cf032c6056a09e535382425b31f9feda.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 American College of Surgeons Dedicated to improving the care of the surgical patient and to safeguarding standards of care in an optimal and ethical practice environment
American College of Surgeons Dedicated to improving the care of the surgical patient and to safeguarding standards of care in an optimal and ethical practice environment
 What NSQIP Is _______________ § Web-Based data collection software § Quality improvement tool § Risk-adjusted, outcomes-based data § Clinically Validated data § Benchmarking
What NSQIP Is _______________ § Web-Based data collection software § Quality improvement tool § Risk-adjusted, outcomes-based data § Clinically Validated data § Benchmarking
 Current Participants _______________ Number of Participating Sites by State and Region (273) CANADA 4 October 31, 2010 3 MIDWEST 78 4 3 8 6 1 5 1 34 2 2 33 2 5 6 4 5 2 10 2 1 1 WEST 57 10 4 2 SOUTH 65 2 NORTHEAST 67 ABU DHABI 1 LEBANON 1 6 1 2 8 10 3 4 6 9 13 3 20 22
Current Participants _______________ Number of Participating Sites by State and Region (273) CANADA 4 October 31, 2010 3 MIDWEST 78 4 3 8 6 1 5 1 34 2 2 33 2 5 6 4 5 2 10 2 1 1 WEST 57 10 4 2 SOUTH 65 2 NORTHEAST 67 ABU DHABI 1 LEBANON 1 6 1 2 8 10 3 4 6 9 13 3 20 22
 Product Features _______________ § § § § § Clinically Rich Data Web-Based Workstation Private & Secure Data Encryption Semi Annual Reports & Other Real-Time Reports Online Return of Investment (ROI) Calculator Best Practices (Expert panel rated guidelines) Case Studies Online Risk Calculator Participant Use File (PUF)
Product Features _______________ § § § § § Clinically Rich Data Web-Based Workstation Private & Secure Data Encryption Semi Annual Reports & Other Real-Time Reports Online Return of Investment (ROI) Calculator Best Practices (Expert panel rated guidelines) Case Studies Online Risk Calculator Participant Use File (PUF)
 Program Staffing _______________ § Surgeon Champion (SC) § Program Mentor/Advocate § Lead Quality Improvement Initiatives § Participate in Monthly SC Conference Calls § Surgical Clinical Reviewer (SCR) § Collect Data § Online/On-going training; CEU’s & Certification - provided by the ACS
Program Staffing _______________ § Surgeon Champion (SC) § Program Mentor/Advocate § Lead Quality Improvement Initiatives § Participate in Monthly SC Conference Calls § Surgical Clinical Reviewer (SCR) § Collect Data § Online/On-going training; CEU’s & Certification - provided by the ACS
