4383b1a90527934b7113e8f1aa4b9738.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 American Revolution and the United States Constitution UNIT 2
American Revolution and the United States Constitution UNIT 2
 Causes and Effects of the AM Rev • British tighten control over the colonies • Colonies protest British policies and taxes • Colonies create civilian militias • Declaration of Independence July 4, 1776 • British lose colonies • US borders extend to FL in South, and Mississippi River in the West • First US gov’t =Articles of Confederation • Inherent weaknesses of AOC lead to the creation of US Constitution
Causes and Effects of the AM Rev • British tighten control over the colonies • Colonies protest British policies and taxes • Colonies create civilian militias • Declaration of Independence July 4, 1776 • British lose colonies • US borders extend to FL in South, and Mississippi River in the West • First US gov’t =Articles of Confederation • Inherent weaknesses of AOC lead to the creation of US Constitution
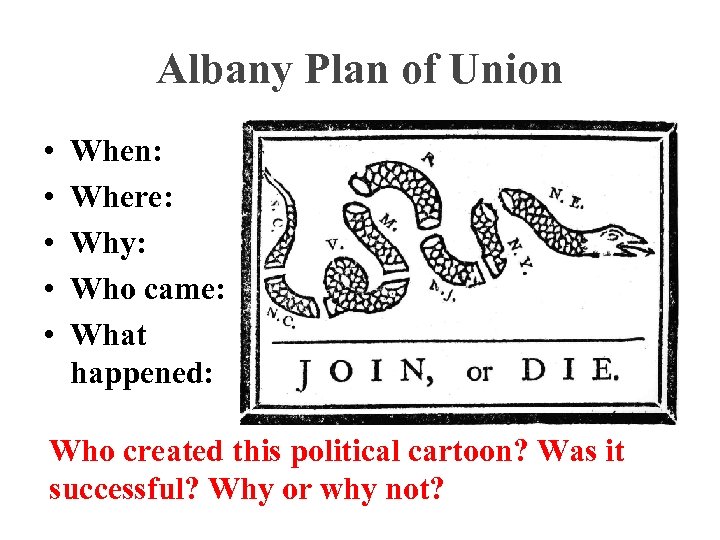 Albany Plan of Union • • • When: Where: Why: Who came: What happened: Who created this political cartoon? Was it successful? Why or why not?
Albany Plan of Union • • • When: Where: Why: Who came: What happened: Who created this political cartoon? Was it successful? Why or why not?
 Influence of the Enlightenment • The “Enlightenment” era in Europe during the 17 th -18 th centuries saw the development of new ideas about the rights of people and their relationship to their rulers. • John Locke was political philosopher whose ideas, more than any other’s, influenced the American belief in self-government.
Influence of the Enlightenment • The “Enlightenment” era in Europe during the 17 th -18 th centuries saw the development of new ideas about the rights of people and their relationship to their rulers. • John Locke was political philosopher whose ideas, more than any other’s, influenced the American belief in self-government.
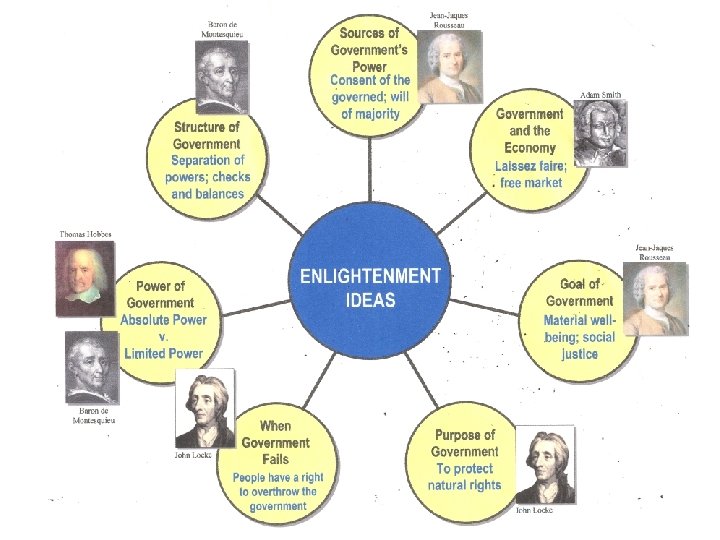
 The Ideas of John Locke wrote about NATURAL RIGHTS · ex: “life, liberty, and property” • that rulers cannot take these away AND must protect them as well · Power comes from “the people” • A “social contract” exists between people and gov’t: – Gov’ts exist to protect people and their natural rights – In return, the people promise to obey the laws and rules – This creates “ordered liberty. ”
The Ideas of John Locke wrote about NATURAL RIGHTS · ex: “life, liberty, and property” • that rulers cannot take these away AND must protect them as well · Power comes from “the people” • A “social contract” exists between people and gov’t: – Gov’ts exist to protect people and their natural rights – In return, the people promise to obey the laws and rules – This creates “ordered liberty. ”
 “Revolutionary” Ideas of John Locke · A government that fails to protect the people’s natural rights, it breaks the social contract • Then the people have the right to change it or overthrow it • Locke’s ideas about the sovereignty and rights of the people were radical for the times • Most of the world was used to absolute rule by kings, emperors, and tribal chieftains. “NO MORE KINGS!”
“Revolutionary” Ideas of John Locke · A government that fails to protect the people’s natural rights, it breaks the social contract • Then the people have the right to change it or overthrow it • Locke’s ideas about the sovereignty and rights of the people were radical for the times • Most of the world was used to absolute rule by kings, emperors, and tribal chieftains. “NO MORE KINGS!”
