c5a8ca452e4d81e0573bbe51de35d2de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 ALLHAT Did Type of Prior Antihypertensive Therapy Influence the Heart Failure Results in ALLHAT? Richard Grimm, Barry Davis, Linda Piller, Karen Margolis, Joshua Barzilay, Richard Dart, James Graumlich, Robert Murden, Otelio Randall, Katrina Sawyer, for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group
ALLHAT Did Type of Prior Antihypertensive Therapy Influence the Heart Failure Results in ALLHAT? Richard Grimm, Barry Davis, Linda Piller, Karen Margolis, Joshua Barzilay, Richard Dart, James Graumlich, Robert Murden, Otelio Randall, Katrina Sawyer, for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group
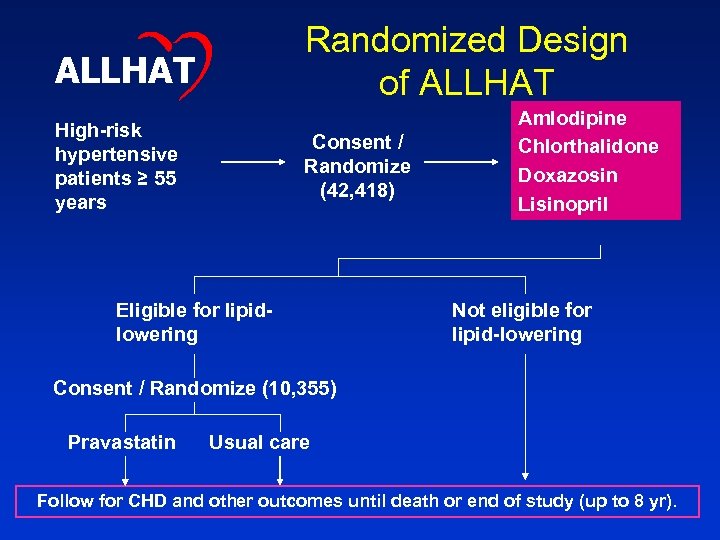 Randomized Design of ALLHAT High-risk hypertensive patients ≥ 55 years Consent / Randomize (42, 418) Eligible for lipidlowering Amlodipine Chlorthalidone Doxazosin Lisinopril Not eligible for lipid-lowering Consent / Randomize (10, 355) Pravastatin Usual care Follow for CHD and other outcomes until death or end of study (up to 8 yr).
Randomized Design of ALLHAT High-risk hypertensive patients ≥ 55 years Consent / Randomize (42, 418) Eligible for lipidlowering Amlodipine Chlorthalidone Doxazosin Lisinopril Not eligible for lipid-lowering Consent / Randomize (10, 355) Pravastatin Usual care Follow for CHD and other outcomes until death or end of study (up to 8 yr).
