3fc345a45c0b28ed14d40113717a3811.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 American Foreign Policy: 1945 -1972 American History: Chapters 26, 28, 30 Cold War, Korea, Vietnam
American Foreign Policy: 1945 -1972 American History: Chapters 26, 28, 30 Cold War, Korea, Vietnam
 The Cold War
The Cold War
 Lifestyle: Soviet vs. US • Soviet Union • Communism—government controlling all aspects of society • Totalitarian government: No opposition to Communist • United States • Capitalism—private citizens control almost all the economic activity. People have a choice. • Democracy: People have a voice • Tensions • Different Lifestyles and Belieft • USSR anger over delayed US attack of Nazi’s and keeping Atomic Bomb a secret
Lifestyle: Soviet vs. US • Soviet Union • Communism—government controlling all aspects of society • Totalitarian government: No opposition to Communist • United States • Capitalism—private citizens control almost all the economic activity. People have a choice. • Democracy: People have a voice • Tensions • Different Lifestyles and Belieft • USSR anger over delayed US attack of Nazi’s and keeping Atomic Bomb a secret
 Yalta Conference • USSR, GB, and USA met to decide what would happen after WWII. • Split Germany into 4 Occupational Zones. • West Germany controlled by USA/GB/France • East Germany controlled by USSR
Yalta Conference • USSR, GB, and USA met to decide what would happen after WWII. • Split Germany into 4 Occupational Zones. • West Germany controlled by USA/GB/France • East Germany controlled by USSR
 United Nations • Was created after WWII in hopes that we would never have another “world war. ” • 50 nations were at a meeting in San Francisco, all of them were trying to figure out a way to create a lasting peace. • Joseph Stalin—leader of the USSR did not like the UN and would not be apart of it.
United Nations • Was created after WWII in hopes that we would never have another “world war. ” • 50 nations were at a meeting in San Francisco, all of them were trying to figure out a way to create a lasting peace. • Joseph Stalin—leader of the USSR did not like the UN and would not be apart of it.
 Cold War • The USA and the USSR never fought each other during this conflict, which is why it is called the “cold war. ” • This conflict lasted from 1945 -1991.
Cold War • The USA and the USSR never fought each other during this conflict, which is why it is called the “cold war. ” • This conflict lasted from 1945 -1991.
 Iron Curtain • Stalin installed communist governments in the following countries (Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania and Poland) • Satellite Nations—nations that were controlled by the USSR. • Containment—US policy in which we would do anything in our power to prevent the extension of communism. This would define most of US foreign policy during the Cold War • Iron Curtain—the division between Eastern and Western Europe
Iron Curtain • Stalin installed communist governments in the following countries (Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania and Poland) • Satellite Nations—nations that were controlled by the USSR. • Containment—US policy in which we would do anything in our power to prevent the extension of communism. This would define most of US foreign policy during the Cold War • Iron Curtain—the division between Eastern and Western Europe
 Truman Doctrine • The United States was very concerned about Turkey and Greece falling to USSR. • Truman gave around 400 million dollars to those countries to fight off communism. • Truman Doctrine—US would support free people throughout the world against communism. • Marshall Plan—US gave 13 billion dollars in aid to European Countries to help them rebuild after WWII. This was done to help ensure that communism would not occur within Western Europe.
Truman Doctrine • The United States was very concerned about Turkey and Greece falling to USSR. • Truman gave around 400 million dollars to those countries to fight off communism. • Truman Doctrine—US would support free people throughout the world against communism. • Marshall Plan—US gave 13 billion dollars in aid to European Countries to help them rebuild after WWII. This was done to help ensure that communism would not occur within Western Europe.
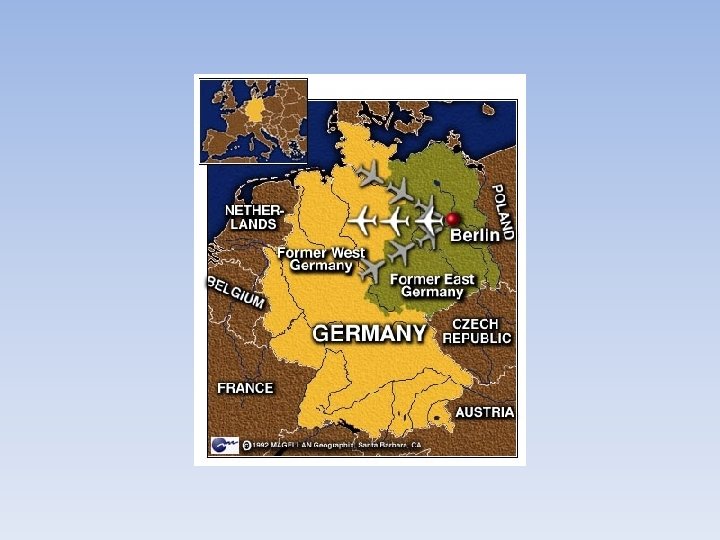
 Issues with Germany • The United States wanted to reunify Germany • Berlin: Germany’s Largest City – Located in Eastern Part of Germany (USSR Controlled) – City itself was controlled by both the USA and USSR • Stalin closed all access to Berlin • Berlin Airlift—American and British troops dropped supplies to West Berlin (2. 3 million tons of supplies) over a years span. • Eventually, the USSR lifted its blockade of Berlin, however, Germany was still divided (East Germany and West Germany)
Issues with Germany • The United States wanted to reunify Germany • Berlin: Germany’s Largest City – Located in Eastern Part of Germany (USSR Controlled) – City itself was controlled by both the USA and USSR • Stalin closed all access to Berlin • Berlin Airlift—American and British troops dropped supplies to West Berlin (2. 3 million tons of supplies) over a years span. • Eventually, the USSR lifted its blockade of Berlin, however, Germany was still divided (East Germany and West Germany)
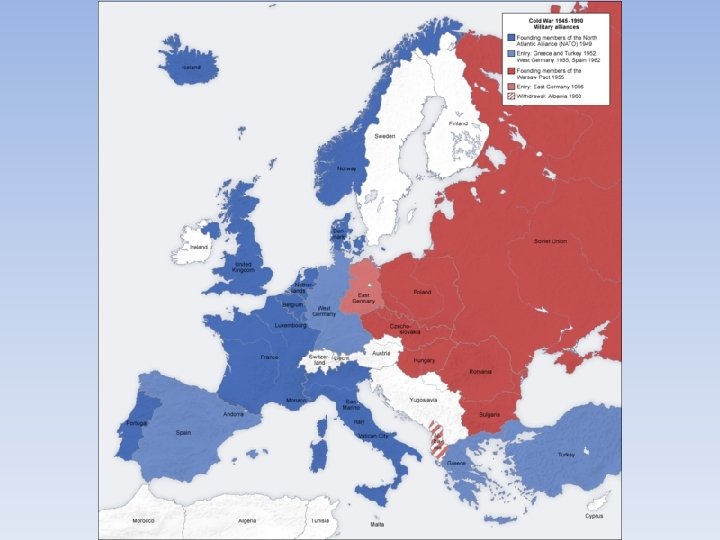
 Military Alliances • NATO—military alliance between all of the countries of Western Europe (Belgium, Denmark, France, GB, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, USA and Canada. • Warsaw Pact—military alliance between all countries under Soviet control
Military Alliances • NATO—military alliance between all of the countries of Western Europe (Belgium, Denmark, France, GB, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, USA and Canada. • Warsaw Pact—military alliance between all countries under Soviet control
 China • Chiang Kai-shek was the leader of the Nationalist Government within China. He had been fighting a communist movement led by Mao Zedong. • As time went on, the Communist Party was able to take control of China (except Taiwan). • This made many people in America very afraid of communism spreading throughout the world, even into America.
