fddede11b84100f565144eeda67d4320.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88

AN APPROACH TO ABDOMINAL PAIN Ahmad Bhat Dr. Shamim Consultant Emergency Medicine King Saud Medical City Riyadh. KSA

INTRODUCTION Types of pain Special Populations Assessment History Examination Investigations Differential Diagnosis Management - overview Cases ( if time permits)

Types Of Pain Visceral Parietal Pain
Visceral Pain Stretching of nerve fibres of walls or capsules of organs Crampy Dull Achy Often unable to lie still Bilateral innervation

Parietal Pain Parietal peritoneum irritated Usually anterior abdominal wall Localised to the dermatome superficial to the site of painful stimulus
Course Visceral Parietal • Non specific • • Localised tenderness Guarding Rigidity Rebound

Referred Pain Examples of referred pain?
Most Common Causes in the ED Non-specific abd pain Appendicitis Biliary tract dz SBO Gyn disease Pancreatitis Renal colic Perforated ulcer Cancer Diverticular dz Other 34% 28% 10% 4% 4% 3% 3% 3% 2% 2% 6%

Special Populations WOMEN OF CHILD BEARING AGE OLD AGE (ELDERLY PATIENTS)

Elderly May lack physical findings despite having serious pathology As patients age increases diagnostic accuracy declines Risk of Vascular Catastrophes Assume surgical cause until proven otherwise 30 -40% of geris with abdo pain need surgery Biliary tract Disease is the commonest cause Age > 65 need to think of reasons not to CT! Mortality is 7% in the over 80’s - equivalent to AMI!

Elderly Patient think Nasties! AAA Ischaemic Gut Bowel Obstruction Diverticulitis Perforated Peptic Ulcer Cholecystitis Appendicitis

Women of Childbearing Age Must Ascertain whether PREGNANT ALL WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE WITH ABDO PAIN NEED BHCG Gravid uterus displaces intra-abdominal organs making presentations atypical Pregnant women still get common surgical abdominal conditions

History What are the key points of the abdominal pain history?

History HPC Pain Provocative Palliative Quality Radiation Symptoms associated with Timing Taken for the pain Consultations/ Presentations Associated Symptoms – Gastro – intestinal Genito-urinary Gynaecologic

History PMH DM HT Liver Disease Renal Disease Sexually Transmitted Infections PSH Abdominal Surgery Pregnancies Deliveries/ Abortions/ Ectopics Trauma

History Meds NSAIDs Steroids OCP/ Fertility Drugs Narcotics Immunosuppressant Chemotherapy agent ALLS Contrast Analgesic

High Yield Questions Which came first – pain or vomiting? How long have you had the pain? Constant or intermittent? History of cancer, diverticulosis, gall stones, Inflammatory BD? Vascular history, HT, heart disease or AF?

Examination Lots of information from the end of the bed Distressed vs. non distressed Lying still - peritonitis Writhing – Renal Colic Vital Signs NEVER ignore abnormal vital signs! Always document as part of your assessment
ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION
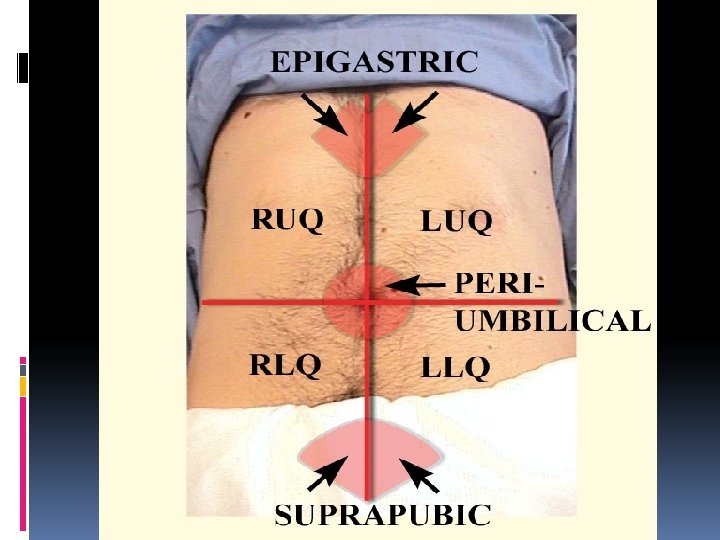
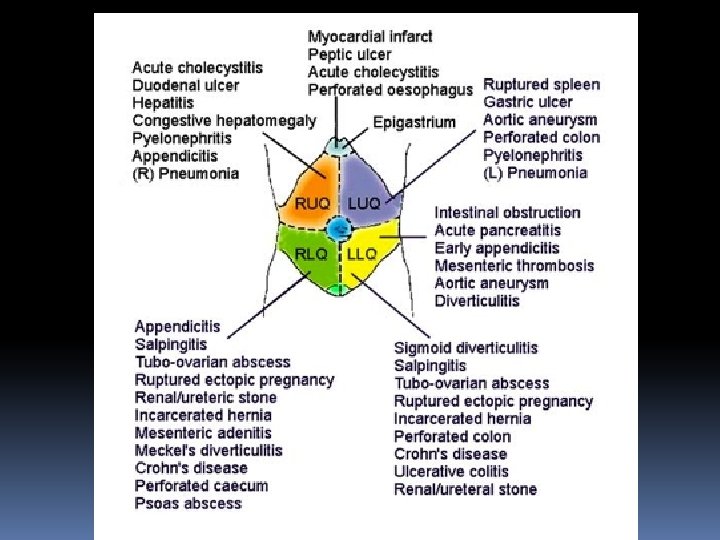

