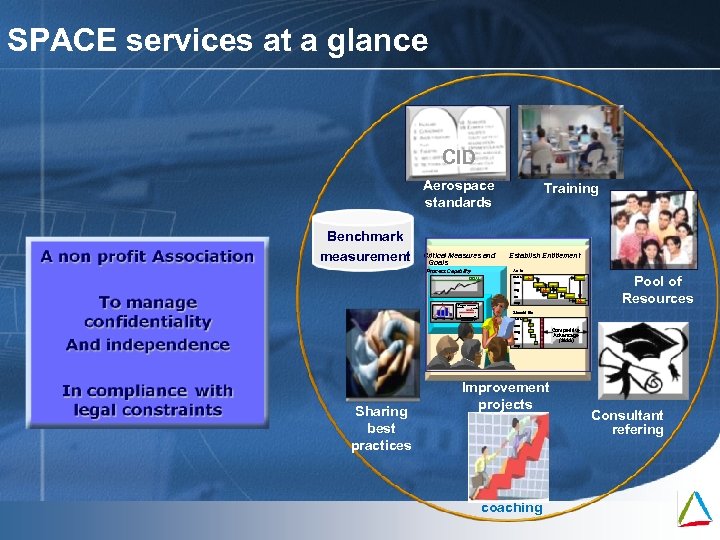
SPACE services at a glance CID Aerospace standards Benchmark measurement Critical Measures and Goals Training Establish Entitlement As Is Process Capability Sales GOAL l CSR Mfg l l QC Capability Histogram Capability Plot Process Tolerance 11. 4481 14. 7185 I I Should Be I 8 16 Specifications 12 13 14 l l Ship I Pool of Resources Sales St. Dev: 0. 54507 CSR Mfg QC Competitive Advantage ($$$$) Ship Sharing best practices Improvement projects coaching Mai 09 Consultant refering

Operations and activities 6 Mai 09

what The Associate members can benefit from support A diagnostic • A service offered by SPACE to the associate member (sub-tier supplier), to develop an action plan, to help this member to improve its efficiency … which is not • A certification system • A rating system and is developped by • “Supply Chain Management Handbook” Supplier Selection and Capability Assessment 7 Mai 09
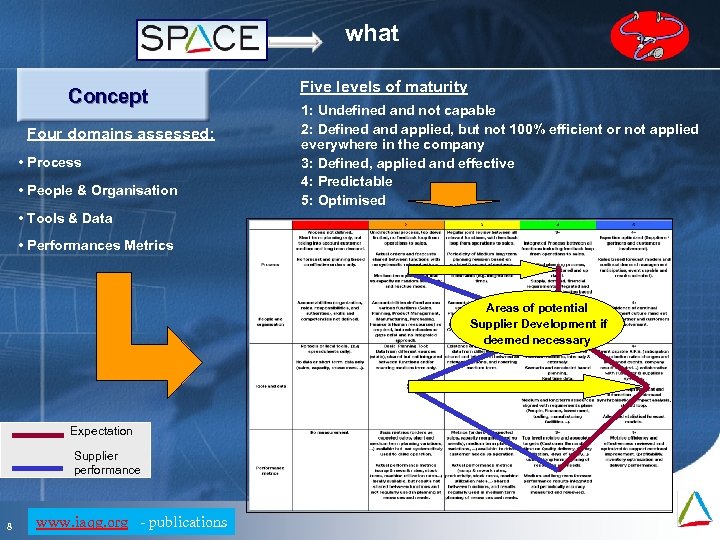
what Concept Four domains assessed: • Process • People & Organisation Five levels of maturity 1: Undefined and not capable 2: Defined and applied, but not 100% efficient or not applied everywhere in the company 3: Defined, applied and effective 4: Predictable 5: Optimised • Tools & Data • Performances Metrics Areas of potential Supplier Development if deemed necessary Expectation Supplier performance 8 www. iaqg. org - publications Mai 09