China • Chiang Kai-shek was the leader of the Nationalist Government within China. He had been fighting a communist movement led by Mao Zedong. • As time went on, the Communist Party was able to take control of China (except Taiwan). • This made many people in America very afraid of communism spreading throughout the world, even into America.
 The Korean War • Korea – Was split into 2 parts after WWII – North went to USSR, South went to USA – Korea was split along the 38 th Parallel – 1949: USSR/North Korea decided to try to take over all of Korea.
The Korean War • Korea – Was split into 2 parts after WWII – North went to USSR, South went to USA – Korea was split along the 38 th Parallel – 1949: USSR/North Korea decided to try to take over all of Korea.
 The Korean War • The North Korean/Communist were able to invade into much of South Korea. • Truman ordered America to go to South Korea and push back the communists under the command of Douglas Mc. Arthur (520, 000 troops) • United States was able to drive the North Korean troops all the way to the border of Korea and China. It appeared as though they would surrender.
The Korean War • The North Korean/Communist were able to invade into much of South Korea. • Truman ordered America to go to South Korea and push back the communists under the command of Douglas Mc. Arthur (520, 000 troops) • United States was able to drive the North Korean troops all the way to the border of Korea and China. It appeared as though they would surrender.
 The Korean War • The Chinese (who were communist) decided to help the North Koreans and were able to help drive the American troops out of North Korea. For 2 years both sides fought to about a stalemate. • Mc. Arthur really wanted to attack China, Truman did not like this idea because he thought it would start WWIII.
The Korean War • The Chinese (who were communist) decided to help the North Koreans and were able to help drive the American troops out of North Korea. For 2 years both sides fought to about a stalemate. • Mc. Arthur really wanted to attack China, Truman did not like this idea because he thought it would start WWIII.
 The Korean War • Truman eventually fired Mc. Arthur (who was still very popular in America). • June 23 rd, 1951, the USSR offered a cease fire agreement that would end the fighting. • The compromise created 2 countries in Korea (North and South). • 54, 000 American Soldiers died in the Korean War and it cost 67 billion dollars • Truman was not re-elected President in 1952…Dwight Eisenhower (Rep) won • http: //users. erols. com/mwhite 28/images/korean_w. gif
The Korean War • Truman eventually fired Mc. Arthur (who was still very popular in America). • June 23 rd, 1951, the USSR offered a cease fire agreement that would end the fighting. • The compromise created 2 countries in Korea (North and South). • 54, 000 American Soldiers died in the Korean War and it cost 67 billion dollars • Truman was not re-elected President in 1952…Dwight Eisenhower (Rep) won • http: //users. erols. com/mwhite 28/images/korean_w. gif
 America during the Cold War • Many Americans became suspicious that there were communist within the American Government. • Ethel and Julius Rosenberg were Americans who were accused of being Russian spies (giving secrets to the USSR about the Atomic Bomb). They were found guilty and sentenced to death. • Joseph Mc. Carthy—Senator from Wisconsin accused many people in Congress of being “secretly communist. ” • Millions of Americans had to take loyalty oaths, labor unions started to decline, people were afraid to speak out against the government • Dwight Eisenhower: Elected President in 1952. Served 2 terms
America during the Cold War • Many Americans became suspicious that there were communist within the American Government. • Ethel and Julius Rosenberg were Americans who were accused of being Russian spies (giving secrets to the USSR about the Atomic Bomb). They were found guilty and sentenced to death. • Joseph Mc. Carthy—Senator from Wisconsin accused many people in Congress of being “secretly communist. ” • Millions of Americans had to take loyalty oaths, labor unions started to decline, people were afraid to speak out against the government • Dwight Eisenhower: Elected President in 1952. Served 2 terms
 Race for the H-Bomb • H-Bomb—Hydrogen Bomb, it would have the force of 1 million tons of TNT (67 times more powerful then the atomic bomb on Hiroshima). Scientist argued about the moral issues. • USA made the first H-Bomb in November of 1952, USSR responded by Sept. of 1953
Race for the H-Bomb • H-Bomb—Hydrogen Bomb, it would have the force of 1 million tons of TNT (67 times more powerful then the atomic bomb on Hiroshima). Scientist argued about the moral issues. • USA made the first H-Bomb in November of 1952, USSR responded by Sept. of 1953
 New Ways of Thinking • Brinkmanship—the idea that the United States would use whatever force necessary to stop the spread of communism • The United States began to trim the Army and Navy while making the Air Force stronger. • CIA—Central Intelligence Agency, used spies to gather as much information on other countries as possible. • CIA also began to do many secret operations designed to protect America.
New Ways of Thinking • Brinkmanship—the idea that the United States would use whatever force necessary to stop the spread of communism • The United States began to trim the Army and Navy while making the Air Force stronger. • CIA—Central Intelligence Agency, used spies to gather as much information on other countries as possible. • CIA also began to do many secret operations designed to protect America.
 Tensions in the Middle East • Suez War—Egyptian leader Gamal Nasser wanted help building a dam on the Suez Canal. He wanted to get help from both America and the USSR. • Once American leaders found out about this, the withdrew their loan. Nasser responded by taking control of the whole canal. • This also really hurt Israel because Nasser would not allow ships for Israel to pass through…. war
Tensions in the Middle East • Suez War—Egyptian leader Gamal Nasser wanted help building a dam on the Suez Canal. He wanted to get help from both America and the USSR. • Once American leaders found out about this, the withdrew their loan. Nasser responded by taking control of the whole canal. • This also really hurt Israel because Nasser would not allow ships for Israel to pass through…. war
 Tensions in the Middle East • The Soviet Union had a lot of interest in actions within the Middle East (Egypt, Iran) • Eisenhower Doctrine—said that the United States would defend the Middle East from any attack by a communist country. • Hungary wanted a democratic government, the USA would not help them in their revolt because it was a Satellite Nation of the Soviet Union.
Tensions in the Middle East • The Soviet Union had a lot of interest in actions within the Middle East (Egypt, Iran) • Eisenhower Doctrine—said that the United States would defend the Middle East from any attack by a communist country. • Hungary wanted a democratic government, the USA would not help them in their revolt because it was a Satellite Nation of the Soviet Union.
 Other venues of the Cold War • Nikita Khrushchev—Soviet leader after Stalin died. He favored a peaceful competition between the two countries (science and economically) • Space Race—competition to see who could get into space and the moon the quickest. • Sputnik—first satellite into space; launched by the Soviets.
Other venues of the Cold War • Nikita Khrushchev—Soviet leader after Stalin died. He favored a peaceful competition between the two countries (science and economically) • Space Race—competition to see who could get into space and the moon the quickest. • Sputnik—first satellite into space; launched by the Soviets.
 Spying Issues • The CIA was making secret high altitude flights over the Soviet Union using a plane called the U-2 (no radar detection). • This was a very controversial program that had a lot of opposition within the American and Soviet Governments. • The Soviet Union shot down one of these planes (both sides had promised not to do these missions). • This significantly increased the tension between the 2 sides heading into the 1960 s.
