3d5c4f8727e46566e0e8fed67d9d8c67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

– an academic spin off company www. medbase. fi

• Medbase is founded by highly trained medical doctors specialised in drug therapy • Medbase products improve drug safety in the main problem areas of: • • • Drug interactions & adverse drug reactions Drug use in pregnancy and lactation Renal failure Hepatic impairment Cross-allergies of drugs Natural products • Recommendations reduce harm, save time and reduce the need for consultation • Recommendations on dosage modification or alternative drugs • Holistic clinically oriented recommendation on patient monitoring
• Quarterly updates guarantee always up-to-date information • Easily integrated SQL databases to portals, EPRs, pharmacy IT -systems, mobile & PDA solutions • New language versions easy and inexpensive to produce • Easy integration to local drug registries – Generic drug name, fully ATC- and Rx. Norm- code compliant • Designed for point of care • Patient versions available for

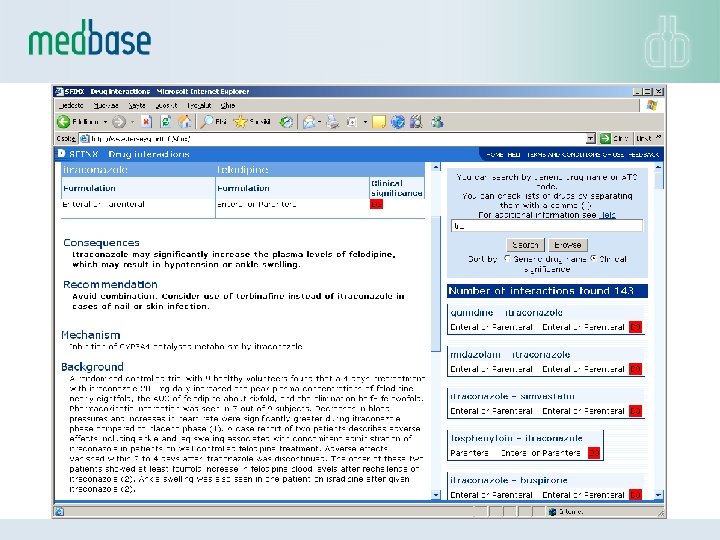
Interaction Database • INXBASE contains information on more than 20. 000 drug interactions (03/2017) - among the most comprehensive drug interaction databases in the market • INXBASE gives a warning on the potential clinical problem with a specific drug interaction taking into account the formulation of the drug • INXBASE provides medical expert recommendations on circumventing or controlling the clinical problem, e. g. by suggesting an alternative choice of drug • The database covers the explanation of interaction mechanisms and a summary of the documentation the interaction is based on, as well as key references
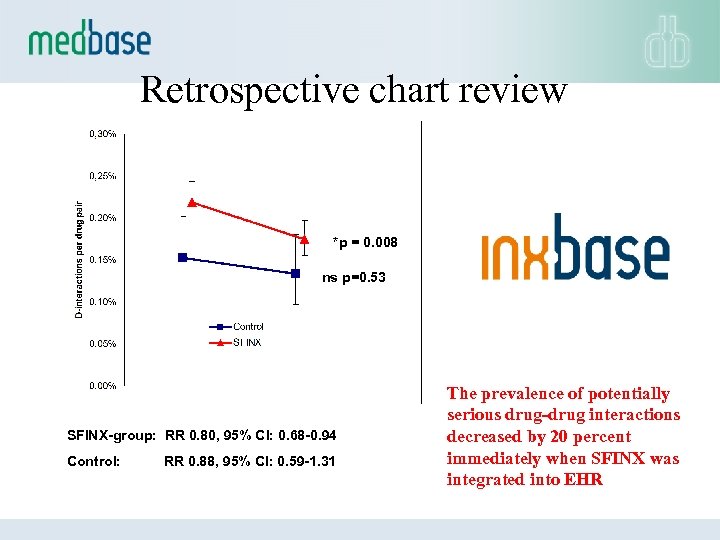
Retrospective chart review *p = 0. 008 ns p=0. 53 SFINX-group: RR 0. 80, 95% CI: 0. 68 -0. 94 Control: RR 0. 88, 95% CI: 0. 59 -1. 31 The prevalence of potentially serious drug-drug interactions decreased by 20 percent immediately when SFINX was integrated into EHR

