936799ae866d9572929302a5f5379945.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

An Attempt at Group Belief Characterization and Detection Danny Dunlavy Computer Science and Informatics Department (1415) Sandia National Laboratories Nick Pattengale, Travis Bauer July 23, 2008 SAND 2008 -5426 P

Disclaimers • We do not think our problem is well formed • We are not sure whether our approach is sound • We are not confident an answer is in our data

Problem Description • Given – Set of beliefs / statements – Set of groups – Beliefs held by groups – Documents associated with groups • Tasks – General: Detect / track / predict beliefs and /or changes – Specific 1: Detect change in belief at a given point in time • Dates: July 2005 -July 2006; split date: January 2006 • Data marked as “Before” and “After” – Specific 2: Differentiate between groups by belief

Beliefs Could have been Jenny Holzerisms 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) Hamas is a people organization Exceptionalterrorist deserve special concessions Hamas should disarm Potential counts for nothing until it's realized Hamas should take part in excellent pasttimes Reticence and secrecy are government Hamas should take part in PNA elections People won't behave if they have nothing to lose Israel is a state Fake or real indifference is a powerful weapon Israel should be destroyed Guilt and self-laceration are indulgences Israel should occupy more intelligible Myth can make reality. Palestine Oslo Accords is a peace solution To disagree presupposes moral integrity Political law is Islamic law It is heroic to try to stop time There exists a two keep going no It can be helpful to state solution matter what
