de58e34e29bd30990374867e13b19f79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 American Gridlock Chapters 12 - 15
American Gridlock Chapters 12 - 15
 Where does political “information” come from? • Traditional Sources (Before 1980 s) 1. Television (NBC, CBS, then ABC) 2. Newspapers 3. Radio 4. News Magazines (Time, Newsweek, opinion magazines)
Where does political “information” come from? • Traditional Sources (Before 1980 s) 1. Television (NBC, CBS, then ABC) 2. Newspapers 3. Radio 4. News Magazines (Time, Newsweek, opinion magazines)
 Sources After 1980 s to 2000 s 1. Cable (explodes in 1960 s and 1970 s) 2. Satellite TV (After 1990) 3. Newspapers 4. Talk Radio (fairness doctrine ends 1987) 5. Magazines (starting to fade)
Sources After 1980 s to 2000 s 1. Cable (explodes in 1960 s and 1970 s) 2. Satellite TV (After 1990) 3. Newspapers 4. Talk Radio (fairness doctrine ends 1987) 5. Magazines (starting to fade)
 More Recent Sources • 1. Cable (peaks 2000, Premium Cable (e. g. , HBO, expands rapidly in 1980 s and 1990 s). • 2. Satellite TV (HDTV by 2006 and still increasing). By 2012 90% had (1) and/or (2). • 3. Traditional Television (mostly older audience) • 4. Newspapers (rapidly dying) • 5. Magazines (basically gone) • 6. The Web – Facebook, etc. • 7. Cell Phone Apps (High Speed Wireless)
More Recent Sources • 1. Cable (peaks 2000, Premium Cable (e. g. , HBO, expands rapidly in 1980 s and 1990 s). • 2. Satellite TV (HDTV by 2006 and still increasing). By 2012 90% had (1) and/or (2). • 3. Traditional Television (mostly older audience) • 4. Newspapers (rapidly dying) • 5. Magazines (basically gone) • 6. The Web – Facebook, etc. • 7. Cell Phone Apps (High Speed Wireless)
 Old vs. Young People 1. Clearly, 3, 4, and 5 are rapidly fading out and only watched/read by older people. 2. Sources (1) and (2) are primarily entertainment for younger people (Game of Thrones, etc. ) 3. Probably (7) > (6) is more important for younger people.
Old vs. Young People 1. Clearly, 3, 4, and 5 are rapidly fading out and only watched/read by older people. 2. Sources (1) and (2) are primarily entertainment for younger people (Game of Thrones, etc. ) 3. Probably (7) > (6) is more important for younger people.