• Survey on usability & perceptions of database in Sweden • 1871 (23%) answers from prescribers or pharmacists • Used at least weekly or more often by 45% of the prescribers and 51% of the pharmacists • Among the prescribers, 74% reported that the information received made them change their action at least sometimes • Sfinx was typically used in a direct patient consultation situation, i. e. at POINT OF CARE International journal of medical informatics 2015: 84; 327– 333.

Analysis of adverse drug effects

Purpose • A tool to analyse 9 clinically important adverse drug effects from patient’s medication: – – – – – Anticholinergic effect QT-prolongation Sedation Orthostatic hypotension Renal toxicity Seizure risk Risk for bleeding Constipation Serotonergic overstimulation

• More than 1500 drugs analysed/characterised • Scoring based on SOP specifically designed for each adverse effect • Scoring: • • 0 - No effect 1 - Mild 2 - Moderate 3 - Severe • Over 13000 scores
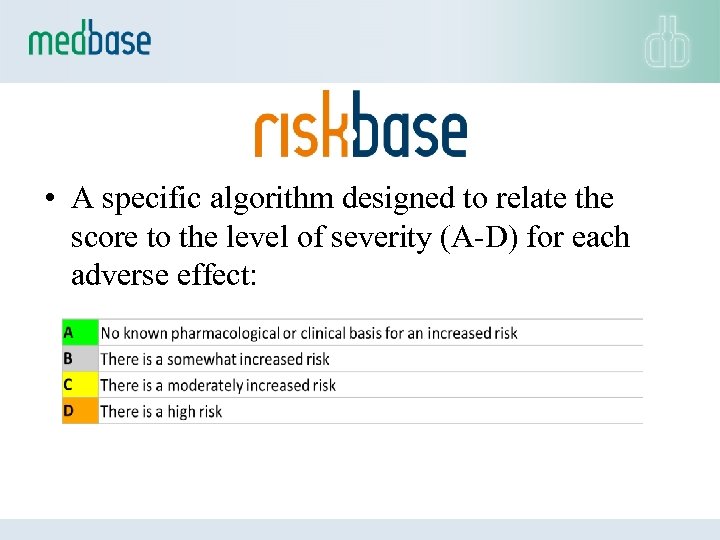
• A specific algorithm designed to relate the score to the level of severity (A-D) for each adverse effect:

• Standard phrases (easy to translate) for each adverse effect, e. g. anticholinergic effect: Consequence There is a high risk for anticholinergic effects such as dry mouth, constipation, urinary impairment or retention, risk of falling, cognitive impairment and confusion. Recommendation The risk is additive. Consider reducing the number of anticholinergic drugs.