Groups • Fatah (F) • Islamic Jihad (IJ) • Israel (I) • Military Wing (MW) • Muslim Brotherhood (MB) • Palistinian Authority (PA) • Political Bureau (PB) • Quds Brigades (QB) • Syria (S) • United States (US)
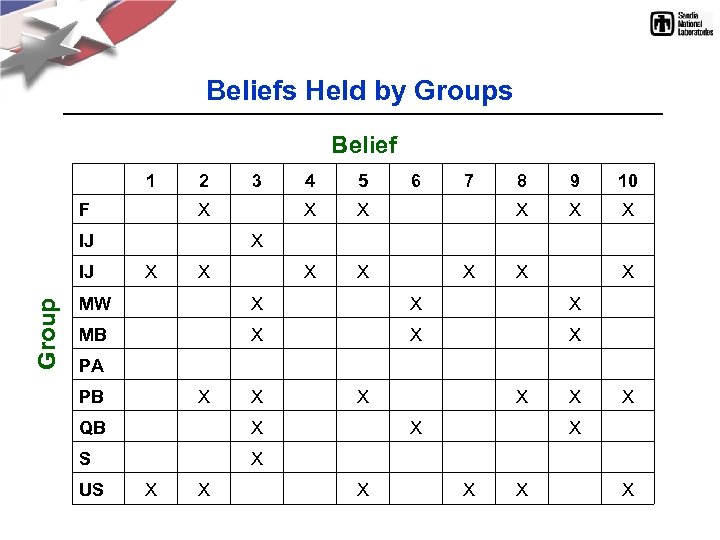
Beliefs Held by Groups Belief 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 F X X X IJ X IJ Group X X X X MW X X X MB X X X PA PB X X X QB X X X S X US X X X X
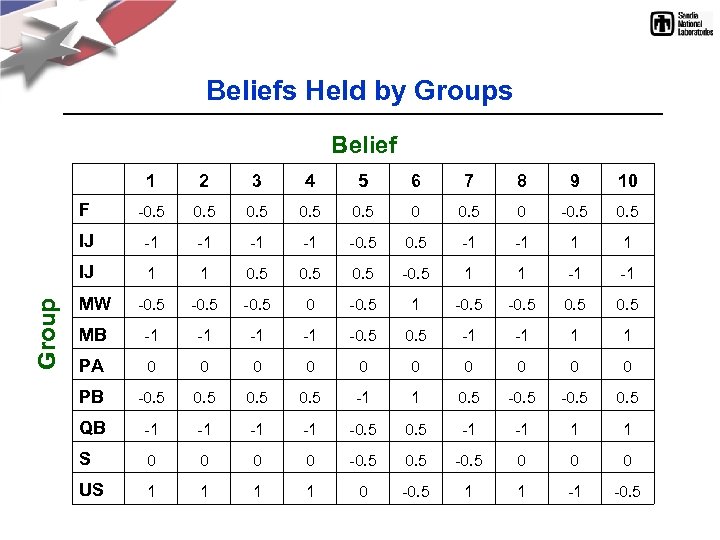
Beliefs Held by Groups Belief 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 F -0. 5 0 -0. 5 IJ -1 -1 -0. 5 -1 -1 1 1 IJ Group 1 1 0. 5 -0. 5 1 1 -1 -1 MW -0. 5 0 -0. 5 1 -0. 5 MB -1 -1 -0. 5 -1 -1 1 1 PA 0 0 0 0 0 PB -0. 5 -1 1 0. 5 -0. 5 QB -1 -1 -0. 5 -1 -1 1 1 S 0 0 -0. 5 0 0 0 US 1 1 0 -0. 5 1 1 -1 -0. 5
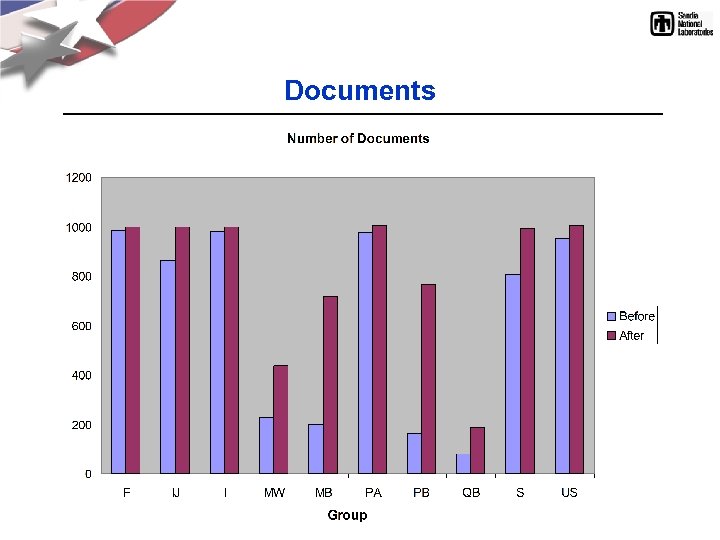
Documents
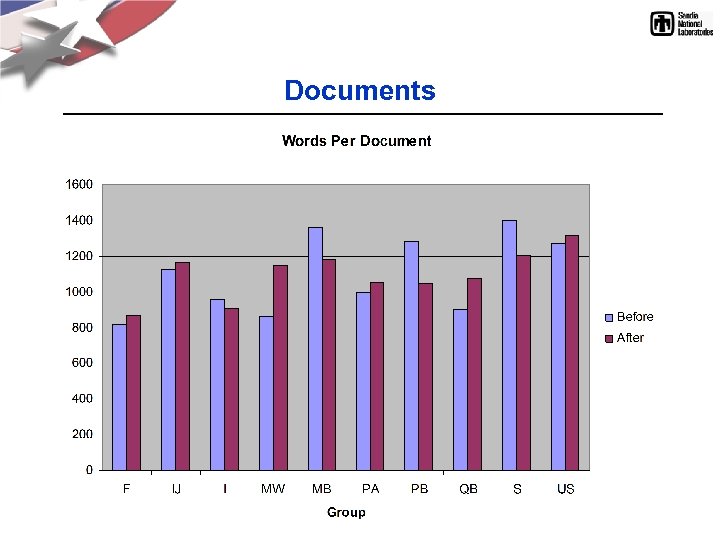
Documents
Solution Approach • Split data into two groups – Before (training) / After (testing) • Create a weighted vector space model – STANLEY – Term space defined by “Before” split • Create binary classifier models – Scenario 1: Model each group per belief – Scenario 2: Model all groups per belief • Apply classifier models – Apply models for a group to that group’s documents • Do test documents align with the same beliefs in general? – Apply model for all groups to each group’s documents • Can we align beliefs and/or groups to specific documents?

