3c1dd45782a9d7d6200c3d10ffa4a5c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40


Always. On Introduction in Denali November 27 th , 2011

Seventh Activity Activities Brief • Introduce the Always. On features of SQL 2011 – Denali • Deep dive of Always. On characters
Attendees • • Tony Wu Eric Xia (Microsoft) Hua Zhu (Microsoft) Simon Liao

Introducing Always. On Active Secondary IT efficiency and cost-effectiveness is critical for businesses – Idle hardware is not an option anymore Always. On Active Secondary enables efficient utilization of high availability hardware resources thereby improving overall IT efficiency Active Secondary can be utilized for read-only queries, or for taking backups without impacting the primary workload.

Active Secondary: Enabling Backup On Secondary Kevin Farlee

Agenda • • Database Mirroring Backups Backup On Secondary Features and Limitations Backup Automation – Current Solutions – Backup On Secondary Solution – Configuring Backup Preferences – Example Configurations • Demo

Database Mirroring Backups • Backups are only allowed on Primary • Secondary cannot be leveraged for backups • Backup Workload impacts production Server

Active Secondary: Offloading Backup • Backups are allowed on any replica – Primary and secondary can be leveraged for backups • Backup workload does not impact production server • Highly requested feature
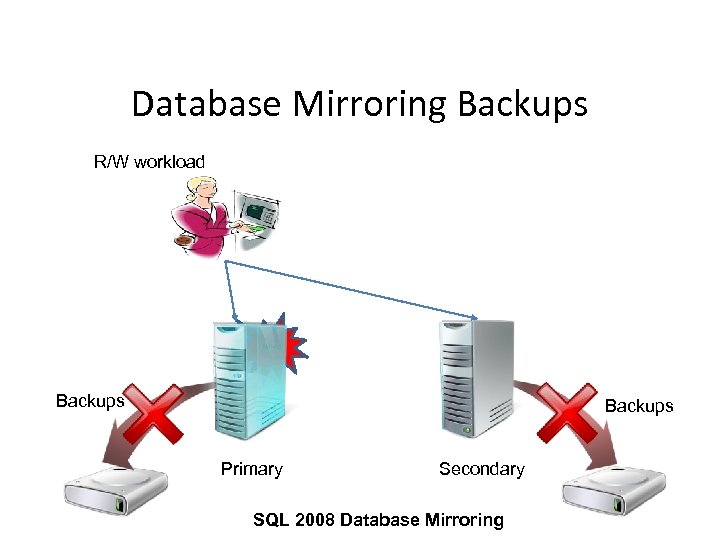
Database Mirroring Backups R/W workload Failed Backups Primary Secondary SQL 2008 Database Mirroring
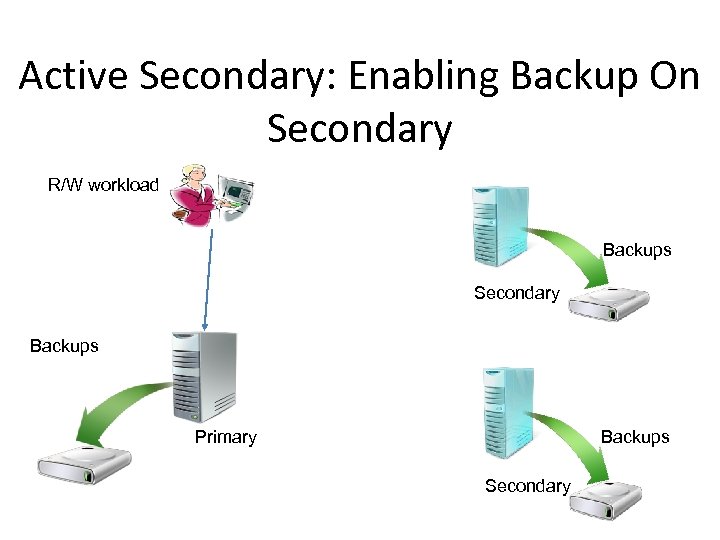
Active Secondary: Enabling Backup On Secondary R/W workload Backups Secondary Backups Primary Secondary