Investigations Bedside UE Blood? Leucocyte Esterase and nitrites Urine HCG ECG – anyone with upper abdominal pain or elderly Bloods ALL WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE NEED BHCG What are your differentials? Avoid machine gun approach!

Radiology CXR –? perforation ? Extra abdominal pathology ? Complications of intra-abdominal disease

Which of the following is NOT an indication for plain abdominal imaging? 1. Bowel Obstruction 2. Constipation 3. Tracking Renal Calculi 4. Foreign Body

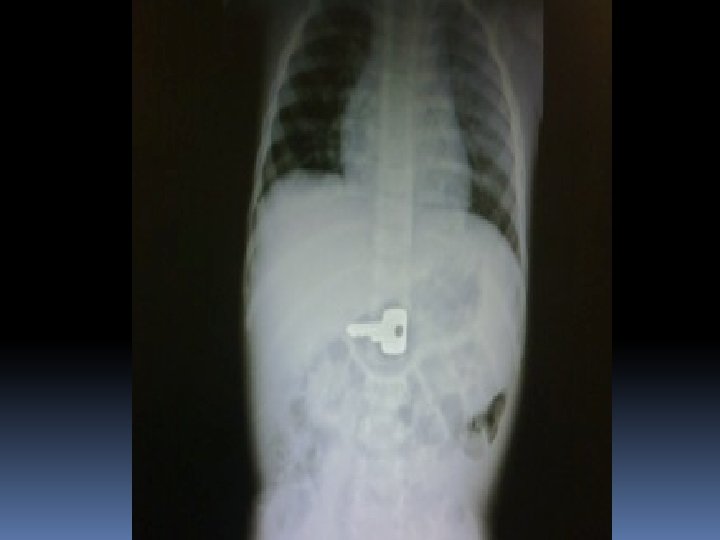
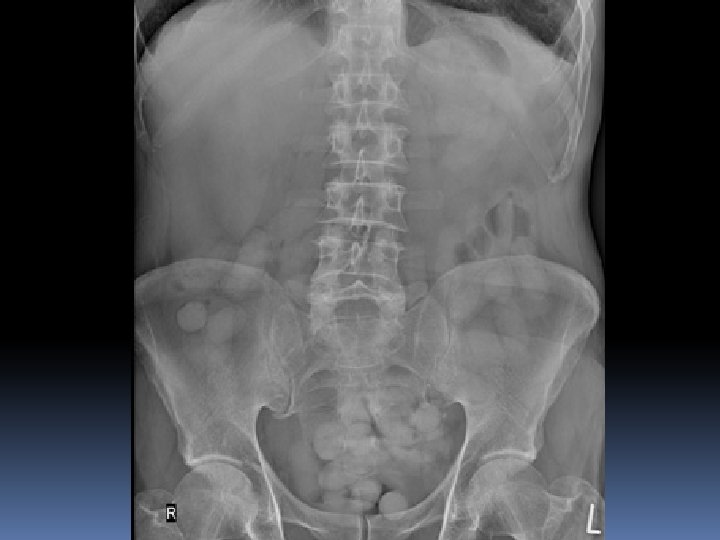
SOME INTRESTING AXRs
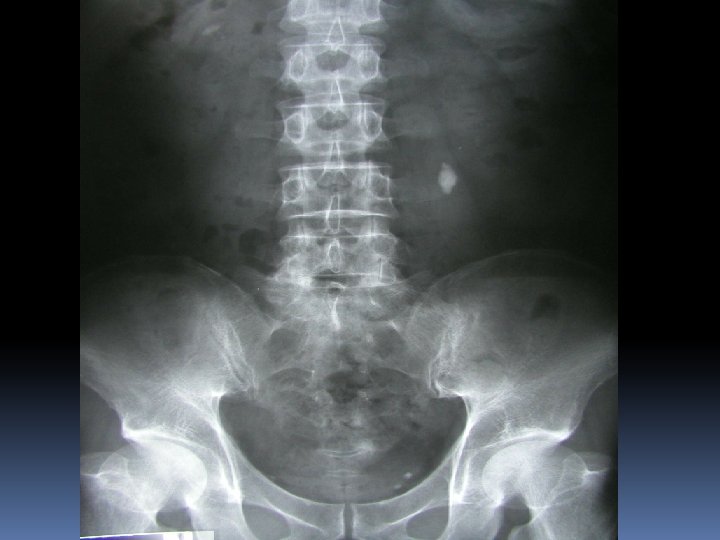