Spying Issues • The CIA was making secret high altitude flights over the Soviet Union using a plane called the U-2 (no radar detection). • This was a very controversial program that had a lot of opposition within the American and Soviet Governments. • The Soviet Union shot down one of these planes (both sides had promised not to do these missions). • This significantly increased the tension between the 2 sides heading into the 1960 s.
 JFK • John F Kennedy was elected President in 1960, beat Richard Nixon in a very close elections • This was a very influential time because many Americans thought we were losing the Cold War • Kennedy used television to gain many supporters (overcame opponents: Catholic, too young) • African American vote helped Kennedy • Kennedy was very much in the “public eye” • He surrounded himself with the “ best and brightest”
JFK • John F Kennedy was elected President in 1960, beat Richard Nixon in a very close elections • This was a very influential time because many Americans thought we were losing the Cold War • Kennedy used television to gain many supporters (overcame opponents: Catholic, too young) • African American vote helped Kennedy • Kennedy was very much in the “public eye” • He surrounded himself with the “ best and brightest”

 JFK’s military policy • Kennedy saw how communism was popular to poorer countries (Republicans didn’t) • Flexible Response—main military strategy in which nuclear weapons would not be the answer/threat to every situation • Increased dollars spend on other factions of the military • Allowed the US to fight limited wars while keeping pace with USSR’s nuclear capability
JFK’s military policy • Kennedy saw how communism was popular to poorer countries (Republicans didn’t) • Flexible Response—main military strategy in which nuclear weapons would not be the answer/threat to every situation • Increased dollars spend on other factions of the military • Allowed the US to fight limited wars while keeping pace with USSR’s nuclear capability
 Cuba • Fidel Castro—leader of a Cuban revolutionary force had taken control of the country and declared the country communist. • This caused the US to cut off ties with Cuba • Hundreds of thousands of Cubans left the country for America, Castro and the United States were at odds, USSR would help.
Cuba • Fidel Castro—leader of a Cuban revolutionary force had taken control of the country and declared the country communist. • This caused the US to cut off ties with Cuba • Hundreds of thousands of Cubans left the country for America, Castro and the United States were at odds, USSR would help.
 Bay of Pigs • CIA began to train Cuban’s who had left the country because they were opposed to Castro. The plan was to have the Cuban exiles go into Cuba and start a revolution. • This plan was a complete failure, the invading group met around 25, 000 Cuban soldiers. Most of the invading forces were either killed or jailed. • Kennedy took a lot of heat, America was embarrassed, and we had to give Cuba 50 million dollars to get our prisoners back.
Bay of Pigs • CIA began to train Cuban’s who had left the country because they were opposed to Castro. The plan was to have the Cuban exiles go into Cuba and start a revolution. • This plan was a complete failure, the invading group met around 25, 000 Cuban soldiers. Most of the invading forces were either killed or jailed. • Kennedy took a lot of heat, America was embarrassed, and we had to give Cuba 50 million dollars to get our prisoners back.
 Cuban Missile Crisis • Khrushchev sent all sorts of weapons to Cuba to help them defend themselves (including nuclear weapons). • Kennedy responded by saying that America would not let this happen. • In October of 1962, American planes revealed that the Soviets had missiles ready to launch that could strike any American city within minutes.
Cuban Missile Crisis • Khrushchev sent all sorts of weapons to Cuba to help them defend themselves (including nuclear weapons). • Kennedy responded by saying that America would not let this happen. • In October of 1962, American planes revealed that the Soviets had missiles ready to launch that could strike any American city within minutes.
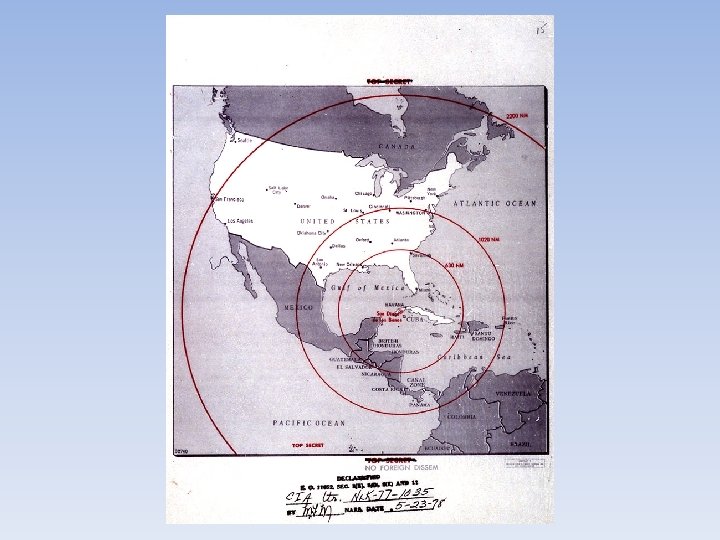