 Pre-Revolutionary thinking • Thomas Paine was an Only Morons want English immigrant to America who produced a to stay colonists!! pamphlet that challenged the rule of the American colonies by the King of England. • Common Sense made more colonists support the idea of independence from England • Message: “Thinking people want Independence”
Pre-Revolutionary thinking • Thomas Paine was an Only Morons want English immigrant to America who produced a to stay colonists!! pamphlet that challenged the rule of the American colonies by the King of England. • Common Sense made more colonists support the idea of independence from England • Message: “Thinking people want Independence”
 The Revolutionary Period • Anglo-French rivalry leading to conflict with the colonies • The rivalry in North America between England France led to the French and Indian War • Ie: The French & Indians vs “The British”…(that’s US as colonies)
The Revolutionary Period • Anglo-French rivalry leading to conflict with the colonies • The rivalry in North America between England France led to the French and Indian War • Ie: The French & Indians vs “The British”…(that’s US as colonies)
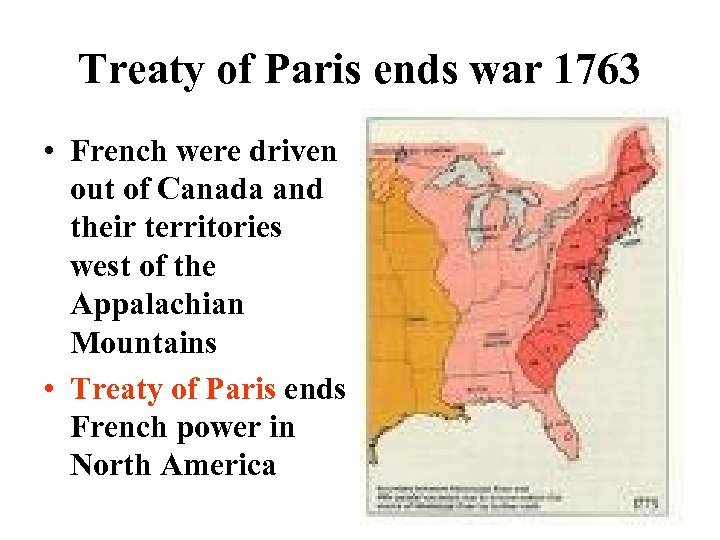 Treaty of Paris ends war 1763 • French were driven out of Canada and their territories west of the Appalachian Mountains • Treaty of Paris ends French power in North America
Treaty of Paris ends war 1763 • French were driven out of Canada and their territories west of the Appalachian Mountains • Treaty of Paris ends French power in North America
 The Road to Revolution • The Proclamation of 1763, which prohibited settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains • New taxes on legal documents (the “Stamp Act”), tea and sugar, to pay costs incurred during the French and Indian War and for British troops to protect colonists.
The Road to Revolution • The Proclamation of 1763, which prohibited settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains • New taxes on legal documents (the “Stamp Act”), tea and sugar, to pay costs incurred during the French and Indian War and for British troops to protect colonists.
 British Acts & Colonial Opposition • • • Proclamation 1763 Sugar Act Currency Act • Stamp Act Quartering Act Townshend Acts Tea Act 1773 “Intolerable Acts” (Coercive and Quebec Acts) ISSUE /Cause for each? Effect or Reaction from Colonists for each?
British Acts & Colonial Opposition • • • Proclamation 1763 Sugar Act Currency Act • Stamp Act Quartering Act Townshend Acts Tea Act 1773 “Intolerable Acts” (Coercive and Quebec Acts) ISSUE /Cause for each? Effect or Reaction from Colonists for each?
 “Sons of Liberty”
“Sons of Liberty”
 Sons of Liberty…Modern
Sons of Liberty…Modern
 “Daughters of Liberty” HOMESPUN
“Daughters of Liberty” HOMESPUN
 Stamp Act Congress 1765 9 colonies sent representatives to say, (basically): “ONLY our colonial political representatives can TAX us…not British Parliament!!” Began NONIMPORTATION/BOYCOTT Of all British goods
Stamp Act Congress 1765 9 colonies sent representatives to say, (basically): “ONLY our colonial political representatives can TAX us…not British Parliament!!” Began NONIMPORTATION/BOYCOTT Of all British goods
 The Road to Revolution Resistance to British rule in the colonies mounted, leading to war: • The Boston Tea Party was staged. • The First Continental Congress was called, to which all of the colonies except Georgia sent representatives, the first time most of the colonies had acted together. • The Boston Massacre took place when British troops fired on anti-British demonstrators. • War began when the “Minutemen” in Massachusetts fought a brief skirmish with British troops at Lexington and Concord.
The Road to Revolution Resistance to British rule in the colonies mounted, leading to war: • The Boston Tea Party was staged. • The First Continental Congress was called, to which all of the colonies except Georgia sent representatives, the first time most of the colonies had acted together. • The Boston Massacre took place when British troops fired on anti-British demonstrators. • War began when the “Minutemen” in Massachusetts fought a brief skirmish with British troops at Lexington and Concord.
 Differences among the Colonists The colonists were divided into three main camps during the Revolution: Patriots: • Believed in complete independence from England • Inspired by the ideas of Locke and Paine and the words of Virginian Patrick Henry • Provided the troops for the American Army, led by George Washington, also of Virginia “Give me liberty, or give me death!”
Differences among the Colonists The colonists were divided into three main camps during the Revolution: Patriots: • Believed in complete independence from England • Inspired by the ideas of Locke and Paine and the words of Virginian Patrick Henry • Provided the troops for the American Army, led by George Washington, also of Virginia “Give me liberty, or give me death!”
 The Declaration of Independence The eventual draft of the Declaration of Independence, authored by Thomas Jefferson of Virginia, reflected the ideas of Locke and Paine
The Declaration of Independence The eventual draft of the Declaration of Independence, authored by Thomas Jefferson of Virginia, reflected the ideas of Locke and Paine
 Road to Independence • Colonies as part of the MERCANTILIST economic system • Salutary Neglect • French and Indian War • Proclamation of 1763 • ACTS, and more ACTS • Colonial Boycotts • Boston “Massacre” • Lexington & Concord, Bunker/Breed’s Hill
Road to Independence • Colonies as part of the MERCANTILIST economic system • Salutary Neglect • French and Indian War • Proclamation of 1763 • ACTS, and more ACTS • Colonial Boycotts • Boston “Massacre” • Lexington & Concord, Bunker/Breed’s Hill
 The Declaration of Independence In Congress, July 4, 1776 “When in the course of human events it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature’s God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation. ”
The Declaration of Independence In Congress, July 4, 1776 “When in the course of human events it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature’s God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation. ”
 The Declaration of Independence “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights, that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. ”
The Declaration of Independence “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights, that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. ”
 The Declaration of Independence “That to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed…”. . That whenever any form of government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the right of the people to alter or abolish it, and to institute new government…
The Declaration of Independence “That to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed…”. . That whenever any form of government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the right of the people to alter or abolish it, and to institute new government…
 The Declaration of Independence “…laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness. ” John Locke’s ideas: Thomas Paine’s ideas:
The Declaration of Independence “…laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness. ” John Locke’s ideas: Thomas Paine’s ideas:
 The Declaration of Independence • Jefferson then went on to detail many of the grievances against King George III • Paine had earlier described many of these “offenses”in Common Sense.
