a50fa1753f4ec63209073b930de6cc18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 American Foreign Policy: 1930 -1941
American Foreign Policy: 1930 -1941
 FDR Recognizes the Soviet Union (late 1933) 5 FDR - bolster the US against Japan. 5 Trade w/ USSRhelp economy during the Depression.
FDR Recognizes the Soviet Union (late 1933) 5 FDR - bolster the US against Japan. 5 Trade w/ USSRhelp economy during the Depression.
 Stalin- USSR - Communism Stalin - Mini. Bio
Stalin- USSR - Communism Stalin - Mini. Bio
 Gulag
Gulag
 Hyper-Inflation in Germany: 1923
Hyper-Inflation in Germany: 1923
 Mussolini - Italy Fascism- nation over the individual, dictatorship w/ an emphasis on a strong military mini-bio
Mussolini - Italy Fascism- nation over the individual, dictatorship w/ an emphasis on a strong military mini-bio
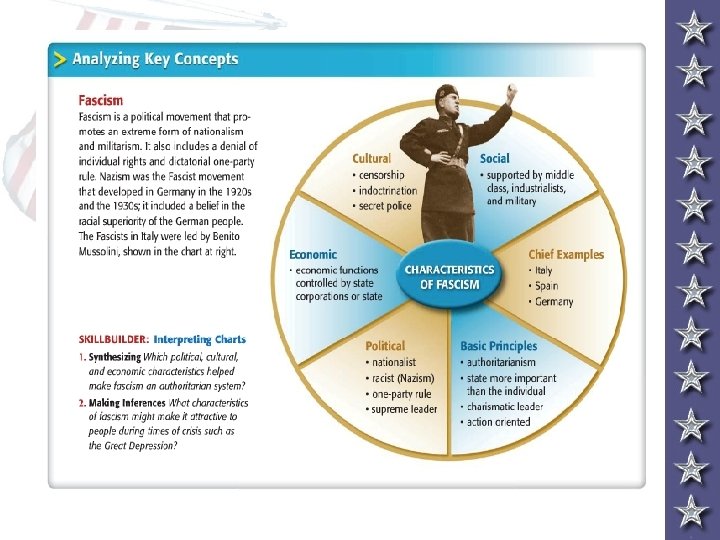
 Adolf Hitler - Germany mini-bio Mein Kampf, Nazi, Economy
Adolf Hitler - Germany mini-bio Mein Kampf, Nazi, Economy
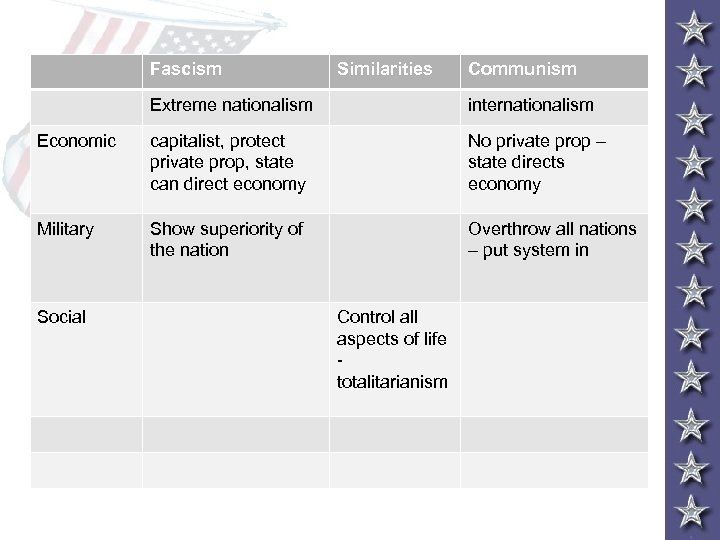 Fascism Similarities Communism Extreme nationalism internationalism Economic capitalist, protect private prop, state can direct economy No private prop – state directs economy Military Show superiority of the nation Overthrow all nations – put system in Social Control all aspects of life totalitarianism
Fascism Similarities Communism Extreme nationalism internationalism Economic capitalist, protect private prop, state can direct economy No private prop – state directs economy Military Show superiority of the nation Overthrow all nations – put system in Social Control all aspects of life totalitarianism
![Fascist Aggression 5 1935: Hitler denounced the Versailles Treaty & League of Nations [re-arming!] Fascist Aggression 5 1935: Hitler denounced the Versailles Treaty & League of Nations [re-arming!]](https://present5.com/presentation/a50fa1753f4ec63209073b930de6cc18/image-10.jpg) Fascist Aggression 5 1935: Hitler denounced the Versailles Treaty & League of Nations [re-arming!] Mussolini attacks Ethiopia. 5 1936: German troops sent into the Rhineland. Fascist forces sent to fight with Franco in Spain. 5 1938: Austrian Anschluss. Rome-Berlin Tokyo Pact [AXIS] Munich Agreement APPEASEMENT! 5 Sudetenland 5 Neville Chamberlain 5