 Cuban Missile Crisis • Kennedy demanded that the missiles be removed from Cuba. • He said that any missile attack from Cuba would send an all-out nuclear attack on the Soviet Union. • For 6 days the world waited for something to happen…meanwhile, American ships were not allowing Soviet ships access to Cuba. • Finally, Khrushchev announced that the Soviet Union would remove missiles if the US would promise not to invade Cuba. (US would removed missiles from Turkey as well)
Cuban Missile Crisis • Kennedy demanded that the missiles be removed from Cuba. • He said that any missile attack from Cuba would send an all-out nuclear attack on the Soviet Union. • For 6 days the world waited for something to happen…meanwhile, American ships were not allowing Soviet ships access to Cuba. • Finally, Khrushchev announced that the Soviet Union would remove missiles if the US would promise not to invade Cuba. (US would removed missiles from Turkey as well)
 Results of the Cuban Missile Crisis • Both Kennedy (brinkmanship, not invading) and Khrushchev (being too weak) took a lot of criticism for what happened with Cuba. • Cuban exiles blamed the Democrats for “losing Cuba” and voted Republican. • Many Cubans left Cuba, Cuban population in Miami increased to around 300, 000
Results of the Cuban Missile Crisis • Both Kennedy (brinkmanship, not invading) and Khrushchev (being too weak) took a lot of criticism for what happened with Cuba. • Cuban exiles blamed the Democrats for “losing Cuba” and voted Republican. • Many Cubans left Cuba, Cuban population in Miami increased to around 300, 000
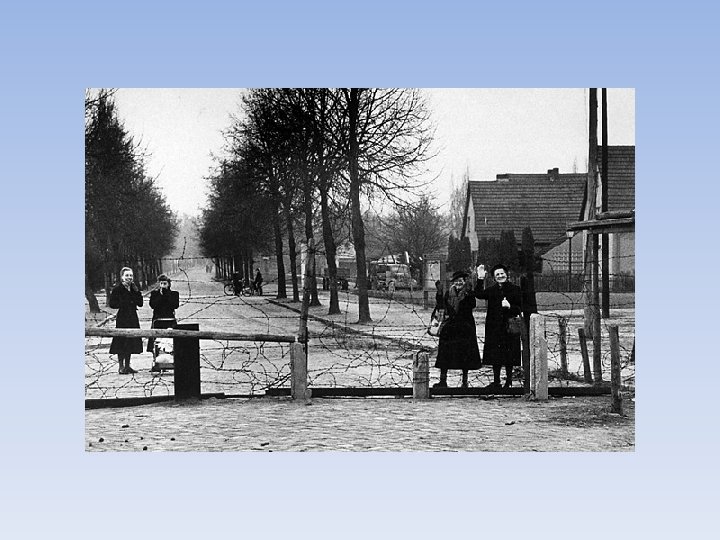
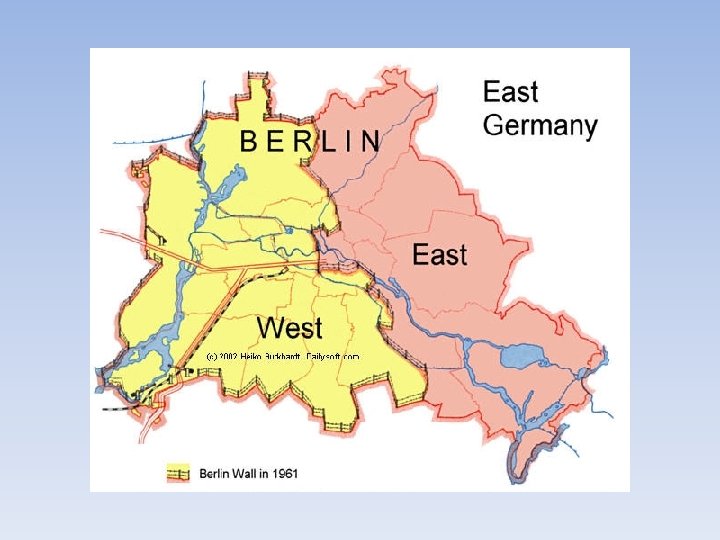
 Berlin • Berlin Wall—concrete wall that split Berlin in two. This was done to prevent people from East Germany from escaping to West Germany. (3 million had fled) • Soviets decided to do this after Kennedy had threatened to attack if the Soviets cut off all access to Berlin. • Became an ugly symbol of the Cold War
Berlin • Berlin Wall—concrete wall that split Berlin in two. This was done to prevent people from East Germany from escaping to West Germany. (3 million had fled) • Soviets decided to do this after Kennedy had threatened to attack if the Soviets cut off all access to Berlin. • Became an ugly symbol of the Cold War
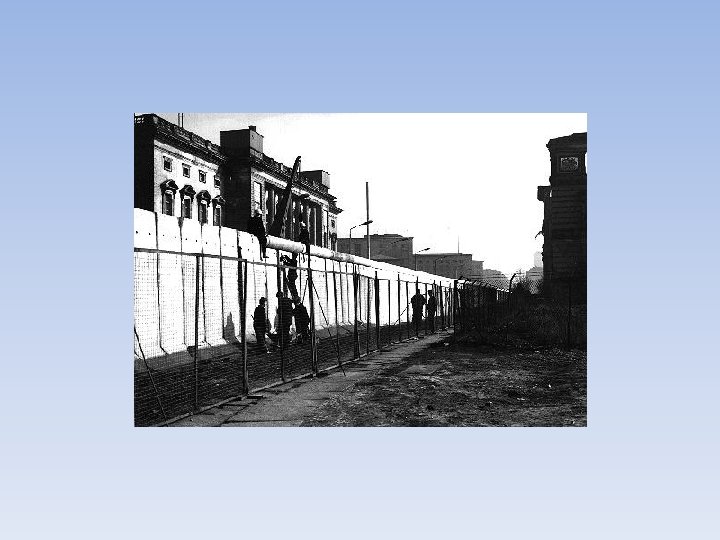



 Things get better • Neither the Soviet Union or America wanted to go to nuclear war. • Hot Line—direct phone connection between the Soviets and Americans. • Limited Test Ban Treaty—agreed on by both countries, barred nuclear testing in the atmosphere
Things get better • Neither the Soviet Union or America wanted to go to nuclear war. • Hot Line—direct phone connection between the Soviets and Americans. • Limited Test Ban Treaty—agreed on by both countries, barred nuclear testing in the atmosphere
 Vietnam
Vietnam
 Early History of Vietnam • French Colony since 1800 s • Opposition to France’s Control – Ho Chi Minh--leader of the Indochinese Communist Party, wanted Vietnam to be independent/communist – Vietminh--organization created by Ho Chi Minh that attempted to win independence. (Vietcong) • Ironically, the USA had supported Ho Chi Minh during WWII b/c he was against the Japanese.
Early History of Vietnam • French Colony since 1800 s • Opposition to France’s Control – Ho Chi Minh--leader of the Indochinese Communist Party, wanted Vietnam to be independent/communist – Vietminh--organization created by Ho Chi Minh that attempted to win independence. (Vietcong) • Ironically, the USA had supported Ho Chi Minh during WWII b/c he was against the Japanese.

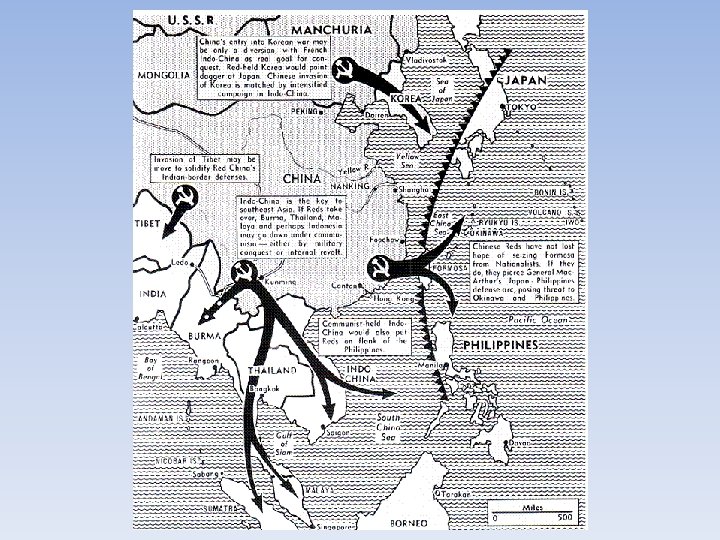
 • Domino Theory (1950’s and 1960’s) • Belief that if Vietnam fell to communism, all the other countries of SE Asia would become communist • Eisenhower would stop communism in SE Asia • Results • French were forced to surrender at Dien Bien Phu • Geneva Accords---temporarily divided Vietnam into 2 countries along the 17 th parallel. • North Vietnam (Communist)--capital of Hanoi • South Vietnam (anti-communist)--capital Saigon. • Election to unify country would be in 1956.
• Domino Theory (1950’s and 1960’s) • Belief that if Vietnam fell to communism, all the other countries of SE Asia would become communist • Eisenhower would stop communism in SE Asia • Results • French were forced to surrender at Dien Bien Phu • Geneva Accords---temporarily divided Vietnam into 2 countries along the 17 th parallel. • North Vietnam (Communist)--capital of Hanoi • South Vietnam (anti-communist)--capital Saigon. • Election to unify country would be in 1956.
