5cb75b47421044088caad3c0bb13c3ac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 American Culture Chapter 1: Understanding the Culture of the United States
American Culture Chapter 1: Understanding the Culture of the United States
 Life in the United States l Some questions about America are easy to answer, for example: – – What is life like in America? What kind of houses do Americans live in? What kind of food do Americans eat? What are American customs?
Life in the United States l Some questions about America are easy to answer, for example: – – What is life like in America? What kind of houses do Americans live in? What kind of food do Americans eat? What are American customs?
 Life in the United States l Questions that are harder to answer are: – – What do Americans believe in? What do Americans value most? What motivates Americans? Why do Americans behave the way they do?
Life in the United States l Questions that are harder to answer are: – – What do Americans believe in? What do Americans value most? What motivates Americans? Why do Americans behave the way they do?
 Life in the United States l 1. 2. l Two important facts about America: America is VERY large America has great ethnic diversity (people from many different places) These two facts can help you understand American culture
Life in the United States l 1. 2. l Two important facts about America: America is VERY large America has great ethnic diversity (people from many different places) These two facts can help you understand American culture
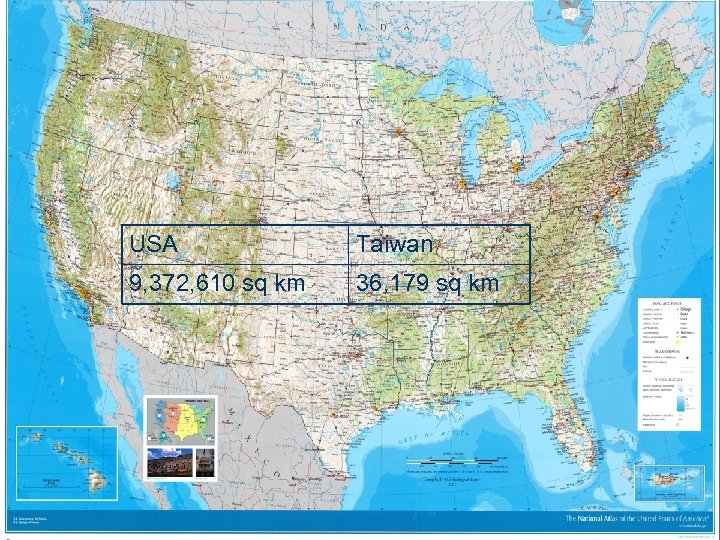 USA Taiwan 9, 372, 610 sq km 36, 179 sq km
USA Taiwan 9, 372, 610 sq km 36, 179 sq km
 Life in the United States l l Ethnic Diversity is probably the most important factor influencing American Life All Americans, except Natives, came from foreign countries. Early settlers came from Spain Later settlers came from Northern Europe – becoming the dominant culture
Life in the United States l l Ethnic Diversity is probably the most important factor influencing American Life All Americans, except Natives, came from foreign countries. Early settlers came from Spain Later settlers came from Northern Europe – becoming the dominant culture
 A Nation of Immigrants l Over time, immigrants came from many different countries including: – – – l China Japan Central, Eastern, Southern Europe Gradually, they became part of the dominant American culture
A Nation of Immigrants l Over time, immigrants came from many different countries including: – – – l China Japan Central, Eastern, Southern Europe Gradually, they became part of the dominant American culture
 A Nation of Immigrants l The diversity of immigrants was written about in plays: America is God’s Crucible, the great Melting. Pot where all the races of Europe are melting and re-forming…. Germans and Frenchmen, Irishmen and Englishmen, Jews and Russians – into the Crucible with you all! God is making the American! - Israel Zangwill 1908
A Nation of Immigrants l The diversity of immigrants was written about in plays: America is God’s Crucible, the great Melting. Pot where all the races of Europe are melting and re-forming…. Germans and Frenchmen, Irishmen and Englishmen, Jews and Russians – into the Crucible with you all! God is making the American! - Israel Zangwill 1908
 A Nation of Immigrants l l l The term “Melting Pot” is used to describe the mixing of different races and cultures in America Despite this, the dominant culture (of Northern Europe) has survived. However, it has been altered by new immigrants settling in America
A Nation of Immigrants l l l The term “Melting Pot” is used to describe the mixing of different races and cultures in America Despite this, the dominant culture (of Northern Europe) has survived. However, it has been altered by new immigrants settling in America
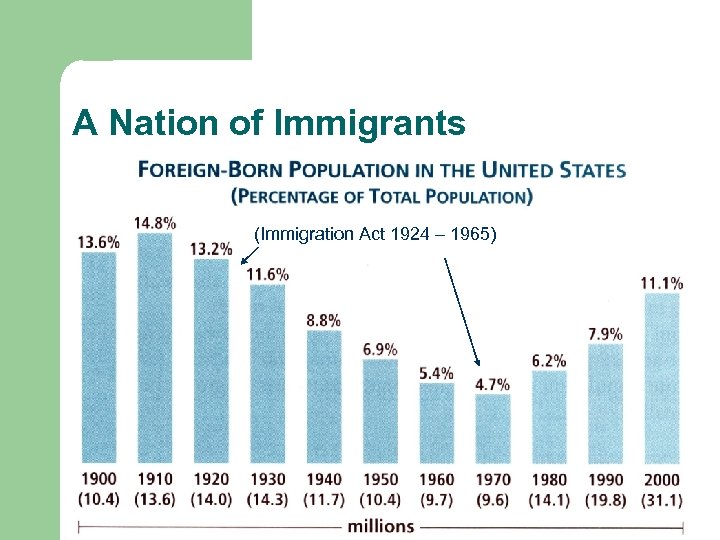 A Nation of Immigrants (Immigration Act 1924 – 1965)
A Nation of Immigrants (Immigration Act 1924 – 1965)