Identified Challenges / Issues / Problems • Beliefs used as labels only – Semantics/meaning of beliefs not used in analysis • Beliefs labeled by subject matter experts based on understanding of groups and beliefs – Data not considered in labeling process • Groups are labeled by beliefs, not data – Documents labeled by group – Groups labeled by beliefs • Data collected using keyword search related to groups only – Beliefs not taken into account – Data is about groups, not authored by groups • Data not labeled for validation of problem we are solving – Detected changes cannot be validated – Method evaluation is difficult
Binary Classifier Methods • Random Forest (D. Dunlavy) – Ensemble of decision tree base classifiers (200) • Data sampling with replacement to train each base classifier (10%) • Feature sampling at each node split in the trees (100) • Information gain (entropy) used to determine feature and split used • Kernel Perceptron (T. Bauer [analysis], J. Basilico [code]) – Classification function: – Linear kernel: – Polynomial kernel: – Radial Basis kernel:
Evaluation • Labeling statistics – Positive: has a belief; negative: does not have belief • • TP: true positives (labeled +, predicted +) TN: true negatives (labeled -, predicted -) FP: false positives (labeled -, predicted +) FN: false negatives (labeled +, predicted -) • Performance Measures – Accuracy: – Precision: – Recall:
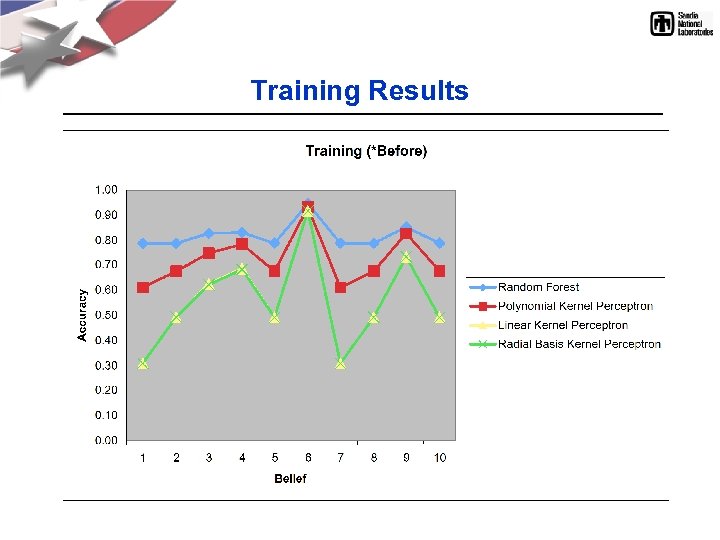
Training Results
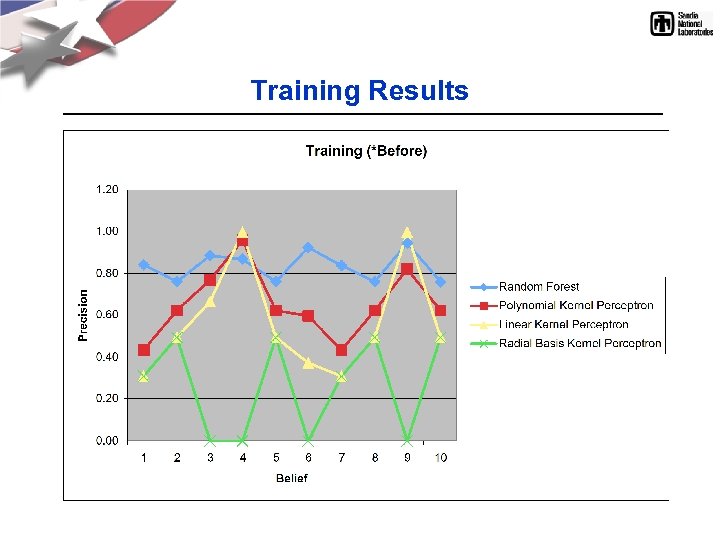
Training Results
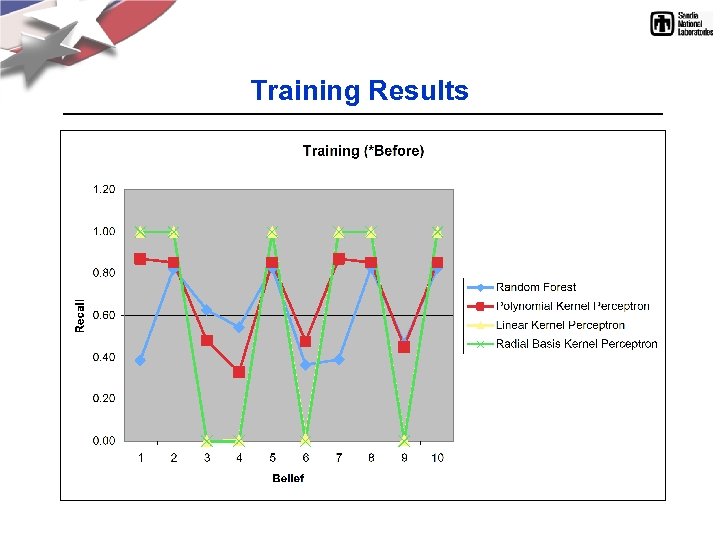