Fascist Aggression 5 1935: Hitler denounced the Versailles Treaty & League of Nations [re-arming!] Mussolini attacks Ethiopia. 5 1936: German troops sent into the Rhineland. Fascist forces sent to fight with Franco in Spain. 5 1938: Austrian Anschluss. Rome-Berlin Tokyo Pact [AXIS] Munich Agreement APPEASEMENT! 5 Sudetenland 5 Neville Chamberlain 5
 So much aggression it takes 2 slides 5 1939: German troops march into the rest of Czechoslovakia. - Hitler-Stalin Non-Aggression Pact. 5 September 1, 1939: German troops march into begins Poland blitzkrieg WW II
So much aggression it takes 2 slides 5 1939: German troops march into the rest of Czechoslovakia. - Hitler-Stalin Non-Aggression Pact. 5 September 1, 1939: German troops march into begins Poland blitzkrieg WW II
 Blitzkrieg 5 check it out
Blitzkrieg 5 check it out
 The appeasement of Hitler continued with the Munich Pact. Britain and France sacrificed the Sudetenland to Germany in return for peace. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and Hitler in Munich But peace was not to come.
The appeasement of Hitler continued with the Munich Pact. Britain and France sacrificed the Sudetenland to Germany in return for peace. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and Hitler in Munich But peace was not to come.
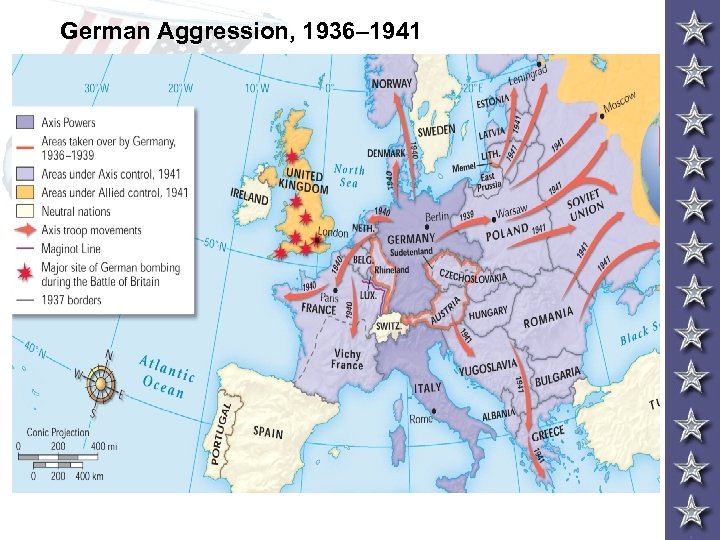 German Aggression, 1936– 1941
German Aggression, 1936– 1941
 Nye Committee Hearings (1934 -1936) 5 The Nye Committee I investigated the charge that WW I was needless and the US entered so munitions owners could make big profits [“merchants of death. ”] 5 The Committee did charge Senator Gerald P. Nye [R-ND] that bankers wanted war to protect their loans & arms manufacturers to make money. 5 Claimed that Wilson had provoked Germany by sailing in to warring nations’ waters. 5 Resulted in Congress passing several Neutrality Acts.