 How well informed are Voters • 1. Older people are better informed than younger people. • 2. Ignorance rather than stupidity. • 3. Big Problem: How do you figure out what information is true?
How well informed are Voters • 1. Older people are better informed than younger people. • 2. Ignorance rather than stupidity. • 3. Big Problem: How do you figure out what information is true?
 Truth • • • (1) What is True (2) What is known to be True (3) What People believe is True Politicians Respond to (3) not (2) -------------------------------1. Knowns -- Things we know 2. Known Unknowns -- Things we know we do not know 3. Unknowns -- Things we do not know that we do not know
Truth • • • (1) What is True (2) What is known to be True (3) What People believe is True Politicians Respond to (3) not (2) -------------------------------1. Knowns -- Things we know 2. Known Unknowns -- Things we know we do not know 3. Unknowns -- Things we do not know that we do not know
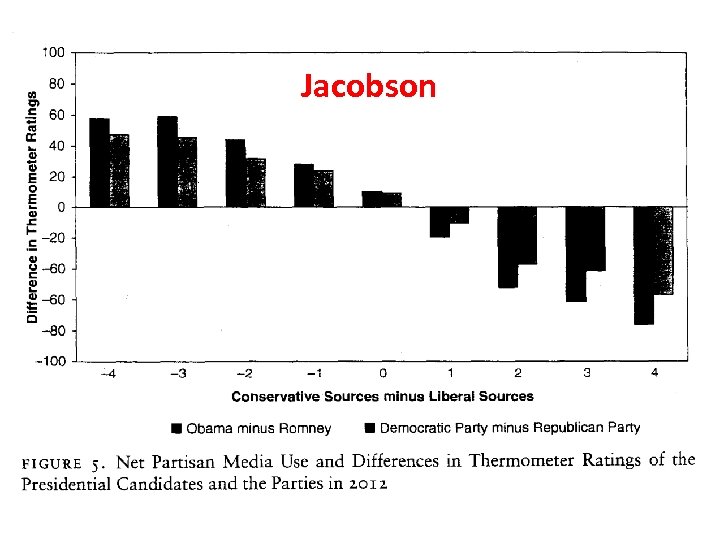
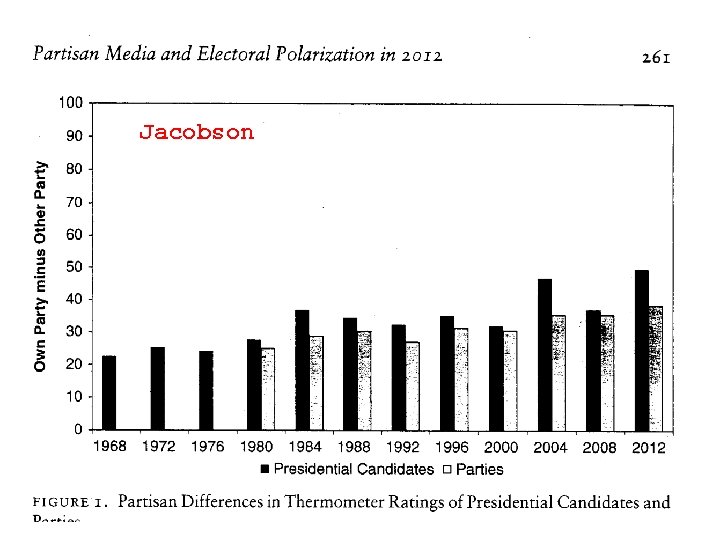 Jacobson
Jacobson
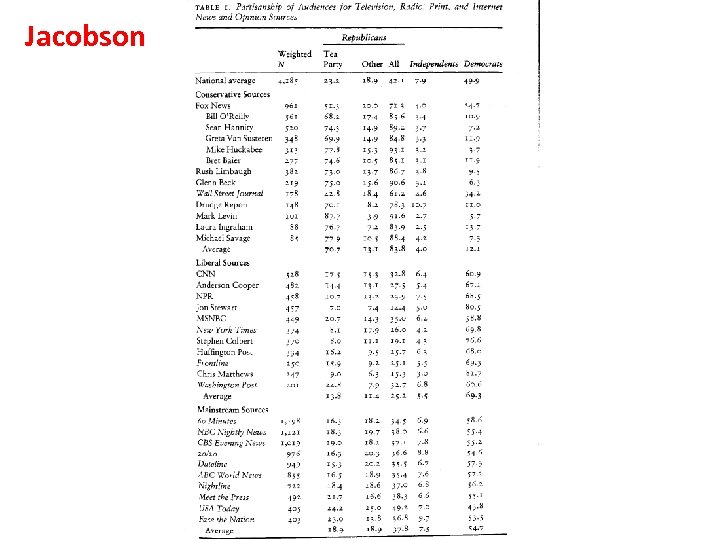 Jacobson
Jacobson
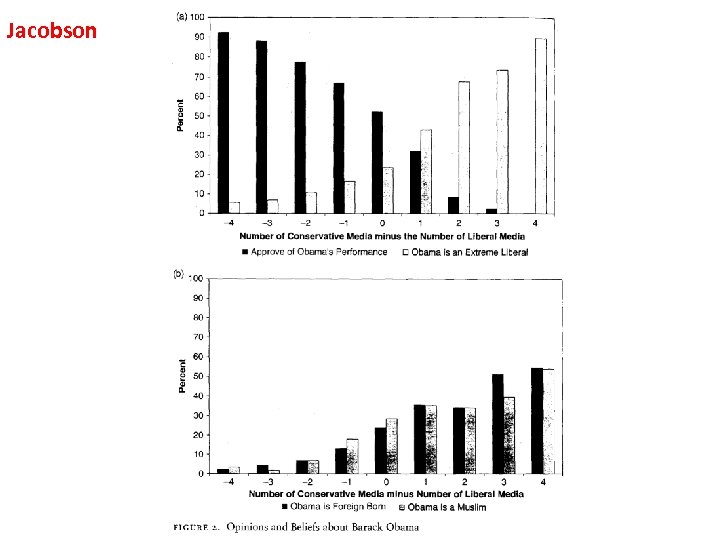
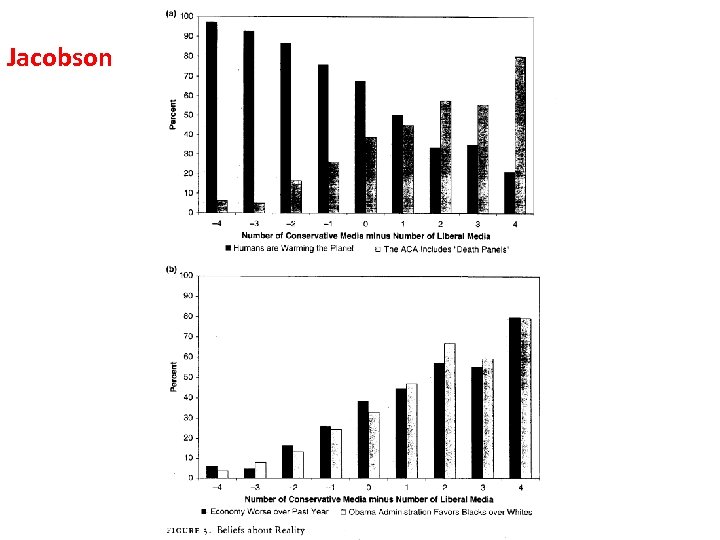
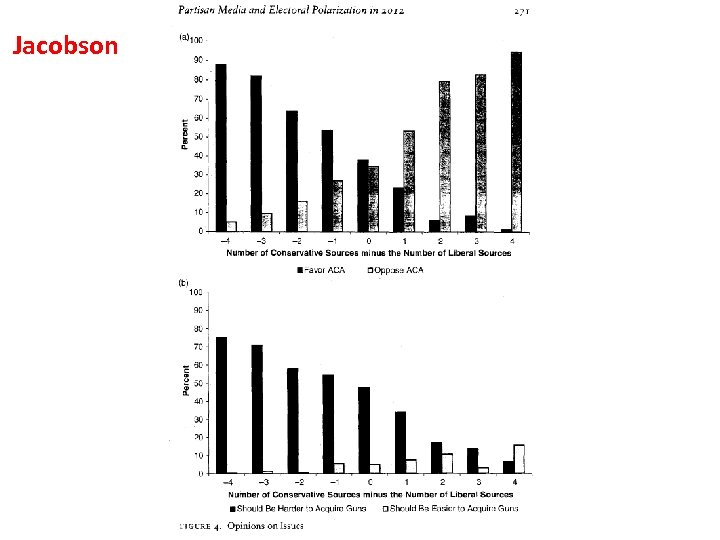
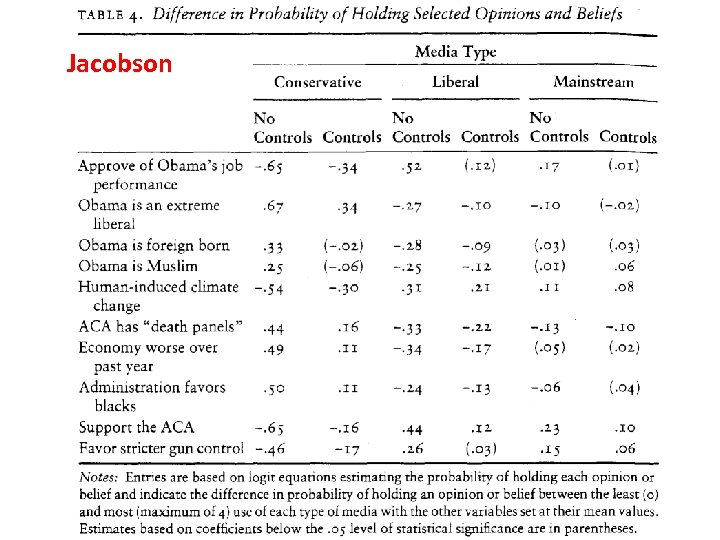
 Is “Mainstream” (“Establishment”) News Ideologically Neutral? • 1. Editorials (probably not). • 2. News Articles (supposed to be neutral but the topic is intensely controversial).
Is “Mainstream” (“Establishment”) News Ideologically Neutral? • 1. Editorials (probably not). • 2. News Articles (supposed to be neutral but the topic is intensely controversial).
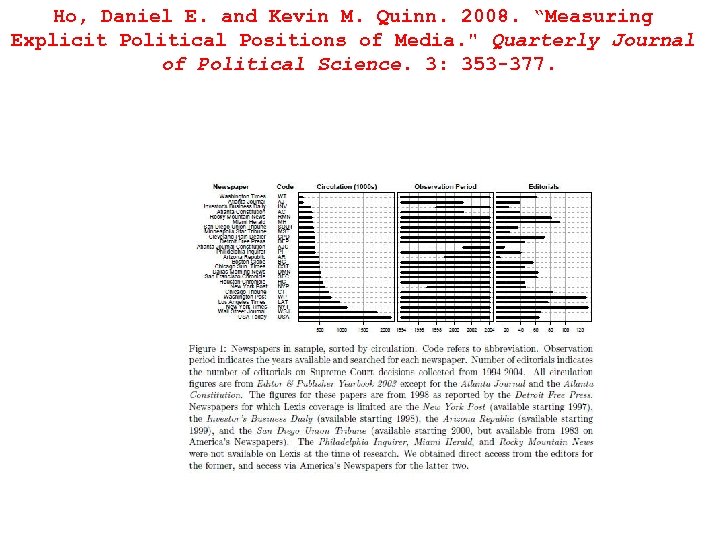 Ho, Daniel E. and Kevin M. Quinn. 2008. “Measuring Explicit Political Positions of Media. " Quarterly Journal of Political Science. 3: 353 -377.
Ho, Daniel E. and Kevin M. Quinn. 2008. “Measuring Explicit Political Positions of Media. " Quarterly Journal of Political Science. 3: 353 -377.
