c90845786159fd97a322a0bd8ff7cc90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 AMERICAN LIFE IN THE CENTURY TH 17
AMERICAN LIFE IN THE CENTURY TH 17
 FOCUS • Social- Class conflict is a key element. Always under the surface of colonial societies. It erupts into full-scale civil war with Bacon’s Rebellion. • The introduction of slavery transforms the social, economic and political make-up of the New World. • Religious hysteria, in the form of witch trials, plague the North American colonies. Especially in New England
FOCUS • Social- Class conflict is a key element. Always under the surface of colonial societies. It erupts into full-scale civil war with Bacon’s Rebellion. • The introduction of slavery transforms the social, economic and political make-up of the New World. • Religious hysteria, in the form of witch trials, plague the North American colonies. Especially in New England
 AP NOTES • Although initially an area where inhabitants rarely survived, the Chesapeake colony region spawned a powerful industry: cultivated and selling tobacco. It helped maintain the economy of the region. Because of its tendency to exhaust the soil, it led to the westward penetration of the Chesapeake colonies • The social life and customs of the North American colonists were considerably shaped and affected by where they lived. Unique cultural traits took root in the New England, middle and southern colonies. Despite the presence of slavery in the colonies, white settlers were not so quick to nurture the type of social stratification that prevailed in Europe.
AP NOTES • Although initially an area where inhabitants rarely survived, the Chesapeake colony region spawned a powerful industry: cultivated and selling tobacco. It helped maintain the economy of the region. Because of its tendency to exhaust the soil, it led to the westward penetration of the Chesapeake colonies • The social life and customs of the North American colonists were considerably shaped and affected by where they lived. Unique cultural traits took root in the New England, middle and southern colonies. Despite the presence of slavery in the colonies, white settlers were not so quick to nurture the type of social stratification that prevailed in Europe.
 UNHEALTHY CHESAPEAKE • Life was hard • Climate was miserable…work was hard…and disease took a toll • Average life span: 45 years • Family life hard. Men outnumbered women 6: 1. • Virginia the most populous colony by 1700
UNHEALTHY CHESAPEAKE • Life was hard • Climate was miserable…work was hard…and disease took a toll • Average life span: 45 years • Family life hard. Men outnumbered women 6: 1. • Virginia the most populous colony by 1700
 THE TOBACCO ECONOMY • Cultivation of tobacco made the Chesapeake Valley • Overplanting became the norm to try to keep a profit when tobacco prices fell
THE TOBACCO ECONOMY • Cultivation of tobacco made the Chesapeake Valley • Overplanting became the norm to try to keep a profit when tobacco prices fell
 HEADRIGHT SYSTEM • Meant to solve labor shortages in the colonies when tobacco became a cash crop • Land grant: immigrant colonists were given 1 headright (50 acres) and an additional headright for paying for an indentured servant to come to the colony. • This increased the division between wealthy land-owners and working poor • Encouraged slavery…each bought slave was worth 1 headright. • Eventually, it was decided the headright system would only apply to English indentured servants • How would this system lead to increased tensions between the colonists and the natives?
HEADRIGHT SYSTEM • Meant to solve labor shortages in the colonies when tobacco became a cash crop • Land grant: immigrant colonists were given 1 headright (50 acres) and an additional headright for paying for an indentured servant to come to the colony. • This increased the division between wealthy land-owners and working poor • Encouraged slavery…each bought slave was worth 1 headright. • Eventually, it was decided the headright system would only apply to English indentured servants • How would this system lead to increased tensions between the colonists and the natives?