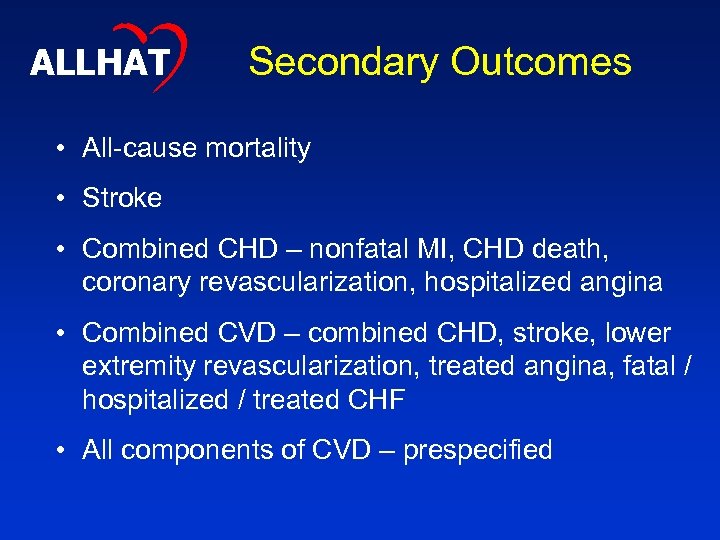 ALLHAT Secondary Outcomes • All-cause mortality • Stroke • Combined CHD – nonfatal MI, CHD death, coronary revascularization, hospitalized angina • Combined CVD – combined CHD, stroke, lower extremity revascularization, treated angina, fatal / hospitalized / treated CHF • All components of CVD – prespecified
ALLHAT Secondary Outcomes • All-cause mortality • Stroke • Combined CHD – nonfatal MI, CHD death, coronary revascularization, hospitalized angina • Combined CVD – combined CHD, stroke, lower extremity revascularization, treated angina, fatal / hospitalized / treated CHF • All components of CVD – prespecified
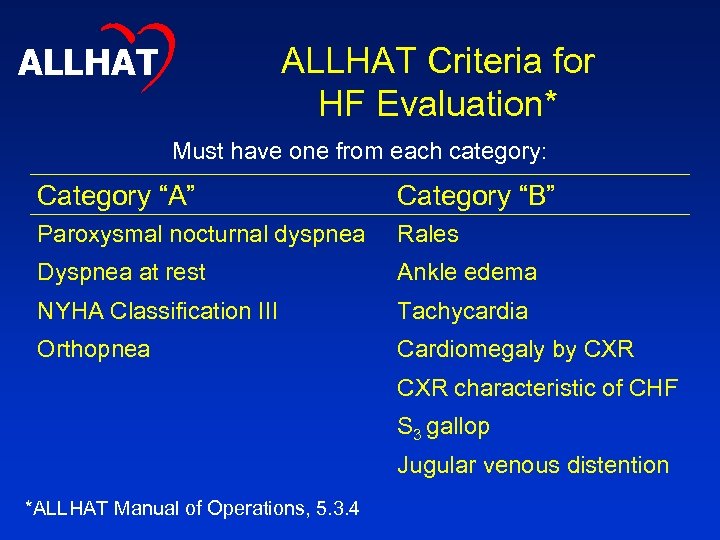 ALLHAT Criteria for HF Evaluation* Must have one from each category: Category “A” Category “B” Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Rales Dyspnea at rest Ankle edema NYHA Classification III Tachycardia Orthopnea Cardiomegaly by CXR characteristic of CHF S 3 gallop Jugular venous distention *ALLHAT Manual of Operations, 5. 3. 4
ALLHAT Criteria for HF Evaluation* Must have one from each category: Category “A” Category “B” Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Rales Dyspnea at rest Ankle edema NYHA Classification III Tachycardia Orthopnea Cardiomegaly by CXR characteristic of CHF S 3 gallop Jugular venous distention *ALLHAT Manual of Operations, 5. 3. 4
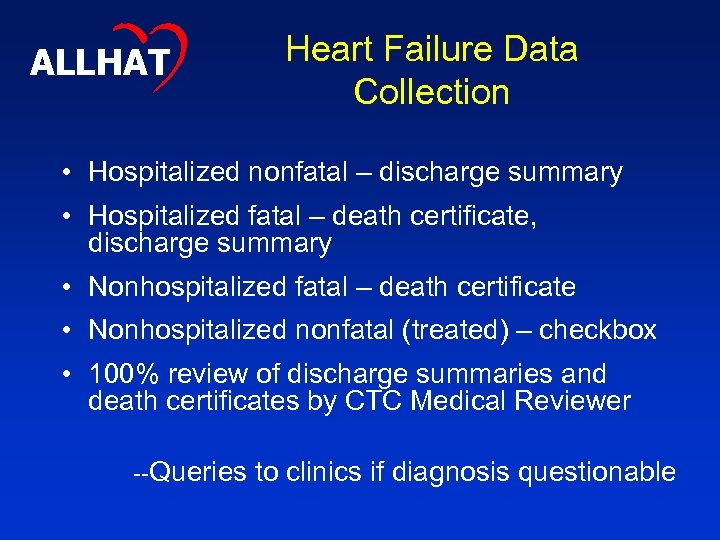 ALLHAT Heart Failure Data Collection • Hospitalized nonfatal – discharge summary • Hospitalized fatal – death certificate, discharge summary • Nonhospitalized fatal – death certificate • Nonhospitalized nonfatal (treated) – checkbox • 100% review of discharge summaries and death certificates by CTC Medical Reviewer --Queries to clinics if diagnosis questionable