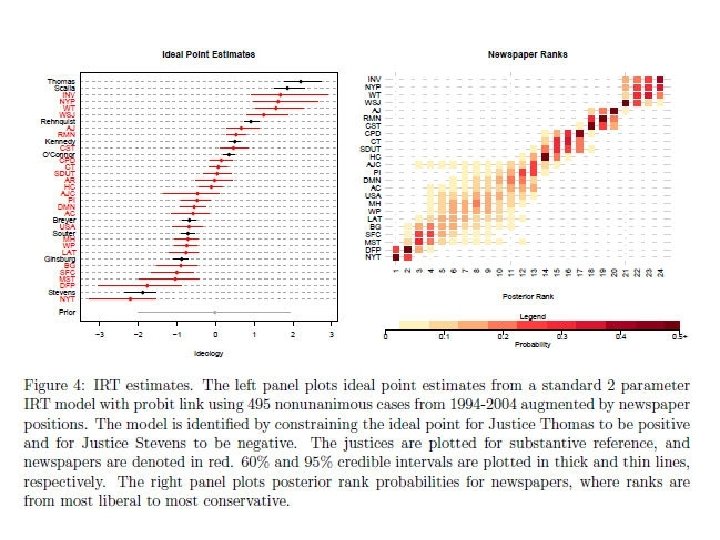
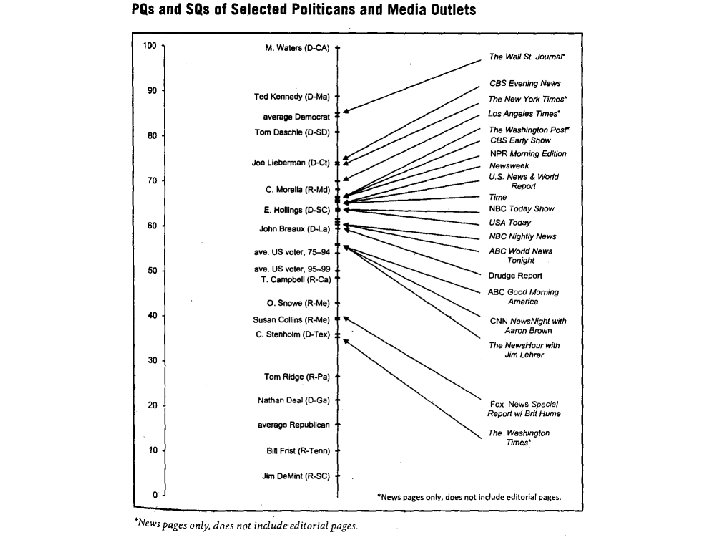
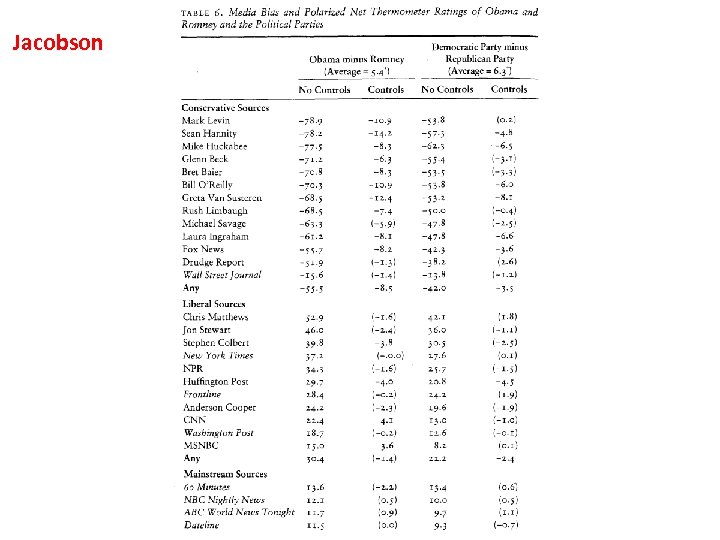
 Jacobson
Jacobson
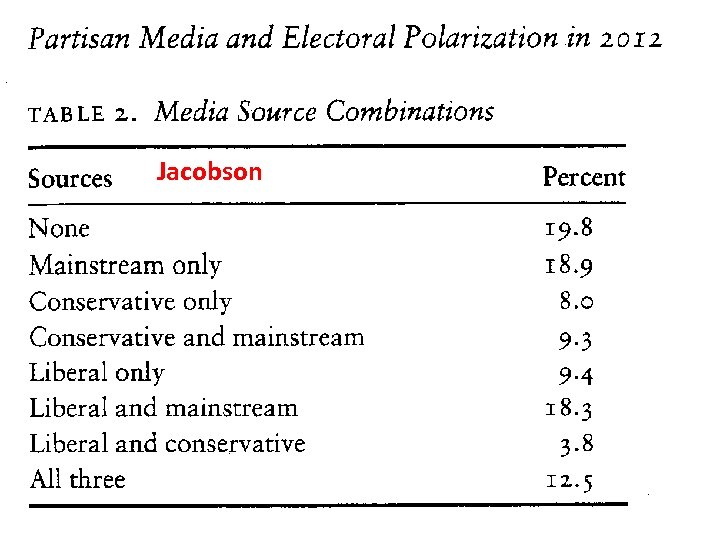
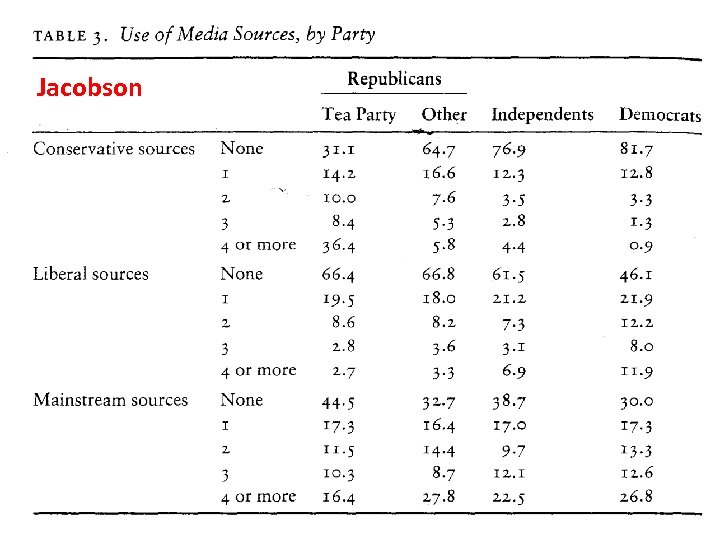 Jacobson
Jacobson
 Jacobson
Jacobson
 Jacobson
Jacobson
 Jacobson
Jacobson
 Jacobson
Jacobson
 Jacobson
Jacobson
 Jacobson
Jacobson
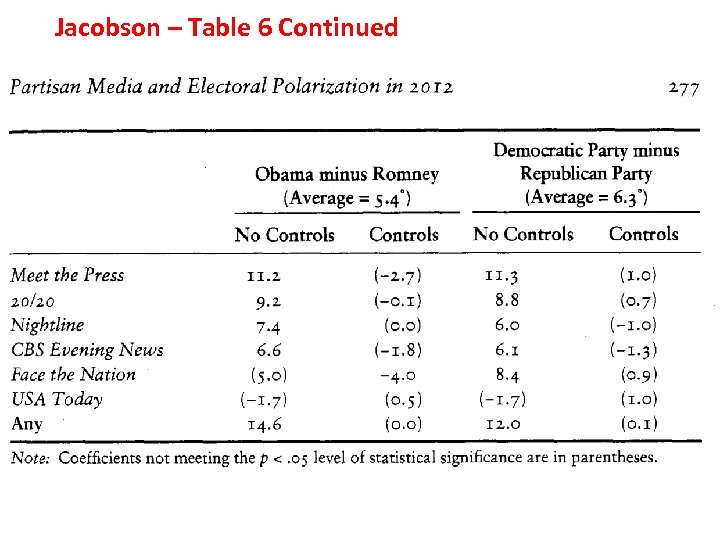 Jacobson – Table 6 Continued
Jacobson – Table 6 Continued
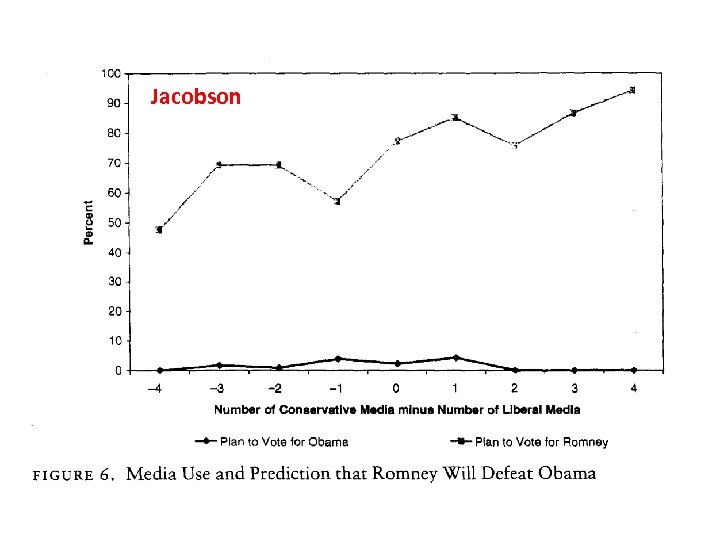 Jacobson
Jacobson
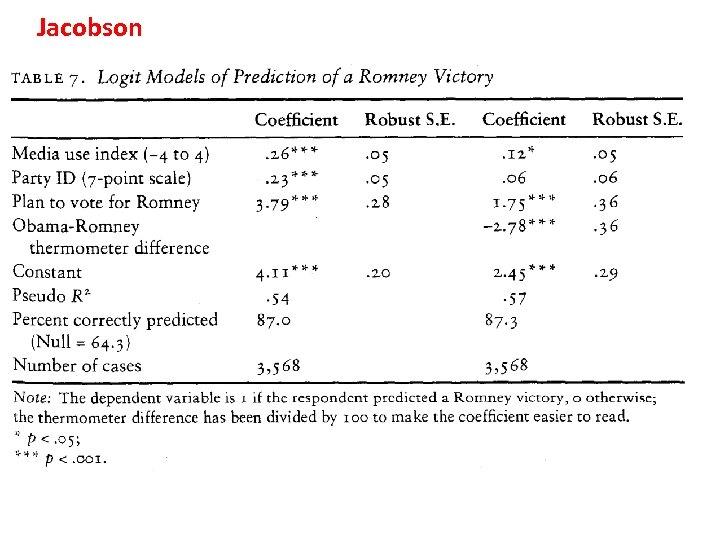 Jacobson