Capabilities • Backups can be done on any replica of a database • Secondary replica may be synchronous or asynchronous • Backups on primary replica still works • Log backups done on all replicas form a single log chain • Recovery Advisor makes restores simple
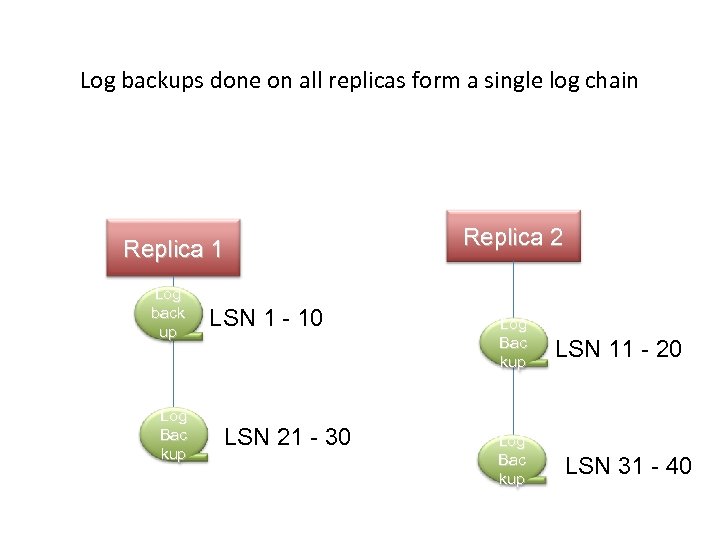
Log backups done on all replicas form a single log chain Replica 1 Log back up Log Bac kup LSN 1 - 10 LSN 21 - 30 Replica 2 Log Bac kup LSN 11 - 20 LSN 31 - 40

Restrictions, cautions, and gotchas • Differential backups are not supported on secondary • Only Copy-only full backups are supported on secondary • The only distinction is the differential bitmap clearing • Advisable for backups to be stored centrally

Automated Backups • • How to choose which replica to use for a backup? DBM: Only the primary would work Now: Backups succeed on all replicas Solution: Declarative policy

Declarative Policy • Preference for which role to use: – Primary Only – Secondary (but use Primary as fallback) – Don’t care • Relative Priority for each replica

Declarative Policy • Logic: – Filter out replicas which are not up & online – Filter out replicas which don’t meet the policy for role – Select the highest priority replica among the remaining set – Use instance name as tie-breaker

Declarative Policy • Policy is advisory only (NOT enforced) • Automatically used by Maintenance Plans and Log Shipping • Implemented as a system function (returns boolean)