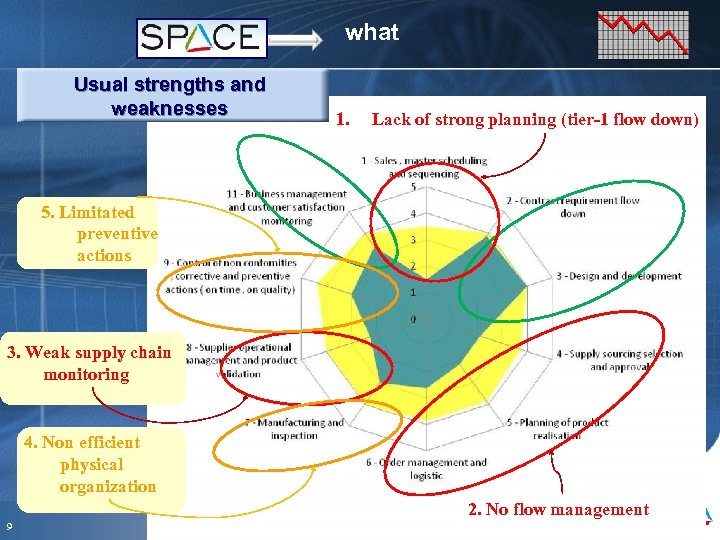
what Usual strengths and weaknesses 1. Lack of strong planning (tier-1 flow down) 5. Limitated preventive actions 3. Weak supply chain monitoring 4. Non efficient physical organization 2. No flow management 9 Mai 09
what No anticipation No realistic schedules 10 Mai 09
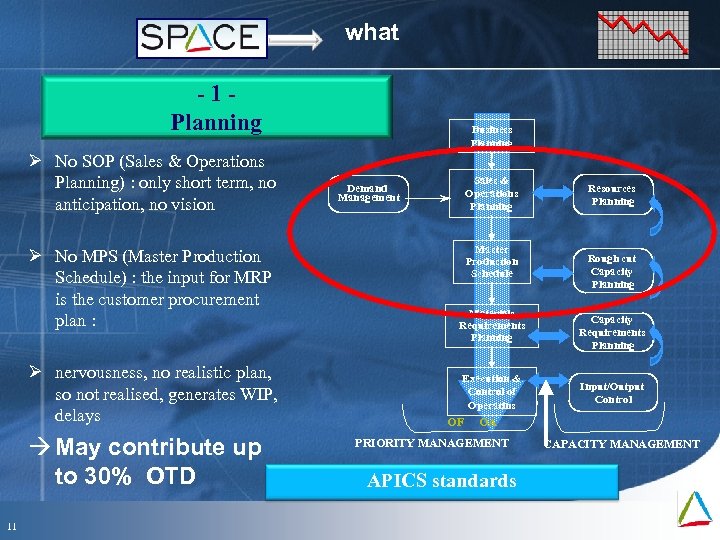
what -1 Planning Ø No SOP (Sales & Operations Planning) : only short term, no anticipation, no vision Ø No MPS (Master Production Schedule) : the input for MRP is the customer procurement plan : Ø nervousness, no realistic plan, so not realised, generates WIP, delays May contribute up to 30% OTD 11 Mai 09 Business Planning Sales & Operations Planning Demand Management Master Production Schedule Materials Requirements Planning Execution & Control of Operatins OF Resources Planning Rough cut Capacity Planning Capacity Requirements Planning Input/Output Control OA PRIORITY MANAGEMENT APICS standards CAPACITY MANAGEMENT

what -2 Flow management Input/Output Control Ø No WIP control : in consequence Ø the WIP is high Ø The lead time is high Planned orders Ø Flow is generally driven by a push system Ø No level flow on the shop floor = order releasing MPS MRP WIP Released orders = Finished orders Shop Floor Permits to save 30% of Finished products WIP Pull Sytems 12 Mai 09