Jacobson
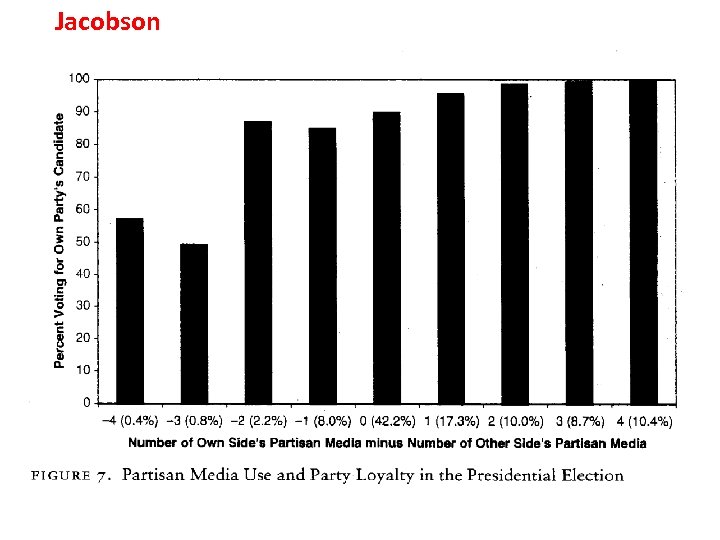 Jacobson
Jacobson
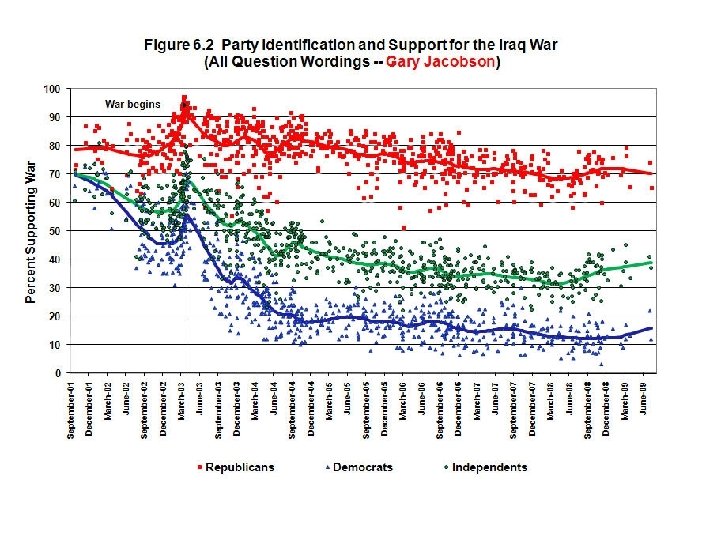
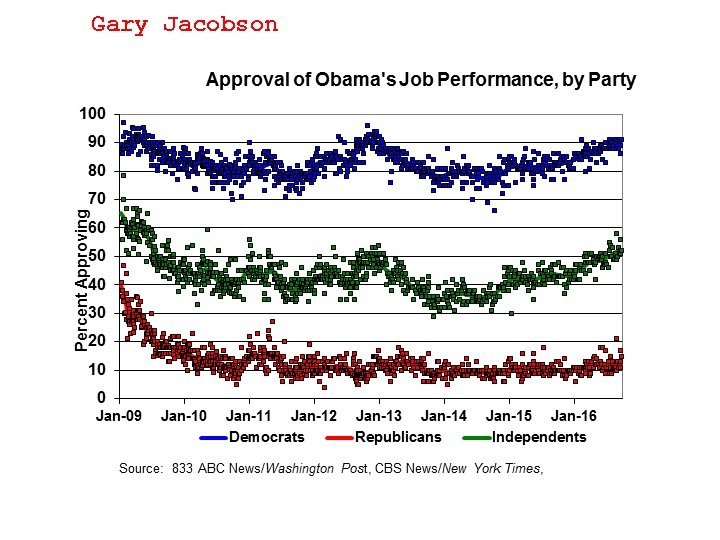 Gary Jacobson
Gary Jacobson
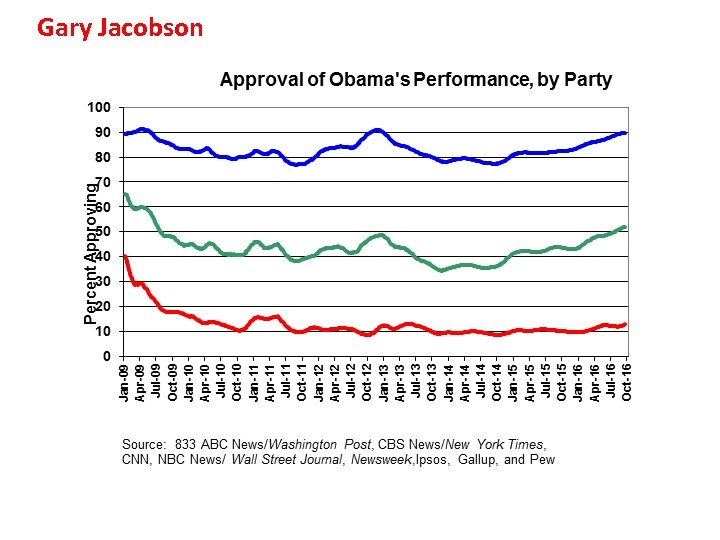 Gary Jacobson
Gary Jacobson
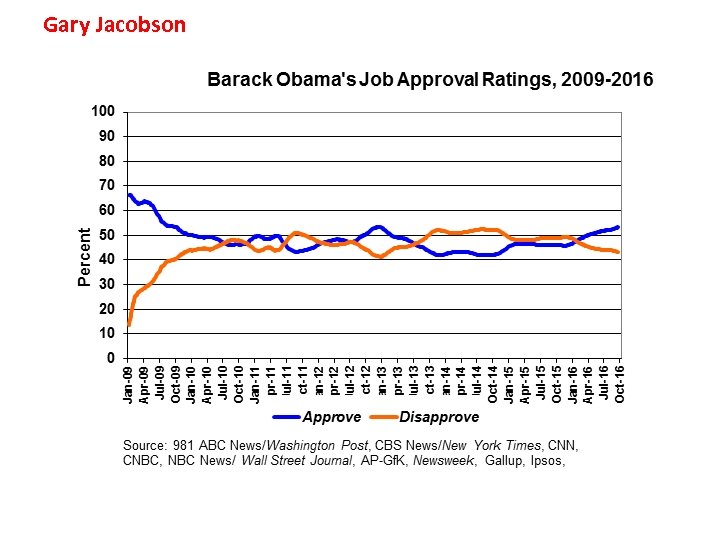 Gary Jacobson
Gary Jacobson
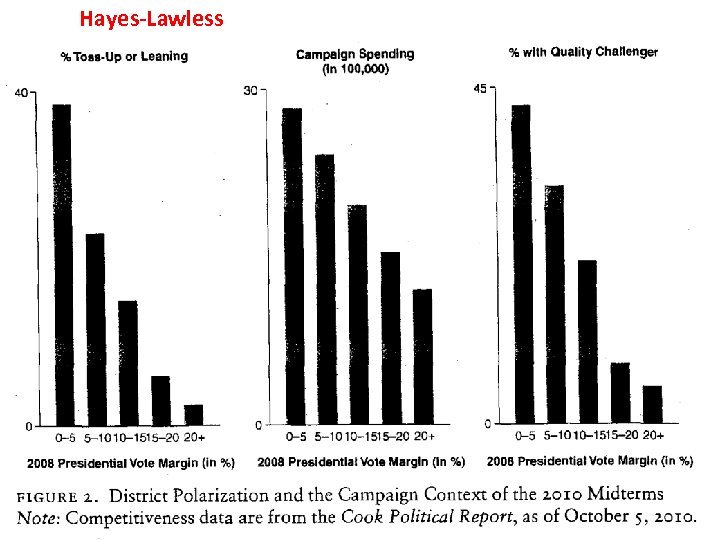
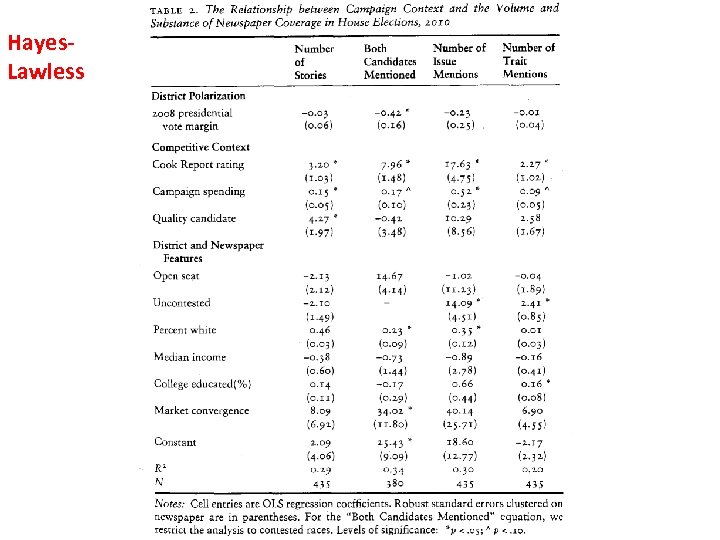
 Hayes & Lawless: District Polarization and Media Coverage of U. S. House Campaigns • They Studied all 435 House districts in the 2010 election. • The greater the polarization within the district the less competitive the district is and the less newspaper coverage the election received. • Only gathered newspapers that were on-line for the study.
Hayes & Lawless: District Polarization and Media Coverage of U. S. House Campaigns • They Studied all 435 House districts in the 2010 election. • The greater the polarization within the district the less competitive the district is and the less newspaper coverage the election received. • Only gathered newspapers that were on-line for the study.