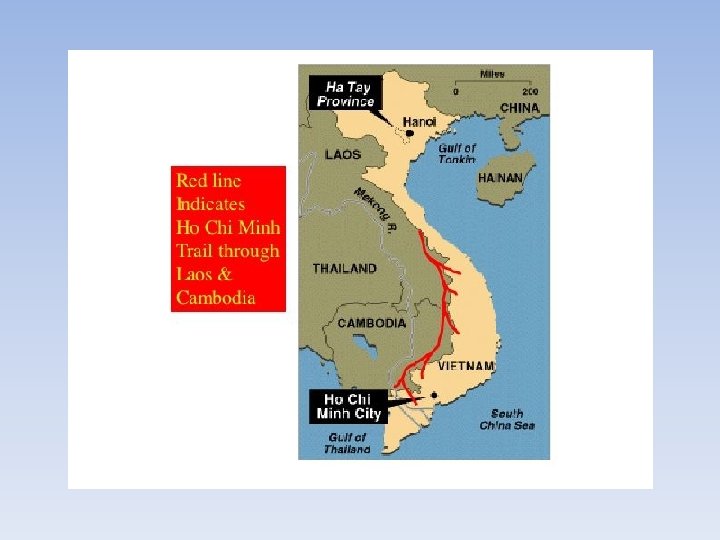
 • US Help: Election of 1956 • Ho Chi Minh--very popular guy in the North b/c he was a national hero • Ngo Dinh Diem--strong anti-communist who was supported by the USA – Diem made everyone mad b/c he lost control of the government, tried to make everyone Catholic, and did not redistribute any land to the poor. Dropped out of race • Vietcong---communist opposition to Diem/S Vietnam, started to become more popular in South Vietnam • Ho Chi Minh Trail--allowed for supplies and men to go between the North and South Vietnam (trail that went through Laos, Thailand Cambodia)
• US Help: Election of 1956 • Ho Chi Minh--very popular guy in the North b/c he was a national hero • Ngo Dinh Diem--strong anti-communist who was supported by the USA – Diem made everyone mad b/c he lost control of the government, tried to make everyone Catholic, and did not redistribute any land to the poor. Dropped out of race • Vietcong---communist opposition to Diem/S Vietnam, started to become more popular in South Vietnam • Ho Chi Minh Trail--allowed for supplies and men to go between the North and South Vietnam (trail that went through Laos, Thailand Cambodia)

 Presidential Response • John F Kennedy (1960) • Sent over thousands of military advisor • Gave more $ to Diem, Diem forced people to move out of villages, also started attacking Buddhism • USA supported a military coup to assassinate Diem • Kennedy was assassinated a few weeks later (1963)
Presidential Response • John F Kennedy (1960) • Sent over thousands of military advisor • Gave more $ to Diem, Diem forced people to move out of villages, also started attacking Buddhism • USA supported a military coup to assassinate Diem • Kennedy was assassinated a few weeks later (1963)

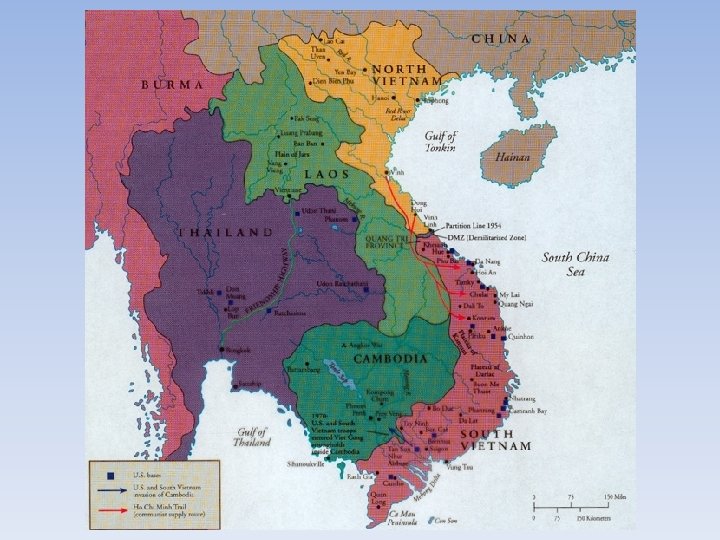
 Presidential Response • Lyndon Johnson (President after Kennedy) • Was willing to do anything to prevent communist from taking over South Vietnam • Tonkin Gulf Resolution • US alleged that the North Vietnamese had been firing at US ships (not true) • Tonkin Gulf Resolution--US would take all steps necessary to stop North Vietnam, started a bombing campaign called “operation rolling thunder” • By March of 1965, over 50, 000 American soldiers were in Vietnam fighting against the Vietcong
Presidential Response • Lyndon Johnson (President after Kennedy) • Was willing to do anything to prevent communist from taking over South Vietnam • Tonkin Gulf Resolution • US alleged that the North Vietnamese had been firing at US ships (not true) • Tonkin Gulf Resolution--US would take all steps necessary to stop North Vietnam, started a bombing campaign called “operation rolling thunder” • By March of 1965, over 50, 000 American soldiers were in Vietnam fighting against the Vietcong
 Johnson’s Plan continued. . • President Johnson’s Plans • Worked with Robert Mc. Namara (Sec of Defense) and Dean Rusk (Sec of State) • All decided to start sending thousands of troops to Vietnam in 1965 (most people were in favor) • Style of Fighting • Vietcong used guerilla warfare (hit/run, surprise) • Tunnel system allowed them to withstand air strikes and hide effectively (leeches, heat, weather) • Lots of booby traps and land minds • Made the fighting very difficult and dangerous
Johnson’s Plan continued. . • President Johnson’s Plans • Worked with Robert Mc. Namara (Sec of Defense) and Dean Rusk (Sec of State) • All decided to start sending thousands of troops to Vietnam in 1965 (most people were in favor) • Style of Fighting • Vietcong used guerilla warfare (hit/run, surprise) • Tunnel system allowed them to withstand air strikes and hide effectively (leeches, heat, weather) • Lots of booby traps and land minds • Made the fighting very difficult and dangerous