ALLHAT Heart Failure Data Collection • Hospitalized nonfatal – discharge summary • Hospitalized fatal – death certificate, discharge summary • Nonhospitalized fatal – death certificate • Nonhospitalized nonfatal (treated) – checkbox • 100% review of discharge summaries and death certificates by CTC Medical Reviewer --Queries to clinics if diagnosis questionable
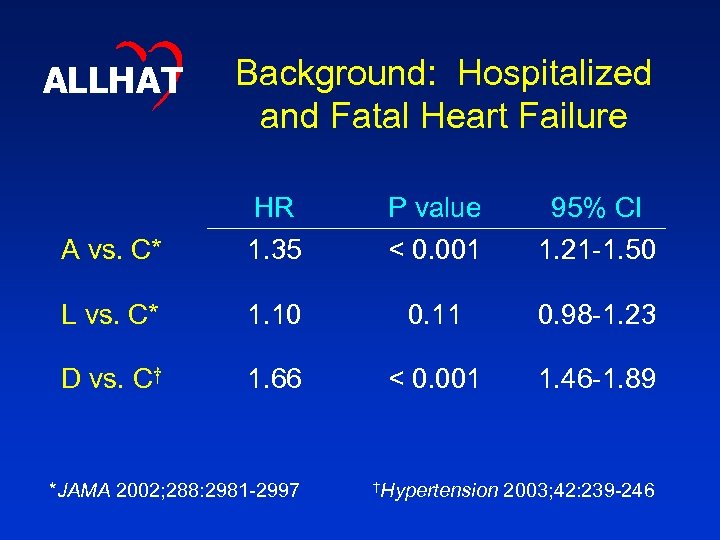 ALLHAT Background: Hospitalized and Fatal Heart Failure A vs. C* HR 1. 35 P value < 0. 001 95% CI 1. 21 -1. 50 L vs. C* 1. 10 0. 11 0. 98 -1. 23 D vs. C† 1. 66 < 0. 001 1. 46 -1. 89 *JAMA 2002; 288: 2981 -2997 †Hypertension 2003; 42: 239 -246
ALLHAT Background: Hospitalized and Fatal Heart Failure A vs. C* HR 1. 35 P value < 0. 001 95% CI 1. 21 -1. 50 L vs. C* 1. 10 0. 11 0. 98 -1. 23 D vs. C† 1. 66 < 0. 001 1. 46 -1. 89 *JAMA 2002; 288: 2981 -2997 †Hypertension 2003; 42: 239 -246
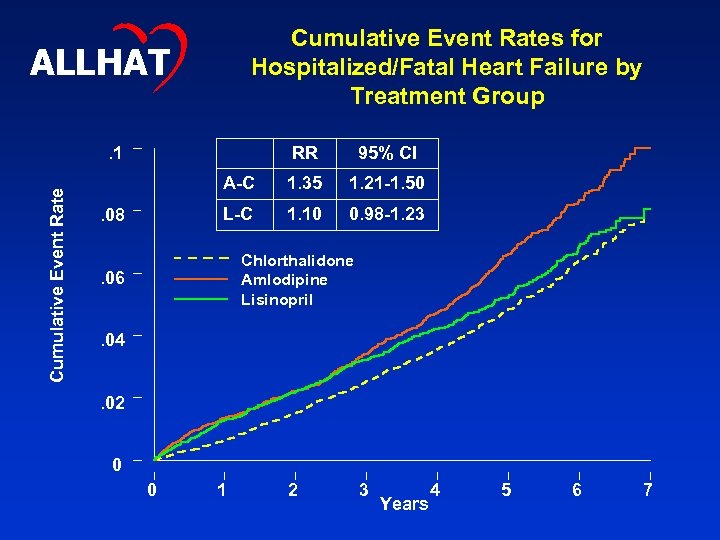 Cumulative Event Rates for Hospitalized/Fatal Heart Failure by Treatment Group ALLHAT Cumulative Event Rate . 1 RR A-C 1. 35 1. 21 -1. 50 L-C . 08 95% CI 1. 10 0. 98 -1. 23 Chlorthalidone Amlodipine Lisinopril . 06. 04. 02 0 0 1 2 3 Years 4 5 6 7
Cumulative Event Rates for Hospitalized/Fatal Heart Failure by Treatment Group ALLHAT Cumulative Event Rate . 1 RR A-C 1. 35 1. 21 -1. 50 L-C . 08 95% CI 1. 10 0. 98 -1. 23 Chlorthalidone Amlodipine Lisinopril . 06. 04. 02 0 0 1 2 3 Years 4 5 6 7