 Data Collection _______________ § Demographics § Surgical Profile § Pre-operative Data (risk factors) § Intra-operative Data § Post operative Data (outcomes)
Data Collection _______________ § Demographics § Surgical Profile § Pre-operative Data (risk factors) § Intra-operative Data § Post operative Data (outcomes)
 Data Collection _______________ Case Selection § Sampling of all operations requiring § General anesthesia § Spinal anesthesia § Epidural anesthesia § Inpatient and Outpatient Surgical Procedures § excluding trauma and transplant
Data Collection _______________ Case Selection § Sampling of all operations requiring § General anesthesia § Spinal anesthesia § Epidural anesthesia § Inpatient and Outpatient Surgical Procedures § excluding trauma and transplant
 Data Collection _______________ Sampling Methodology § A randomized sampling system called the 8 -day cycle § Process ensures that cases have an equal chance of being selected from each day of the week
Data Collection _______________ Sampling Methodology § A randomized sampling system called the 8 -day cycle § Process ensures that cases have an equal chance of being selected from each day of the week
 Data Collection _______________ Clinical vs. Administrative Data Clinical Data tends to tell us more… NSQIP Admin % Missed by Admin Total Complications 28% 11% 61% SSI 13% 1% 97% Wound Disruption 6% 1% 83% UTI 6% 0% 100% Mortality 3% 3% 0%
Data Collection _______________ Clinical vs. Administrative Data Clinical Data tends to tell us more… NSQIP Admin % Missed by Admin Total Complications 28% 11% 61% SSI 13% 1% 97% Wound Disruption 6% 1% 83% UTI 6% 0% 100% Mortality 3% 3% 0%
 Risk Adjustment _______________ Observed vs. Expected O/E Ratios § O/E ratio = par on a golf course – the score that is expected § An O/E ratio is a mathematical construct accurately showing the risk-adjusted outcome for a specific site § ‘O’ represents the total number of observed postoperative events (deaths or complications) § ‘ E’ represents the number of expected events based on the preoperative risk and other factors in a given patient population § An O/E ratio < 1 means that the site is performing better than expected, while a ratio > 1 indicates an excess of adverse events
Risk Adjustment _______________ Observed vs. Expected O/E Ratios § O/E ratio = par on a golf course – the score that is expected § An O/E ratio is a mathematical construct accurately showing the risk-adjusted outcome for a specific site § ‘O’ represents the total number of observed postoperative events (deaths or complications) § ‘ E’ represents the number of expected events based on the preoperative risk and other factors in a given patient population § An O/E ratio < 1 means that the site is performing better than expected, while a ratio > 1 indicates an excess of adverse events