The Declaration of Independence • Jefferson then went on to detail many of the grievances against King George III • Paine had earlier described many of these “offenses”in Common Sense.
 Differences among the Colonists Loyalists (Tories) • Remained loyal to Britain, based on cultural and economic ties • Believed that taxation of the colonies was justified to pay for British troops to protect American settlers from Indian attacks Neutrals • The many colonists who tried to stay as uninvolved in the war as possible
Differences among the Colonists Loyalists (Tories) • Remained loyal to Britain, based on cultural and economic ties • Believed that taxation of the colonies was justified to pay for British troops to protect American settlers from Indian attacks Neutrals • The many colonists who tried to stay as uninvolved in the war as possible
 Factors leading to colonial victory Diplomatic • Benjamin Franklin negotiated a Treaty of Alliance with France (SARATOGA= turning point) Military • George Washington, general of the American army, avoided any situation that threatened the destruction of his army, and his leadership kept the army together when defeat seemed inevitable. • Americans benefited from the presence of the French army and navy at the Battle of Yorktown, which ended the war with an American victory.
Factors leading to colonial victory Diplomatic • Benjamin Franklin negotiated a Treaty of Alliance with France (SARATOGA= turning point) Military • George Washington, general of the American army, avoided any situation that threatened the destruction of his army, and his leadership kept the army together when defeat seemed inevitable. • Americans benefited from the presence of the French army and navy at the Battle of Yorktown, which ended the war with an American victory.
 The Articles of Confederation • Provided for a weak national government • Gave Congress no power to tax • No power to regulate commerce among the states • Provided for no common currency • Gave each state one vote regardless of size • Provided for no chief executive • Nor a judicial branch • **No power to ENFORCE laws in the states!!
The Articles of Confederation • Provided for a weak national government • Gave Congress no power to tax • No power to regulate commerce among the states • Provided for no common currency • Gave each state one vote regardless of size • Provided for no chief executive • Nor a judicial branch • **No power to ENFORCE laws in the states!!

 The Articles of Confederation Things that the Articles DID manage to do: 1. Call the country “The United States of America” (has a nice ring to it) 2. Northwest Ordinance: • • Provided method for adopting new states and settling NW Territory Outlawed slavery in the new territory 3. Land Ordinance of 1785 • Area west of Appalachian Mtns was divided into 6 x 6 miles squares called townships and subdivided again into 1 sq. mile plots *1 set aside for education
The Articles of Confederation Things that the Articles DID manage to do: 1. Call the country “The United States of America” (has a nice ring to it) 2. Northwest Ordinance: • • Provided method for adopting new states and settling NW Territory Outlawed slavery in the new territory 3. Land Ordinance of 1785 • Area west of Appalachian Mtns was divided into 6 x 6 miles squares called townships and subdivided again into 1 sq. mile plots *1 set aside for education
 Shay’s Rebellion, 1786 -7
Shay’s Rebellion, 1786 -7
 SHAYS’ REBELLION (Left) Rebellious Massachusetts farmers close the courts to prevent confiscation of their lands for unpaid back taxes. (Below) The insurrection caused George Washington to question if Americans were capable of governing themselves.
SHAYS’ REBELLION (Left) Rebellious Massachusetts farmers close the courts to prevent confiscation of their lands for unpaid back taxes. (Below) The insurrection caused George Washington to question if Americans were capable of governing themselves.
 Key leaders of the Constitutional Convention • George Washington, Chairman of the Convention, seldom participated in the debates, but lent his prestige to the proceedings • James Madison, “Father of the Constitution, ” (Virginian) led the debate and kept records of what transpired at the Constitutional Convention.
Key leaders of the Constitutional Convention • George Washington, Chairman of the Convention, seldom participated in the debates, but lent his prestige to the proceedings • James Madison, “Father of the Constitution, ” (Virginian) led the debate and kept records of what transpired at the Constitutional Convention.
 VA Plan: Favors BIG pop. states • The Virginia Plan • 3 Branches – with the legislature that would chose people to serve in the executive and judicial branches. • Legislature: Two houses (bicameral) – House of Reps elected by “the people” – Senate was elected by the state legislatures • Both houses to be represented proportionally by state population. • Other Powers – legislature would regulate interstate trade, strike down laws deemed unconstitutional and use armed forces to enforce laws.
VA Plan: Favors BIG pop. states • The Virginia Plan • 3 Branches – with the legislature that would chose people to serve in the executive and judicial branches. • Legislature: Two houses (bicameral) – House of Reps elected by “the people” – Senate was elected by the state legislatures • Both houses to be represented proportionally by state population. • Other Powers – legislature would regulate interstate trade, strike down laws deemed unconstitutional and use armed forces to enforce laws.
 NJ PLAN: Favors small pop. states • 3 Branches – (leg, exec, and jud) – legislature appoints people to serve in the executive branch and would have only one house (unicameral) and States would have EQUAL REPRESENTATION, (all states would have the same power) – executive branch selects the justices of the Supreme Court – Other Powers: • The national government could levy taxes and import duties, regulate trade, and state laws would be subordinate to laws passed by the national legislature.
NJ PLAN: Favors small pop. states • 3 Branches – (leg, exec, and jud) – legislature appoints people to serve in the executive branch and would have only one house (unicameral) and States would have EQUAL REPRESENTATION, (all states would have the same power) – executive branch selects the justices of the Supreme Court – Other Powers: • The national government could levy taxes and import duties, regulate trade, and state laws would be subordinate to laws passed by the national legislature.