Nye Committee Hearings (1934 -1936) 5 The Nye Committee I investigated the charge that WW I was needless and the US entered so munitions owners could make big profits [“merchants of death. ”] 5 The Committee did charge Senator Gerald P. Nye [R-ND] that bankers wanted war to protect their loans & arms manufacturers to make money. 5 Claimed that Wilson had provoked Germany by sailing in to warring nations’ waters. 5 Resulted in Congress passing several Neutrality Acts.
 FDR’s “I hate war” Speech (1936)
FDR’s “I hate war” Speech (1936)
 Neutrality Acts: 1935, 1936, 1937 5 Learn lessons from WWI § no sales of arms to belligerent nations. § no loans/credits to belligerent nations. § Forbade US cit. to travel on ships of nations at war § “cash-and-carry” pay in cash, pick it up § Banned involvement in the Spanish Civil War. 5 limited the options of the POTUS in a crisis. 5 US declined to build up its forces!
Neutrality Acts: 1935, 1936, 1937 5 Learn lessons from WWI § no sales of arms to belligerent nations. § no loans/credits to belligerent nations. § Forbade US cit. to travel on ships of nations at war § “cash-and-carry” pay in cash, pick it up § Banned involvement in the Spanish Civil War. 5 limited the options of the POTUS in a crisis. 5 US declined to build up its forces!
 US Neutrality
US Neutrality
 Franco – Spain – Fascism
Franco – Spain – Fascism

 Spanish Civil War (1936 -1939) The American “Lincoln Brigade”
Spanish Civil War (1936 -1939) The American “Lincoln Brigade”
 1939 Neutrality Act 5 Germany’s invasion of Poland. 5 aids European democracies in a limited way 5 Results of the 1939 Neutrality Act: § Aggressors could not send ships to buy US munitions. § The US economy improves 5 America becomes the “Arsenal of Democracy”
1939 Neutrality Act 5 Germany’s invasion of Poland. 5 aids European democracies in a limited way 5 Results of the 1939 Neutrality Act: § Aggressors could not send ships to buy US munitions. § The US economy improves 5 America becomes the “Arsenal of Democracy”
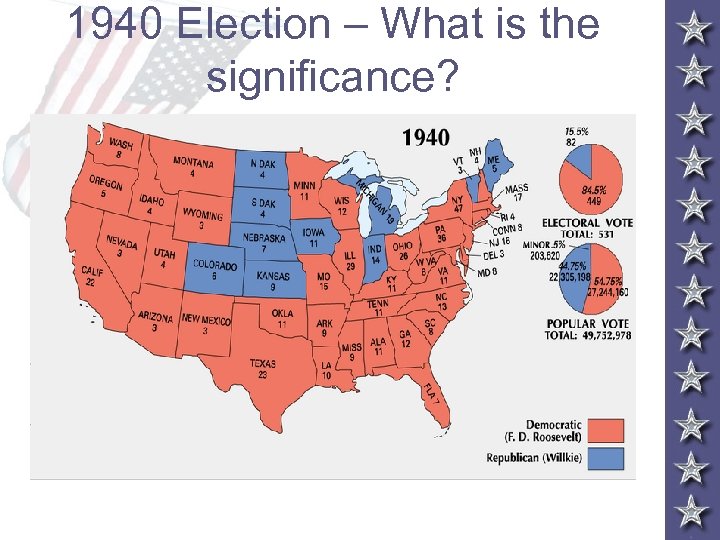 1940 Election – What is the significance?