what -3 Suppliers management Ø No formal supplier approval Ø No strategy for reducing the supplier base Ø The supplier performance is often measured but not communicated nor used for improvement Major issue in assembly workcenters Supplier Performance Management 13 Mai 09

what -4 Physical flow Ø Layout is generally triggered by process (job shop and not flow shop) Ø No visual management Ø Effort to be done on house-keeping (5 S) Lead time can be reduced by 30% Lean – TPS (Toyota Production System) standards 14 Mai 09

what - 5 –Quality – problem solving Ø No structured and systematic method for problem solving Ø Problems are identified and highligted (usually measured) Ø The metrics are not systematically used to manage and to improve the business Basics of quality improvement Quality tools – Problem solving 15 Mai 09

PROJECTS and RESULTS 16 Mai 09
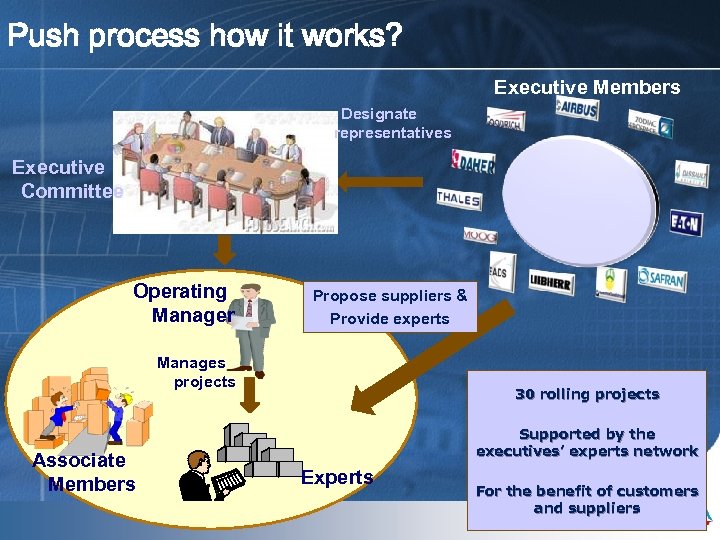
Push process how it works? Executive Members Designate representatives Executive Committee Operating Manager Propose suppliers & Provide experts Manages projects Associate Members Mai 09 30 rolling projects Supported by the executives’ experts network Experts For the benefit of customers and suppliers