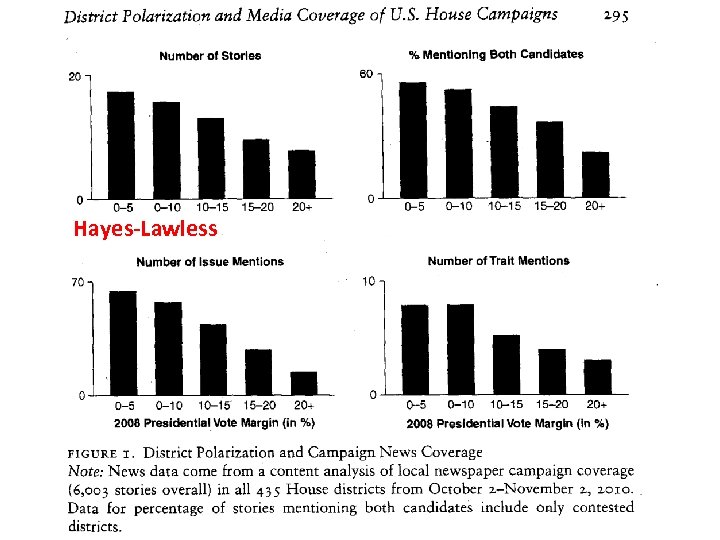 Hayes-Lawless
Hayes-Lawless
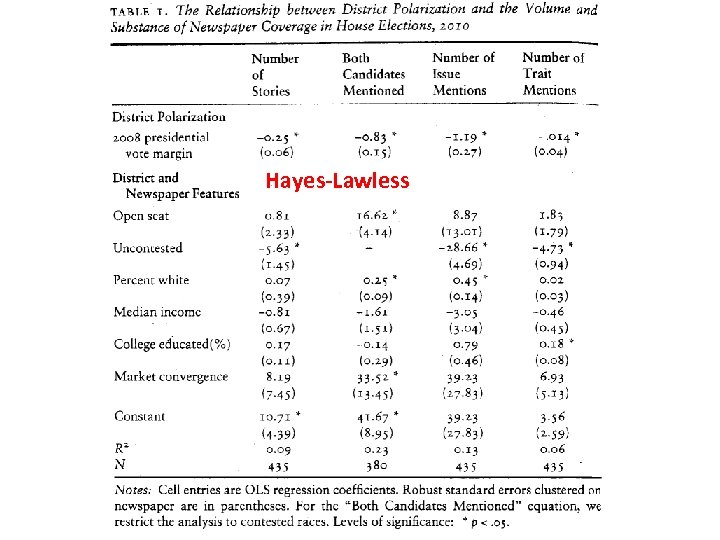 Hayes-Lawless
Hayes-Lawless
 Hayes-Lawless
Hayes-Lawless
 Hayes. Lawless
Hayes. Lawless
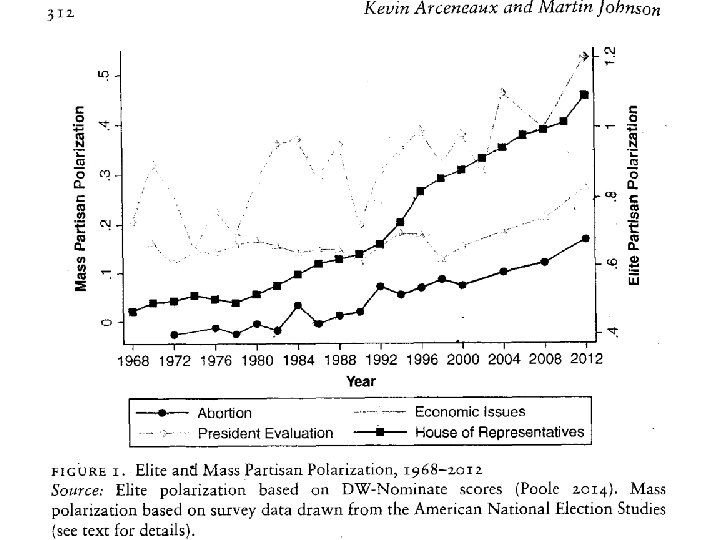
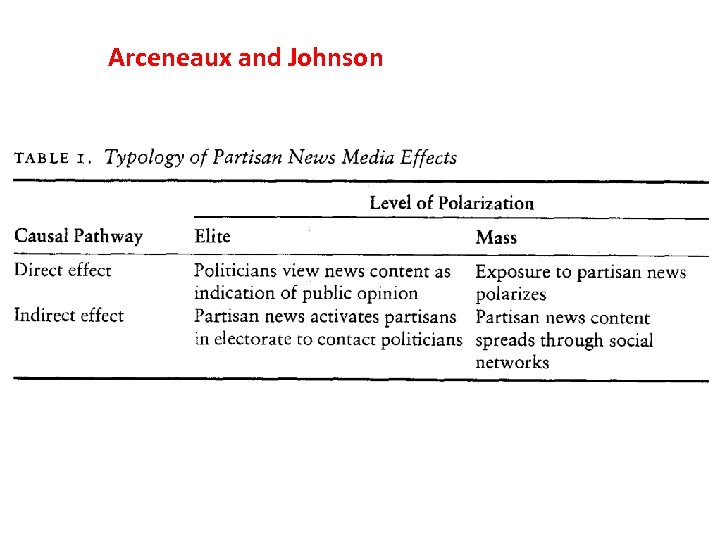
 Arceneaux and Johnson: Polarization and Partisan News Media in America • 1. “Partisan news media are more likely a symptom of a polarized party system than a cause. ” (cf. MPR, Chapter 3, p. 97, mass polarization follows elite polarization) • 2. Strong Affective Polarization. Partisans intensely dislike members of the opposite Party. • 3. “Polarization at the elite and the mass levels is real. ”
Arceneaux and Johnson: Polarization and Partisan News Media in America • 1. “Partisan news media are more likely a symptom of a polarized party system than a cause. ” (cf. MPR, Chapter 3, p. 97, mass polarization follows elite polarization) • 2. Strong Affective Polarization. Partisans intensely dislike members of the opposite Party. • 3. “Polarization at the elite and the mass levels is real. ”
 Arceneaux and Johnson (continued) • 4. “Partisan polarization at the elite level began well in advance of Fox News’ debut” (see graphs by Poole & Rosenthal). • 5. “News Media, including mainstream and partisan outlets, are megaphones more than motivators of partisan polarization. ”