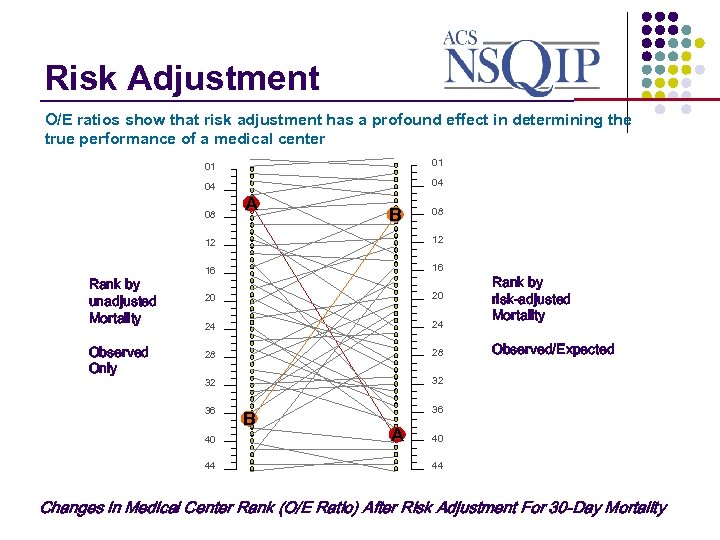 Risk Adjustment _______________ O/E ratios show that risk adjustment has a profound effect in determining the true performance of a medical center 01 01 04 04 08 A B 08 12 Rank by unadjusted Mortality Observed Only 12 16 16 20 20 24 24 28 28 32 32 36 40 44 B Rank by risk-adjusted Mortality Observed/Expected 36 A 40 44 Changes in Medical Center Rank (O/E Ratio) After Risk Adjustment For 30 -Day Mortality
Risk Adjustment _______________ O/E ratios show that risk adjustment has a profound effect in determining the true performance of a medical center 01 01 04 04 08 A B 08 12 Rank by unadjusted Mortality Observed Only 12 16 16 20 20 24 24 28 28 32 32 36 40 44 B Rank by risk-adjusted Mortality Observed/Expected 36 A 40 44 Changes in Medical Center Rank (O/E Ratio) After Risk Adjustment For 30 -Day Mortality
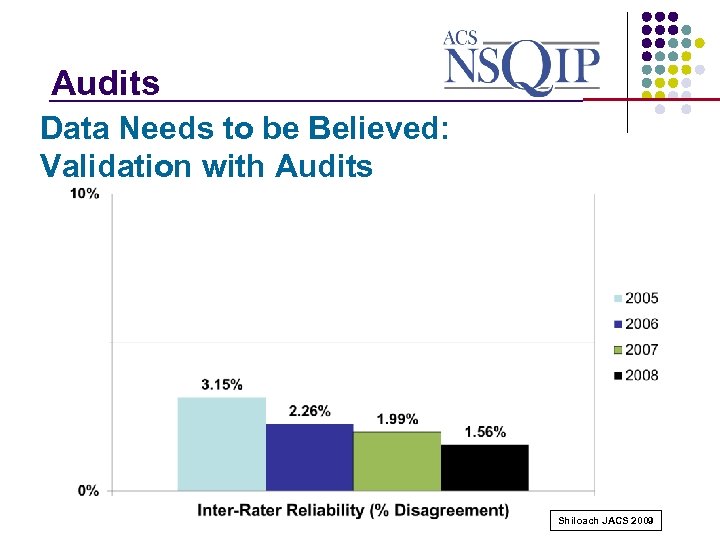 Audits _______________ Data Needs to be Believed: Validation with Audits Shiloach JACS 2009
Audits _______________ Data Needs to be Believed: Validation with Audits Shiloach JACS 2009
 Reporting _______________ Real-Time and Semiannual Reports § Real-time, continuously updated benchmarked online reports § § § Pre-programmed library of reports Real-time data Not risk adjusted Able to benchmark with all or like sites Semiannual benchmarked report § § Risk Adjusted Available 1 st and 3 rd quarters
Reporting _______________ Real-Time and Semiannual Reports § Real-time, continuously updated benchmarked online reports § § § Pre-programmed library of reports Real-time data Not risk adjusted Able to benchmark with all or like sites Semiannual benchmarked report § § Risk Adjusted Available 1 st and 3 rd quarters
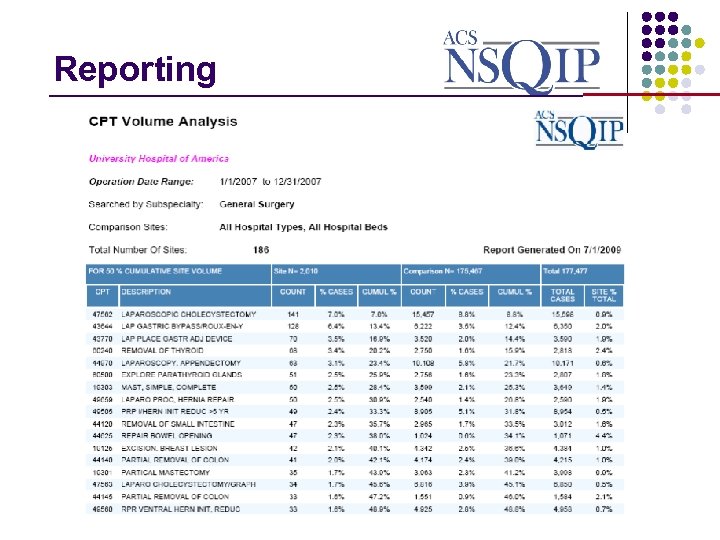
 Reporting _______________ Real-Time Reports § Workflow Reports § Site-Level Reports § Database Statistics § Data Analysis § ACS Reports
Reporting _______________ Real-Time Reports § Workflow Reports § Site-Level Reports § Database Statistics § Data Analysis § ACS Reports
 Reporting _______________
Reporting _______________
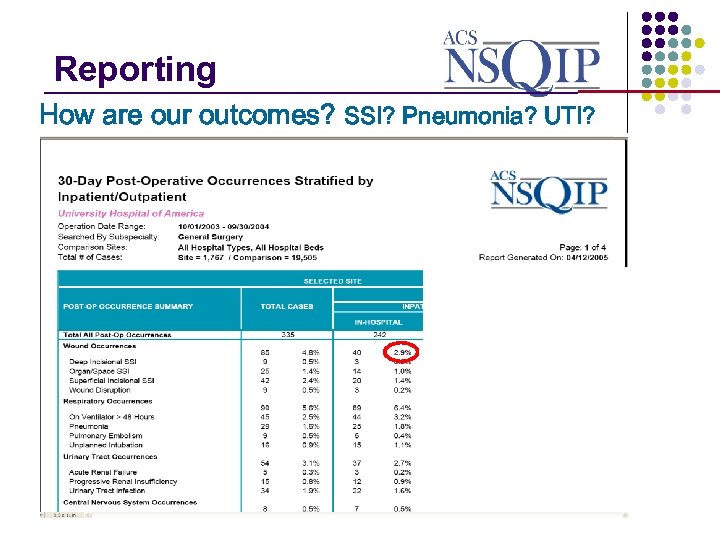
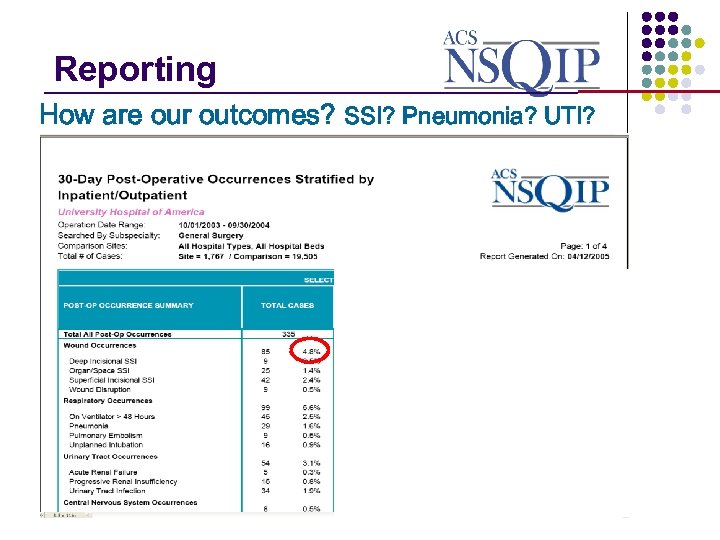 Reporting _______________ How are our outcomes? SSI? Pneumonia? UTI?
Reporting _______________ How are our outcomes? SSI? Pneumonia? UTI?
 Reporting _______________ How are our outcomes? SSI? Pneumonia? UTI?