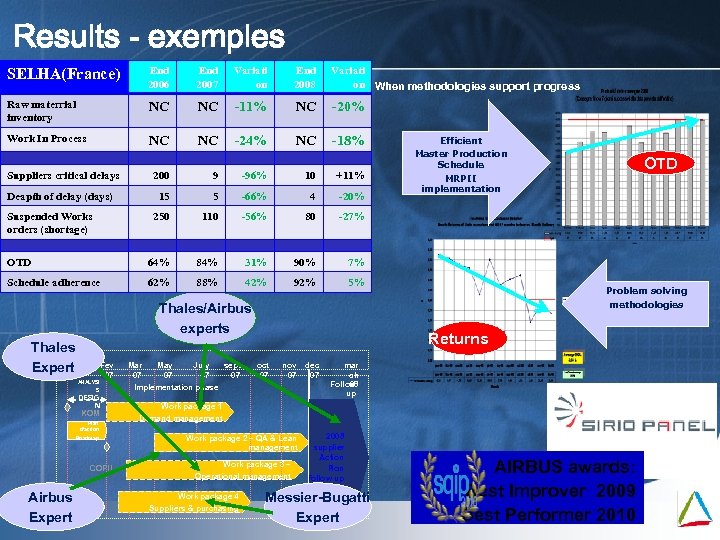
Results - exemples SELHA(France) End 2006 End 2007 Variati on End 2008 Variati on When methodologies support progress Raw materrial inventory NC NC -11% NC -20% Work In Process NC NC -24% NC -18% Suppliers critical delays 200 9 -96% 10 +11% 15 5 -66% 4 -20% 250 110 -56% 80 64% 84% 31% 90% 62% 88% 42% 92% 5% OTD 7% Schedule adherence Master Production Schedule -27% OTD Efficient Deapth of delay (days) Suspended Works orders (shortage) ANALYSI Fev 07 S DESIG N KOM Plan d’action Roadmap COPIL Airbus Expert Mai 09 Mar 07 May 07 July 07 sept 07 OTD Problem solving methodologies Thales/Airbus experts Thales Déc Expert 06 MRPII implementation Returns oct 07 nov dec 07 07 Implementation phase Work package 1 mar ch Follow 08 up phase Demand management Work package 2 – QA & Lean management Work package 3 – Operational management Work package 4 Suppliers & purchasing 2008 supplier Action Plan Follow up Messier-Bugatti Expert AIRBUS awards: Best Improver 2009 Best Performer 2010
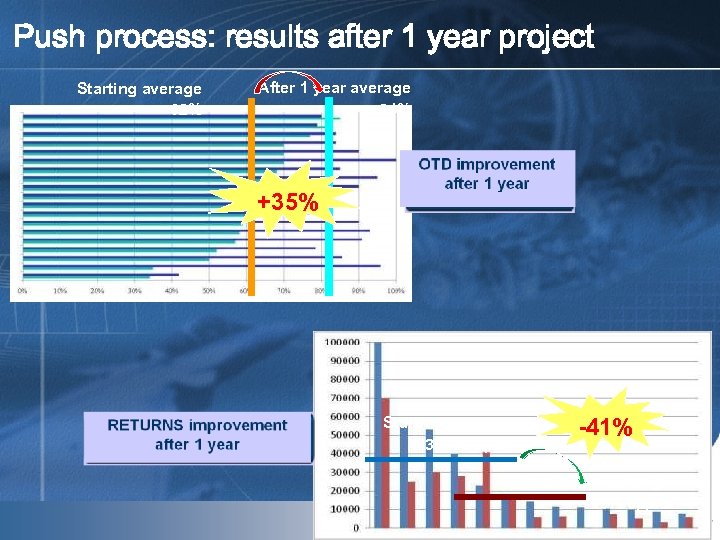
Push process: results after 1 year project Starting average 62% After 1 year average 84% +35% Starting average 31700 ppm -41% After 1 year average 18700 ppm Mai 09
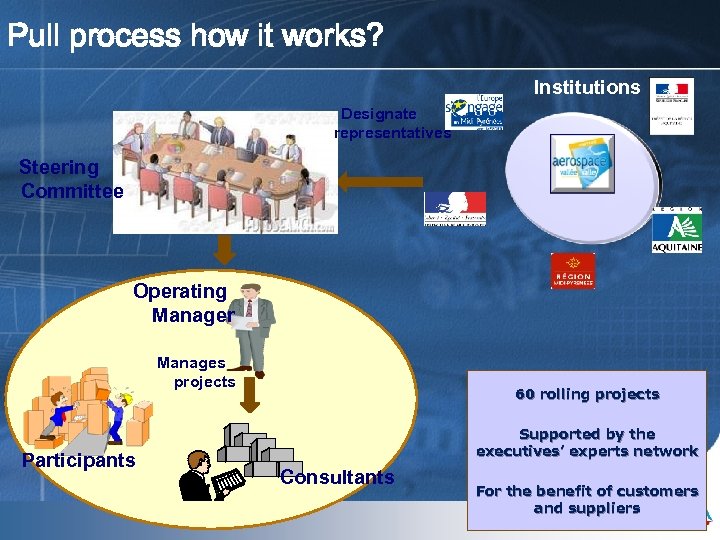