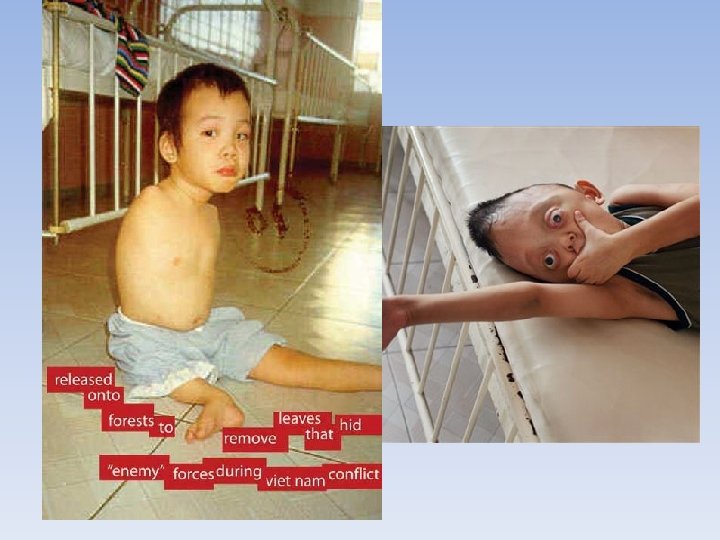
 Problems fighting • Too Much Jungle • Napalm—gasoline based bomb that set fire to jungle • Agent Orange—leaf killing chemical, destroyed everything, caused cancer for both Vietnamese and Americans. • Don’t know who they are fighting • Search and Destroy Missions—getting rid of civilians who are suspected as being with the Vietcong • Destroying entire villages
Problems fighting • Too Much Jungle • Napalm—gasoline based bomb that set fire to jungle • Agent Orange—leaf killing chemical, destroyed everything, caused cancer for both Vietnamese and Americans. • Don’t know who they are fighting • Search and Destroy Missions—getting rid of civilians who are suspected as being with the Vietcong • Destroying entire villages
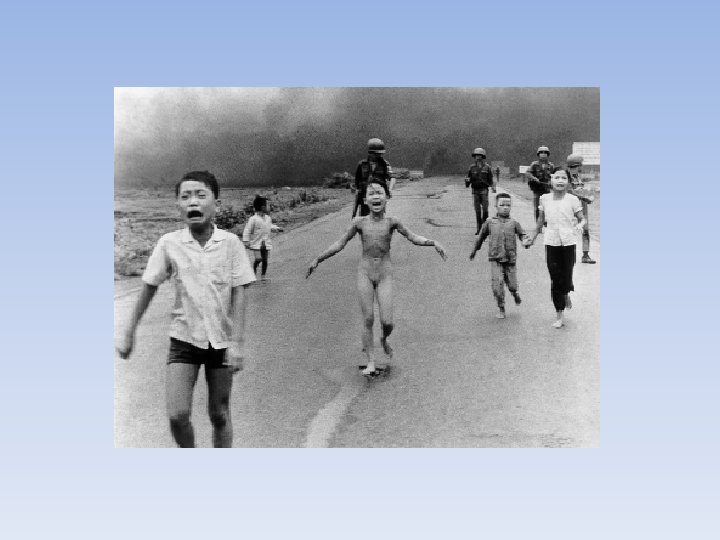


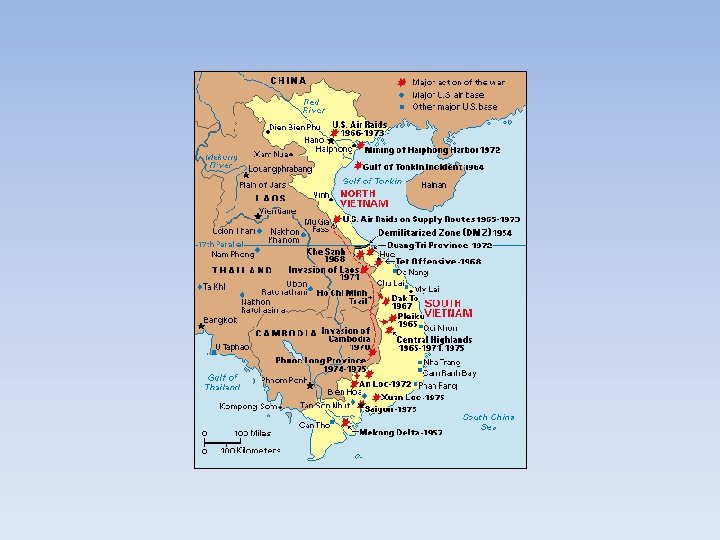
 Mental Issues • Sinking Morale • • Guerilla war, bad conditions, not winning, death All made soldiers very upset Drugs became very popular POW Camps • Issues at Home • Living Room War—combat footage appeared on the nightly news, showed the reality of the war. • Led to people questioning whether our government was telling the truth • Also led to more people opposing the war in America
Mental Issues • Sinking Morale • • Guerilla war, bad conditions, not winning, death All made soldiers very upset Drugs became very popular POW Camps • Issues at Home • Living Room War—combat footage appeared on the nightly news, showed the reality of the war. • Led to people questioning whether our government was telling the truth • Also led to more people opposing the war in America
 War at Home • Draft • All males had to register with their local draft boards • Could get out of service with: doctors note, join the coast guard, go to college, run away • Over 80% of the soldiers in Vietnam were from the lower class • African Americans • Forced into the worst situations, very high number of deaths
War at Home • Draft • All males had to register with their local draft boards • Could get out of service with: doctors note, join the coast guard, go to college, run away • Over 80% of the soldiers in Vietnam were from the lower class • African Americans • Forced into the worst situations, very high number of deaths
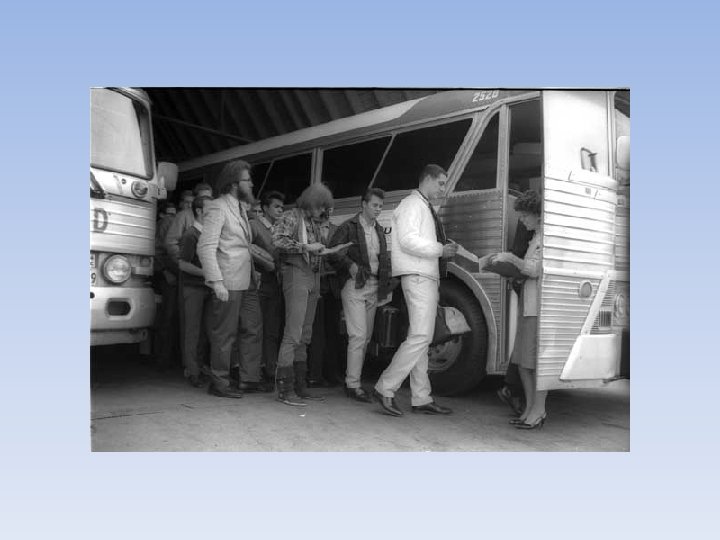


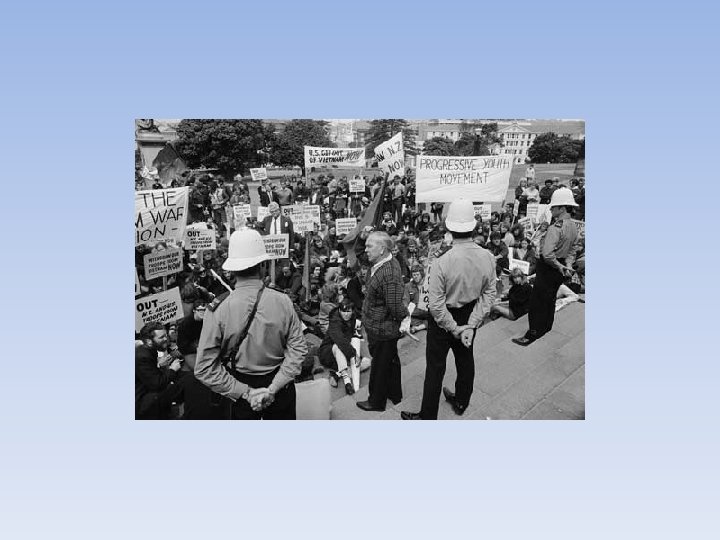
 War at Home • USA Divided • College students formed many groups in opposition to the Vietnam War (SDS, FSM) • Felt that issues in Vietnam were a Civil War, government in S. Vietnam was worse than N. Vietnam, US can’t police the globe, war is bad. • Doves—people that wanted peace, US withdrawal • Hawks—greater military force need to win
War at Home • USA Divided • College students formed many groups in opposition to the Vietnam War (SDS, FSM) • Felt that issues in Vietnam were a Civil War, government in S. Vietnam was worse than N. Vietnam, US can’t police the globe, war is bad. • Doves—people that wanted peace, US withdrawal • Hawks—greater military force need to win
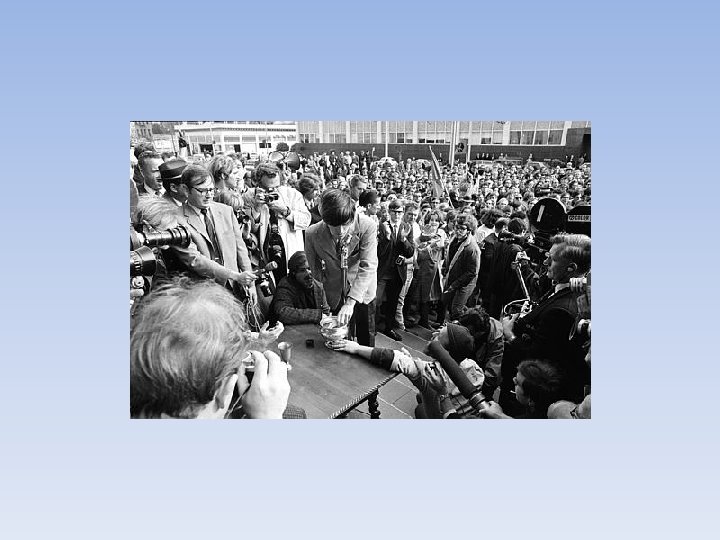



 1968 • Tet Offensive • Surprise attack by the North Vietnamese on over 100 towns in South Vietnam • Lasted for around a month • Military it was a bad move for N. Vietnam (lost almost 10 times as many men) • Psychologically and politically it was a great move by N. Vietnam » Shocked Americans who had been told that N. Vietnam was close to surrendering.