 Compromises Made 1. Connecticut Compromise (aka, “The Great Compromise”…. . took parts of both the VA and NJ Plans – 3 branches of gov’t (Thank you Montesquieu) – Bicameral legislature; 1 house based on state population, the other house based on equal representation
Compromises Made 1. Connecticut Compromise (aka, “The Great Compromise”…. . took parts of both the VA and NJ Plans – 3 branches of gov’t (Thank you Montesquieu) – Bicameral legislature; 1 house based on state population, the other house based on equal representation
 Key issues of the Constitution 1. federal law is supreme law of the land 2. Balanced power between large and small states Senate (equal rep as in NJ plan) House of Reps (based on population as in VA plan) Senate House
Key issues of the Constitution 1. federal law is supreme law of the land 2. Balanced power between large and small states Senate (equal rep as in NJ plan) House of Reps (based on population as in VA plan) Senate House
 House of Representatives • Representation was to be based on a state’s population – How to “count” slaves? – North wants slaves in South counted for taxation …. South would pay more – South wants slaves counted for more members in the House (Southern influence would be stronger in federal gov’t)
House of Representatives • Representation was to be based on a state’s population – How to “count” slaves? – North wants slaves in South counted for taxation …. South would pay more – South wants slaves counted for more members in the House (Southern influence would be stronger in federal gov’t)
 House of Representatives • Compromise: for every 5 slaves in the South, the gov’t would count “ 3” for both taxation purposes AND representation in the House • Known as “the 3/5 Compromise” – (The issue of slavery itself was not debated at this time…. too touchy)
House of Representatives • Compromise: for every 5 slaves in the South, the gov’t would count “ 3” for both taxation purposes AND representation in the House • Known as “the 3/5 Compromise” – (The issue of slavery itself was not debated at this time…. too touchy)
 3 branches = Divided Gov’t Power LEGISLATIVE JUDICIAL EXECUTIVE
3 branches = Divided Gov’t Power LEGISLATIVE JUDICIAL EXECUTIVE
 • Each branch gets to “check” the other 2 branches…. which “balances” political power – Balance between the branches – Balance between populated and less populated states – Balance between “people” and “government”
• Each branch gets to “check” the other 2 branches…. which “balances” political power – Balance between the branches – Balance between populated and less populated states – Balance between “people” and “government”
 Legislative “Bicameral” Balance • Outlined in Article I • Senate (where each state gets two senators) • House of Representatives (with membership based on population) • Override VETO by executive with ¾ vote
Legislative “Bicameral” Balance • Outlined in Article I • Senate (where each state gets two senators) • House of Representatives (with membership based on population) • Override VETO by executive with ¾ vote
 Executive Balance of Power • Outlined in Article II • President appoints justices to Supreme Court for lifetime terms • VETO power over legislative branch
Executive Balance of Power • Outlined in Article II • President appoints justices to Supreme Court for lifetime terms • VETO power over legislative branch
 Judicial Balance of Power • Outlined in Article III • Lifetime appointments • Can declare Laws passed by Congress UNCONSTITUTIONAL
Judicial Balance of Power • Outlined in Article III • Lifetime appointments • Can declare Laws passed by Congress UNCONSTITUTIONAL
 Final draft done…. but will it “pass” the public approval test for ratification?
Final draft done…. but will it “pass” the public approval test for ratification?
 “Federal” Stuff to keep Straight • Federalism = division of power between national and state gov’t • A Federalist = – Before ratification, a Federalist was a supporter of the constitution as it was written at the convention (without a bill of rights) – AFTER ratification, a Federalist was a member of the political party of the same name • An ANTI-Federalist = person who thought the constitution gave too much power to the central gov’t and not enough protection to the people
“Federal” Stuff to keep Straight • Federalism = division of power between national and state gov’t • A Federalist = – Before ratification, a Federalist was a supporter of the constitution as it was written at the convention (without a bill of rights) – AFTER ratification, a Federalist was a member of the political party of the same name • An ANTI-Federalist = person who thought the constitution gave too much power to the central gov’t and not enough protection to the people
 “Federal” Stuff to keep Straight • Finally, The Federalist Papers were a series of essays written by John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, and James Madison explaining the benefits of the stronger central government created in the constitution. – written public relations campaign to get public support for ratification – 9 states were needed to ratify it