DEMO • Backup On Secondary Session Code | Session Title 21

Active Secondary: Off-loading Reporting Workload Sunil Agarwal

Agenda • Readable Secondary – Reporting Workloads Today – Value Proposition – Architecture – Impact and Performance – Demo – Application Connectivity
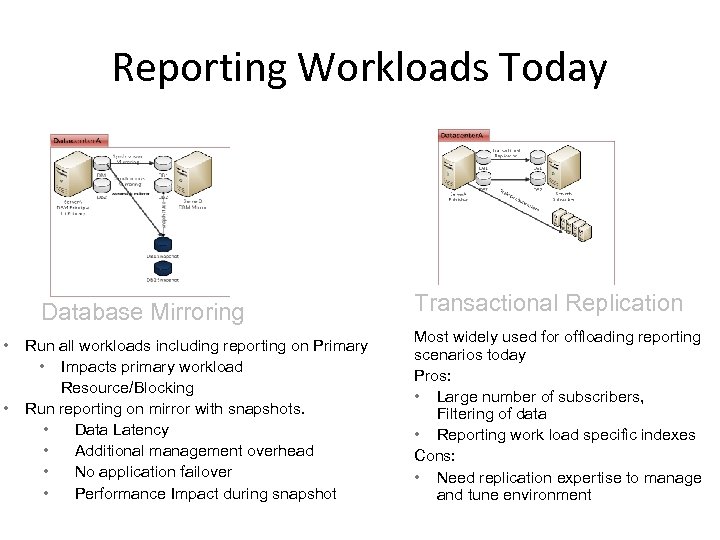
Reporting Workloads Today Database Mirroring • • Run all workloads including reporting on Primary • Impacts primary workload Resource/Blocking Run reporting on mirror with snapshots. • Data Latency • Additional management overhead • No application failover • Performance Impact during snapshot Transactional Replication Most widely used for offloading reporting scenarios today Pros: • Large number of subscribers, Filtering of data • Reporting work load specific indexes Cons: • Need replication expertise to manage and tune environment
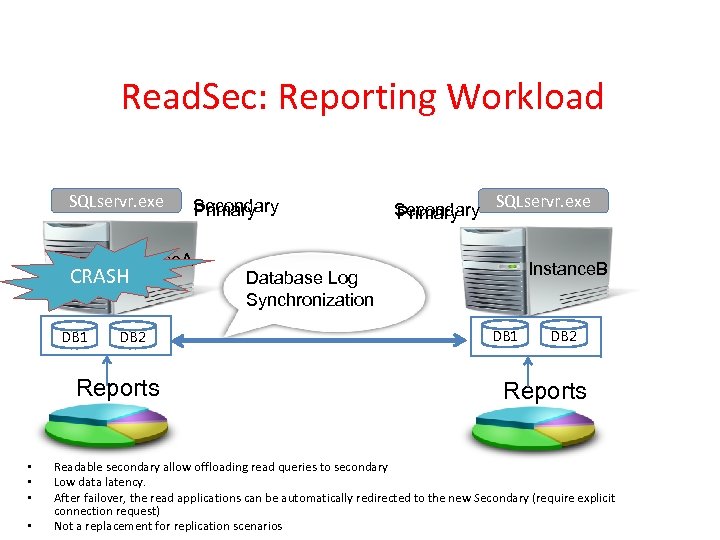
Read. Sec: Reporting Workload SQLservr. exe Instance. A CRASH DB 1 DB 2 Reports • • Secondary Primary SQLservr. exe Instance. B Database Log Synchronization DB 1 DB 2 Reports Readable secondary allow offloading read queries to secondary Low data latency. After failover, the read applications can be automatically redirected to the new Secondary (require explicit connection request) Not a replacement for replication scenarios
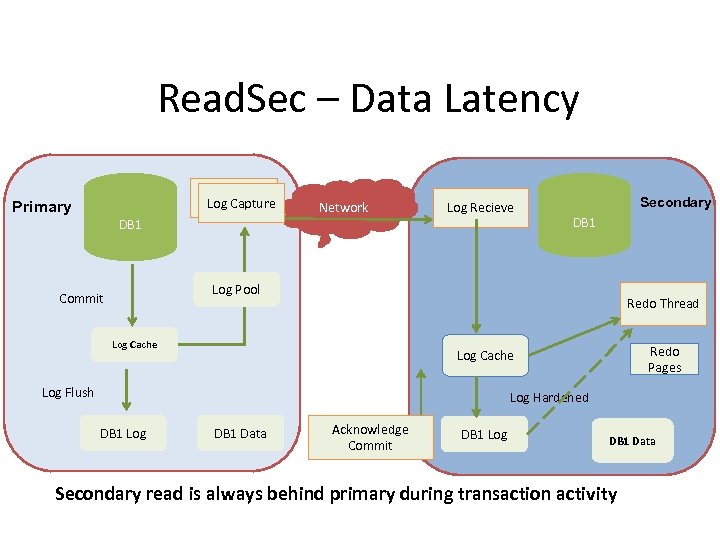
Read. Sec – Data Latency Log Capture Primary DB 1 Network Log Recieve Secondary DB 1 Log Pool Commit Redo Thread Log Cache Redo Pages Log Cache Log Flush Log Hardened DB 1 Log DB 1 Data Acknowledge Commit DB 1 Log DB 1 Data Secondary read is always behind primary during transaction activity
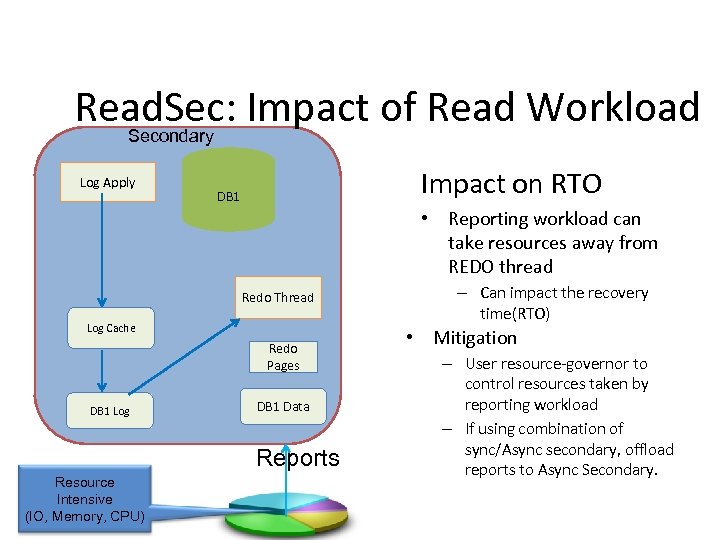
Read. Sec: Impact of Read Workload Secondary Log Apply Impact on RTO DB 1 • Reporting workload can take resources away from REDO thread Redo Thread Log Cache Redo Pages DB 1 Log DB 1 Data Reports Resource Intensive (IO, Memory, CPU) – Can impact the recovery time(RTO) • Mitigation – User resource-governor to control resources taken by reporting workload – If using combination of sync/Async secondary, offload reports to Async Secondary.