1968 • Tet Offensive • Surprise attack by the North Vietnamese on over 100 towns in South Vietnam • Lasted for around a month • Military it was a bad move for N. Vietnam (lost almost 10 times as many men) • Psychologically and politically it was a great move by N. Vietnam » Shocked Americans who had been told that N. Vietnam was close to surrendering.
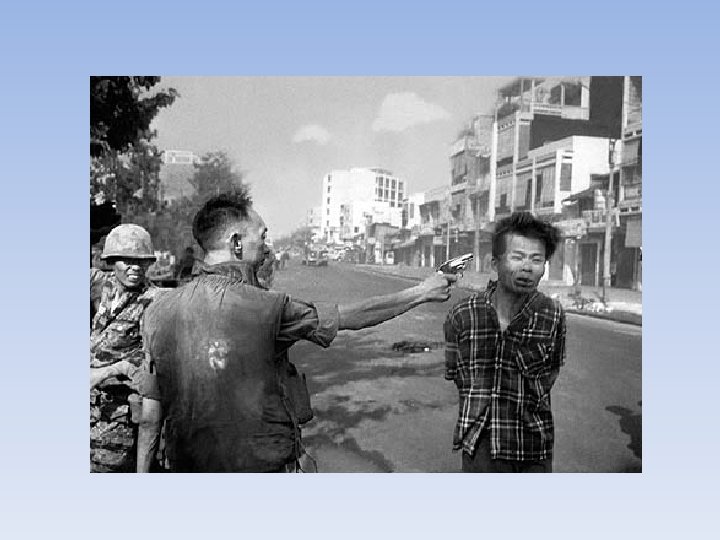

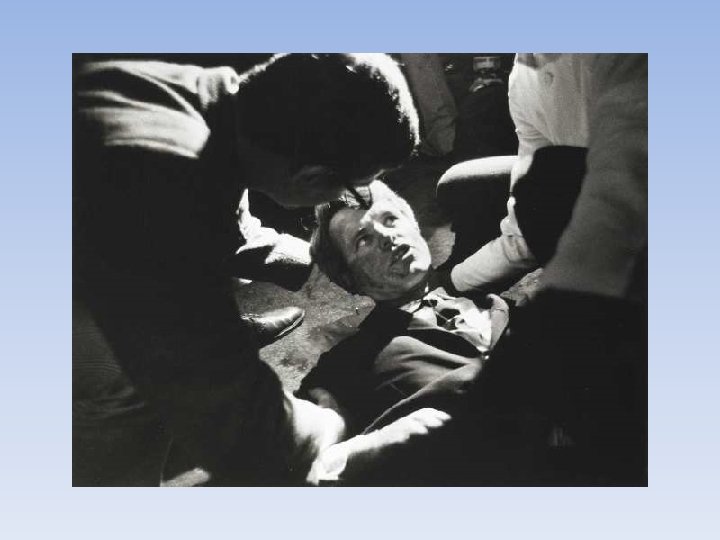
 1968 • Violence in America • Assassinations (MLK JR, Robert F Kennedy) • Riots in Chicago at the Democratic National Convention • New President • Lyndon Johnson chose not to run in 1968 • Richard Nixon won the election (Rep)
1968 • Violence in America • Assassinations (MLK JR, Robert F Kennedy) • Riots in Chicago at the Democratic National Convention • New President • Lyndon Johnson chose not to run in 1968 • Richard Nixon won the election (Rep)
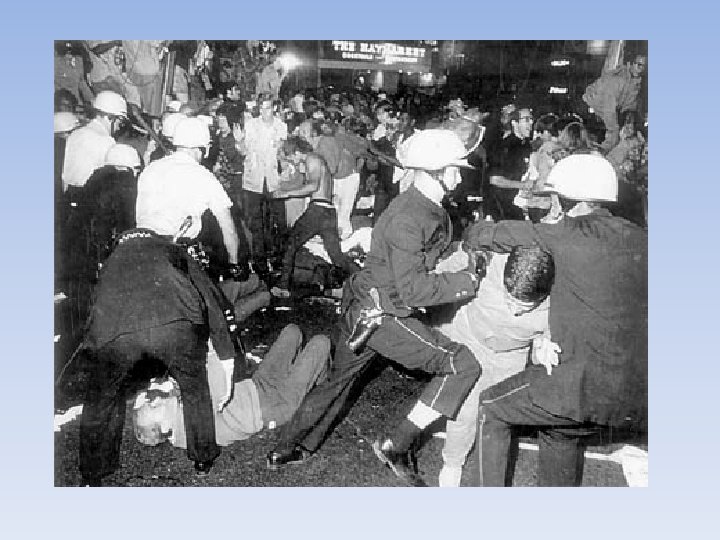


 The End of the War • Richard Nixon • Told reporters that they would get troops out of Vietnam • Negotiations for a withdrawal went nowhere • Henry Kissinger • National Security Advisor • Vietnamization—gradual withdrawal of troops from South Vietnam (let them rule themselves) • Within 3 years, number of troops went from 500, 000 to under 25, 000 • Nixon did order a massive bombing campaign on North Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia
The End of the War • Richard Nixon • Told reporters that they would get troops out of Vietnam • Negotiations for a withdrawal went nowhere • Henry Kissinger • National Security Advisor • Vietnamization—gradual withdrawal of troops from South Vietnam (let them rule themselves) • Within 3 years, number of troops went from 500, 000 to under 25, 000 • Nixon did order a massive bombing campaign on North Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia
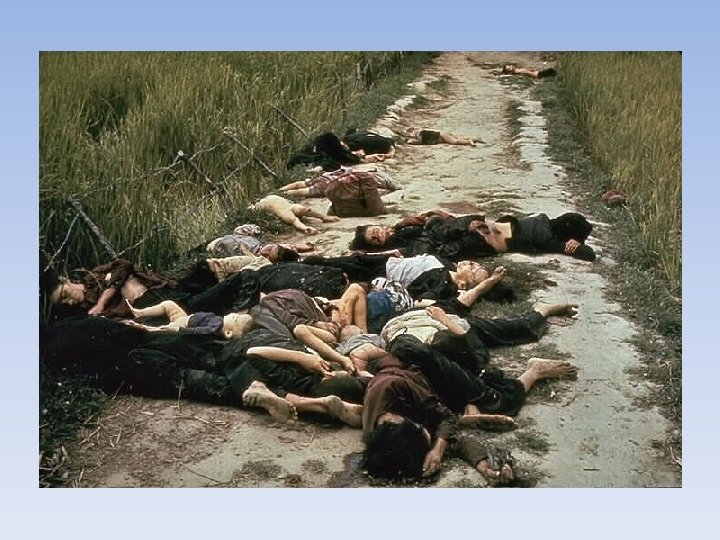
 Troubles with Withdrawal • My Lai Massacre • Massacre of an entire village by US troops in 1968 • Calley (leader) was convicted and imprisoned • Country was SHOCKED • Invasion of Cambodia • US invaded Cambodia in 1970 • Done to try to ruin the Ho Chi Minh Trail • Lots of protest within America (colleges)
Troubles with Withdrawal • My Lai Massacre • Massacre of an entire village by US troops in 1968 • Calley (leader) was convicted and imprisoned • Country was SHOCKED • Invasion of Cambodia • US invaded Cambodia in 1970 • Done to try to ruin the Ho Chi Minh Trail • Lots of protest within America (colleges)