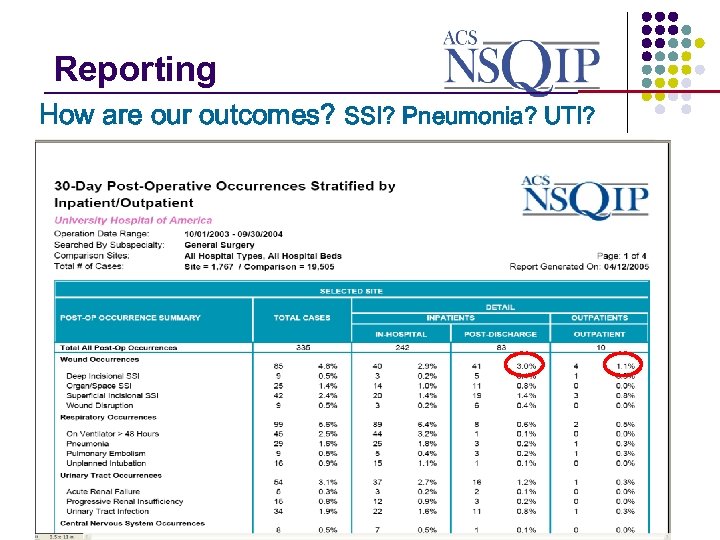
Reporting _______________ How are our outcomes? SSI? Pneumonia? UTI?
 Reporting _______________ How are our outcomes? SSI? Pneumonia? UTI?
Reporting _______________ How are our outcomes? SSI? Pneumonia? UTI?
 Reporting _______________ Further drilling down on the data
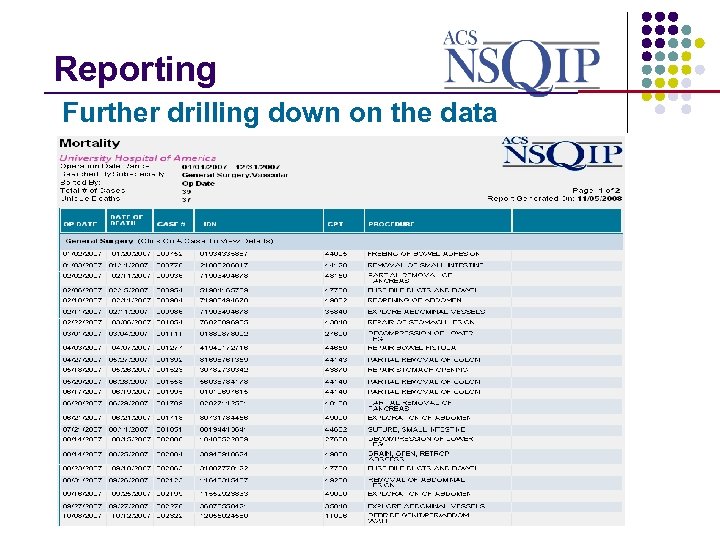
Reporting _______________ Further drilling down on the data
 Reporting _______________ Real Time Analyses i. e, Mortality in Colectomy cases with or without UTI
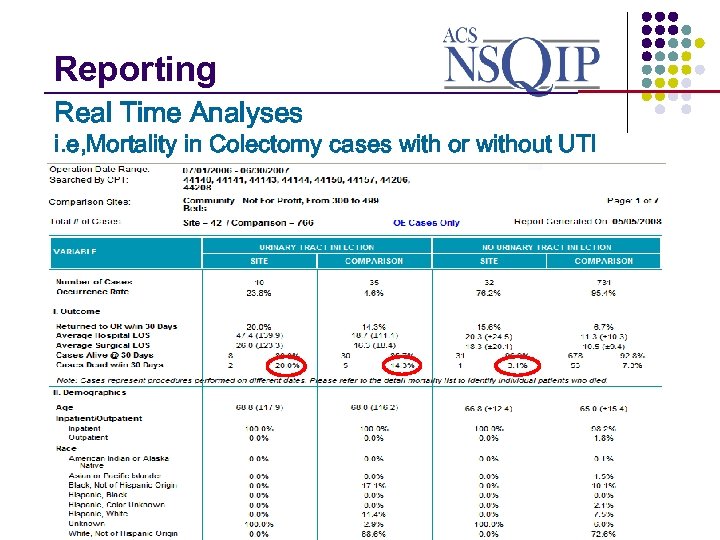
Reporting _______________ Real Time Analyses i. e, Mortality in Colectomy cases with or without UTI
 Reporting _______________ Semiannual Report Risk adjusted for hospital-to-hospital patient mix differences.
Reporting _______________ Semiannual Report Risk adjusted for hospital-to-hospital patient mix differences.
