122814e0845847dfc4acbf5312599aa1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

"American Progress, " by John Gast, 1872

Second Industrial Revolution 1850 -1915

So, What Changed? u u Focus shifted from agriculture to industry Fueled by: • • • Entrepreneurs New inventions Cheap labor

Steel…………the new Gold? u Bessemer Process made steel-making faster and cheaper (1850’s) • • • u Locomotives / RR Bigger bridges Taller buildings Steel Machinery Every day items Steel transformed U. S. to modern industrial economy http: //www. teacherlink. org/content/social/instr uctional/industrialrevolution/home. html
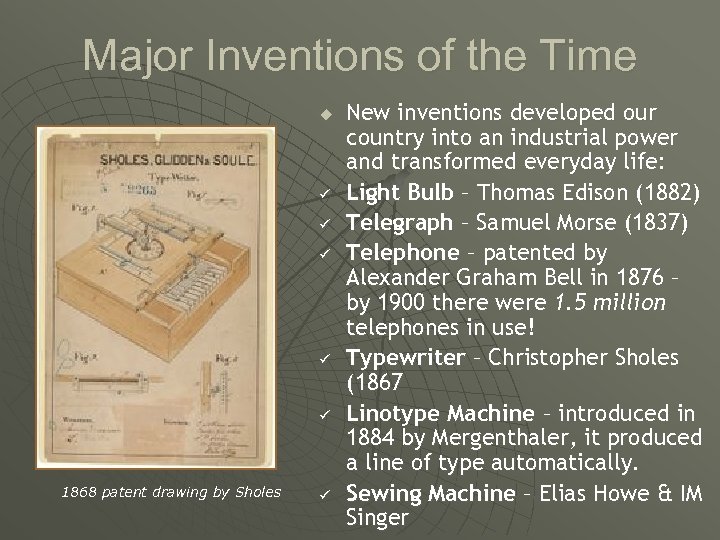
Major Inventions of the Time u ü ü ü 1868 patent drawing by Sholes ü New inventions developed our country into an industrial power and transformed everyday life: Light Bulb – Thomas Edison (1882) Telegraph – Samuel Morse (1837) Telephone – patented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876 – by 1900 there were 1. 5 million telephones in use! Typewriter – Christopher Sholes (1867 Linotype Machine – introduced in 1884 by Mergenthaler, it produced a line of type automatically. Sewing Machine – Elias Howe & IM Singer
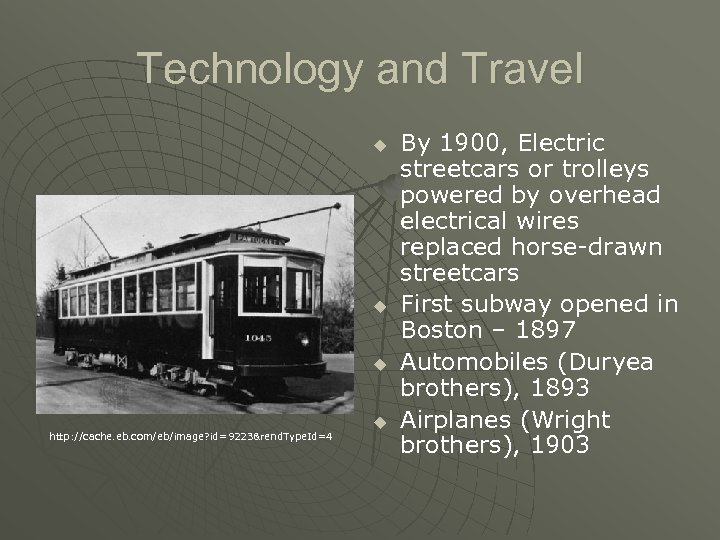
Technology and Travel u u u http: //cache. eb. com/eb/image? id=9223&rend. Type. Id=4 u By 1900, Electric streetcars or trolleys powered by overhead electrical wires replaced horse-drawn streetcars First subway opened in Boston – 1897 Automobiles (Duryea brothers), 1893 Airplanes (Wright brothers), 1903