Other imaging ULTRASOUND Biliary Disease Good for gynae complaints Rule out Ectopic pregnancy Appendicitis in children No radiation

CT ABDOMEN CT is accurate for diagnosis of Renal colic Appendicitis Diverticulitis AAA Intra abdominal Abscesses Mesenteric Ischaemia Bowel Obstruction Avoid repeated CT scans Limit use in younger patients Avoid where possible in pregnant females
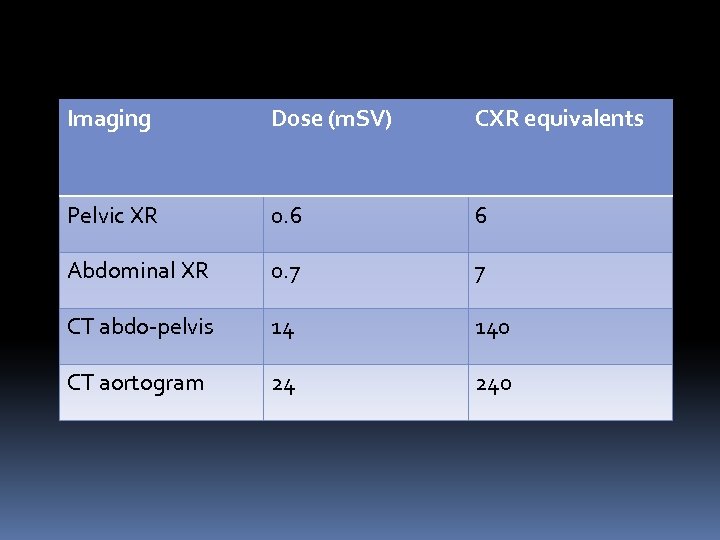
Imaging Dose (m. SV) CXR equivalents Pelvic XR 0. 6 6 Abdominal XR 0. 7 7 CT abdo-pelvis 14 140 CT aortogram 24 240

Management Resuscitate with ABC APPROACH Large bore access N Saline bolus 20 ml/kg x 2 if shocked If bleeding think hypotensive resuscitation All should be NBM until provisional diagnosis Ensure normothermia Maintenance fluids and fluid balance Analgesia doesn’t mask signs Use a the pain scale Morphine titrated to pain. Normally 0. 1 mg/Kg Paracetamol adjunct NSAIDs for renal colic Correct Electrolytes Thromboprophylaxis

Cases

Case 1 21 year old female 24 hour history of vague peri-umbilical abdominal pain. Moved down to the RIF. Now constant and sharp. Associated with 2 x vomits and feels flushed No appetite Normal Bowels

What clinical signs may lead you to a diagnosis of appendicitis? Lie still RIF tenderness Rebound Rovsig’s sign Psoas Sign

Imaging? AXR rarely useful USS Not as good as CT Good for female to exclude gynae pathology If appendix is visualised is useful CT Only if there is doubt about diagnosis Sensitivity up to 98% High radiation dose Diagnose other pathology if no appendicitis Elderly
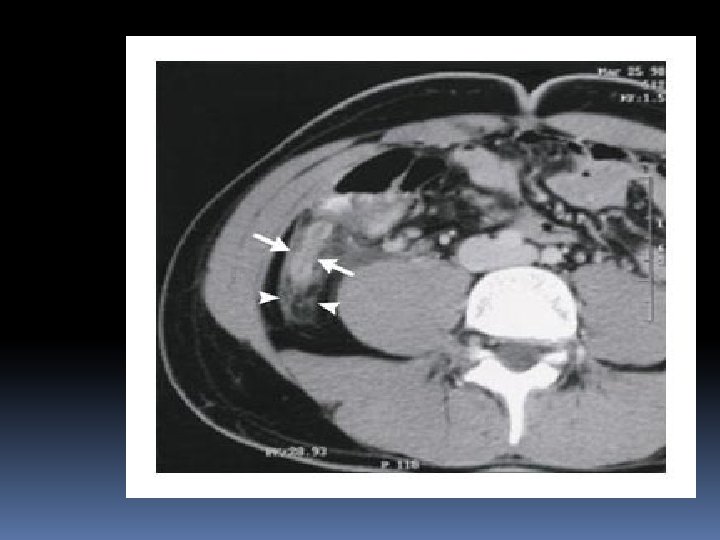