 LIFE OF AN INDENTURED SERVANT • Indentured servant contract usually 5 years • At the end of the contract, the servant would receive a “freedom due”- but only about 40% lived to the end of the contract • Women servants were constantly harassed • If they became pregnant they had years added onto their contracts • Freed servants were given land, however, it was land in the mountainous regions to the west that was hard to farm and brought them into conflict with Indians • As a result, a class of angry, poor farmers began to emerge in the late 17 th century
LIFE OF AN INDENTURED SERVANT • Indentured servant contract usually 5 years • At the end of the contract, the servant would receive a “freedom due”- but only about 40% lived to the end of the contract • Women servants were constantly harassed • If they became pregnant they had years added onto their contracts • Freed servants were given land, however, it was land in the mountainous regions to the west that was hard to farm and brought them into conflict with Indians • As a result, a class of angry, poor farmers began to emerge in the late 17 th century
 “ANGRY YOUNG MEN” IN VIRGINIA • Poor colonists in Virginia • Why were they so mad? . . . they could not vote because they did not own land • Good land was expensive and most of it was already taken • They moved inland to buy less expensive, poor quality land…hard to farm and brought them into conflict with Indians • Tobacco prices had fallen • These guys were unhappy with the rich landowners and Gov. Berkeley who was doing nothing about their Indian problems
“ANGRY YOUNG MEN” IN VIRGINIA • Poor colonists in Virginia • Why were they so mad? . . . they could not vote because they did not own land • Good land was expensive and most of it was already taken • They moved inland to buy less expensive, poor quality land…hard to farm and brought them into conflict with Indians • Tobacco prices had fallen • These guys were unhappy with the rich landowners and Gov. Berkeley who was doing nothing about their Indian problems
 BACON’S REBELLION (1676) • Uprising in Virginia led by Nathaniel Bacon • A thousand Virginians banded together against Gov. William Berkeley’s friendly policies towards the Native Americans • In a fit of rage, they burned Jamestown to the ground • Berkeley was recalled to England • Nothing would stop colonists from moving west into Indian lands
BACON’S REBELLION (1676) • Uprising in Virginia led by Nathaniel Bacon • A thousand Virginians banded together against Gov. William Berkeley’s friendly policies towards the Native Americans • In a fit of rage, they burned Jamestown to the ground • Berkeley was recalled to England • Nothing would stop colonists from moving west into Indian lands
 MIDDLE PASSAGE • Part of triangular trade in which African slaves were shipped to the New World • Slave traders wanted to deliver a large and healthy cargo • The sick were thrown overboard to keep disease from spreading
MIDDLE PASSAGE • Part of triangular trade in which African slaves were shipped to the New World • Slave traders wanted to deliver a large and healthy cargo • The sick were thrown overboard to keep disease from spreading
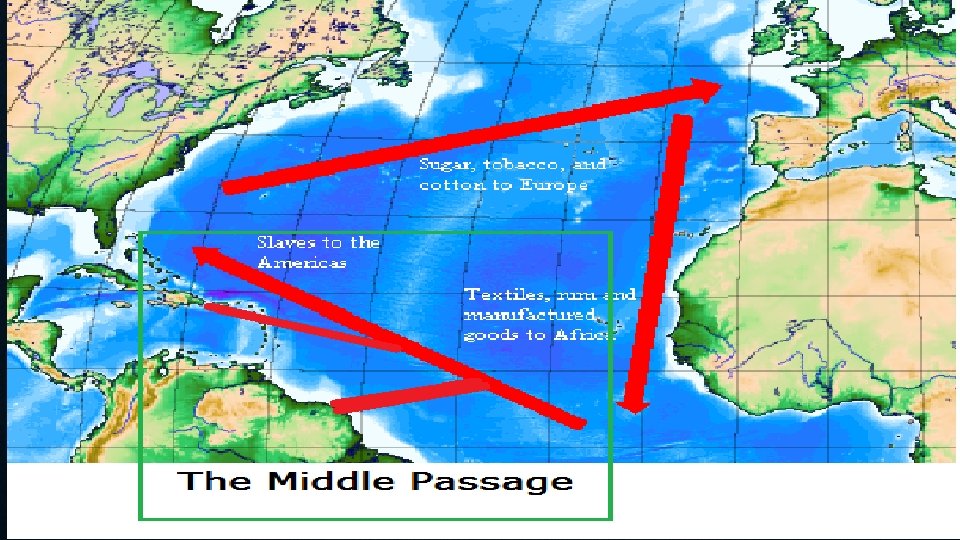
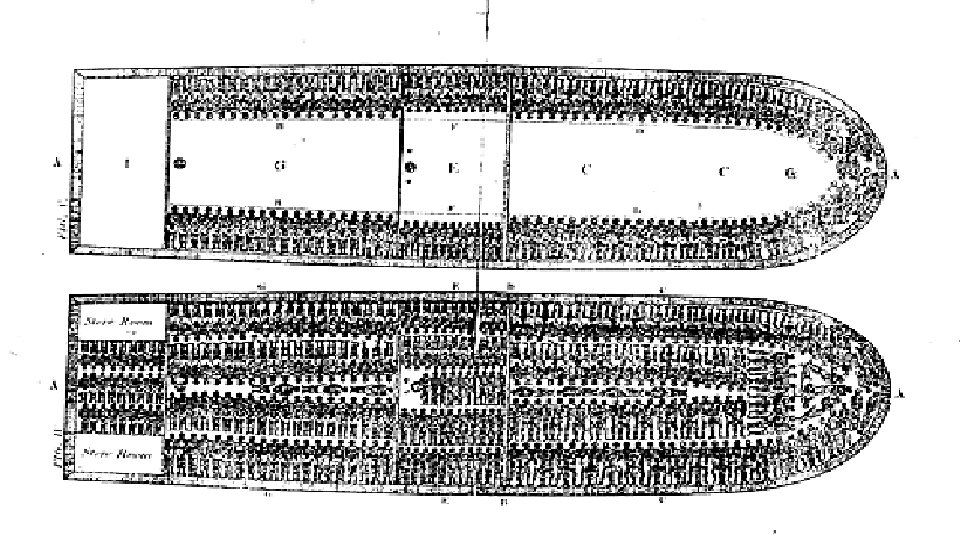

 SLAVE ARRIVAL IN AMERICA • Slaves were distributed to all parts of N. America after arrival • Slaves and their children were property, not people. They were called “chattels” • It was a crime to teach slaves to read & write. Slaves that converted to Christianity were not given their freedom
