afdd67bf1b5e523a2a1071368874b6e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Amplifiers and Feedback: 3 Dr. Un-ki Yang Particle Physics Group ukyang@hep. manchester. ac. uk or Shuster 5. 15 1
Web page for Amp & Feedback 2

Realistic OP Amplifier: review Ø Gain is NOT infinite Gain drops at high frequency Ø Gain is NOT constant against frequency Bandwidth: a stable range. -3 d. B Ø Output response is NOT instantaneous Slew rate: response rate Ø Output impedance is NOT zero Ø Input impedance is NOT infinite 3
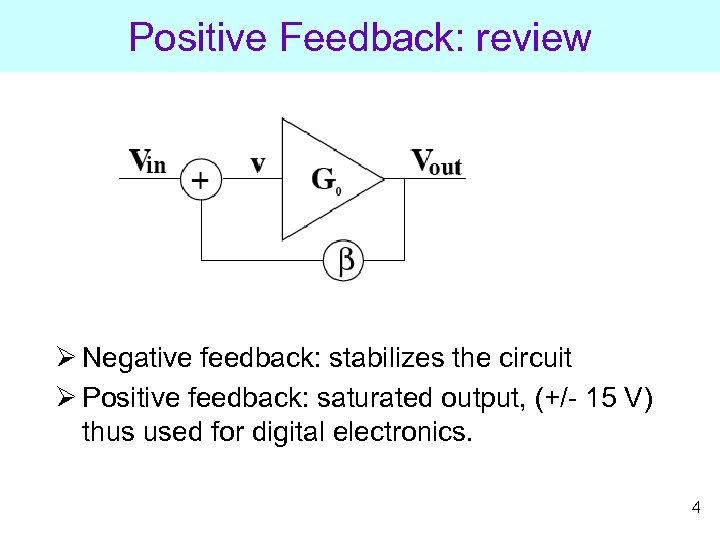
Positive Feedback: review Ø Negative feedback: stabilizes the circuit Ø Positive feedback: saturated output, (+/- 15 V) thus used for digital electronics. 4
Schmitt Trigger: review Ø Two different thresholds V+, depending on Vout: fix a problem for noisy signal 5
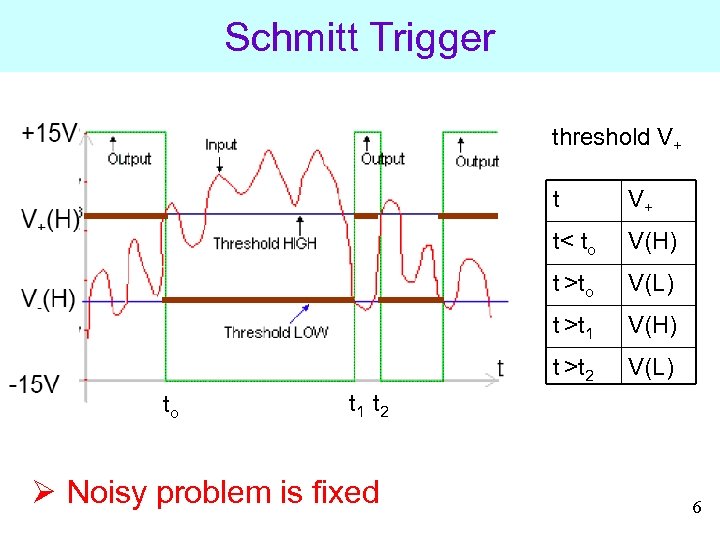
Schmitt Trigger threshold V+ t t< to V(H) t >to V(L) t >t 1 V(H) t >t 2 to V+ V(L) t 1 t 2 Ø Noisy problem is fixed 6
Analogue to Digital conversion (ADC) Ø Why digitized signal? • Analogue signals can be distorted and attenuated • Practically impossible to analyze many analogue channels 7
Analogue to Digital conversion (ADC) Ø Fast conversion (sampling rate) Ø High accuracy (resolution) Ø Linearity 8
ADC Ø Sampling rate: how often do we need to digitize analogue signal? • good to have a high sampling rate but requires fast processing • Nyquist rate = use 2 x highest frequency of the signal Ø Resolution: digitization introduces uncertainty due to a finite step size. • Good resolution: large number of ADC bits: 2 n, but requires fast processing and many chips • Resolution: LSB/2 9
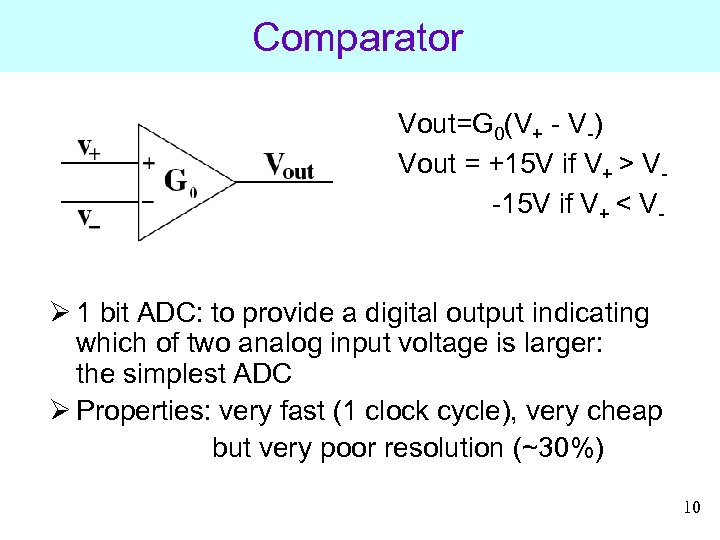
Comparator Vout=G 0(V+ - V-) Vout = +15 V if V+ > V-15 V if V+ < V- Ø 1 bit ADC: to provide a digital output indicating which of two analog input voltage is larger: the simplest ADC Ø Properties: very fast (1 clock cycle), very cheap but very poor resolution (~30%) 10
Flash ADC Ø For n-bit, use 2 n-1 comparators Ø Each comparator has its own threshold voltage, separated by 1 LSB Ø The input to all comparators in parallel (one clock cycle) Ø Output goes to an encoder to get binary format 3 -bit ADC 11
Flash ADC Ø Very fast (basically one clock cycle): good to process high rate events (10 k Hz etc) Ø Buy requires so many comparators for high accuracy (good resolution): very expansive. (32 -bit : 4 X 10 E 9 comparators ) 12

Slope Converter Slope ~ 1/RC* Vin Ø Use one integrator and one comparator 13
Slope Converter ADC Ø Advantage: good resolution with only two comparators Ø Does not require precise components: cheap, designed to average out noise Ø Disadvantage: slow, 2 n clock cycles for n-bits 14
Successive Approximation ADC Ø Use a successive approximation register Ø Comparator: check Vin vs DAC reference signal ( MSB --> LSB ): binary search Ø Advantage: faster, only n clock cycles for n-bit Ø Disadvantage: register for DAC need to be extremely accurate 15
DAC (Digital-Analogue-Converter) MSB LSB 16
afdd67bf1b5e523a2a1071368874b6e7.ppt