 Cumulative Event Rates for Hospitalized/ Fatal Heart Failure by Treatment Group Cumulative Fatal+Hosp HF Event Rate ALLHAT. 12 RR (95% CI) D/C p value 1. 66 (1. 46 -1. 89) <0. 001 . 09 . 06 Doxazosin . 03 Chlorthalidone 0 0 1 2 3 Years to Fatal or Hosp HF 4 5
Cumulative Event Rates for Hospitalized/ Fatal Heart Failure by Treatment Group Cumulative Fatal+Hosp HF Event Rate ALLHAT. 12 RR (95% CI) D/C p value 1. 66 (1. 46 -1. 89) <0. 001 . 09 . 06 Doxazosin . 03 Chlorthalidone 0 0 1 2 3 Years to Fatal or Hosp HF 4 5
 ALLHAT Question to be Addressed by these Analyses Kaplan-Meier curves for the HF outcome show an early divergence of the curves for chlorthalidone vs. amlodipine, lisinopril, or doxazosin. Question: Can the heart failure findings in part be explained by discontinuing antihypertensive medications such as diuretics and ACE-inhibitors upon entry into ALLHAT?
ALLHAT Question to be Addressed by these Analyses Kaplan-Meier curves for the HF outcome show an early divergence of the curves for chlorthalidone vs. amlodipine, lisinopril, or doxazosin. Question: Can the heart failure findings in part be explained by discontinuing antihypertensive medications such as diuretics and ACE-inhibitors upon entry into ALLHAT?
 ALLHAT HF Validation Study – BP Meds at Entry • 2091 pts w/ 3032 hosp/fatal HF cases centrally reviewed • Criteria – ALLHAT, Framingham, reviewer judgment • 70 -84% confirmed on central review (similar across Rx groups; Rx group effects larger in confirmed cases) • Requested information about pts’ BP drug use at trial entry just before end of study • Received information for 1418 pts (~ 2/3 total) population for this study