 A Nation of Immigrants l l The Immigration Act of 1924 put a quota on the number of immigrants that could come from each country – it favoured people from Northern and Western Europe This system was used until 1965, when immigration began to rise again (including illegal immigration)
A Nation of Immigrants l l The Immigration Act of 1924 put a quota on the number of immigrants that could come from each country – it favoured people from Northern and Western Europe This system was used until 1965, when immigration began to rise again (including illegal immigration)
 A Nation of Immigrants l l l Today, fewer immigrants are coming from Europe. The descendants of early Eurpeans settlers have inter-married with other cultures They no longer identify with their “home” country
A Nation of Immigrants l l l Today, fewer immigrants are coming from Europe. The descendants of early Eurpeans settlers have inter-married with other cultures They no longer identify with their “home” country
 A Nation of Immigrants l l l Most new immigrants are from Latin America (South & Central America) These “Hispanics” have settled mainly in the South and West of America Many of these people speak Spanish as a first language
A Nation of Immigrants l l l Most new immigrants are from Latin America (South & Central America) These “Hispanics” have settled mainly in the South and West of America Many of these people speak Spanish as a first language
 A Nation of Immigrants
A Nation of Immigrants
 Cultural Pluralism in the U. S. l l l “Cultural Pluralism” is the principle that different cultures can live together peacefully This means that immigrants keep their own culture, but are still considered “American” Cultural pluralism is more accepted today than it was in the past (e. g. multi-lingual exams, the census, etc)
Cultural Pluralism in the U. S. l l l “Cultural Pluralism” is the principle that different cultures can live together peacefully This means that immigrants keep their own culture, but are still considered “American” Cultural pluralism is more accepted today than it was in the past (e. g. multi-lingual exams, the census, etc)
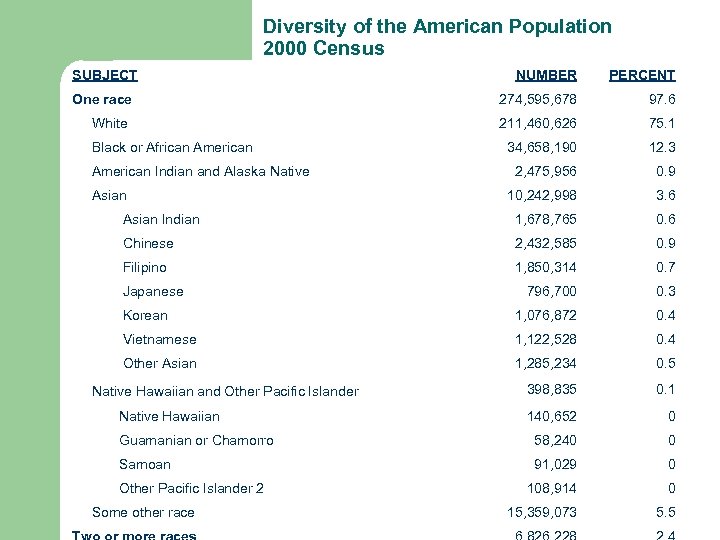 Diversity of the American Population 2000 Census SUBJECT NUMBER PERCENT 274, 595, 678 97. 6 211, 460, 626 75. 1 34, 658, 190 12. 3 2, 475, 956 0. 9 10, 242, 998 3. 6 Asian Indian 1, 678, 765 0. 6 Chinese 2, 432, 585 0. 9 Filipino 1, 850, 314 0. 7 796, 700 0. 3 Korean 1, 076, 872 0. 4 Vietnamese 1, 122, 528 0. 4 Other Asian 1, 285, 234 0. 5 398, 835 0. 1 140, 652 0 Guamanian or Chamorro 58, 240 0 Samoan 91, 029 0 108, 914 0 15, 359, 073 5. 5 One race White Black or African American Indian and Alaska Native Asian Japanese Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander Native Hawaiian Other Pacific Islander 2 Some other race
Diversity of the American Population 2000 Census SUBJECT NUMBER PERCENT 274, 595, 678 97. 6 211, 460, 626 75. 1 34, 658, 190 12. 3 2, 475, 956 0. 9 10, 242, 998 3. 6 Asian Indian 1, 678, 765 0. 6 Chinese 2, 432, 585 0. 9 Filipino 1, 850, 314 0. 7 796, 700 0. 3 Korean 1, 076, 872 0. 4 Vietnamese 1, 122, 528 0. 4 Other Asian 1, 285, 234 0. 5 398, 835 0. 1 140, 652 0 Guamanian or Chamorro 58, 240 0 Samoan 91, 029 0 108, 914 0 15, 359, 073 5. 5 One race White Black or African American Indian and Alaska Native Asian Japanese Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander Native Hawaiian Other Pacific Islander 2 Some other race
 Cultural Pluralism in the U. S. l l Even though many Americans maintain their ethnic heritage, the number of interracial marriages is increasing. “The Tiger Woods” effect: – – Caucasian (white) Black Indian Asian
Cultural Pluralism in the U. S. l l Even though many Americans maintain their ethnic heritage, the number of interracial marriages is increasing. “The Tiger Woods” effect: – – Caucasian (white) Black Indian Asian
 Cultural Pluralism in the U. S. l Many ethnic groups are sensitive about what they should be called: Black Indian Hispanic African-American Native American / American Indian Latino
Cultural Pluralism in the U. S. l Many ethnic groups are sensitive about what they should be called: Black Indian Hispanic African-American Native American / American Indian Latino