Arceneaux and Johnson (continued) • 4. “Partisan polarization at the elite level began well in advance of Fox News’ debut” (see graphs by Poole & Rosenthal). • 5. “News Media, including mainstream and partisan outlets, are megaphones more than motivators of partisan polarization. ”
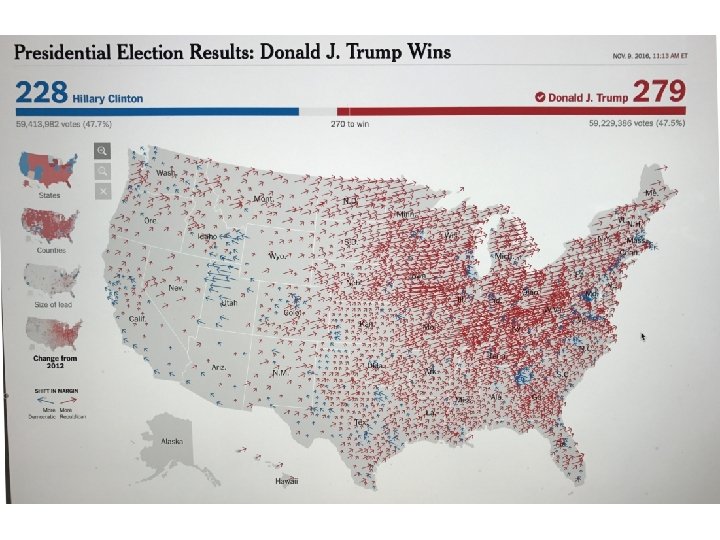
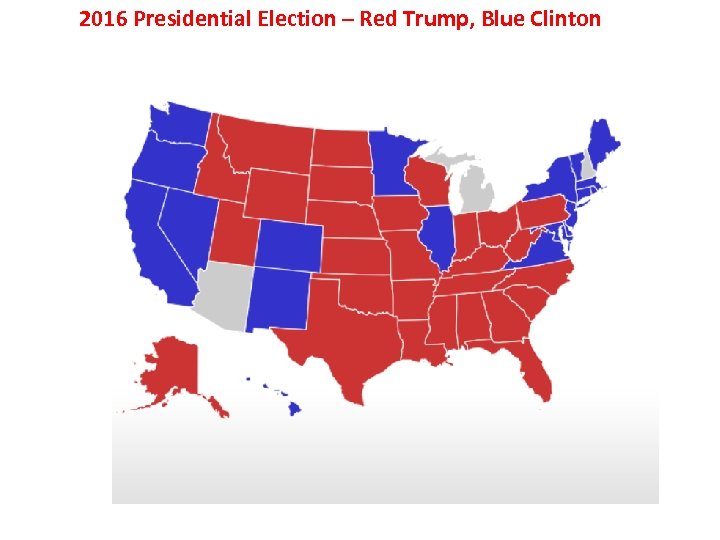 2016 Presidential Election – Red Trump, Blue Clinton
2016 Presidential Election – Red Trump, Blue Clinton
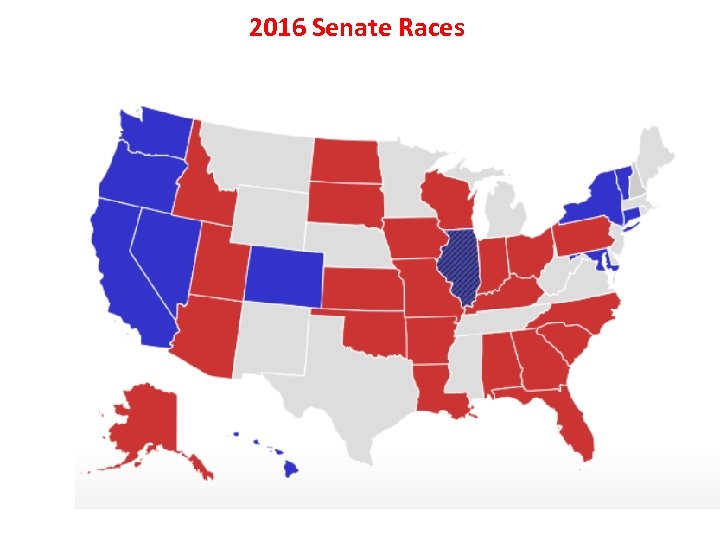 2016 Senate Races
2016 Senate Races
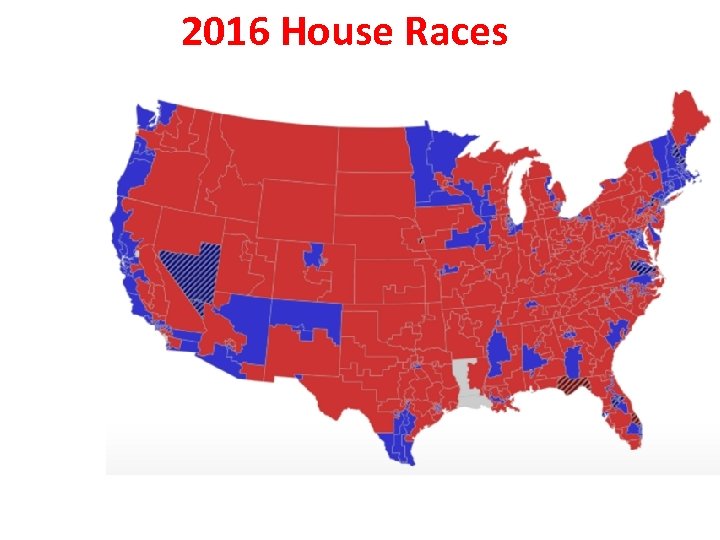 2016 House Races
2016 House Races
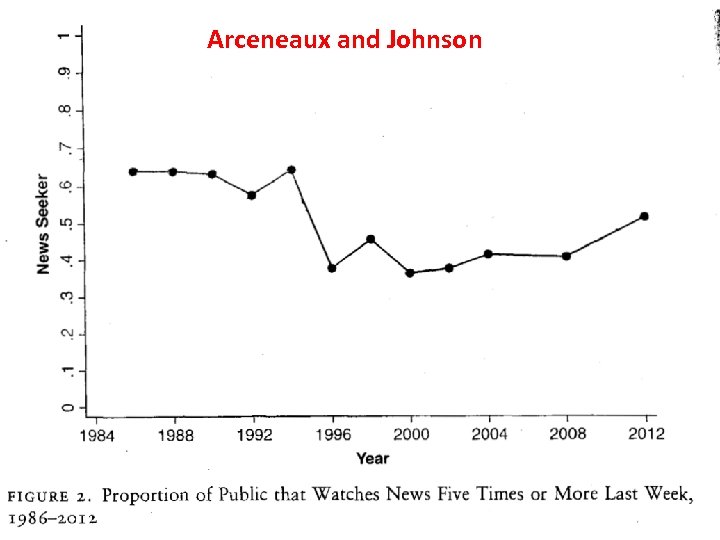
 Arceneaux and Johnson
Arceneaux and Johnson
 Arceneaux and Johnson
Arceneaux and Johnson
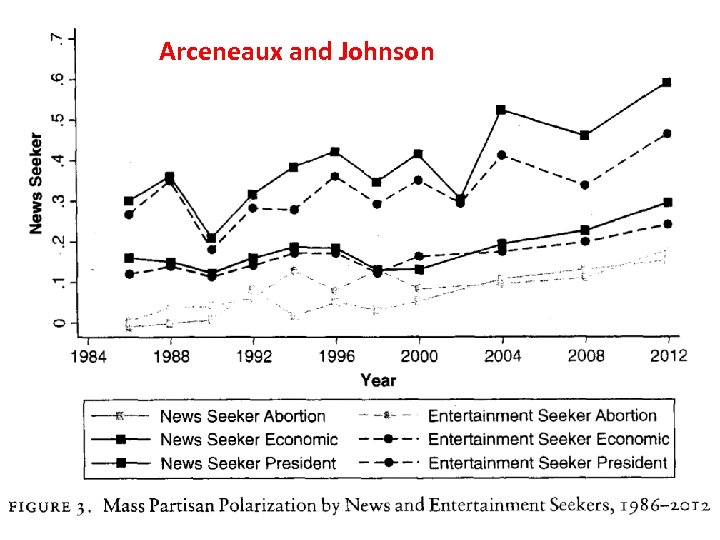 Arceneaux and Johnson
Arceneaux and Johnson
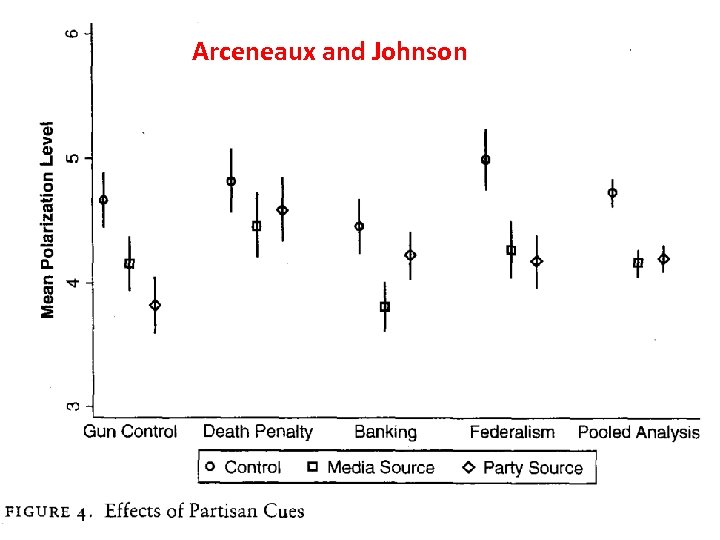 Arceneaux and Johnson
Arceneaux and Johnson
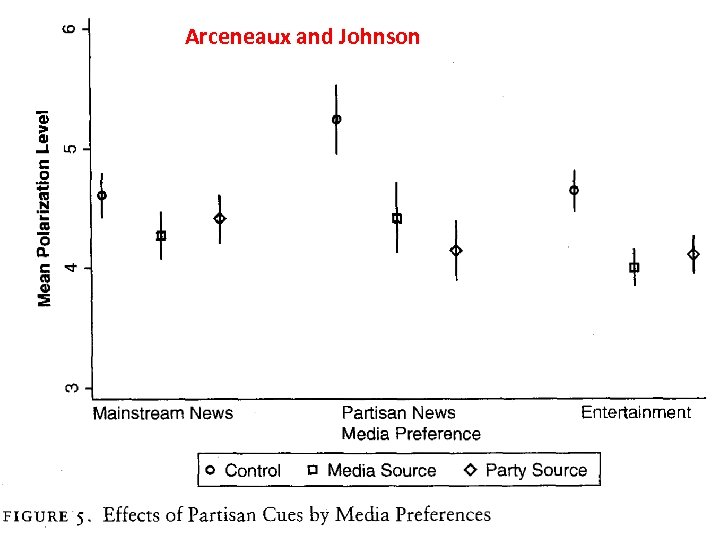 Arceneaux and Johnson
Arceneaux and Johnson
 Stroud & Curry: The Polarizing Effects of Partisan and Mainstream News • 1. They focus on a single issue – The Keystone XL pipeline. • 2. They use Fox News Channel, MSNBC, and NBC Nightly News as their TV News Sources. • 3. Partisanship is related to attitudes on Keystone. • 4. NBC alone did not have a polarizing effect. • 5. Fox News and MSNBC did have a polarizing effect.