ALLHAT HF Validation Study – BP Meds at Entry • 2091 pts w/ 3032 hosp/fatal HF cases centrally reviewed • Criteria – ALLHAT, Framingham, reviewer judgment • 70 -84% confirmed on central review (similar across Rx groups; Rx group effects larger in confirmed cases) • Requested information about pts’ BP drug use at trial entry just before end of study • Received information for 1418 pts (~ 2/3 total) population for this study
 ALLHAT
ALLHAT
 ALLHAT Received ALLHAT BLOOD PRESSURE MEDICATION AT STUDY ENTRY ID bel La
ALLHAT Received ALLHAT BLOOD PRESSURE MEDICATION AT STUDY ENTRY ID bel La
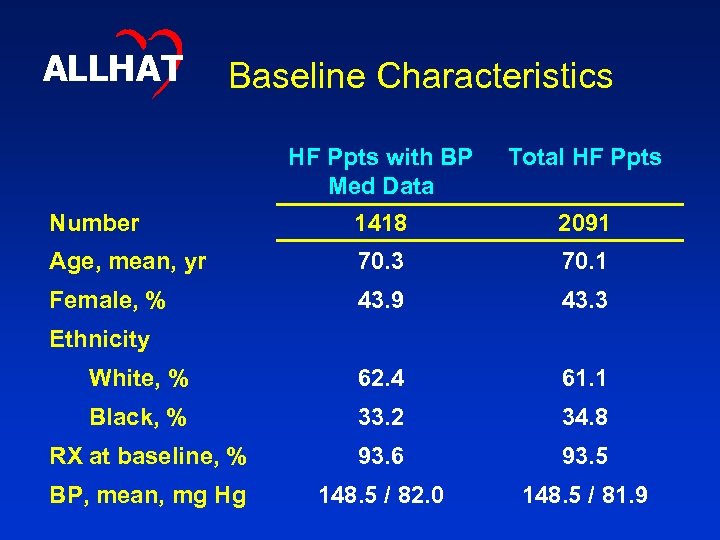 ALLHAT Baseline Characteristics HF Ppts with BP Med Data Total HF Ppts Number 1418 2091 Age, mean, yr 70. 3 70. 1 Female, % 43. 9 43. 3 White, % 62. 4 61. 1 Black, % 33. 2 34. 8 RX at baseline, % 93. 6 93. 5 BP, mean, mg Hg 148. 5 / 82. 0 148. 5 / 81. 9 Ethnicity
ALLHAT Baseline Characteristics HF Ppts with BP Med Data Total HF Ppts Number 1418 2091 Age, mean, yr 70. 3 70. 1 Female, % 43. 9 43. 3 White, % 62. 4 61. 1 Black, % 33. 2 34. 8 RX at baseline, % 93. 6 93. 5 BP, mean, mg Hg 148. 5 / 82. 0 148. 5 / 81. 9 Ethnicity
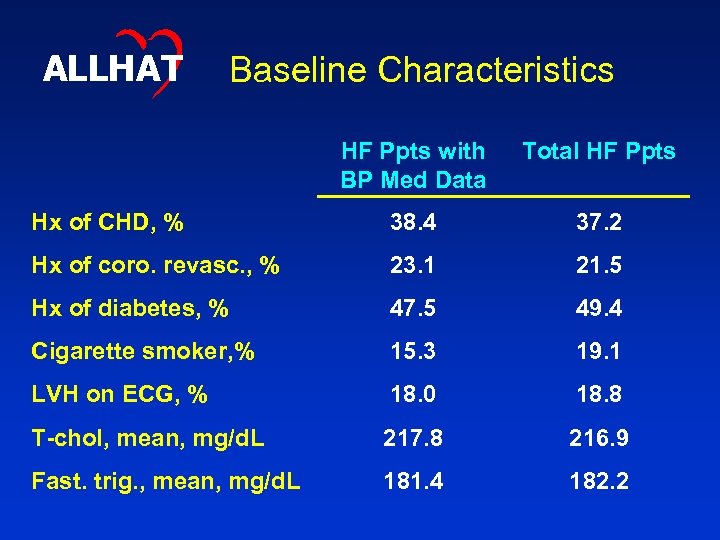 ALLHAT Baseline Characteristics HF Ppts with BP Med Data Total HF Ppts Hx of CHD, % 38. 4 37. 2 Hx of coro. revasc. , % 23. 1 21. 5 Hx of diabetes, % 47. 5 49. 4 Cigarette smoker, % 15. 3 19. 1 LVH on ECG, % 18. 0 18. 8 T-chol, mean, mg/d. L 217. 8 216. 9 Fast. trig. , mean, mg/d. L 181. 4 182. 2