Management NPO Analgesia Anti-emetic if necessary Maintenance fluids IVABs – e. g. Ceftriaxone, Gentamicin and Metronidazole Surgical Referral
Case 2 40 yr old obese female RUQ pain Pain is constant nausea, vomiting fevers and chills PMH Asthma MEDS OCP SH Drinks 2 std / week Smokes 20/day Nil drugs
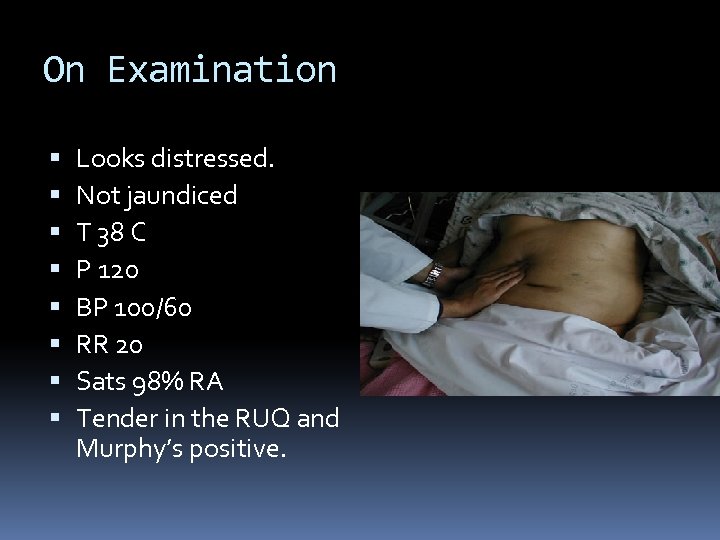
On Examination Looks distressed. Not jaundiced T 38 C P 120 BP 100/60 RR 20 Sats 98% RA Tender in the RUQ and Murphy’s positive.

What blood Tests will you order on this patient?

HB 13. 8 WCC 16. 0 Neuts 12. 4 Lymph 1. 6 EUC Normal Bil 9 (<18) ALP 450 (30 -130) GGT 320 (<60) ALT 41 (5 -55) AST 30 (5 -55) Amylase 28 (<120) Lipase 40 (<60)
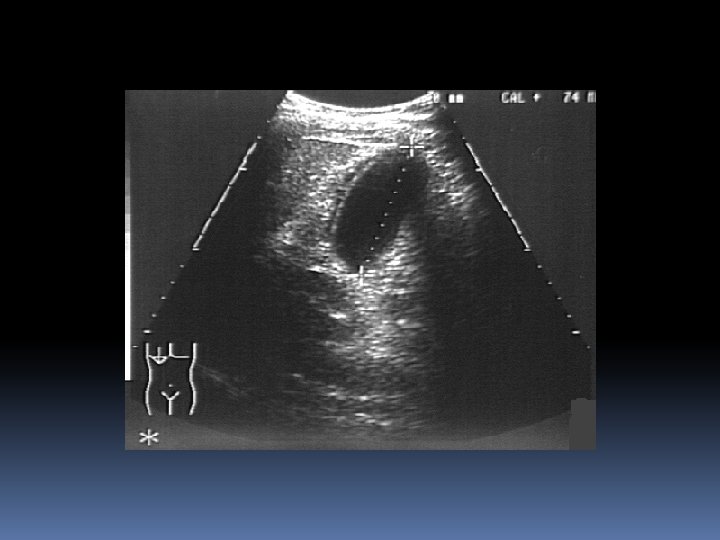
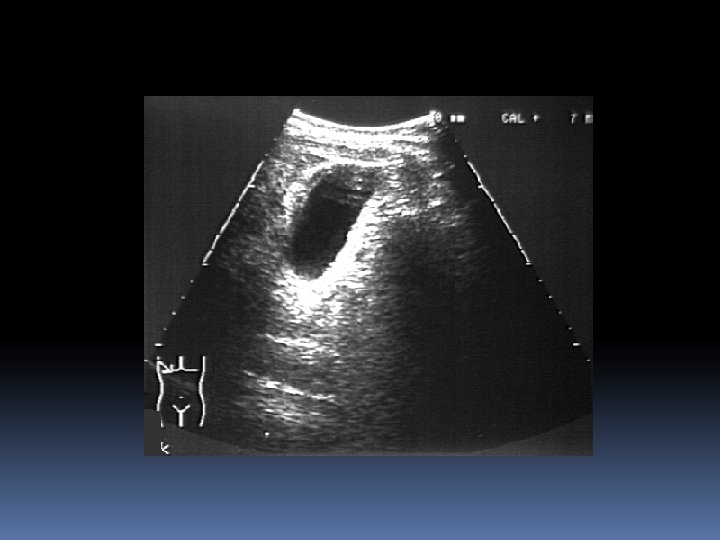

Management NPO IVF IV abs –Ampicillin + Gentamicin Analgesia +- anti emetic Refer to surgeons