• Decision support for drug use in pregnancy - and lactation - – Concise understanding on the of the safety of clinically used drugs during different stages of pregnancy and during lactation, including information on: – Clinical, ultrasound, laboratory etc. monitoring – Dosage modification, recommendation on folic acid substitution – Vitamins, micronutrients, illicit drugs – Covers extensively the documentation from the medical literature, manufacturer given information and different national surveillance registers – Same structure as INXBASE has (similar easy integration) – Enables quick comparison of different drug within one drug group to ease the right choice of medication
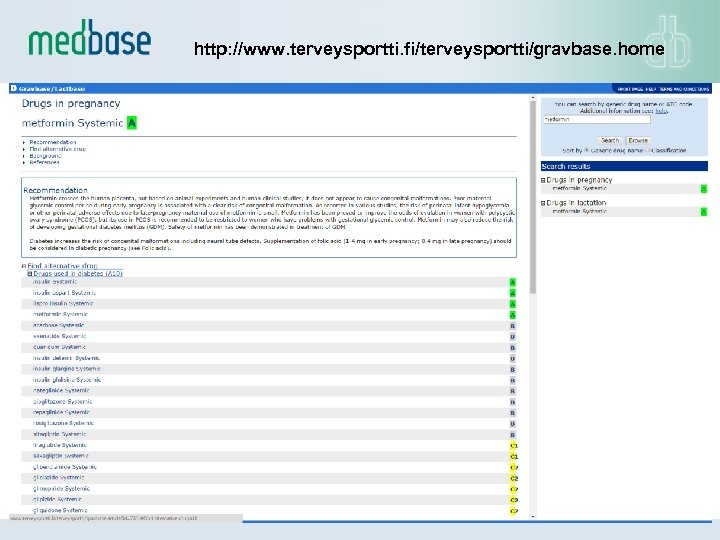
http: //www. terveysportti. fi/terveysportti/gravbase. home
• The most comprehensive database in the world for drug dosing in renal failure • Information on the safety and detailed dosage recommendations of drugs in renal failure • Dosage recommendations based on glomerular filtration rate (GFR) • Evaluation of nephrotoxicity • A fully referenced, ATC & Rx. Norm-compliant decision support database for portals and integration
Prevalence of renal failure • In the U. S. 35. 000 people are estimated to suffer from chronic renal failure • 13% of the population • Measured GFR<60 ml/min or demonstrated renal injury • A recent meta-analysis estimated that in the Western population 23%-36% of people >64 years of age has GFR<60 ml/min
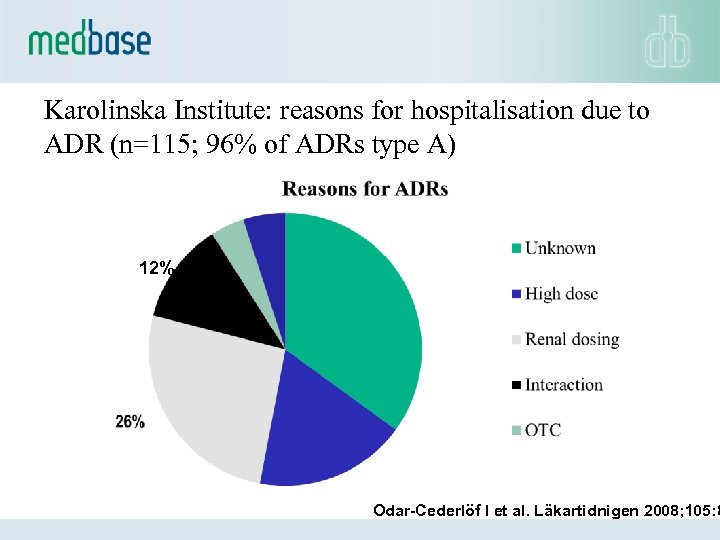
Karolinska Institute: reasons for hospitalisation due to ADR (n=115; 96% of ADRs type A) 12% Odar-Cederlöf I et al. Läkartidnigen 2008; 105: 8
Blix HS et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21: 3164 -71. • Prospective study in general hospitals • 201 patients (GFR<60 ml/min; 25% of the whole population) used an average of 10 drugs • Approximately 40% of drugs were harmful to the kidneys or required modification of the dose; 5% fully