1940 Election – What is the significance?
 Unneutral Neutrality 5 Selective Service Act § 1 st peacetime draft in US History 5 Destroyers for Bases Agreement § US Destroyers => GB § GB Bases => US
Unneutral Neutrality 5 Selective Service Act § 1 st peacetime draft in US History 5 Destroyers for Bases Agreement § US Destroyers => GB § GB Bases => US
 “America First” Committee Charles Lindbergh
“America First” Committee Charles Lindbergh
 “Lend-Lease” Act (1941) – sell/lend war supplies to any country that was vital to safety of US Great Britain. . . $31 billion Soviet Union. . . . $11 billion France. . . . . $ 3 billion China. . . . . $1. 5 billion Other European. . . . $500 million South America. . . . . $400 million The amount totaled: $48, 601, 365, 000
“Lend-Lease” Act (1941) – sell/lend war supplies to any country that was vital to safety of US Great Britain. . . $31 billion Soviet Union. . . . $11 billion France. . . . . $ 3 billion China. . . . . $1. 5 billion Other European. . . . $500 million South America. . . . . $400 million The amount totaled: $48, 601, 365, 000
 Winston Churchill - GB Mini-bio
Winston Churchill - GB Mini-bio
 Quotes of Winnie I may be drunk, Miss, but in the morning I will be sober and you will still be ugly. ” Lady Astor: “Winston, if I were your wife I’d put poison in your coffee. ” Winston Churchill: “Nancy, if I were your husband I’d drink it. ” Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few
Quotes of Winnie I may be drunk, Miss, but in the morning I will be sober and you will still be ugly. ” Lady Astor: “Winston, if I were your wife I’d put poison in your coffee. ” Winston Churchill: “Nancy, if I were your husband I’d drink it. ” Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few
 Atlantic Charter 5 5 5 1. not pursue terr. Expansion 2. right to choose own gov’t 3. international trade 4. to raw materials 5. be disarmed 6. rid the world of fear & poverty 5 BASIS FOR THE UNITED NATIONS
Atlantic Charter 5 5 5 1. not pursue terr. Expansion 2. right to choose own gov’t 3. international trade 4. to raw materials 5. be disarmed 6. rid the world of fear & poverty 5 BASIS FOR THE UNITED NATIONS

 Roosevelt’s Four Freedoms Speech He highlighted four freedoms precious to Americans. • freedom of speech • freedom of worship • freedom from want • freedom from fear All of these freedoms, he argued, were threatened by German and Japanese militarism.
Roosevelt’s Four Freedoms Speech He highlighted four freedoms precious to Americans. • freedom of speech • freedom of worship • freedom from want • freedom from fear All of these freedoms, he argued, were threatened by German and Japanese militarism.
 Hitler’s Biggest Mistake – Invasion of Russia
Hitler’s Biggest Mistake – Invasion of Russia
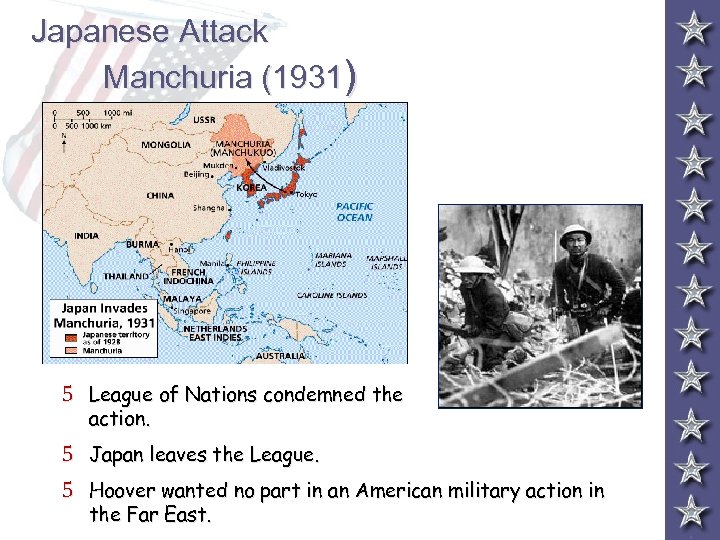 Japanese Attack Manchuria (1931) 5 League of Nations condemned the action. 5 Japan leaves the League. 5 Hoover wanted no part in an American military action in the Far East.