Case 3 52 yr old alcoholic Constant epigastric pain radiating to the back. Worsening over the past 2 days Improved with sitting up and forwards Nausea and vomiting Bowels OK PMH Chronic Airways Limitation Alcoholic Gastritis MEDS Thiamine 100 mg daily SH Boarding house resident Drinks 4 litres wine/day Smokes 20/day
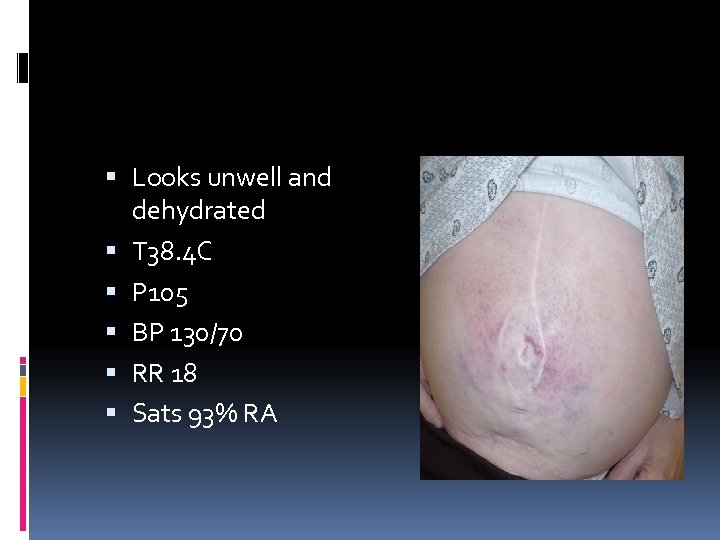
Looks unwell and dehydrated T 38. 4 C P 105 BP 130/70 RR 18 Sats 93% RA
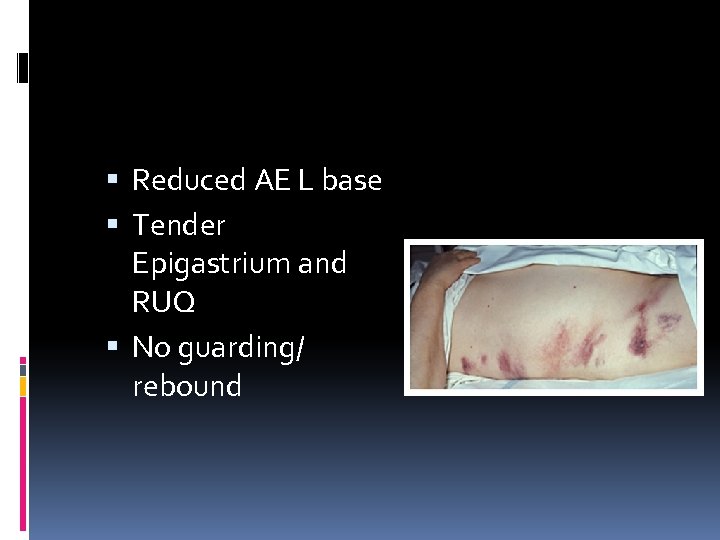
Reduced AE L base Tender Epigastrium and RUQ No guarding/ rebound

What blood tests will you order?

Blood Results Biochem Na 129 K 4. 0 Cr 62 Ur 8. 0 Amylase 1080 (<120) Lipase 950 (<60) Bil 11 ( 18) GGT 900 (<60) ALP 200 ( < 140) AST 300 (5 -55) ALT 250 (5 -55) LDH 800( 105 -333) Glucose 15 Alb 23 Ca (Corr) 2. 0 Haem HB 114 WCC 17 Coags Normal
What imaging will you perform ( if any)?
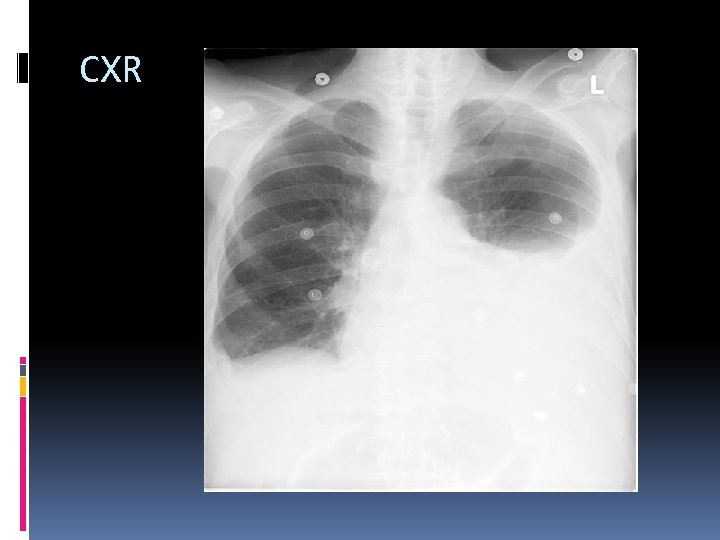
CXR

Imaging CT Confirms diagnosis Identifies complications Help’s grade severity Not always necessary in ED USS Poor visualisation of pancreas Good for looking at gall stones/ biliary tree dilatation CXR Look for complications Pleural Effusion, Atelectasis, ARDS

Management O 2 NBM IVF Analgesia +-Antibiotics (controversial) Correct Electrolytes Thromboprophylaxis ICD/Art-line/CVC depending on severity Surgical Admit +_ ICU review

Causes G all stones E toh T rauma S teroids M umps A utoimmune S corpion Bites H yperlidaemia/ hypercalcaemia/hypothermia E RCP D rugs