ALLHAT Baseline Characteristics HF Ppts with BP Med Data Total HF Ppts Hx of CHD, % 38. 4 37. 2 Hx of coro. revasc. , % 23. 1 21. 5 Hx of diabetes, % 47. 5 49. 4 Cigarette smoker, % 15. 3 19. 1 LVH on ECG, % 18. 0 18. 8 T-chol, mean, mg/d. L 217. 8 216. 9 Fast. trig. , mean, mg/d. L 181. 4 182. 2
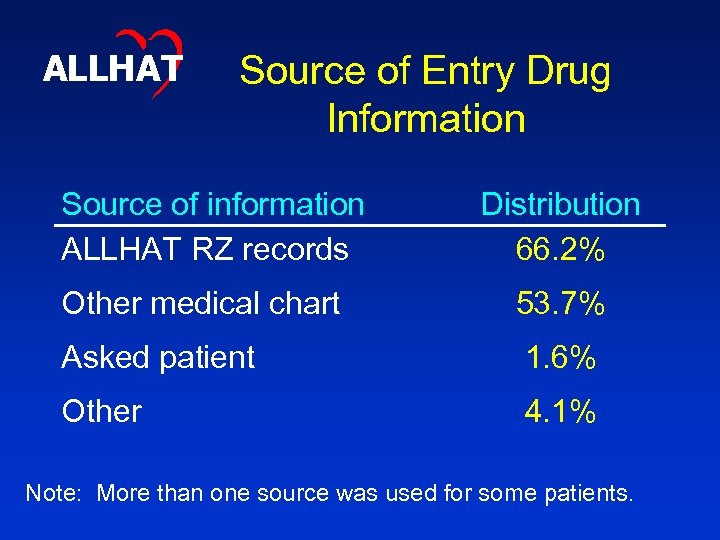 ALLHAT Source of Entry Drug Information Source of information ALLHAT RZ records Distribution 66. 2% Other medical chart 53. 7% Asked patient 1. 6% Other 4. 1% Note: More than one source was used for some patients.
ALLHAT Source of Entry Drug Information Source of information ALLHAT RZ records Distribution 66. 2% Other medical chart 53. 7% Asked patient 1. 6% Other 4. 1% Note: More than one source was used for some patients.
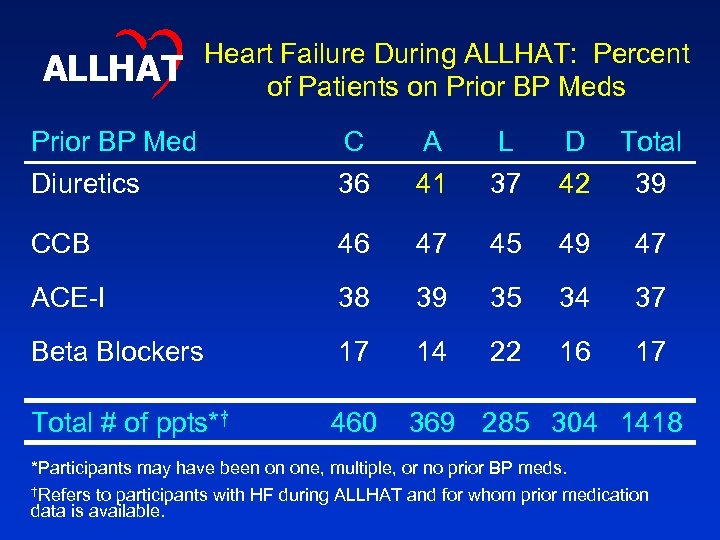 ALLHAT Heart Failure During ALLHAT: Percent of Patients on Prior BP Meds Prior BP Med Diuretics C 36 A 41 L 37 D 42 Total 39 CCB 46 47 45 49 47 ACE-I 38 39 35 34 37 Beta Blockers 17 14 22 16 17 Total # of ppts*† 460 369 285 304 1418 *Participants may have been on one, multiple, or no prior BP meds. †Refers to participants with HF during ALLHAT and for whom prior medication data is available.
ALLHAT Heart Failure During ALLHAT: Percent of Patients on Prior BP Meds Prior BP Med Diuretics C 36 A 41 L 37 D 42 Total 39 CCB 46 47 45 49 47 ACE-I 38 39 35 34 37 Beta Blockers 17 14 22 16 17 Total # of ppts*† 460 369 285 304 1418 *Participants may have been on one, multiple, or no prior BP meds. †Refers to participants with HF during ALLHAT and for whom prior medication data is available.