Japanese Attack Manchuria (1931) 5 League of Nations condemned the action. 5 Japan leaves the League. 5 Hoover wanted no part in an American military action in the Far East.
 Prime Minister Tojo
Prime Minister Tojo
 Emperor Hirohito
Emperor Hirohito
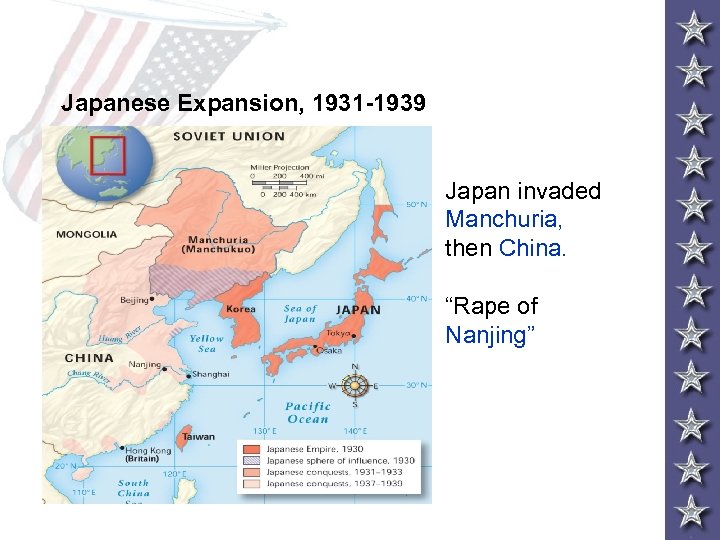 Japanese Expansion, 1931 -1939 Japan invaded Manchuria, then China. “Rape of Nanjing”
Japanese Expansion, 1931 -1939 Japan invaded Manchuria, then China. “Rape of Nanjing”
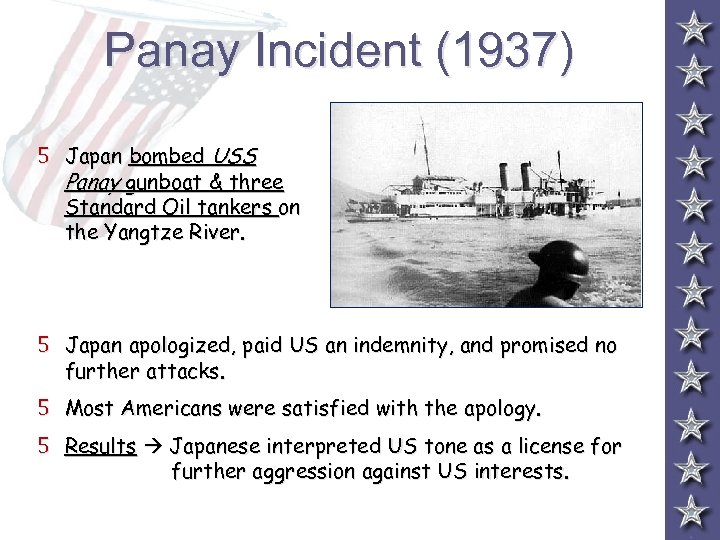 Panay Incident (1937) 5 Japan bombed USS Panay gunboat & three Standard Oil tankers on the Yangtze River. 5 Japan apologized, paid US an indemnity, and promised no further attacks. 5 Most Americans were satisfied with the apology. 5 Results Japanese interpreted US tone as a license for further aggression against US interests.
Panay Incident (1937) 5 Japan bombed USS Panay gunboat & three Standard Oil tankers on the Yangtze River. 5 Japan apologized, paid US an indemnity, and promised no further attacks. 5 Most Americans were satisfied with the apology. 5 Results Japanese interpreted US tone as a license for further aggression against US interests.
 French Indochina - 1941 5 FDR – froze all Japanese assets in US 5 Embargo § Gas § Machine tools § Scrap iron § steel
French Indochina - 1941 5 FDR – froze all Japanese assets in US 5 Embargo § Gas § Machine tools § Scrap iron § steel