Case 4 27 yr old female 6/40 LIF constant severe sharp pain Radiating to the back Light bright red PV spotting Feels light headed PMH IVF Previous D+C x 2 Ovarian Cysts MEDS Nil SH Lives with partner Non-smoker Non-Drinker

On Examination Looks unwell. Pale, diaphoretic, restless P 150 BP 70/40 RR 26 Sats 98% RA Tender and guarding in the LIF PV Bright red blood spotting L adnexal tenderness ++

How do you manage this patient? Panic! ( don’t!) Call for senior help Large bore IV access x 2 (16 G or larger) Urgent Cross Match Fluid resuscitation Call O+G urgently Needs OR immediately
Case 5 88 yr old female. Peri-umbilical, colicky abdominal pain for 2 days Abdominal distension Vomits x 10 Reduced flatus for 2 days. PMH Cholecystectomy appendectomy TAH BSO Hypertension

On examination Looks distressed Lying Still T 37. 5 P 110 sinus BP 150/80 RR 18 Sats 98% RA Abdomen Distended Generally tender No guarding rebound or rigidity High pitched bowel sounds

Investigations

Investigations Labs AXR CT
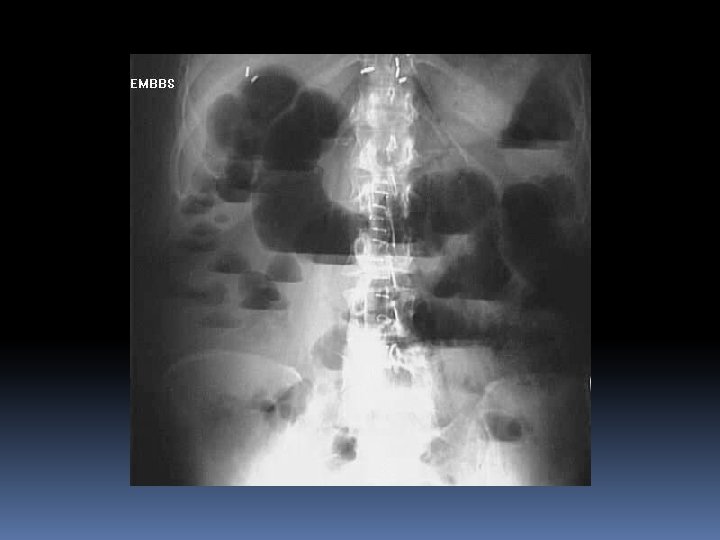
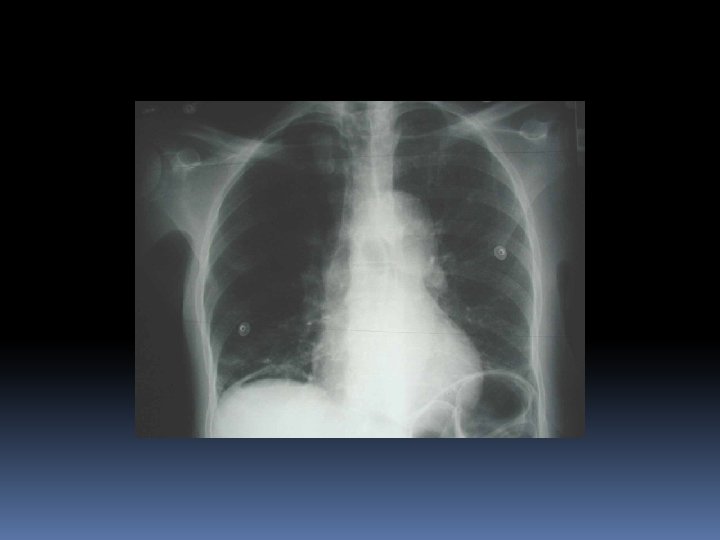