 Reporting _______________ Over 40 Risk Adjusted Outcomes § § § 30 -Day Mortality & Morbidity/ Serious Morbidity O/E Ratios in All Patients 30 -Day Morbidity/Serious Morbidity O/E Ratios in patients >65 Cardiac Occurrences Pneumonia Unplanned Intubation Ventilator Dependence >48 hours DVT/PE Renal Failure Urinary Tract Infection/UTI O/E Ratios Surgical Site Infection/Deep & Organ Space O/E Ratios Colorectal 30 -Day Death or Serious Morbidity O/E Ratios
Reporting _______________ Over 40 Risk Adjusted Outcomes § § § 30 -Day Mortality & Morbidity/ Serious Morbidity O/E Ratios in All Patients 30 -Day Morbidity/Serious Morbidity O/E Ratios in patients >65 Cardiac Occurrences Pneumonia Unplanned Intubation Ventilator Dependence >48 hours DVT/PE Renal Failure Urinary Tract Infection/UTI O/E Ratios Surgical Site Infection/Deep & Organ Space O/E Ratios Colorectal 30 -Day Death or Serious Morbidity O/E Ratios
 Interpretation of Results Reporting _______________ Observed to Expected (O/E) Ratio Represents the hospital’s outcomes compared to the other ACS NSQIP hospitals, adjusted for inter-hospital differences in patients’ characteristics, comorbidities, and preoperative laboratory values LOW OUTLIER: If the upper bound of the O/E confidence interval is <1. 0, the hospital’s outcomes are statistically better than expected. Thus, the hospital’s outcomes are “Exemplary. ” AS EXPECTED ACS NSQIP Hospital ID Number HIGH OUTLIER: If the lower bound of the O/E ratio is >1. 0, the hospital’s outcomes are statistically worse than expected. Thus, the hospital’s outcomes “Need Improvement. ”
Interpretation of Results Reporting _______________ Observed to Expected (O/E) Ratio Represents the hospital’s outcomes compared to the other ACS NSQIP hospitals, adjusted for inter-hospital differences in patients’ characteristics, comorbidities, and preoperative laboratory values LOW OUTLIER: If the upper bound of the O/E confidence interval is <1. 0, the hospital’s outcomes are statistically better than expected. Thus, the hospital’s outcomes are “Exemplary. ” AS EXPECTED ACS NSQIP Hospital ID Number HIGH OUTLIER: If the lower bound of the O/E ratio is >1. 0, the hospital’s outcomes are statistically worse than expected. Thus, the hospital’s outcomes “Need Improvement. ”
 Return on Investment _______________ NSQIP Improves Outcomes and Saves Money
Return on Investment _______________ NSQIP Improves Outcomes and Saves Money
 Return on Investment _______________ Does Surgical Quality Improve using the ACS NSQIP? § § § 82% of NSQIP hospitals had decreased surgical complications 66% of NSQIP hospitals had decreased mortality Each hospital is projected to avoid between 250 -500 complications per year – on average
Return on Investment _______________ Does Surgical Quality Improve using the ACS NSQIP? § § § 82% of NSQIP hospitals had decreased surgical complications 66% of NSQIP hospitals had decreased mortality Each hospital is projected to avoid between 250 -500 complications per year – on average
 Return on Investment _______________ § Example … § If 250 complications are avoided § And each complication costs $10, 000 § The potential savings is $2, 500, 000
Return on Investment _______________ § Example … § If 250 complications are avoided § And each complication costs $10, 000 § The potential savings is $2, 500, 000
 Return on Investment _______________ § § § Beaumont Hospital saved $2. 2 million and reduced average LOS by 6. 5 days by reducing SSI. In 2009, the hospital estimates it prevented nearly 300 SSI’s. Surrey Memorial Hospital reduced SSI’s over 4 years for savings of $2. 54 million Henry Ford Hospital reduced LOS for annual savings of $2 million
Return on Investment _______________ § § § Beaumont Hospital saved $2. 2 million and reduced average LOS by 6. 5 days by reducing SSI. In 2009, the hospital estimates it prevented nearly 300 SSI’s. Surrey Memorial Hospital reduced SSI’s over 4 years for savings of $2. 54 million Henry Ford Hospital reduced LOS for annual savings of $2 million
 Return on Investment _______________ § § Henry Ford Hospital reduced their length of stay by an average of 1. 54 days after reviewing data from all patients who underwent a general, vascular, or colorectal procedure translating into an annual savings of $2 million. Surrey Memorial Hospital avoided an estimated $380, 000 in costs over a four-month period through initiatives to reduce the number of urinary tract infections.
Return on Investment _______________ § § Henry Ford Hospital reduced their length of stay by an average of 1. 54 days after reviewing data from all patients who underwent a general, vascular, or colorectal procedure translating into an annual savings of $2 million. Surrey Memorial Hospital avoided an estimated $380, 000 in costs over a four-month period through initiatives to reduce the number of urinary tract infections.