“Federal” Stuff to keep Straight • Finally, The Federalist Papers were a series of essays written by John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, and James Madison explaining the benefits of the stronger central government created in the constitution. – written public relations campaign to get public support for ratification – 9 states were needed to ratify it
 Federalist Position (pro-ratification) • strong national government (sharing some power with the states) – to facilitate interstate commerce – to manage foreign trade and relations – national defense • checks and balances already exist
Federalist Position (pro-ratification) • strong national government (sharing some power with the states) – to facilitate interstate commerce – to manage foreign trade and relations – national defense • checks and balances already exist
 Federalist position (pro-ratification) • They argued that a national Bill of Rights would be redundant – Constitution itself protected basic rights – most states already had bills of rights that clearly defined basic rights that the governments could not abolish
Federalist position (pro-ratification) • They argued that a national Bill of Rights would be redundant – Constitution itself protected basic rights – most states already had bills of rights that clearly defined basic rights that the governments could not abolish
 Anti-Federalist Position (anti-ratification) • Thought the consitution as written had WAY too much power and would take power away from states • Rich people will abuse power • national Bill of Rights was necessary • *Anti-Feds had no alternative document to offer public
Anti-Federalist Position (anti-ratification) • Thought the consitution as written had WAY too much power and would take power away from states • Rich people will abuse power • national Bill of Rights was necessary • *Anti-Feds had no alternative document to offer public
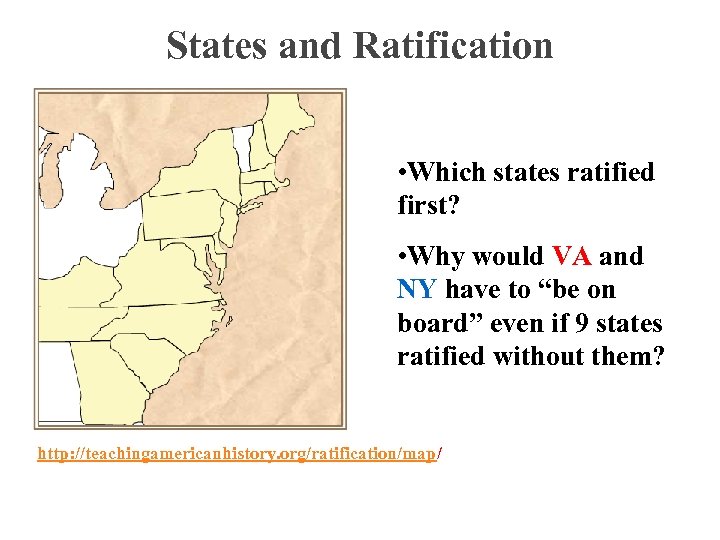 States and Ratification • Which states ratified first? • Why would VA and NY have to “be on board” even if 9 states ratified without them? http: //teachingamericanhistory. org/ratification/map/
States and Ratification • Which states ratified first? • Why would VA and NY have to “be on board” even if 9 states ratified without them? http: //teachingamericanhistory. org/ratification/map/
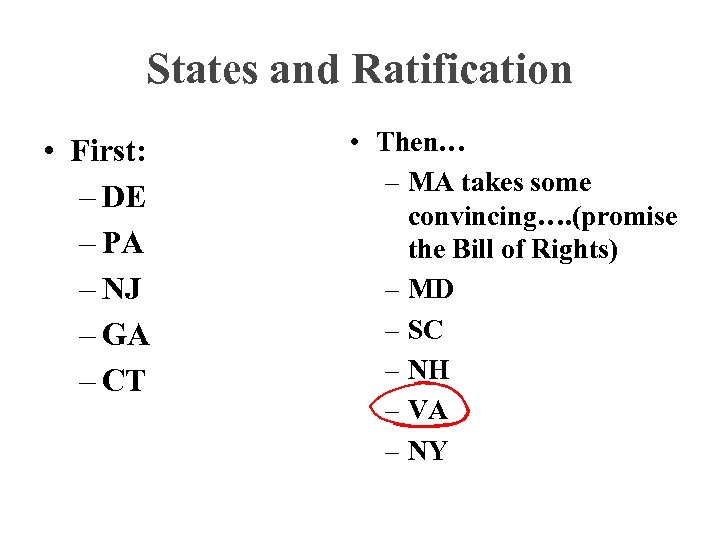 States and Ratification • First: – DE – PA – NJ – GA – CT • Then… – MA takes some convincing…. (promise the Bill of Rights) – MD – SC – NH – VA – NY
States and Ratification • First: – DE – PA – NJ – GA – CT • Then… – MA takes some convincing…. (promise the Bill of Rights) – MD – SC – NH – VA – NY
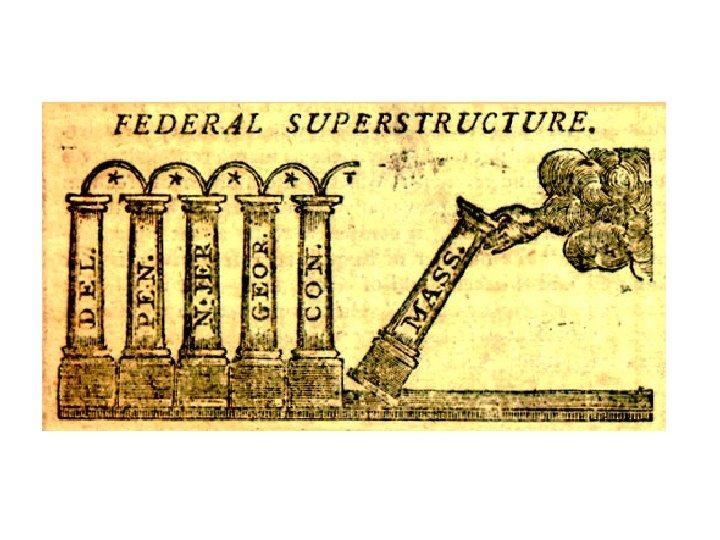
 Finally: “all the pillars in place”! • NC and …. . • …. eventually and by a narrow margin, • Rhode Island comes on board • After Ratification, the payoff (The Bill of Rights) needs writing, revising, editing, and amending
Finally: “all the pillars in place”! • NC and …. . • …. eventually and by a narrow margin, • Rhode Island comes on board • After Ratification, the payoff (The Bill of Rights) needs writing, revising, editing, and amending
 Principles of the Bill of Right • Virginia Declaration of Rights (George Mason…VA) • Reiterated the notion that basic human rights should not be violated by governments
Principles of the Bill of Right • Virginia Declaration of Rights (George Mason…VA) • Reiterated the notion that basic human rights should not be violated by governments
 Principles of the Bill of Rights • Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom (Thomas Jefferson…VA) • Outlawed the established church — that is, the practice of government support for one favored church
Principles of the Bill of Rights • Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom (Thomas Jefferson…VA) • Outlawed the established church — that is, the practice of government support for one favored church
 Principles of the Bill of Rights • James Madison…VA used TJ’s Va Declaration of Rights and the VA Statute for Religious Freedom when drafting the amendments that eventually became the United States Bill of Rights.
Principles of the Bill of Rights • James Madison…VA used TJ’s Va Declaration of Rights and the VA Statute for Religious Freedom when drafting the amendments that eventually became the United States Bill of Rights.
 “The Bill of Rights” 1. Freedom of speech, press, religion, petition, assembly 2. Right to bear arms 3. No troops in homes 4. Unreasonable search & seizure of property 5. No self-incrimination, no double jeopardy, etc. 6. Speedy trial by unbiased jury, legal counsel, witnesses must attend in presence of the accused 7. Jury trials for civil cases over $20. 00 8. No excessive bail/cruel unusual punishments 9. “more rights than listed in constitution” 10. Powers not given to federal gov’t go to states/people
“The Bill of Rights” 1. Freedom of speech, press, religion, petition, assembly 2. Right to bear arms 3. No troops in homes 4. Unreasonable search & seizure of property 5. No self-incrimination, no double jeopardy, etc. 6. Speedy trial by unbiased jury, legal counsel, witnesses must attend in presence of the accused 7. Jury trials for civil cases over $20. 00 8. No excessive bail/cruel unusual punishments 9. “more rights than listed in constitution” 10. Powers not given to federal gov’t go to states/people
 Nice “layered” slides on the Bill of Rights? Extra Credit anyone? ? ?