Training Results
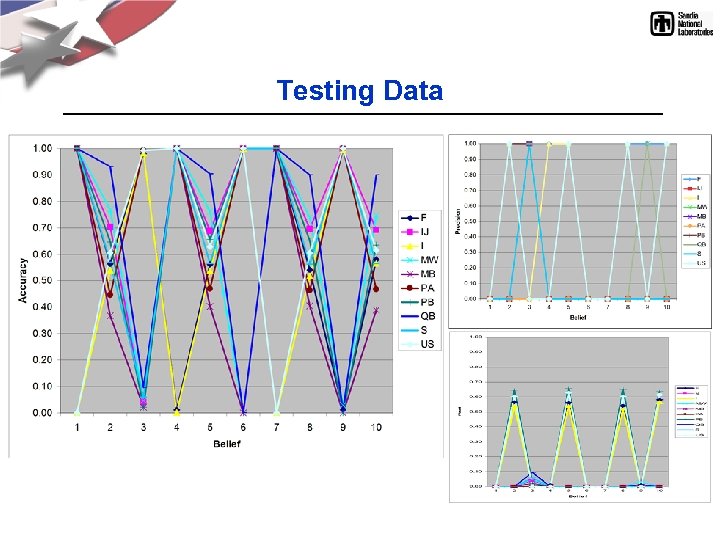
Testing Data
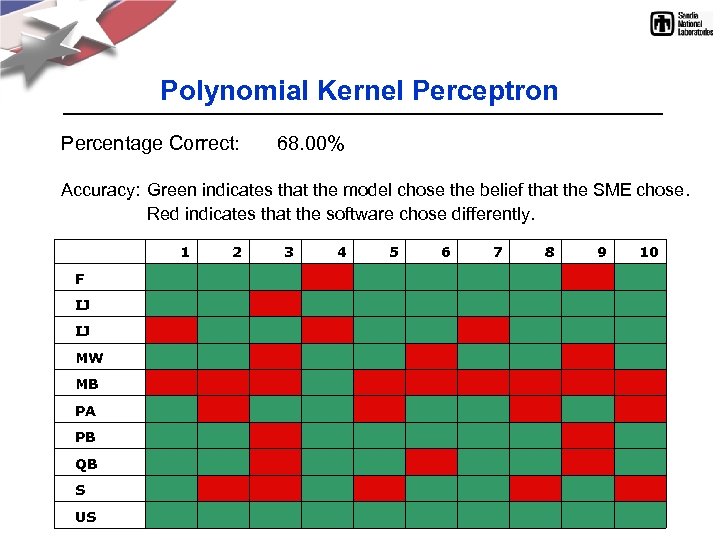
Polynomial Kernel Perceptron Percentage Correct: 68. 00% Accuracy: Green indicates that the model chose the belief that the SME chose. Red indicates that the software chose differently. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 F IJ MW MB PA PB QB S US
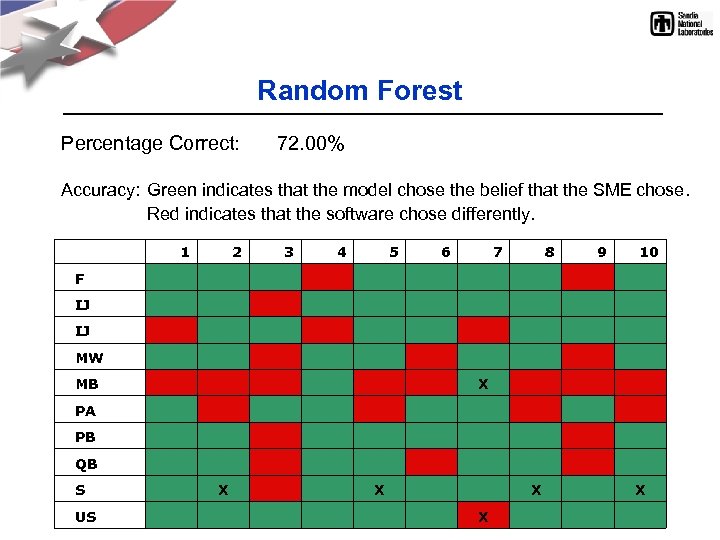
Random Forest Percentage Correct: 72. 00% Accuracy: Green indicates that the model chose the belief that the SME chose. Red indicates that the software chose differently. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 F IJ MW MB X PA PB QB S X X US X

General Thoughts / Questions • What features are important / available? – We used terms • Problems: negation, lack of context, intent – Audience, purpose, goal, context of document • Would you say something different if different people were here? • Are we modeling groups or individuals? – Outliers, subgroup detection • Who/what is the source of data/documents? – Group members versus outsiders (reporters, etc. ) – Level of intimacy with or knowledge of group – Can we incorporate / model perspective into analysis? • Can we identify / define an ideology? – Do we need to in order to model changes in ideology? • Is there a topology of ideologies? – Are relationships between ideologies important?

Thank You An Attempt at Group Belief Characterization and Detection Danny Dunlavy dmdunla@sandia. gov http: //www. cs. sandia. gov/~dmdunla
936799ae866d9572929302a5f5379945.ppt