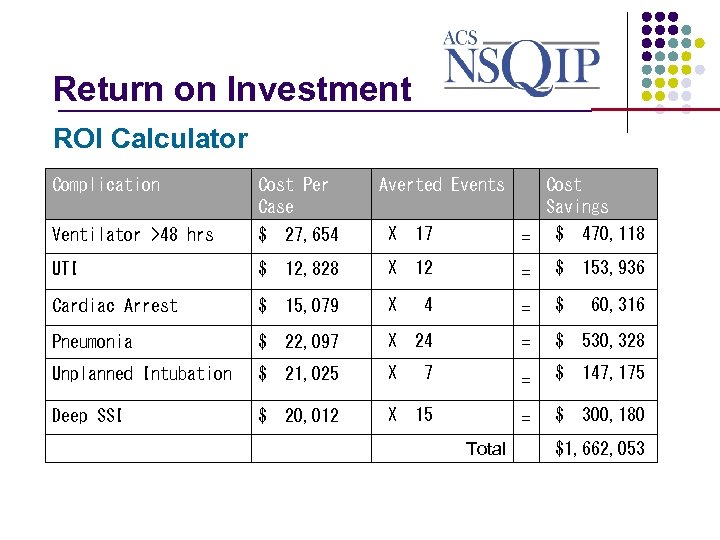 Return on Investment _______________ ROI Calculator Complication Cost Per Case Averted Events Ventilator >48 hrs $ 27, 654 X 17 = $ 470, 118 UTI $ 12, 828 X 12 = $ 153, 936 Cardiac Arrest $ 15, 079 X 4 = $ 60, 316 Pneumonia $ 22, 097 X 24 = $ 530, 328 Unplanned Intubation $ 21, 025 X 7 = $ 147, 175 Deep SSI $ 20, 012 X 15 = $ 300, 180 Total Cost Savings $1, 662, 053
Return on Investment _______________ ROI Calculator Complication Cost Per Case Averted Events Ventilator >48 hrs $ 27, 654 X 17 = $ 470, 118 UTI $ 12, 828 X 12 = $ 153, 936 Cardiac Arrest $ 15, 079 X 4 = $ 60, 316 Pneumonia $ 22, 097 X 24 = $ 530, 328 Unplanned Intubation $ 21, 025 X 7 = $ 147, 175 Deep SSI $ 20, 012 X 15 = $ 300, 180 Total Cost Savings $1, 662, 053
 Return on Investment _______________ Non-Monetary Benefits … § Valid National benchmarking for surgical outcomes § Provides proactive, value-oriented performance measurement before it’s dictated by outside agents § Improves local market position through publicly visible improvement programs § Optimizes cross-departmental partnerships and collaboration through shared knowledge § Helps build high performance surgical teams and employee retention, (i. e. nurses) § Offers CME’s for Surgeon Champions and CEU’s for SCR’s
Return on Investment _______________ Non-Monetary Benefits … § Valid National benchmarking for surgical outcomes § Provides proactive, value-oriented performance measurement before it’s dictated by outside agents § Improves local market position through publicly visible improvement programs § Optimizes cross-departmental partnerships and collaboration through shared knowledge § Helps build high performance surgical teams and employee retention, (i. e. nurses) § Offers CME’s for Surgeon Champions and CEU’s for SCR’s
 Best Practice Guidelines _______________ § § Complete yet concise resource for health care providers and QI professionals Evidence-based Expert panel-rated Framework to: § Prevent postsurgical complications § Prioritize/direct QI efforts aimed at reducing incidence/impact of postsurgical complications
Best Practice Guidelines _______________ § § Complete yet concise resource for health care providers and QI professionals Evidence-based Expert panel-rated Framework to: § Prevent postsurgical complications § Prioritize/direct QI efforts aimed at reducing incidence/impact of postsurgical complications
 Best Practice Case Studies _______________ § Kaiser Sunnyside Medical Center used NSQIP data to optimize glucose and temperature control in the operating room § Advocate Good Samaritan Hospital used NSQIP data to improve postoperative Renal Outcomes § Scripps Green Hospital used NSQIP data to reduce surgical site infection rates in vascular surgery § Morristown Memorial Hospital used NSQIP data to prevent surgical site infections
Best Practice Case Studies _______________ § Kaiser Sunnyside Medical Center used NSQIP data to optimize glucose and temperature control in the operating room § Advocate Good Samaritan Hospital used NSQIP data to improve postoperative Renal Outcomes § Scripps Green Hospital used NSQIP data to reduce surgical site infection rates in vascular surgery § Morristown Memorial Hospital used NSQIP data to prevent surgical site infections
 The Options _______________ Four Adult NSQIP options 1. 2. 3. 4. NSQIP Classic NSQIP Essentials NSQIP Small &Rural NSQIP Procedure Targeted
The Options _______________ Four Adult NSQIP options 1. 2. 3. 4. NSQIP Classic NSQIP Essentials NSQIP Small &Rural NSQIP Procedure Targeted