Nice “layered” slides on the Bill of Rights? Extra Credit anyone? ? ?
 The Legacy of the founding fathers lives on in Virginia….
The Legacy of the founding fathers lives on in Virginia….
 Washington’s Administration • 1789 -1797 • Sought advice from trusted, talented men who became his “CABINET” – T. Jefferson to Dept. of State – A. Hamilton to Dept. of Treasury – H. Knox as Postmaster Gen. • Hamilton’s Financial Program…led to…. . • Emergence of first political parties began with “vision differences” between Jefferson and Hamilton
Washington’s Administration • 1789 -1797 • Sought advice from trusted, talented men who became his “CABINET” – T. Jefferson to Dept. of State – A. Hamilton to Dept. of Treasury – H. Knox as Postmaster Gen. • Hamilton’s Financial Program…led to…. . • Emergence of first political parties began with “vision differences” between Jefferson and Hamilton
 Hamilton’s Financial Program • PROS • Fund national debt at FACE value • Federal Gov’t assume the debts of ALL the states • Establish a national bank (Bank of the United States) • Spark economy with subsidies and tax incentives • Raise revenue with higher tariffs on imports and…. • Taxes on Whiskey • CONS • $ Benefit would only go to speculators who bought debts at low prices • (Original buyers should get something from the deal • Taxes would fall heaviest on small farmers • “The whole program is designed to make a small group of already rich men RICHER…and it ain’t fair!”
Hamilton’s Financial Program • PROS • Fund national debt at FACE value • Federal Gov’t assume the debts of ALL the states • Establish a national bank (Bank of the United States) • Spark economy with subsidies and tax incentives • Raise revenue with higher tariffs on imports and…. • Taxes on Whiskey • CONS • $ Benefit would only go to speculators who bought debts at low prices • (Original buyers should get something from the deal • Taxes would fall heaviest on small farmers • “The whole program is designed to make a small group of already rich men RICHER…and it ain’t fair!”
 Political and Philosophical Differences lead to Political Parties Hamilton Jefferson
Political and Philosophical Differences lead to Political Parties Hamilton Jefferson
 Federalist Party “platform” • Strong central gov’t Alexander • Only wealthy, educated men should vote Hamilton • LOOSE/ broad interpretation USCon. • National Bank • High tariffs & whiskey tax • Alien & Sedition Acts necessary • Opposed Fr. Rev • Support base: manufacturers, business, coastal ports
Federalist Party “platform” • Strong central gov’t Alexander • Only wealthy, educated men should vote Hamilton • LOOSE/ broad interpretation USCon. • National Bank • High tariffs & whiskey tax • Alien & Sedition Acts necessary • Opposed Fr. Rev • Support base: manufacturers, business, coastal ports
 Democratic-Republican Party “platform” • Stronger State/Indiv powers • All landowners should vote • STRICT/narrow interpretion of USCons. • National Bank idea stinks! • No or LOW tariffs • Alien & Sedition Acts are WRONG! • Fr. Rev is GREAT! • Support base: rural small farmers, big planters, French Thomas Jefferson
Democratic-Republican Party “platform” • Stronger State/Indiv powers • All landowners should vote • STRICT/narrow interpretion of USCons. • National Bank idea stinks! • No or LOW tariffs • Alien & Sedition Acts are WRONG! • Fr. Rev is GREAT! • Support base: rural small farmers, big planters, French Thomas Jefferson
 Alexander Hamilton is on our 10 dollar bill!
Alexander Hamilton is on our 10 dollar bill!
 Thomas Jefferson is on still on our money…….
Thomas Jefferson is on still on our money…….
 Foreign Affairs under Washington • French Revolution & War in Europe: USA is officially neutral – American ships traded with both sides – **French West Indies were big $$$$ – British retaliated with impressment and ship seizures
Foreign Affairs under Washington • French Revolution & War in Europe: USA is officially neutral – American ships traded with both sides – **French West Indies were big $$$$ – British retaliated with impressment and ship seizures
 Foreign Affairs under Washington • “Jay’s Treaty” (prevents war with England) • Issues: – England won’t leave frontier posts (NW Terr) as per Paris Peace ending Rev War – Practice of Impressment (making sailors serve in British navy) • Terms: – 2 yrs to get lost – Pay for ship seizures – Some trade with West Indies
Foreign Affairs under Washington • “Jay’s Treaty” (prevents war with England) • Issues: – England won’t leave frontier posts (NW Terr) as per Paris Peace ending Rev War – Practice of Impressment (making sailors serve in British navy) • Terms: – 2 yrs to get lost – Pay for ship seizures – Some trade with West Indies
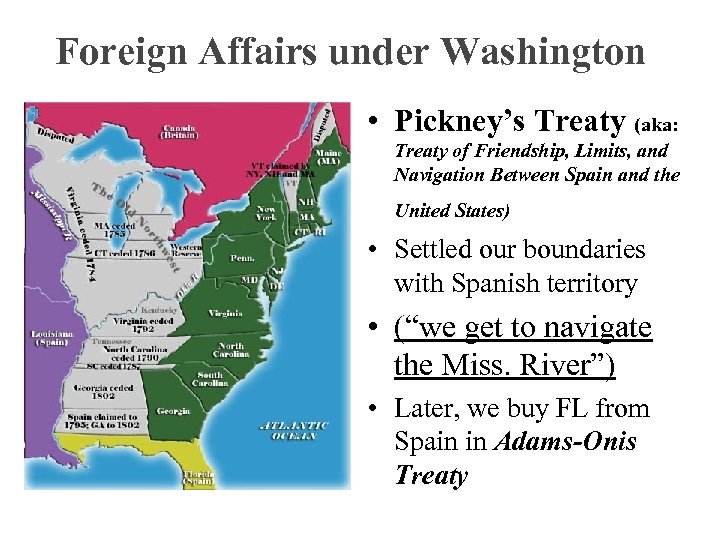 Foreign Affairs under Washington • Pickney’s Treaty (aka: Treaty of Friendship, Limits, and Navigation Between Spain and the United States) • Settled our boundaries with Spanish territory • (“we get to navigate the Miss. River”) • Later, we buy FL from Spain in Adams-Onis Treaty
Foreign Affairs under Washington • Pickney’s Treaty (aka: Treaty of Friendship, Limits, and Navigation Between Spain and the United States) • Settled our boundaries with Spanish territory • (“we get to navigate the Miss. River”) • Later, we buy FL from Spain in Adams-Onis Treaty
 Washington Leaves Office • Farewell Address: letter written to Americans refusing a 3 rd term in office • Warnings: – Political Parties and “party politics” stink – Sectionalism (N, S, E, W) is – BAD NEWS – Foreign Alliances should be avoided – (we can’t have a moral country devoid of religion)
Washington Leaves Office • Farewell Address: letter written to Americans refusing a 3 rd term in office • Warnings: – Political Parties and “party politics” stink – Sectionalism (N, S, E, W) is – BAD NEWS – Foreign Alliances should be avoided – (we can’t have a moral country devoid of religion)
 1796 Election • Federalist John Adams becomes 2 nd POTUS – X, Y, Z Affair with French diplomats over bribes “A million for Defense, not one cent for tribute” – Presides over a “Quasi. War” with France
1796 Election • Federalist John Adams becomes 2 nd POTUS – X, Y, Z Affair with French diplomats over bribes “A million for Defense, not one cent for tribute” – Presides over a “Quasi. War” with France
 Gov’t sux! Alien and Sedition Acts 1798 Dude, watch your mouth! • Designed to make criticism (by Dem-Republicans) of the government and getting citizenship TOUGHER • “Alien”: – Naturalization Act, passed by Congress on June 18. This act required that aliens be residents for 14 years instead of 5 years before they became eligible for U. S. citizenship. – Alien Act on June 25, authorizing the President to deport aliens "dangerous to the peace and safety of the United States" during peacetime. – Alien Enemies Act, was enacted by Congress on July 6. This act allowed the wartime arrest, imprisonment and deportation of any alien subject to an enemy power.