SLAVE ARRIVAL IN AMERICA • Slaves were distributed to all parts of N. America after arrival • Slaves and their children were property, not people. They were called “chattels” • It was a crime to teach slaves to read & write. Slaves that converted to Christianity were not given their freedom
 AFRICANS IN AMERICA • Life for slaves hard…especially on tobacco plantations • Unique African-American emerged as cultures mixed • Slaves did attempt to escape and occasionally revolted
AFRICANS IN AMERICA • Life for slaves hard…especially on tobacco plantations • Unique African-American emerged as cultures mixed • Slaves did attempt to escape and occasionally revolted
 SOUTHERN SOCIETY • A gap between rich and poor emerged in the South • Virginia was becoming a colony of aristocratic plantation owners • Next…small farmers also known as “yeoman” farmers • At the bottom were landless whites…then slaves that had no social status or rights • Due to plantations, there were very few schools, churches or towns. The plantation was your life
SOUTHERN SOCIETY • A gap between rich and poor emerged in the South • Virginia was becoming a colony of aristocratic plantation owners • Next…small farmers also known as “yeoman” farmers • At the bottom were landless whites…then slaves that had no social status or rights • Due to plantations, there were very few schools, churches or towns. The plantation was your life
 THE NEW ENGLAND FAMILY • The climate and conditions were much healthier in New England than in the South • Average life span: up to 70 years • More families emigrated to New England…singles emigrated to Chesapeake • Very large families (8 -10 kids)
THE NEW ENGLAND FAMILY • The climate and conditions were much healthier in New England than in the South • Average life span: up to 70 years • More families emigrated to New England…singles emigrated to Chesapeake • Very large families (8 -10 kids)
 LIFE IN NEW ENGLAND TOWNS • Town life was very structured due to the Puritan tradition • Education highly valued…towns of 50 built primary schools. Towns of 100 built secondary schools • Harvard America’s first college (1636)trained men for the ministry • Church still ran towns from their congregationalist churches
LIFE IN NEW ENGLAND TOWNS • Town life was very structured due to the Puritan tradition • Education highly valued…towns of 50 built primary schools. Towns of 100 built secondary schools • Harvard America’s first college (1636)trained men for the ministry • Church still ran towns from their congregationalist churches
 JEREMIADS • Puritan leaders were worried that over time, generations were losing their religious zeal • Jeremiads were texts that denounced society for wickedness and predict their downfall • Example: “Sinners in the hand of an angry god”- Jonathan Edwards
JEREMIADS • Puritan leaders were worried that over time, generations were losing their religious zeal • Jeremiads were texts that denounced society for wickedness and predict their downfall • Example: “Sinners in the hand of an angry god”- Jonathan Edwards
 HALF-WAY COVENANT • Allowed for partial church membership for the children and grandchildren of church members…meant to keep them in the church • Partial members could not receive communion or vote • The strict religious purity of the Puritans was sacrificed in order to have a larger congregation.
HALF-WAY COVENANT • Allowed for partial church membership for the children and grandchildren of church members…meant to keep them in the church • Partial members could not receive communion or vote • The strict religious purity of the Puritans was sacrificed in order to have a larger congregation.