 The Options _______________ Regardless of Which Option, All Hospitals Will Receive: § § § Semi Annual Reports Real Time Online Reports (including new SPCs) National Benchmarking NSQIP Best Practices/Guidelines NSQIP Improvement Case Studies Additional Items (e. g. Risk Calculator, Public Use File)
The Options _______________ Regardless of Which Option, All Hospitals Will Receive: § § § Semi Annual Reports Real Time Online Reports (including new SPCs) National Benchmarking NSQIP Best Practices/Guidelines NSQIP Improvement Case Studies Additional Items (e. g. Risk Calculator, Public Use File)
 The Options _______________ For All Options, the Rigor and Validity of ACS NSQIP is Unchanged § § § Risk Adjustment 30 Day Post Surgical Outcomes Clinical Data SCR Training SCR Certification
The Options _______________ For All Options, the Rigor and Validity of ACS NSQIP is Unchanged § § § Risk Adjustment 30 Day Post Surgical Outcomes Clinical Data SCR Training SCR Certification
 NSQIP Classic _______________ § General/Vascular = 1, 680 cases per year, 8 -day sampling cycle § Multispecialty = 20% total case volume by specialty, 8 -day sampling cycle § 1 FTE
NSQIP Classic _______________ § General/Vascular = 1, 680 cases per year, 8 -day sampling cycle § Multispecialty = 20% total case volume by specialty, 8 -day sampling cycle § 1 FTE
 NSQIP Essentials _______________ § General/Vascular = 1, 680 cases per year, 8 -day sampling cycle § Multispecialty = 20% total case volume by specialty, 8 -day sampling cycle § 1 FTE
NSQIP Essentials _______________ § General/Vascular = 1, 680 cases per year, 8 -day sampling cycle § Multispecialty = 20% total case volume by specialty, 8 -day sampling cycle § 1 FTE
 NSQIP Small & Rural _______________ § § Small Hospital: < 1, 680 cases per year OR Rural Hospital: ZIP code is defined within RUCA data codes § 100% collection of cases across all specialties § Collection of core variables for QI purposes § 1 FTE (or less depending upon case volume)
NSQIP Small & Rural _______________ § § Small Hospital: < 1, 680 cases per year OR Rural Hospital: ZIP code is defined within RUCA data codes § 100% collection of cases across all specialties § Collection of core variables for QI purposes § 1 FTE (or less depending upon case volume)
 NSQIP Procedure Targeted _______________ § Larger hospitals targeting high-risk/high volume procedures § Hospital selects procedures § Selection may be CPT code-driven § Minimum of 1, 680 cases per year: - 15 “Core” cases per 8 -day cycle - 25 “Procedure Targeted” cases per 8 -day cycle § Minimum 1 FTE (or more depending on volume)
NSQIP Procedure Targeted _______________ § Larger hospitals targeting high-risk/high volume procedures § Hospital selects procedures § Selection may be CPT code-driven § Minimum of 1, 680 cases per year: - 15 “Core” cases per 8 -day cycle - 25 “Procedure Targeted” cases per 8 -day cycle § Minimum 1 FTE (or more depending on volume)
 NSQIP Procedure Targeted _______________ Nine Subspecialties § § § § § General Surgery Vascular Gynecologic Urologic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Otolaryngology Orthopedic Surgery Neurosurgery Thoracic Surgery
NSQIP Procedure Targeted _______________ Nine Subspecialties § § § § § General Surgery Vascular Gynecologic Urologic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Otolaryngology Orthopedic Surgery Neurosurgery Thoracic Surgery