Gov’t sux! Alien and Sedition Acts 1798 Dude, watch your mouth! • Designed to make criticism (by Dem-Republicans) of the government and getting citizenship TOUGHER • “Alien”: – Naturalization Act, passed by Congress on June 18. This act required that aliens be residents for 14 years instead of 5 years before they became eligible for U. S. citizenship. – Alien Act on June 25, authorizing the President to deport aliens "dangerous to the peace and safety of the United States" during peacetime. – Alien Enemies Act, was enacted by Congress on July 6. This act allowed the wartime arrest, imprisonment and deportation of any alien subject to an enemy power.
 Alien and Sedition Acts 1798 • Sedition: declared that any treasonable activity, including the publication of "any false, scandalous and malicious writing, " was a high misdemeanor, punishable by fine and imprisonment
Alien and Sedition Acts 1798 • Sedition: declared that any treasonable activity, including the publication of "any false, scandalous and malicious writing, " was a high misdemeanor, punishable by fine and imprisonment
 Is this Freedom of Speech? !!
Is this Freedom of Speech? !!
 VA and KY Resolutions • Said that the Alien and Sedition Acts were garbage and “unconstitutional” – Said, “states and NULLIFY” bogus gov’t laws – Authored by:
VA and KY Resolutions • Said that the Alien and Sedition Acts were garbage and “unconstitutional” – Said, “states and NULLIFY” bogus gov’t laws – Authored by:
 Election of 1800 • Dem-Republican Thomas Jefferson becomes 3 rd POTUS • **Important election because America showed the world political power could transfer peacefully from one party to another…”our democracy works”
Election of 1800 • Dem-Republican Thomas Jefferson becomes 3 rd POTUS • **Important election because America showed the world political power could transfer peacefully from one party to another…”our democracy works”
 Jefferson as President • • • Dem-Rep Party takes over from the Federalists Shows the world a peaceful transfer of political power (his election is also called “The Revolution of 1800”) Jefferson’s style in office is less formal than that of Washington and Adams
Jefferson as President • • • Dem-Rep Party takes over from the Federalists Shows the world a peaceful transfer of political power (his election is also called “The Revolution of 1800”) Jefferson’s style in office is less formal than that of Washington and Adams
 Jefferson as President • Jefferson's vision for government is: – Small federal gov’t – Limits on federal power – STRICT CONSTRUCTIVISM (rigid interpretation of Article I of the US Constitution) ie: follow the rules as they are written, (ENUMERATED)
Jefferson as President • Jefferson's vision for government is: – Small federal gov’t – Limits on federal power – STRICT CONSTRUCTIVISM (rigid interpretation of Article I of the US Constitution) ie: follow the rules as they are written, (ENUMERATED)
 Jefferson as President • Limits on Federal power: – Attempted to IMPEACH Federalist judges – Repealed Act that gave the “Midnight Judges” offices • Lead to est. that IMPEACHMENT is to be used for CRIMINAL ACTS only! (not politics) • Lead John Marshall to use JUDICIAL REVIEW with the MARBURY v. MADISON case
Jefferson as President • Limits on Federal power: – Attempted to IMPEACH Federalist judges – Repealed Act that gave the “Midnight Judges” offices • Lead to est. that IMPEACHMENT is to be used for CRIMINAL ACTS only! (not politics) • Lead John Marshall to use JUDICIAL REVIEW with the MARBURY v. MADISON case
 Jefferson as President • Territorial Expansion: Louisiana Purchase – 1803 US buys LA and French debts for $15 million • DOUBLES the size of the United States • Gives US control of the Mississippi River • Shows that Jefferson can use IMPLIED Federal Powers to make a purchase……
Jefferson as President • Territorial Expansion: Louisiana Purchase – 1803 US buys LA and French debts for $15 million • DOUBLES the size of the United States • Gives US control of the Mississippi River • Shows that Jefferson can use IMPLIED Federal Powers to make a purchase……
 Jefferson as President • Lewis & Clark and the Corps of Discovery explore the new territory – Sacagewa was the female Shoshone guide who went with them
Jefferson as President • Lewis & Clark and the Corps of Discovery explore the new territory – Sacagewa was the female Shoshone guide who went with them
 Jefferson as President – Politically: The LA Purchase spooks the Federalists…some want to take New England OUT of the United States – Political fight turns deadly: • Aaron Burr and Alexander Hamilton get into a serious argument, challenge each other to a duel and Hamilton Dies…Burr leaves the country
Jefferson as President – Politically: The LA Purchase spooks the Federalists…some want to take New England OUT of the United States – Political fight turns deadly: • Aaron Burr and Alexander Hamilton get into a serious argument, challenge each other to a duel and Hamilton Dies…Burr leaves the country
 Jefferson as President • Economic Policies – EMBARGO ACT OF 1807 • Attempt to deal with shipping attacks and IMPRESSMENT of American soldiers by the British • Cuts off trade with Europe • Embargo hurts USA more than Britain or France (North: killed shipping profits, even though some still had business…passed the cost on to customers…; South : hurt farmers)
Jefferson as President • Economic Policies – EMBARGO ACT OF 1807 • Attempt to deal with shipping attacks and IMPRESSMENT of American soldiers by the British • Cuts off trade with Europe • Embargo hurts USA more than Britain or France (North: killed shipping profits, even though some still had business…passed the cost on to customers…; South : hurt farmers)