Changes in Production u Mass production of goods § Sped up manufacturing = increasing quantity of goods produced. § Increased investor’s profits. § Increased demand for unskilled labor. § Increased demand for raw materials. § Resulted in lower prices on goods for the consumer.
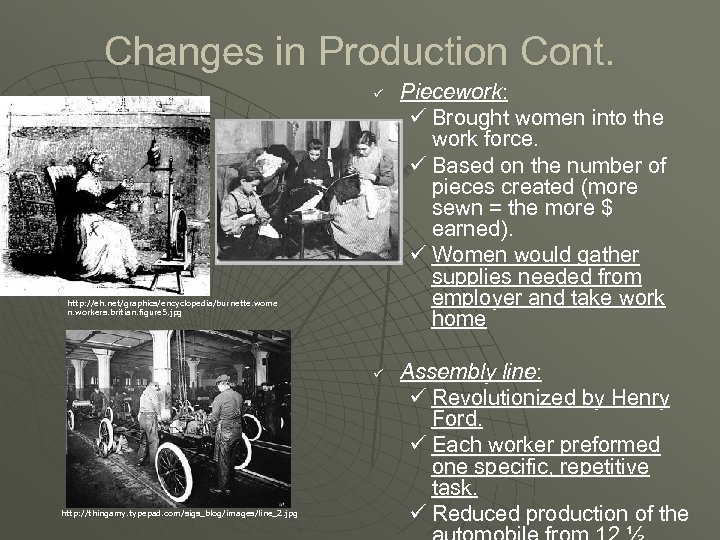
Changes in Production Cont. ü http: //eh. net/graphics/encyclopedia/burnette. wome n. workers. britian. figure 5. jpg ü http: //thingamy. typepad. com/sigs_blog/images/line_2. jpg Piecework: ü Brought women into the work force. ü Based on the number of pieces created (more sewn = the more $ earned). ü Women would gather supplies needed from employer and take work home Assembly line: ü Revolutionized by Henry Ford. ü Each worker preformed one specific, repetitive task. ü Reduced production of the

Changes in Industry Stir the Melting Pot…

Bye - Bye Skilled Labor, Hello Immigrants! u Cheap labor = necessity for industrial success • Machines replaced skill • Workers needed to run machines u Immigrants poured into America and workers left rural areas to search for factory jobs

“Give Me Your Tired, Your poor…” ~ Emma Lazarus ü Employment opportunities in America attract immigration because…: ü Poor economic conditions existed in Europe ü Religious persecution ü $$$$$$$$$ ü ü Ellis Island reaches peak years of operation as the “gateway” to America. Statue of Liberty is unveiled in 1886 as a gift from the French to the USA

From Tractor Lights to City Lights u u America became an urban society – a society based on city life. These factors helped: • electric power = power machines ü railways = provide markets & transport for raw materials ü new industry = many cities specialized in a product (Pittsburgh steel ) ü steel frames = “skyscrapers” – steel could hold the weight of many stories and allowed for buildings to grow up ü rural workers = lost farms due to mechanization & provided The Flatiron Building. NYC’s first skyscraper - 1902

Unfortunately, Rapid Industrial, Population, and City Growth has its Consequences And they were not that pretty!

They Worked Hard for No Money Working class poor is created by industrialization: q. Unskilled people flocking to cities looking for opportunity. § Immigrants. § Rural unemployed people. q. Harsh working conditions result from the rise of manufacturing & the availability of labor. § Low wages & long hours. § Tedious jobs with unsafe conditions. u

Harsh Living Conditions q Housing is an issue. § Slums and tenements develop. Many people share a small space. § Company towns are created. Intended to benefit the worker but instead made them feel controlled by the company.

Time for a Change

What’s happening here?

Does this help?

So, what are these people doing again?

Jump or Burn…what would you do?

Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire Victims

The Labor Movement u u ü Labor Movements created in reaction to harsh working conditions Workers joined together to create labor unions: ü Knights of Labor: Founded in 1869 to organize all workers – skilled & unskilled. ü American Federation of Labor (AFL): Began in 1886, it organized skilled workers into local unions based upon specific skills. They fought for an 8 hour workday, better working

United They Fought! u Unions used various “tools” to influence management to make changes: üStrikes – refusing to work üBoycotts – refusing to buy a product

The Gilded Age Mark Twain labeled this time in American History (turn of the 20 th century) the Gilded Age – the country looked prosperous on the outside, but was corrupt on the inside

America, a Gold Plated Nation u u u Corruption is rampant during the Gilded Age. Rich and powerful people live glamorous lives and hide the dishonest ways they earned their money. It is the dark underside of life in the USA. The Federal Government is corrupt: ü Congressmen are taking bribes and establishing plans to profit from government actions. ü The Spoils System is in full swing & many government employees are unqualified. People with the best

A “Not to be Trusted” Government u Corrupt City Governments: ü Political machines control local politics. ü “Boss” Tweed ruled NY City politics at Tammany Hall. ü Muckrakers are journalists who exposed the dark side of industry & local government. William Mercy “Boss” Tweed

I Sense a Reform Coming On…….

Change is Good… u Reform Movements develop in response to society’s problems. Legislation is passed to regulate businesses & government: ü Civil service exams become required for certain federal jobs. This would eliminate unqualified people. ü The Civil Service Reform Act is passed in 1883. It set aside 15, 000 jobs that would be filled through a test so only people who proved capable would be hired. ü Interstate Commerce Act is passed in 1887 to regulate transportation & railroads. It is important because it established the governments right to regulate business.
122814e0845847dfc4acbf5312599aa1.ppt