Read. Sec: Impact of read workload Impact on RTO (cont. ) • Concurrency and Blocking – REDO can get blocked by reporting workload – REDO thread and read workload can deadlock • Solution – Internally map read workload to non blocking isolation levels (no application changes required) • Read Uncommitted Snapshot Isolation • Read Committed Snapshot Isolation • Repeatable Read Snapshot Isolation • Serializable Snapshot Isolation • Ignore all locking hints – Never choose REDO as deadlock victim • Result – Blocking and deadlock between Reporting workload (i. e. Query) and REDO thread is eliminated – No issues with DML (INSERT/DELETE/UPDATE) as it is not allowed – Will incur additional cost of row versioning.
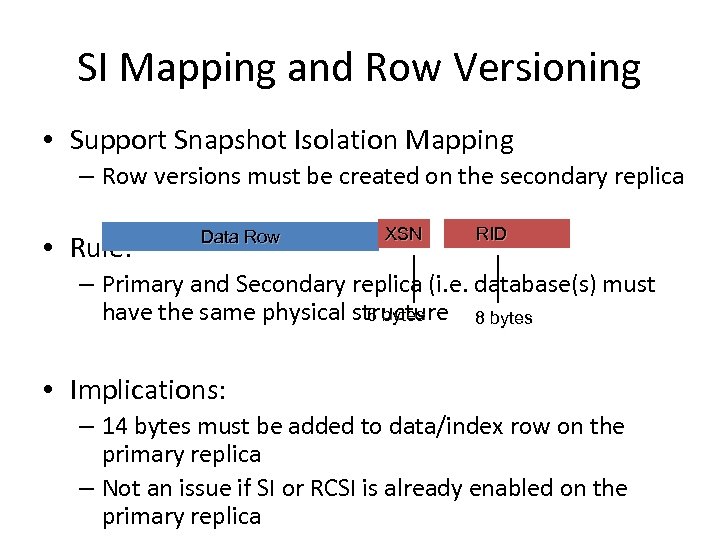
SI Mapping and Row Versioning • Support Snapshot Isolation Mapping – Row versions must be created on the secondary replica • Rule: Data Row XSN RID – Primary and Secondary replica (i. e. database(s) must have the same physical structure 8 bytes 6 bytes • Implications: – 14 bytes must be added to data/index row on the primary replica – Not an issue if SI or RCSI is already enabled on the primary replica
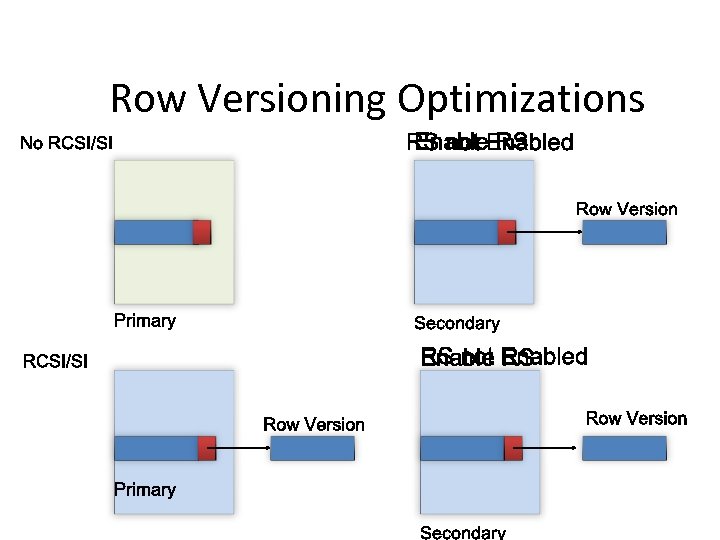
Row Versioning Optimizations
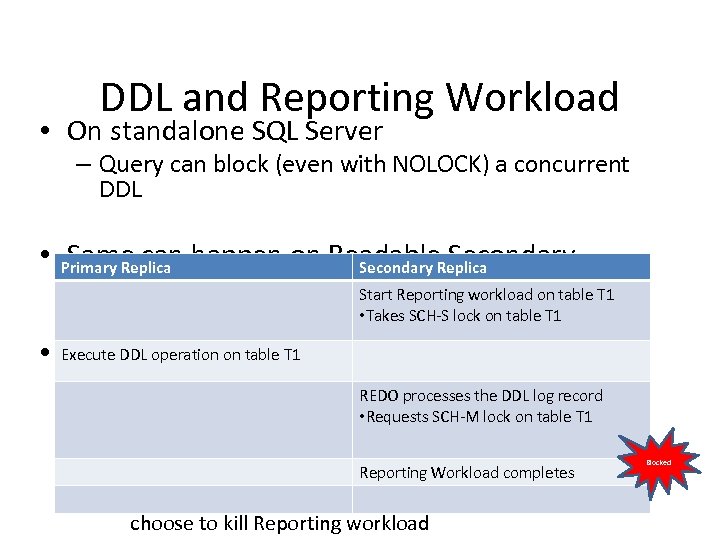
DDL and Reporting Workload • On standalone SQL Server – Query can block (even with NOLOCK) a concurrent DDL • Primary Replica happen on Readable. Replica Same can Secondary – REDO can block Reporting Workload Start Reporting workload on table T 1 – Read workload can block • Takes SCH-S lock on table T 1 REDO thread • Execute DDL operation on table T 1 Mitigation – DDL not common in production environment REDO processes the DDL log record • Requests SCH-M lock on table T 1 – You may have flexibility in scheduling maintenance jobs with concurrent Reporting Workload – Tools to identify blocking. Reporting Workload completes • An XEvent is generated when REDO is blocked. You can choose to kill Reporting workload Blocked