Management NPO Fluid resuscitation Monitor volume status – may have large volume shifts Correct Electrolytes Analgesia NG if vomiting IV Abs – Ceftriaxone, metronidazole Urgent Surgical consult for OR
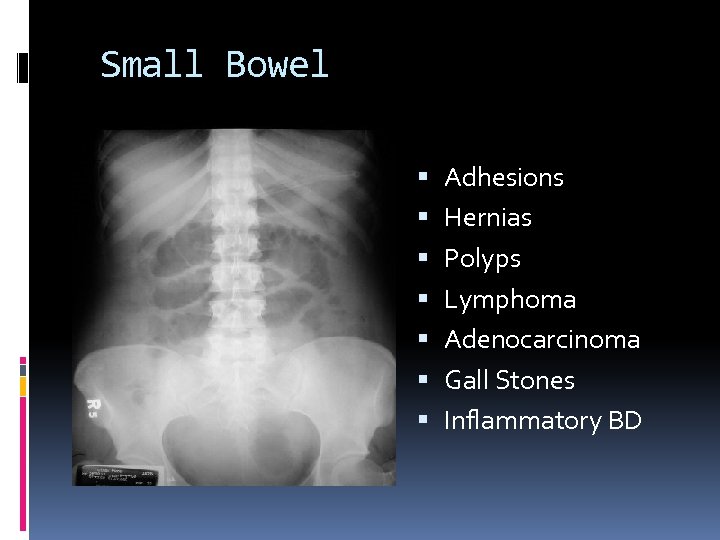
Small Bowel Adhesions Hernias Polyps Lymphoma Adenocarcinoma Gall Stones Inflammatory BD
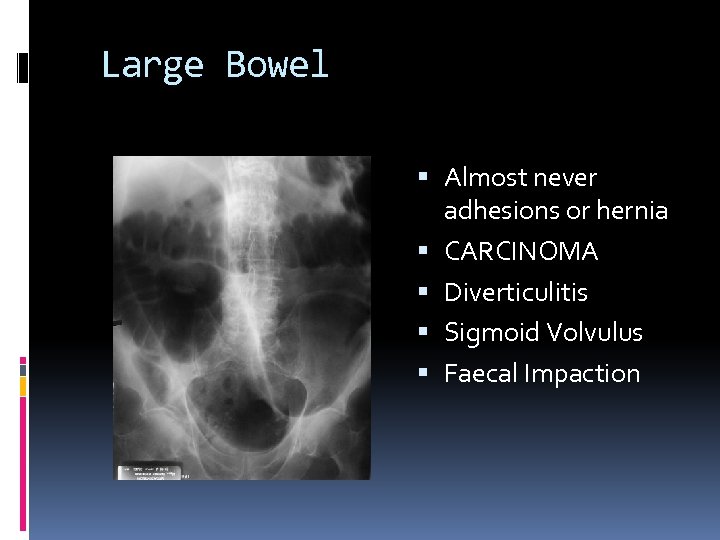
Large Bowel Almost never adhesions or hernia CARCINOMA Diverticulitis Sigmoid Volvulus Faecal Impaction

Case 6 73 yr old male presents with sudden onset of central abdominal pain radiating to the back. He also reports weakness to both legs PMH HT Hypercholesterolemia Current smoker 30/day MEDS Aspirin 100 mg Daily Perindopril 5 mg Daily Atorvastatin 10 mg Daily SH Lives Alone Fully independent with ALS Occasional alcohol
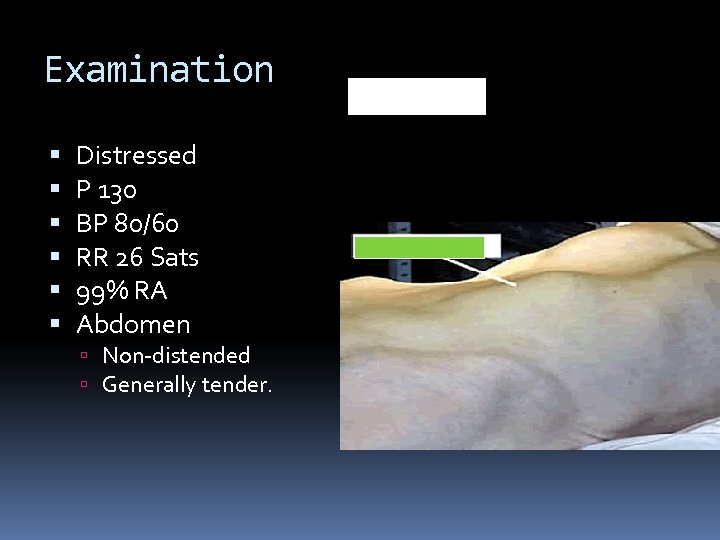
Examination Distressed P 130 BP 80/60 RR 26 Sats 99% RA Abdomen Non-distended Generally tender.
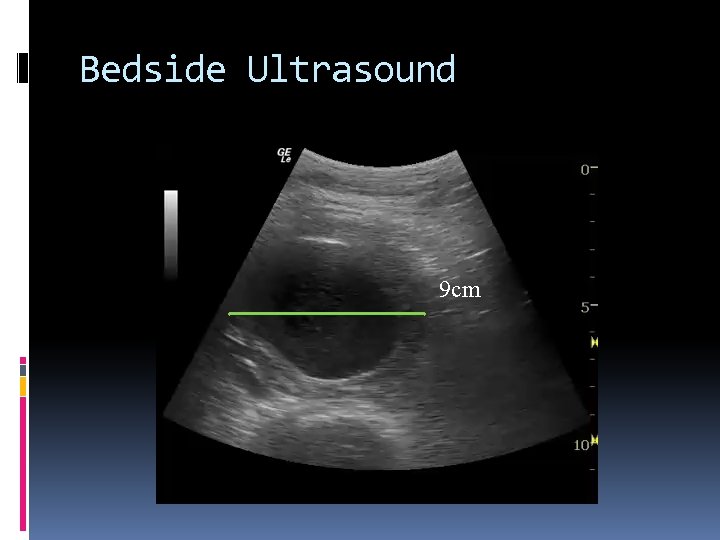
Bedside Ultrasound 9 cm

Management of ruptured AAA Senior help ABC Large Bore IV Access x 2 Hypotensive resuscitation Analgesia Ensure O neg available Ensure normothermia Urgent Vascular Consult To OR