 NSQIP Procedure Targeted _______________ 30+ Procedures Pancreatectomy▪ Colectomy ▪ Ventral Hernia Repair ▪ Bariatric ▪ Proctectomy ▪ Hepatectomy ▪ Tyroidectomy ▪ Esophagectomy ▪ Appendectomy ▪ Cartoid Endarterectomy ▪ Cartoid Artery Stenting ▪ Open AAA Repair ▪ EVAR ▪ Open Aortoiliac Bypass ▪ Endo Aortoiliac Repair ▪ Lower Extremity Open Bypass ▪ Lower Extremity Repair Endovascular ▪ Hysterectomy ▪ Myomectomy ▪ Reconstructive Procedures ▪ TURP ▪ Bladder Suspension ▪ Radial Prostatectomy ▪ Radical Nephrectomy ▪ Radical Cystectomy ▪ Muscle/Myocutaneous Flap ▪ Reduction Mammoplasty ▪ Breast Reconstruction ▪ Abdominoplasty ▪ Thyroidectomy ▪ Total Hip Arthroplasty ▪ Total Knee Arthroplasty ▪ Spine Surgery ▪ Hip Fracture ▪ Brain Tumor Procedure ▪Spine Procedure ▪ Lung Resection
NSQIP Procedure Targeted _______________ 30+ Procedures Pancreatectomy▪ Colectomy ▪ Ventral Hernia Repair ▪ Bariatric ▪ Proctectomy ▪ Hepatectomy ▪ Tyroidectomy ▪ Esophagectomy ▪ Appendectomy ▪ Cartoid Endarterectomy ▪ Cartoid Artery Stenting ▪ Open AAA Repair ▪ EVAR ▪ Open Aortoiliac Bypass ▪ Endo Aortoiliac Repair ▪ Lower Extremity Open Bypass ▪ Lower Extremity Repair Endovascular ▪ Hysterectomy ▪ Myomectomy ▪ Reconstructive Procedures ▪ TURP ▪ Bladder Suspension ▪ Radial Prostatectomy ▪ Radical Nephrectomy ▪ Radical Cystectomy ▪ Muscle/Myocutaneous Flap ▪ Reduction Mammoplasty ▪ Breast Reconstruction ▪ Abdominoplasty ▪ Thyroidectomy ▪ Total Hip Arthroplasty ▪ Total Knee Arthroplasty ▪ Spine Surgery ▪ Hip Fracture ▪ Brain Tumor Procedure ▪Spine Procedure ▪ Lung Resection
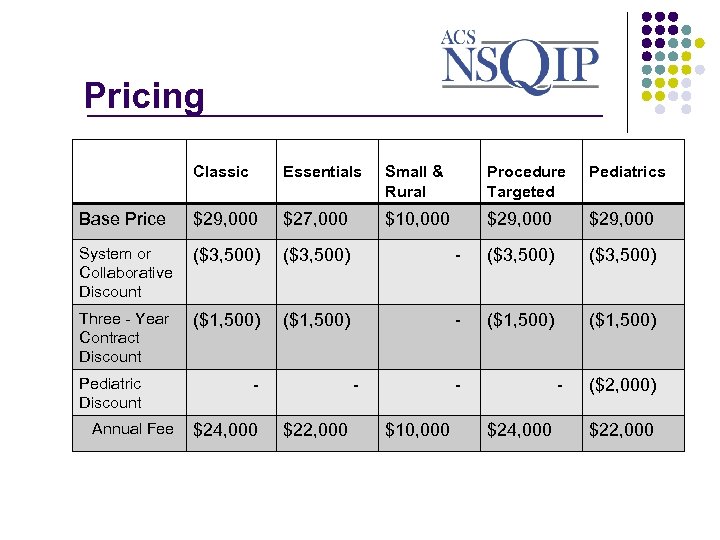 Pricing _______________ Classic Essentials Small & Rural Procedure Targeted Pediatrics Base Price $29, 000 $27, 000 $10, 000 $29, 000 System or Collaborative Discount ($3, 500) - ($3, 500) Three - Year Contract Discount ($1, 500) - ($1, 500) Pediatric Discount Annual Fee $24, 000 $22, 000 $10, 000 $24, 000 ($2, 000) $22, 000
Pricing _______________ Classic Essentials Small & Rural Procedure Targeted Pediatrics Base Price $29, 000 $27, 000 $10, 000 $29, 000 System or Collaborative Discount ($3, 500) - ($3, 500) Three - Year Contract Discount ($1, 500) - ($1, 500) Pediatric Discount Annual Fee $24, 000 $22, 000 $10, 000 $24, 000 ($2, 000) $22, 000
 Recognition ________________ Meets MOC Part 4 - Evaluation of performance in practice through tools such as outcome measures and quality improvement programs, and the evaluation of behaviors such as communication and professionalism.
Recognition ________________ Meets MOC Part 4 - Evaluation of performance in practice through tools such as outcome measures and quality improvement programs, and the evaluation of behaviors such as communication and professionalism.
 Recognition ________________ Institute of Medicine named NSQIP “the best in the nation” for measuring & reporting surgical quality and outcomes.
Recognition ________________ Institute of Medicine named NSQIP “the best in the nation” for measuring & reporting surgical quality and outcomes.
 Summary ________________ § § § Risk adjusted Data Clinically Robust Data Validated Data Best Practices Tools, Guidelines, and Case Studies Proven! (improve quality AND decrease costs)
Summary ________________ § § § Risk adjusted Data Clinically Robust Data Validated Data Best Practices Tools, Guidelines, and Case Studies Proven! (improve quality AND decrease costs)
 ________________ Tresha Russell Business Development Representative tresharussell@facs. org 312 -202 -5441
________________ Tresha Russell Business Development Representative tresharussell@facs. org 312 -202 -5441
 ________________ Thank you
________________ Thank you