Query Performance on Secondary Optimized Query Plans • Goal: Comparable query plan on Readable Secondary • Query Optimization and Statistics – SQL Server uses cost based optimizer that heavily relies on object statistics – If statistics are missing, SQL Server automatically creates them and persists • Auto-stat on readable secondary will require physical Changes – Example: Table T 1 (C 1, C 2, C 3) • Query on primary with predicate (C 3 > 10). • SQL Server auto-create the statistics, if needed, on column C 3 on primary replica • Won’t work on Readable Secondary as it will cause physical changes to the database. – Similar issue if the statistical information is stale on the secondary replica. • Solution – Auto-create statistics on the secondary replica but persist them in Temp. DB
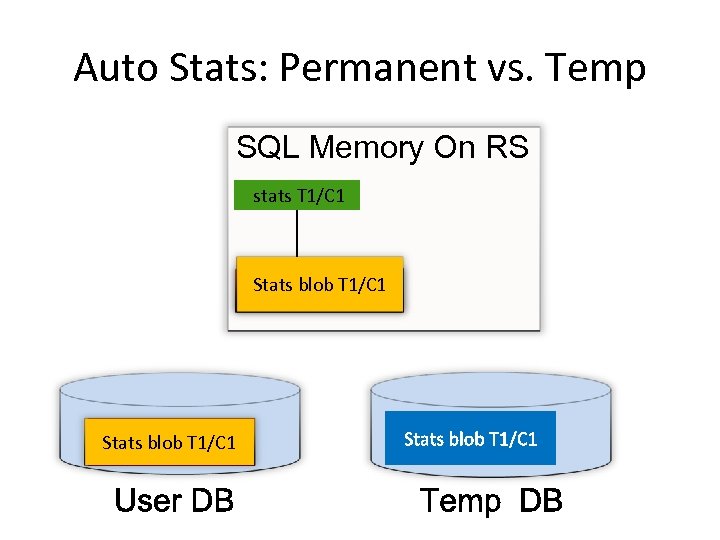
Auto Stats: Permanent vs. Temp SQL Memory On RS stats T 1/C 1 Stats blob T 1/C 1
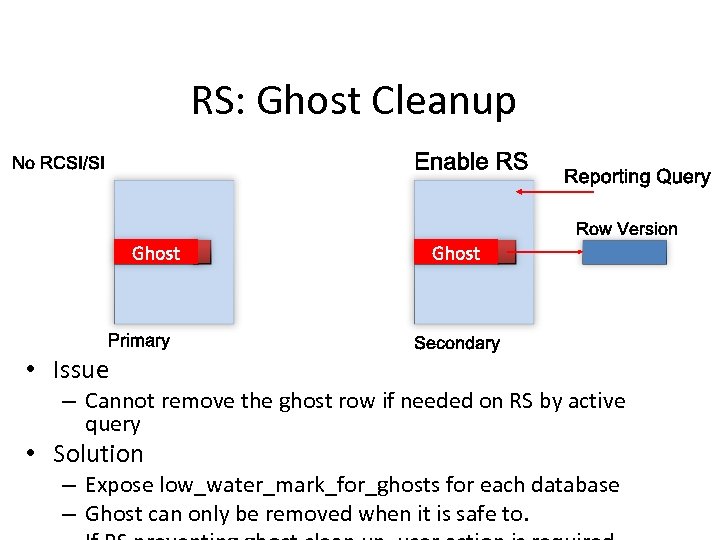
RS: Ghost Cleanup • Issue – Cannot remove the ghost row if needed on RS by active query • Solution – Expose low_water_mark_for_ghosts for each database – Ghost can only be removed when it is safe to.
DEMO • Readable Secondary Session Code | Session Title 35
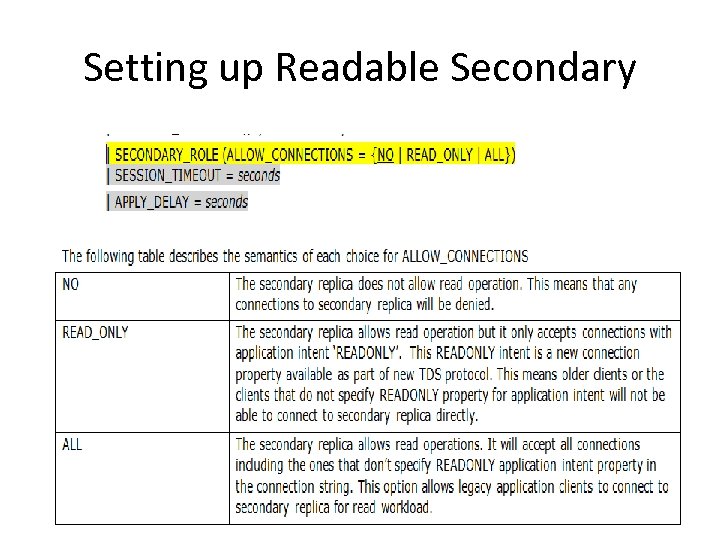
Setting up Readable Secondary

