167d02e568bd067d19d20e2138250a30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

AMATEUR RADIO TRAINING Electromagnetic Compatibility Release: v 1. 21 hamtrain. co. uk

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY • What causes interference? • Ways to reduce interference • Transmission modes • Antennas & earths • Good station design
What is EMC? • Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is the avoidance of interference between two pieces of electronic equipment • Transmitters can cause interference to other equipment, such as a neighbour’s TV and radio • You need to understand the impact, and how to minimise the likelihood of causing unwanted interference

Interference • There is a chance that your signals can cause interference to: • TV sets / computer monitors • FM, AM & DAB Radio • Hi-fi units • Cordless and fixed-line phones • Touch lamps • Baby monitors • Security alarms / CCTV
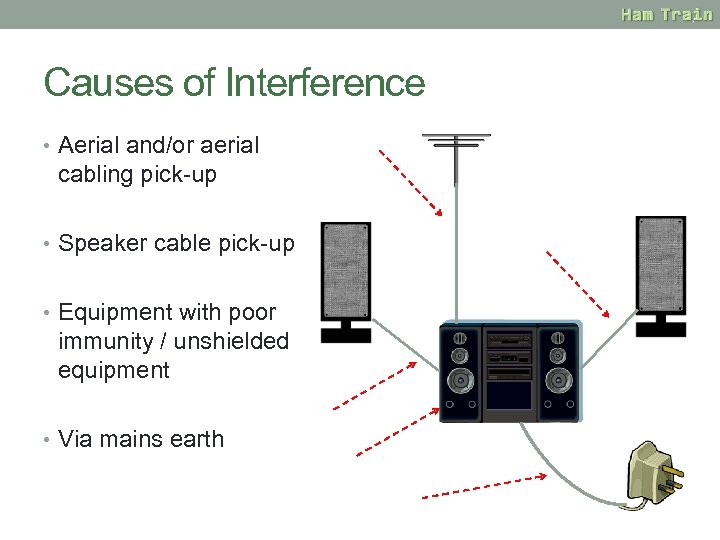
Causes of Interference • Aerial and/or aerial cabling pick-up • Speaker cable pick-up • Equipment with poor immunity / unshielded equipment • Via mains earth

Digital TV Interference • RF interference to digital TV will pixelate the picture and cause breakup to sound • Worse if weak Freeview signal, or using a TV signal booster

Video: Digital TV Interference

Digital TV Pixelation

Minimising Interference Depending on the problem: • Reduce field strength by moving the transmitting antenna further away • Reduce the power • Fit filters to the ‘pickup’ cabling • Using filters on mains power supply leads • Addressing earth problems

Filters Clip-on ferrite Wound ferrite ring High-pass or band-pass TV filter Ferrite filter on a power lead Safety note: Home-made filters are potentially dangerous
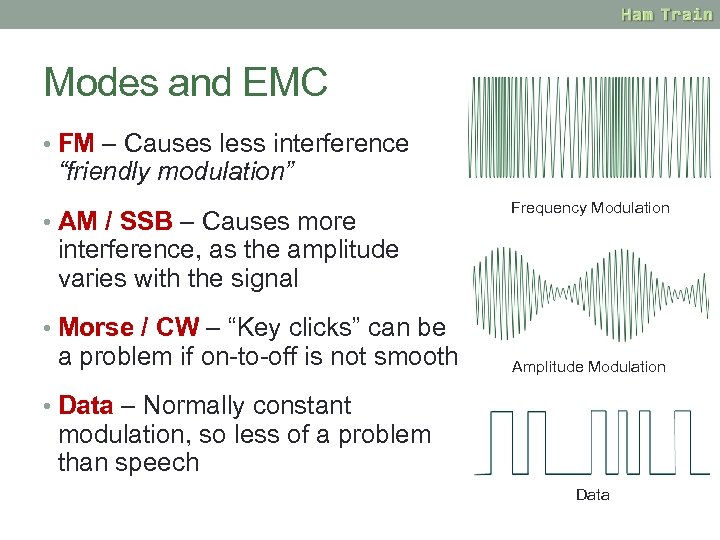
Modes and EMC • FM – Causes less interference “friendly modulation” • AM / SSB – Causes more Frequency Modulation interference, as the amplitude varies with the signal • Morse / CW – “Key clicks” can be a problem if on-to-off is not smooth Amplitude Modulation • Data – Normally constant modulation, so less of a problem than speech Data