 Jefferson as President • EMBARGO: people hate it, it hurts their MONEY$$$$. . Jefferson’s approval ratings go waaaaaay down
Jefferson as President • EMBARGO: people hate it, it hurts their MONEY$$$$. . Jefferson’s approval ratings go waaaaaay down
 WAR of 1812 • Also called “Mr. Madison’s War” • James Madison (Father of the Constitution, author of some Federalist Papers, is a Democratic-Republican elected to be 4 th POTUS) • Madison declares war on British
WAR of 1812 • Also called “Mr. Madison’s War” • James Madison (Father of the Constitution, author of some Federalist Papers, is a Democratic-Republican elected to be 4 th POTUS) • Madison declares war on British
 WAR of 1812 • Support in Congress comes from – WAR HAWKS: 1. South and Western regions wanted war because trade restrictions hurt their people who relied on shipping farm products (Eastern coastal and Northern merchants could stay in business by passing increased costs on to farmers) 2. Westerners also blamed British for selling weapons to Indians (to discourage further Westward expansion)
WAR of 1812 • Support in Congress comes from – WAR HAWKS: 1. South and Western regions wanted war because trade restrictions hurt their people who relied on shipping farm products (Eastern coastal and Northern merchants could stay in business by passing increased costs on to farmers) 2. Westerners also blamed British for selling weapons to Indians (to discourage further Westward expansion)
 Native Americans on the frontier Tecumseh “The Prophet” Tenskwatawa
Native Americans on the frontier Tecumseh “The Prophet” Tenskwatawa
 WAR of 1812 • Battle of Tippecanoe: future president Wm. Henry Harrison is a hero of this bloody battle with Tecumseh’s brother • Invasion of Canada failed (lack of soldiers) • Commodore Perry on Lake Erie
WAR of 1812 • Battle of Tippecanoe: future president Wm. Henry Harrison is a hero of this bloody battle with Tecumseh’s brother • Invasion of Canada failed (lack of soldiers) • Commodore Perry on Lake Erie
 WAR of 1812 • Washington, DC is burned (Ft. Mc. Henry is where Francis Scott Key writes “Star Spangled Banner”) • US win battle on Lake Champlain
WAR of 1812 • Washington, DC is burned (Ft. Mc. Henry is where Francis Scott Key writes “Star Spangled Banner”) • US win battle on Lake Champlain
 WAR of 1812 • Hartford Convention: Federalists don’t like the war and meet to discuss seceding New England from the USA…. . • Treaty of Ghent ends the war in 1814 – (Federalists are seen as traitors, fall from grace, and end as a political party)
WAR of 1812 • Hartford Convention: Federalists don’t like the war and meet to discuss seceding New England from the USA…. . • Treaty of Ghent ends the war in 1814 – (Federalists are seen as traitors, fall from grace, and end as a political party)
 WAR of 1812 • Treaty of Ghent: – Restores pre-war boundaries – Gave the USA “prestige” as a country that battled the British twice and won both – Gave the USA “self-esteem” and “sense of growing patriotism…. book calls it “nationalism” but beware of this definition compared to the nationalism that tears up Europe and continues to haunt the world
WAR of 1812 • Treaty of Ghent: – Restores pre-war boundaries – Gave the USA “prestige” as a country that battled the British twice and won both – Gave the USA “self-esteem” and “sense of growing patriotism…. book calls it “nationalism” but beware of this definition compared to the nationalism that tears up Europe and continues to haunt the world
 WAR of 1812 • Treaty of Ghent does NOT – Address the issue of attacks on shipping – Address the issue of impressment – Address the issue of selling weapons to the Indians
WAR of 1812 • Treaty of Ghent does NOT – Address the issue of attacks on shipping – Address the issue of impressment – Address the issue of selling weapons to the Indians
 WAR of 1812 – Last Battle of the War of 1812, happened after the Treaty was signed……news traveled much slower to New Orleans – Battle of New Orleans: Great victory for the USA over the British…. . makes Andrew Jackson a war hero • Inspired a fun song by Johnny Horton…. . ”In 1814 we took a little trip, along with Colonel Jackson down the mighty Mississip, . . we took a little bacon and we took a little beans and we beat the bloody British at the town of New Orleans…. ”
WAR of 1812 – Last Battle of the War of 1812, happened after the Treaty was signed……news traveled much slower to New Orleans – Battle of New Orleans: Great victory for the USA over the British…. . makes Andrew Jackson a war hero • Inspired a fun song by Johnny Horton…. . ”In 1814 we took a little trip, along with Colonel Jackson down the mighty Mississip, . . we took a little bacon and we took a little beans and we beat the bloody British at the town of New Orleans…. ”
 WAR of 1812 • End of the war brings relief • National Pride • International …. . ”OK…you are the “USA” • Thus begins the so-called » “ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS”
WAR of 1812 • End of the war brings relief • National Pride • International …. . ”OK…you are the “USA” • Thus begins the so-called » “ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS”
 End Unit 2 • Complete Unit Comps…. use concrete evidence for your support • Review and memorize Vocabulary • Review homework in the order it was assigned • Review Bellwork Journal entries!! • Read previously NOT Read sections
End Unit 2 • Complete Unit Comps…. use concrete evidence for your support • Review and memorize Vocabulary • Review homework in the order it was assigned • Review Bellwork Journal entries!! • Read previously NOT Read sections