 SALEM WITCH TRIALS (1692) • “hysterical’ hunt for witches led to the murder of 20 people and 2 dogs by pressing
SALEM WITCH TRIALS (1692) • “hysterical’ hunt for witches led to the murder of 20 people and 2 dogs by pressing
 CAUSES OF THE WITCH TRIALS • 1. overzealous religious faith fueled by superstition, panic and rumor • 2. rye mold that contained chemical basis for LSD. Also has been blamed for Spanish Inquisition • 3. economic jealousy of group of people who felt alienated and wanted revenge on landowners and wealthy citizens • 4. demonic possession
CAUSES OF THE WITCH TRIALS • 1. overzealous religious faith fueled by superstition, panic and rumor • 2. rye mold that contained chemical basis for LSD. Also has been blamed for Spanish Inquisition • 3. economic jealousy of group of people who felt alienated and wanted revenge on landowners and wealthy citizens • 4. demonic possession
 NEW ENGLAND WAY OF LIFE • Rocky New England soil dictated the way of life…hard to grow crops • Agriculture very limited and done for subsistence, not for the economy • Shipbuilding the main industry due to the abundance of timber. Fishing also a big industry • Slavery tried early on, but died out due to the lack of large-scale farming
NEW ENGLAND WAY OF LIFE • Rocky New England soil dictated the way of life…hard to grow crops • Agriculture very limited and done for subsistence, not for the economy • Shipbuilding the main industry due to the abundance of timber. Fishing also a big industry • Slavery tried early on, but died out due to the lack of large-scale farming
 LEISLER’S REBELLION (1689 -1691) • Jacob Leisler- German merchant who emigrated to New York. Ardent Protestant • When word of the Glorious Revolution reached New York, an armed mob took over Fort James and named Leisler governor. • Leisler created a legislative assembly that was representative of the people- not just wealthy landowners and merchants • William III sent a new governor who named Leisler a traitor and had him executed
LEISLER’S REBELLION (1689 -1691) • Jacob Leisler- German merchant who emigrated to New York. Ardent Protestant • When word of the Glorious Revolution reached New York, an armed mob took over Fort James and named Leisler governor. • Leisler created a legislative assembly that was representative of the people- not just wealthy landowners and merchants • William III sent a new governor who named Leisler a traitor and had him executed
 LEGAL STATUS OF WOMEN IN NEW ENGLAND COLONIES • No legal or political standing (rules of coverture or femme covert) a woman was first under the control of her father, and later husband • Not allowed to own property, enter into contracts, earn wages or bring lawsuits • In case of divorce, it was generally thought to the be woman’s fault. Children were given to the husband • Violence allowed by the “rule of thumb”
LEGAL STATUS OF WOMEN IN NEW ENGLAND COLONIES • No legal or political standing (rules of coverture or femme covert) a woman was first under the control of her father, and later husband • Not allowed to own property, enter into contracts, earn wages or bring lawsuits • In case of divorce, it was generally thought to the be woman’s fault. Children were given to the husband • Violence allowed by the “rule of thumb”
 • Widows had the most legal opportunities…they were allowed to act on their dead husband’s behalf • Rule of jointure protected property a woman brought into a marriage • An “invisible economy” existed in which women would trade domestic work of themselves and their daughters for other goods and services from others
• Widows had the most legal opportunities…they were allowed to act on their dead husband’s behalf • Rule of jointure protected property a woman brought into a marriage • An “invisible economy” existed in which women would trade domestic work of themselves and their daughters for other goods and services from others
 FOCUS QUESTIONS • How did the climate in the southern colonies influence life expectancy, family life, immigration and economic development? • What role did Bacon’s Rebellion play in adopting and expanding slavery in the southern colonies? • What contribution did enslaved Africans provide the colonies? • How was life expectancy, family life, immigration and economic development different in New England as compared with the southern colonies? • What are the differences in the legal standing of women in southern colonies and New England colonies?
FOCUS QUESTIONS • How did the climate in the southern colonies influence life expectancy, family life, immigration and economic development? • What role did Bacon’s Rebellion play in adopting and expanding slavery in the southern colonies? • What contribution did enslaved Africans provide the colonies? • How was life expectancy, family life, immigration and economic development different in New England as compared with the southern colonies? • What are the differences in the legal standing of women in southern colonies and New England colonies?