RF Earth Use an RF earth to minimise RF leaking into mains • Do not use mains earth for RF! • Do not use radiators / water pipes • Use a copper stake in the ground close to shack • Use heavy-gauge wire to connect from transmitter or ATU
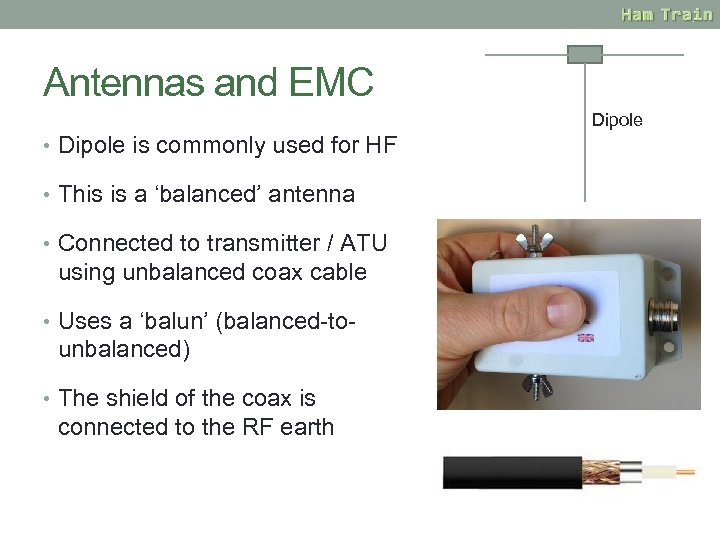
Antennas and EMC Dipole • Dipole is commonly used for HF • This is a ‘balanced’ antenna • Connected to transmitter / ATU using unbalanced coax cable • Uses a ‘balun’ (balanced-to- unbalanced) • The shield of the coax is connected to the RF earth
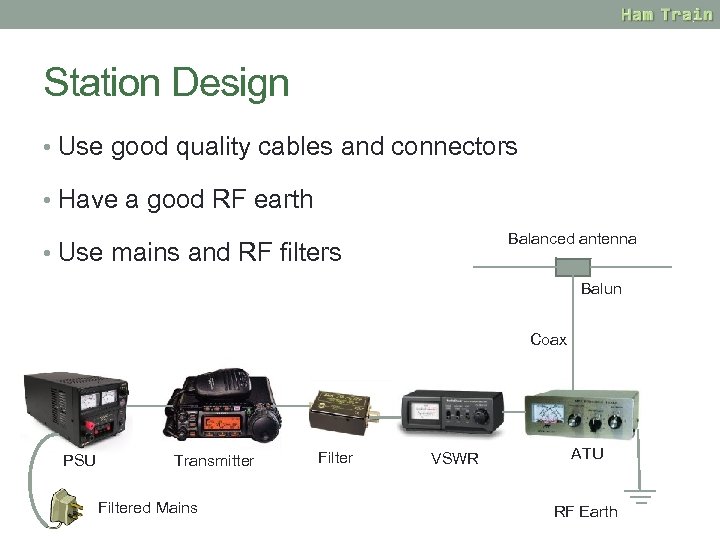
Station Design • Use good quality cables and connectors • Have a good RF earth Balanced antenna • Use mains and RF filters Balun Coax PSU Transmitter Filtered Mains Filter VSWR ATU RF Earth
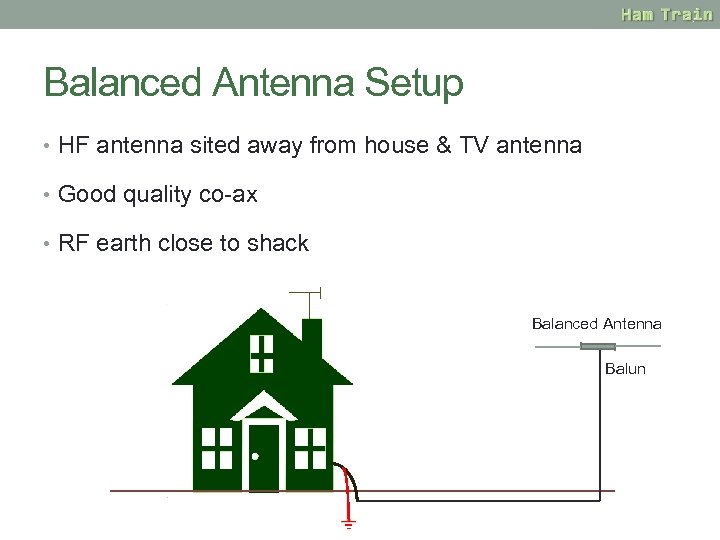
Balanced Antenna Setup • HF antenna sited away from house & TV antenna • Good quality co-ax • RF earth close to shack Balanced Antenna Balun
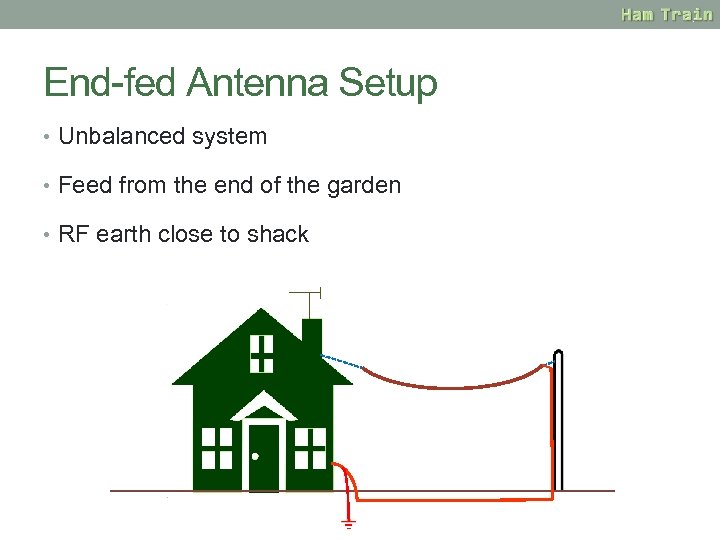
End-fed Antenna Setup • Unbalanced system • Feed from the end of the garden • RF earth close to shack