Stroud & Curry: The Polarizing Effects of Partisan and Mainstream News • 1. They focus on a single issue – The Keystone XL pipeline. • 2. They use Fox News Channel, MSNBC, and NBC Nightly News as their TV News Sources. • 3. Partisanship is related to attitudes on Keystone. • 4. NBC alone did not have a polarizing effect. • 5. Fox News and MSNBC did have a polarizing effect.
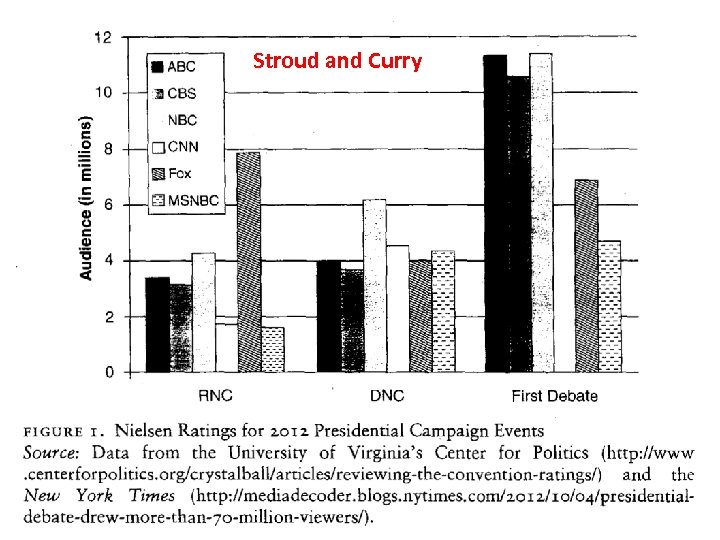 Stroud and Curry
Stroud and Curry
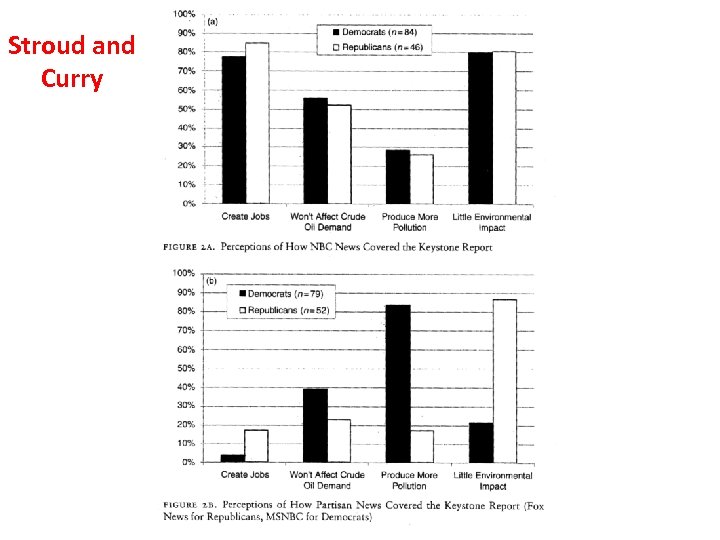 Stroud and Curry
Stroud and Curry
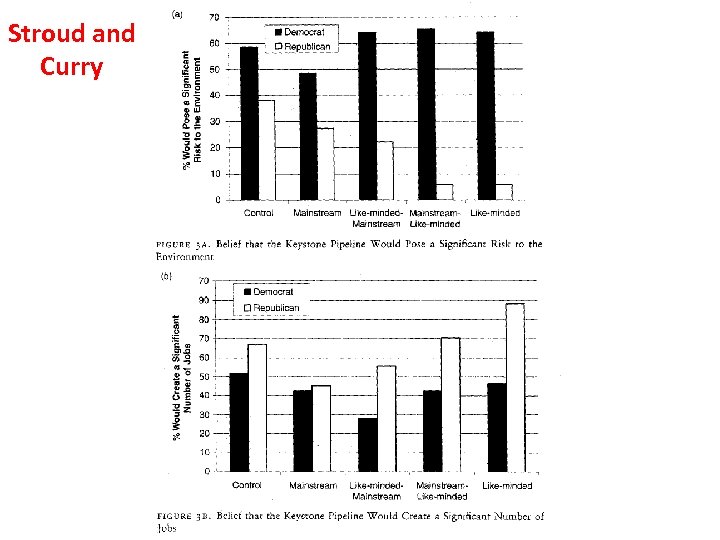 Stroud and Curry
Stroud and Curry
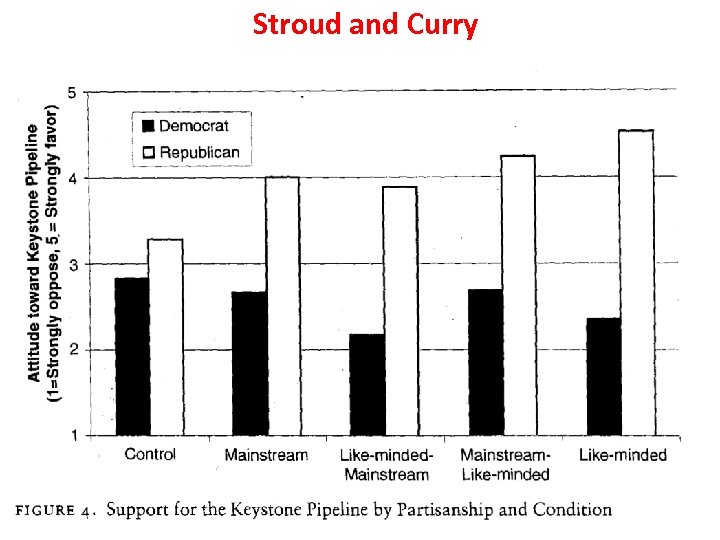 Stroud and Curry
Stroud and Curry