Pull process how it works? Institutions Designate representatives Steering Committee Operating Manager Manages projects Participants Mai 09 60 rolling projects Supported by the executives’ experts network Consultants For the benefit of customers and suppliers
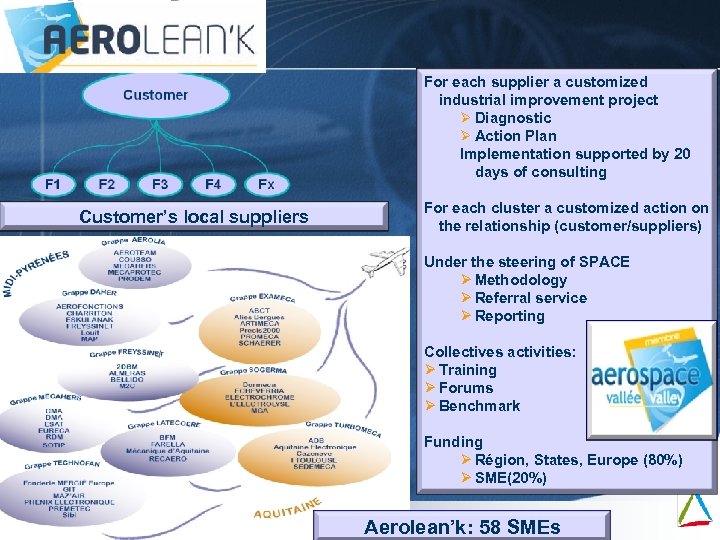
For each supplier a customized industrial improvement project Ø Diagnostic Ø Action Plan Implementation supported by 20 days of consulting Customer’s local suppliers Under the steering of SPACE Ø Methodology Ø Referral service Ø Reporting Porteur de Projet F F 1 F 2 1 Mai 09 F 3 F 2 F 4 F 3 For each cluster a customized action on the relationship (customer/suppliers) F x F 4 Collectives activities: Ø Training Ø Forums Ø Benchmark F x Funding Ø Région, States, Europe (80%) Ø SME(20%) Aerolean’k: 58 SMEs
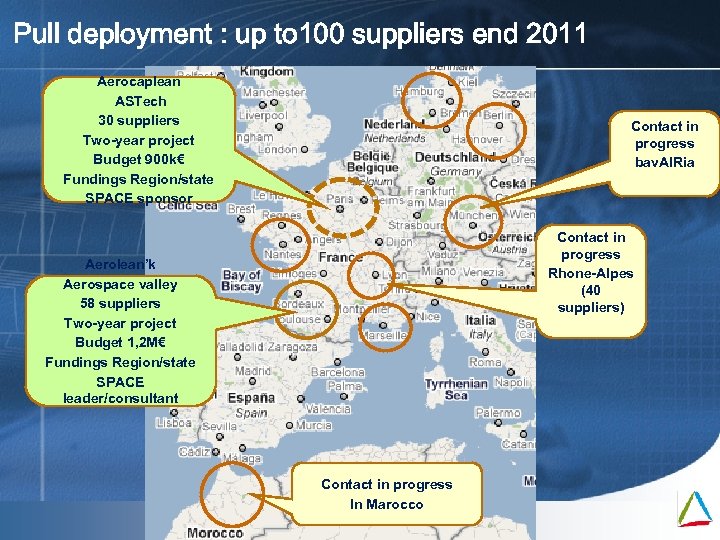
Pull deployment : up to 100 suppliers end 2011 Aerocaplean ASTech 30 suppliers Two-year project Budget 900 k€ Fundings Region/state SPACE sponsor Contact in progress bav. AIRia Contact in progress Rhone-Alpes (40 suppliers) Aerolean’k Aerospace valley 58 suppliers Two-year project Budget 1, 2 M€ Fundings Region/state SPACE leader/consultant Contact in progress In Marocco Mai 09

Development and Conclusion 23 Mai 09
af04b9d0913d0479ffdebb60d4c66812.ppt