contraindicated • Almost all patients were co-administered a minimum of two harmful drugs • Typical risk drug toxicity in 62% of exposed patients • 26% of risk drug exposures caused toxicity – – – Beta-lactam antibiotics, ciprofloxacin, aminoglycosides antithrombotic agents and anticoagulants anti-inflammatory drugs, codeine, tramadol ACE-inhibitors/sartans, spironolactone/potassium Allopurinol, metformin, sulphonylureas
Nielsen AL. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2014; 114: 407 -13 • Study in Denmark with 232 patients with e. GFR 10 -50 ml/min (moderate to severe renal failure) using • 1633 drugs were administered to these patients • 15% of prescriptions were not following dosing recommendations • 26 prescriptions were contraindicated • 23% of the study patients received at least one drug that was not dosed in agreement with guidelines • Conclusion: automated decision support is needed to reduce inappropriate prescribing in RF
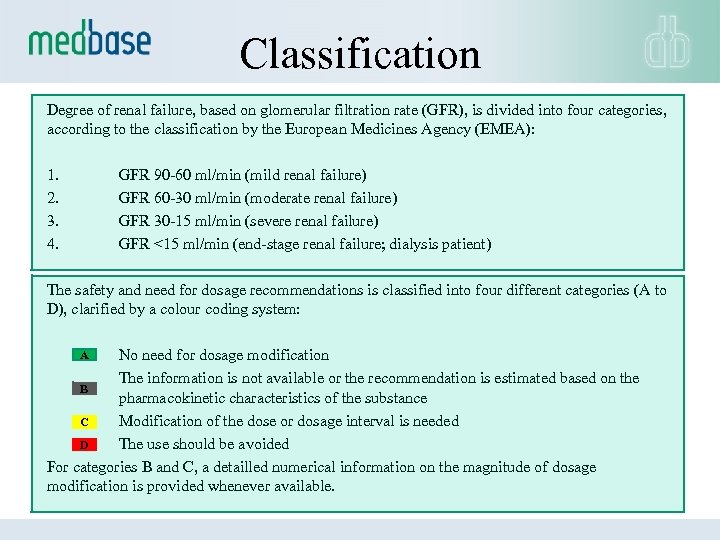
Classification Degree of renal failure, based on glomerular filtration rate (GFR), is divided into four categories, according to the classification by the European Medicines Agency (EMEA): 1. GFR 90 -60 ml/min (mild renal failure) 2. GFR 60 -30 ml/min (moderate renal failure) 3. GFR 30 -15 ml/min (severe renal failure) 4. GFR <15 ml/min (end-stage renal failure; dialysis patient) The safety and need for dosage recommendations is classified into four different categories (A to D), clarified by a colour coding system: A No need for dosage modification The information is not available or the recommendation is estimated based on the B pharmacokinetic characteristics of the substance Modification of the dose or dosage interval is needed C The use should be avoided D For categories B and C, a detailled numerical information on the magnitude of dosage modification is provided whenever available.
http: //www. terveysportti. fi/terveysportti/renbase. home