Application Connectivity Application. Intent – A New Connection Property – Used to gate access to secondary – Applicable when Secondary Replica set with ALLOW_CONNECTIONS =READ_ONLY Connection String – Connect directly to a secondary instance • Server=N 2; Database=Db 1; Application. Intent = Read. Only Read-Only Routing – Connection behavior optimized for automatic routing of read only applications to secondary

Supportability • Catalog Views – Sys. availability_replicas (used to see if secondary allows READ) – Sys. stats • New column to indicate if the statistics is temporary • DMVs – Sys. dm_hadr_database_replica_states • Xevents – REDO Blocked – REDO Unblocked

Summary • Better return on hardware investment – Primary workload can better use available resources – Reporting workload can use secondary replicas • Comparable query plans on secondary replica • Easy to manage and setup

Complete the Evaluation Form to Win! • Win a Dell Mini Netbook – every day – just for submitting your completed form. Each session evaluation form represents a chance to win. • Pick up your evaluation form: – In each presentation room – Online on the PASS Summit website Sponsored by Dell • Drop off your completed form: – Near the exit of each presentation room – At the Registration desk – Online on the PASS Summit website Session Code | Session Title 40

Thank you for attending this session and the 2011 PASS Summit in Seattle

Microsoft SQL Server Clinic Microsoft Product Pavilion Ask The Experts @ Dev Pods Hands-on Labs Work through your technical issues with SQL Server CSS & get architectural guidance from SQLCAT Talk with Microsoft SQL Server & BI experts to learn about the next version of SQL Server and check out the new Database Consolidation Appliance Meet Microsoft SQL Server Engineering team members & SQL MVPs Get experienced through self-paced & instructor-led labs on our cloud based lab platform - bring your laptop or use HP provided hardware Room 611 Expo Hall 6 th Floor Lobby Room 618 -620 Session Code | Session Title 42
3c1dd45782a9d7d6200c3d10ffa4a5c7.ppt