 Ammeter
Ammeter
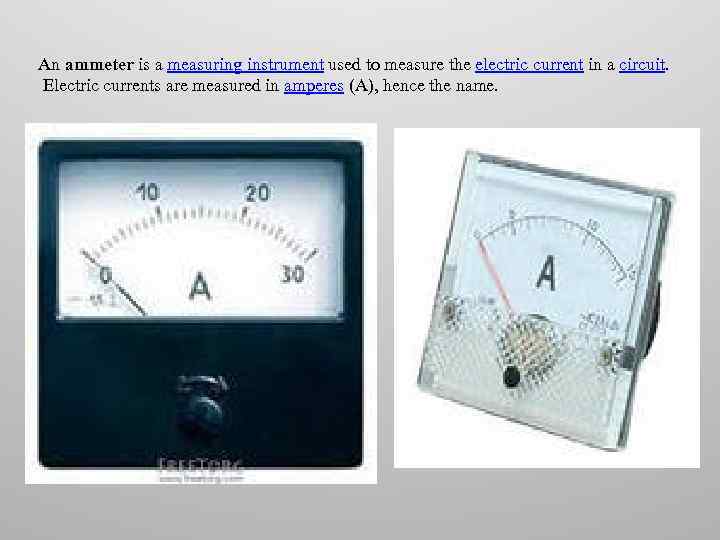 An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name.
An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name.
 Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the mill amperes or microampere range, are designated as millimeters or micrometers.
Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the mill amperes or microampere range, are designated as millimeters or micrometers.
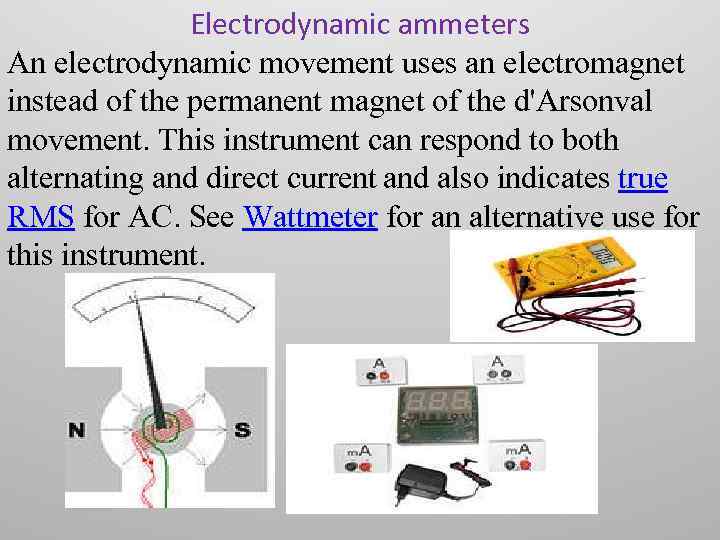 Electrodynamic ammeters An electrodynamic movement uses an electromagnet instead of the permanent magnet of the d'Arsonval movement. This instrument can respond to both alternating and direct current and also indicates true RMS for AC. See Wattmeter for an alternative use for this instrument.
Electrodynamic ammeters An electrodynamic movement uses an electromagnet instead of the permanent magnet of the d'Arsonval movement. This instrument can respond to both alternating and direct current and also indicates true RMS for AC. See Wattmeter for an alternative use for this instrument.
 Hot-wire ammeters In a hot-wire ammeter, a current passes through a wire which expands as it heats. Although these instruments have slow response time and low accuracy, they were sometimes used in measuring radio-frequency current. These also measure true RMS for an applied AC current.
Hot-wire ammeters In a hot-wire ammeter, a current passes through a wire which expands as it heats. Although these instruments have slow response time and low accuracy, they were sometimes used in measuring radio-frequency current. These also measure true RMS for an applied AC current.
 Digital ammeters In much the same way as the analogue ammeter formed the basis for a wide variety of derived meters, including voltmeters, the basic mechanism for a digital meter is a digital voltmeter mechanism, and other types of meter are built around this.
Digital ammeters In much the same way as the analogue ammeter formed the basis for a wide variety of derived meters, including voltmeters, the basic mechanism for a digital meter is a digital voltmeter mechanism, and other types of meter are built around this.
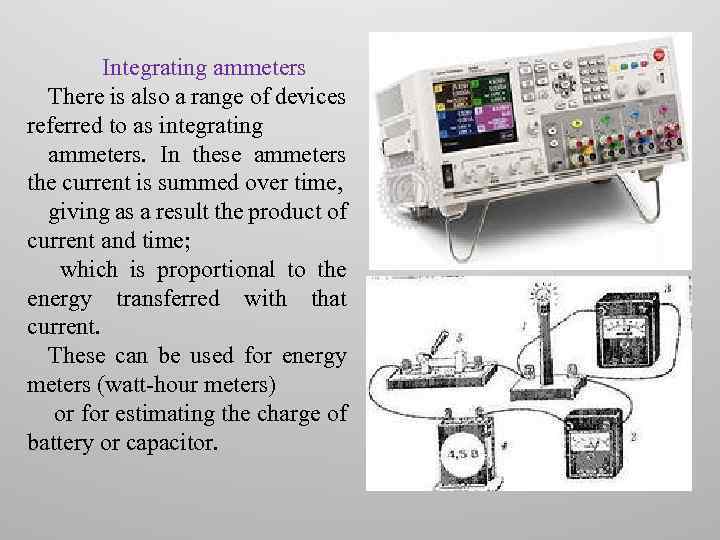 Integrating ammeters There is also a range of devices referred to as integrating ammeters. In these ammeters the current is summed over time, giving as a result the product of current and time; which is proportional to the energy transferred with that current. These can be used for energy meters (watt-hour meters) or for estimating the charge of battery or capacitor.
Integrating ammeters There is also a range of devices referred to as integrating ammeters. In these ammeters the current is summed over time, giving as a result the product of current and time; which is proportional to the energy transferred with that current. These can be used for energy meters (watt-hour meters) or for estimating the charge of battery or capacitor.