Drug treatment in hepatic impairment

• The disease state that affects drug treatment is cirrhosis – Prevalence about 0. 3% of the population • One of the key disease states that requires documentation for new drugs • In dosing of about 1500 drugs is characterised in hepatic impairment
Hepatic impairment and AEs Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013; 69: 1565 -73. • Retrospective chart study in 400 patients with cirrhosis at hospital admission (Child-Pugh: A 18%; B 39%; C 43%) • Altogether 1653 prescriptions (0 -15 / patient) – Every fifth (336) prescription with an error (184 patients) • 36 contraindicated; 300 too high dose (no adjustment) – 69 adverse events related to non-adjustment of the dose in relation to the hepatic function • 68% preventable – Flaws in prescribing led to 94 extra in-hospital days – Problems drugs: • NSAIDs (g-i bleeding), hypnotics and other benzodiazepines,
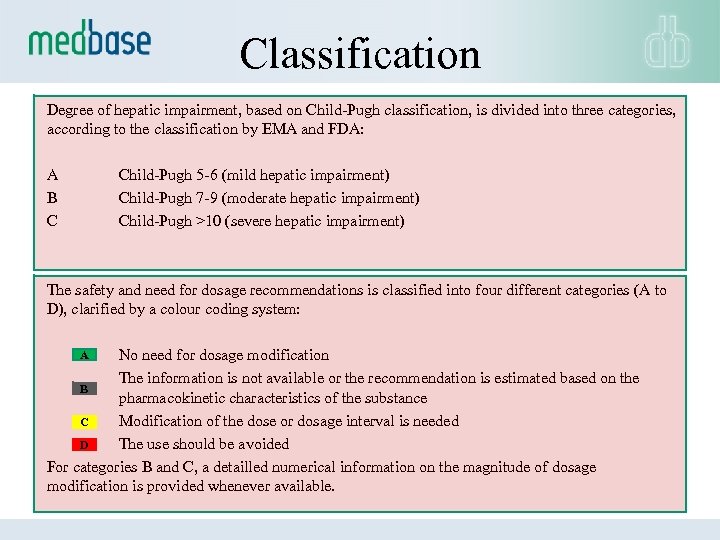
Classification Degree of hepatic impairment, based on Child-Pugh classification, is divided into three categories, according to the classification by EMA and FDA: A B C Child-Pugh 5 -6 (mild hepatic impairment) Child-Pugh 7 -9 (moderate hepatic impairment) Child-Pugh >10 (severe hepatic impairment) The safety and need for dosage recommendations is classified into four different categories (A to D), clarified by a colour coding system: A No need for dosage modification The information is not available or the recommendation is estimated based on the B pharmacokinetic characteristics of the substance Modification of the dose or dosage interval is needed C The use should be avoided D For categories B and C, a detailled numerical information on the magnitude of dosage modification is provided whenever available.

– cross-allergies between drugs
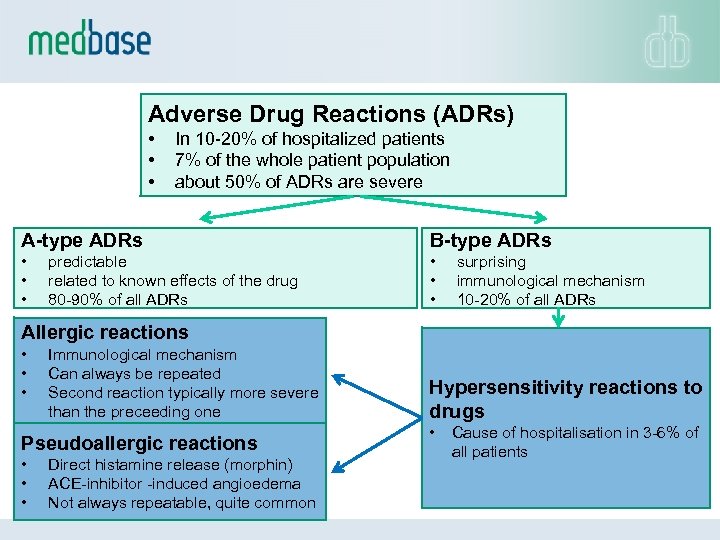
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) • • • In 10 -20% of hospitalized patients 7% of the whole patient population about 50% of ADRs are severe A-type ADRs B-type ADRs • • • predictable related to known effects of the drug 80 -90% of all ADRs surprising immunological mechanism 10 -20% of all ADRs Allergic reactions • • • Immunological mechanism Can always be repeated Second reaction typically more severe than the preceeding one Pseudoallergic reactions • • • Direct histamine release (morphin) ACE-inhibitor -induced angioedema Not always repeatable, quite common Hypersensitivity reactions to drugs • Cause of hospitalisation in 3 -6% of all patients