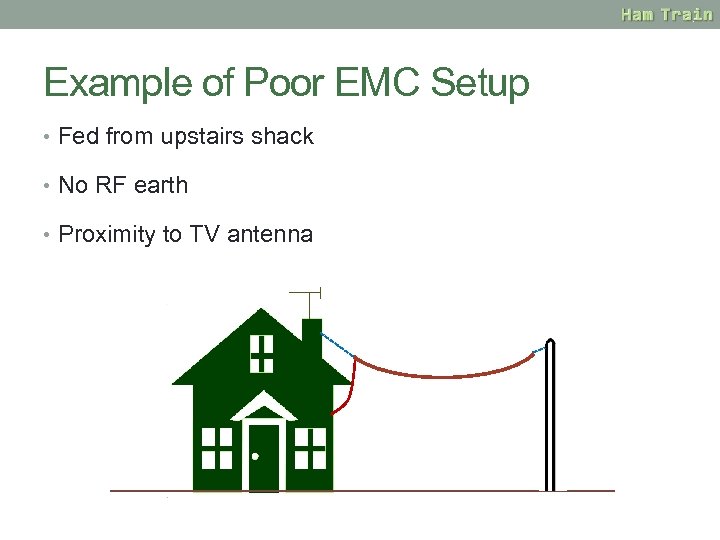
Example of Poor EMC Setup • Fed from upstairs shack • No RF earth • Proximity to TV antenna

EMC and Neighbours • It pays to be helpful and co-operative • Most problems can be resolved easily and cheaply • Get free advice from the RSGB EMC Committee • Your neighbour may consult Ofcom (for a fee). • Ofcom may ask you and the neighbour to keep a log to confirm interference is related to your transmissions
EMC Summary • EMC – Electromagnetic Compatibility • Understand the symptoms & causes • Have a good RF earth • Use the right type of antenna and good quality cable • Understand how to position an antenna to minimise interference • Correct station and shack set-up • FM is more “friendly” than other modes such as AM / SSB • Understand the type (and correct use) of filters • Resolving problems – Keep a log, and consult RSGB EMC Committee

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY Any questions? Ham. Train. co. uk © Essex. Ham. co. uk
167d02e568bd067d19d20e2138250a30.ppt