Last Case! 85 yr old male. Nursing home resident Central Abdominal Pain Sudden onset. Severe PMH MEDS Dementia MI SH Clopidogrel 75 mg Daily Metoprolol 25 mg BD Perindopril 5 mg daily Mild dementia Forgetful Requires some assistance with bathing and toileting Feeds Self Walks with frame Non-smoker Non-drinker

Examination Looks dry and emaciated P 120 - 140 BP 110/70 RR 30 Sats 96% RA T 37. 4 C Abdomen Generally tender No guarding rigidity or rebound
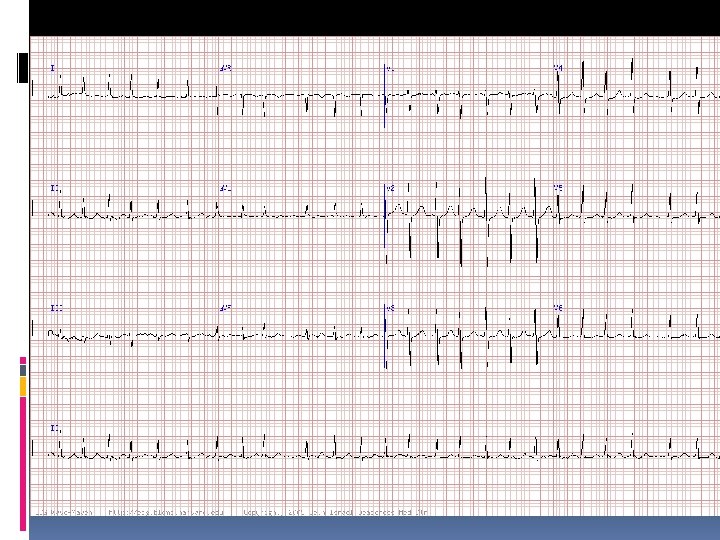
ECG
Differential?

ABG p. H 7. 10 p. CO 2 15 P 02 80 Bic 8 BE -15 Lactate 10. 2
Management ABC NPO IV access IVF Analgesia IV abs Urgent Surgical Consult Urgent CT mesenteric angiogram OR

Mesenteric Ischaemia Surgical Emergency Small bowel has warm ischaemic time of 2 -3 hours Rapidly progresses to gangrene, septic shock and death Need high index of suspicion to diagnose it Severe pain but little tenderness on examination

Case 7 40 yr old male presents with sudden onset of severe R loin to groin pain. Excruciating pain. Coming in waves. Feels nauseated and has vomited x 2. Patient is agitated, pacing around the room, unable to sit still. Screaming in pain. P 120 sinus BP 160/80 T 37. 0 C RR 18 Sats 99% RA R renal angle tender

Differential Diagnosis? Renal Colic Pancreatitis Cholecystitis Appendicitis Ruptured/leaking AAA

UA Erythrocytes ++++ No leucocytes No nitrites
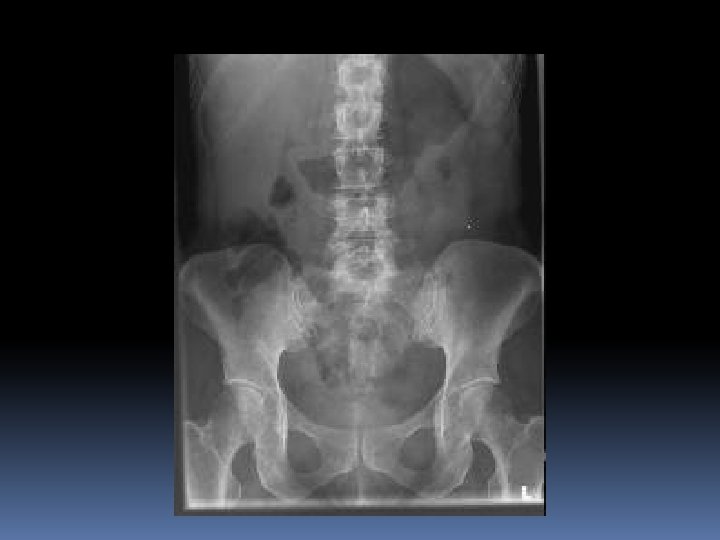

Investigations UA EUC FBC (other bloods if diagnosis unclear) CT KUB

Management Analgesia NSAID Morphine IV titrated to pain IV fluids – maintenance only Observe

Who should we CT On going pain Impaired renal function Fever Diagnosis not clear

Indications for admission Infection Impaired Renal Function Pain ongoing– needing IV opiates Stone > 5 mm Obstruction/hydronephrosis on CT Stag horn Calculus on CT

Take Home Message Exclude life threatening pathology BHCG in female of child bearing age Be mindful of radiation exposure Beware of Abdominal pain in the Elderly Never ignore abnormal vital signs Ask for help if not sure about diagnosis/Rx

Thanks for your patience!
fddede11b84100f565144eeda67d4320.ppt