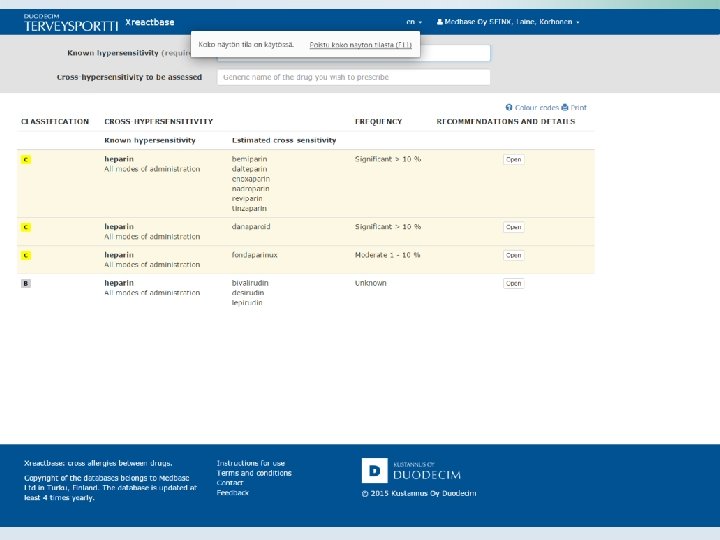
• Hypersensitivity is a common adverse drug reaction • Some of the reactions are life-threathening • Cross-hypersensivity between drugs is not uncommon • On the other hand some of the cross-reactions which are commonly feared in clinical work (e. g. sulfonamide antibiotics vs. non-antibiotics) are not true and unnecessarily prevent effective drug treatment • Skin tests are often useful in the diagnostic search of alternative treatments to prevent cross-reactions • Alternative drug can be found in most cases
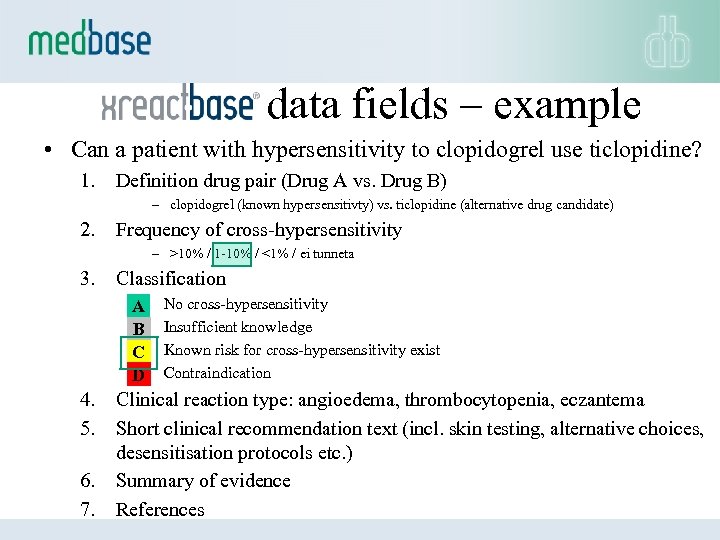
data fields – example • Can a patient with hypersensitivity to clopidogrel use ticlopidine? 1. Definition drug pair (Drug A vs. Drug B) – clopidogrel (known hypersensitivty) vs. ticlopidine (alternative drug candidate) 2. Frequency of cross-hypersensitivity – >10% / 1 -10% / <1% / ei tunneta 3. Classification A B C D 4. 5. 6. 7. No cross-hypersensitivity Insufficient knowledge Known risk for cross-hypersensitivity exist Contraindication Clinical reaction type: angioedema, thrombocytopenia, eczantema Short clinical recommendation text (incl. skin testing, alternative choices, desensitisation protocols etc. ) Summary of evidence References
Partnering Strategy Local partner -Translations and feedback -Customising for the national formulary -Expertise in the market -Rapid spreading of the decision support system -Service in end-user’s native language -Long-lasting national collaboration -Well-organised end-user service

• Customer support: • Content-related questions from end-users • Experience from making the connection between medbase databases and various drug registries – Lists of drug formulations – code for each formulation – Combination preparations • Language versions can be maintained in medbase webbased translation module
3d5c4f8727e46566e0e8fed67d9d8c67.ppt