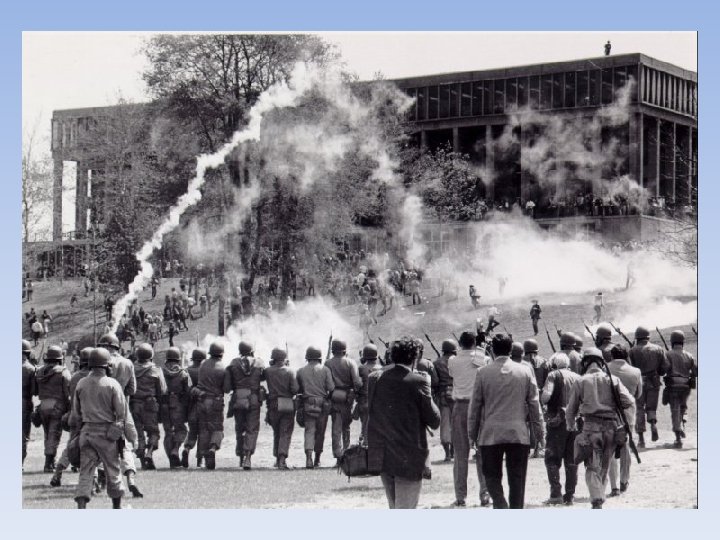
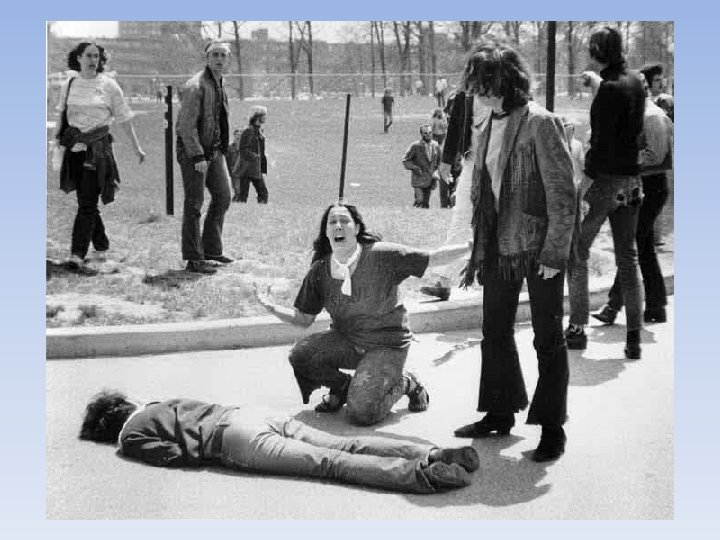
 Other Problems • Kent State Massacre • • Massive student protest over invasion of Cambodia National Guard came in to stop the protest National Guard shot at the crowd, killed 4, injured 9 Same thing happened at Jackson State College • US Actions • US continued to bomb N. Vietnam • Stalemate
Other Problems • Kent State Massacre • • Massive student protest over invasion of Cambodia National Guard came in to stop the protest National Guard shot at the crowd, killed 4, injured 9 Same thing happened at Jackson State College • US Actions • US continued to bomb N. Vietnam • Stalemate


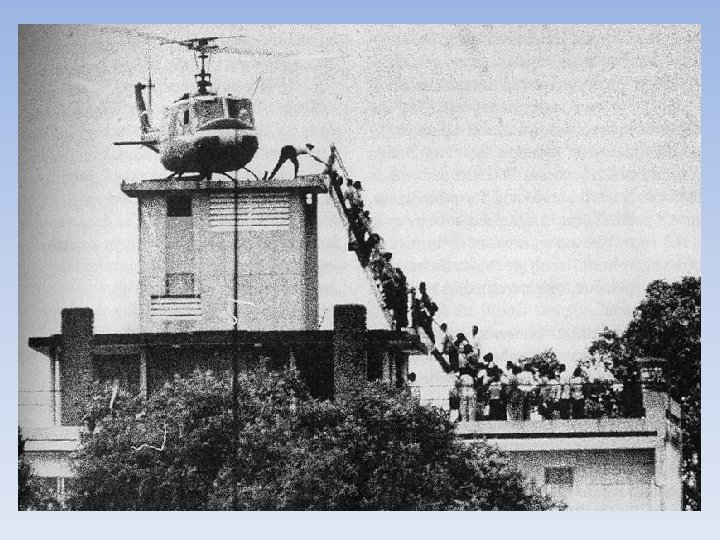
 End of the War • Final Push • Negations between N. Vietnam, S. Vietnam and USA were going nowhere. • Christmas Bombings—USA dropped over 100, 000 for 11 days straight on N. Vietnam • The USSR finally stepped in and negotiated a peace between the countries. • US troops left Vietnam on March 29, 1973, two years later North Vietnamese Troops invaded and took control of South Vietnam. (Saigon) • Communist took over, imprisoned over 400, 000, over 1. 5 million left Vietnam • Cambodia went into a Civil War (1 million dead)
End of the War • Final Push • Negations between N. Vietnam, S. Vietnam and USA were going nowhere. • Christmas Bombings—USA dropped over 100, 000 for 11 days straight on N. Vietnam • The USSR finally stepped in and negotiated a peace between the countries. • US troops left Vietnam on March 29, 1973, two years later North Vietnamese Troops invaded and took control of South Vietnam. (Saigon) • Communist took over, imprisoned over 400, 000, over 1. 5 million left Vietnam • Cambodia went into a Civil War (1 million dead)


 End Results • Death/Injury Toll • 58, 000 Americans died • 303, 000 Americans wounded • USA • • • Soldiers did not receive a warm welcome on return home 15% of soldiers suffered from PTSD Thousands committed suicide Drug Abuse New way of thinking concerning war and government
End Results • Death/Injury Toll • 58, 000 Americans died • 303, 000 Americans wounded • USA • • • Soldiers did not receive a warm welcome on return home 15% of soldiers suffered from PTSD Thousands committed suicide Drug Abuse New way of thinking concerning war and government