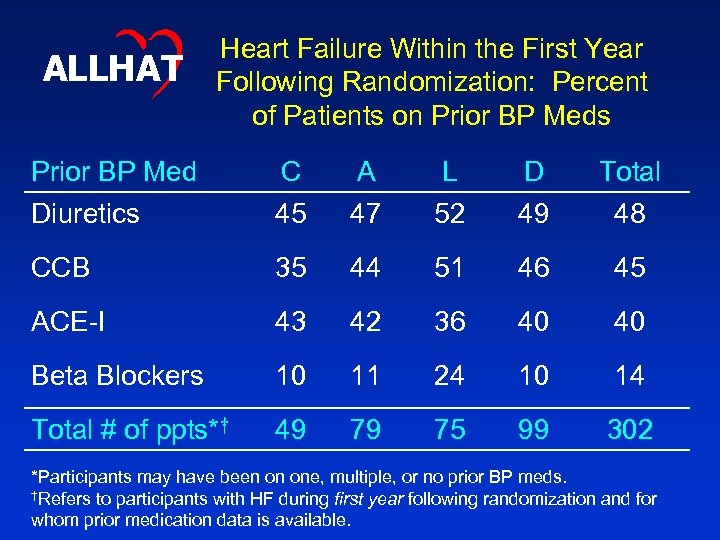 ALLHAT Heart Failure Within the First Year Following Randomization: Percent of Patients on Prior BP Meds Prior BP Med Diuretics C 45 A 47 L 52 D 49 Total 48 CCB 35 44 51 46 45 ACE-I 43 42 36 40 40 Beta Blockers 10 11 24 10 14 Total # of ppts*† 49 79 75 99 302 *Participants may have been on one, multiple, or no prior BP meds. †Refers to participants with HF during first year following randomization and for whom prior medication data is available.
ALLHAT Heart Failure Within the First Year Following Randomization: Percent of Patients on Prior BP Meds Prior BP Med Diuretics C 45 A 47 L 52 D 49 Total 48 CCB 35 44 51 46 45 ACE-I 43 42 36 40 40 Beta Blockers 10 11 24 10 14 Total # of ppts*† 49 79 75 99 302 *Participants may have been on one, multiple, or no prior BP meds. †Refers to participants with HF during first year following randomization and for whom prior medication data is available.
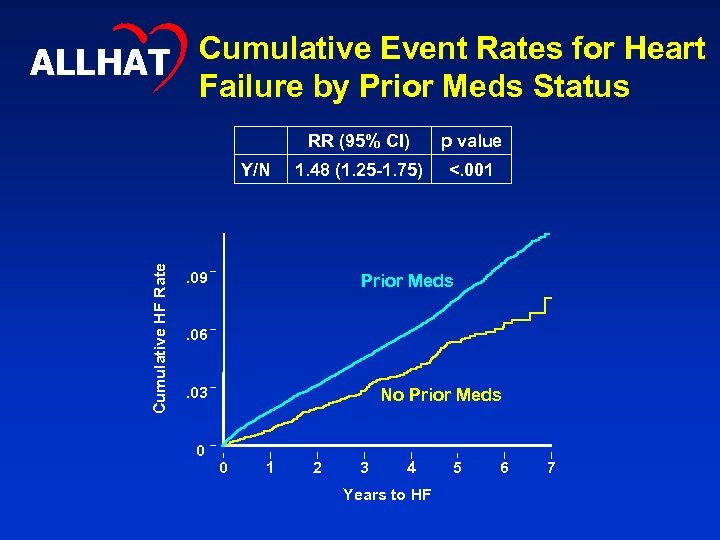 Cumulative Event Rates for Heart ALLHAT Failure by Prior Meds Status RR (95% CI) Cumulative HF Rate Y/N p value 1. 48 (1. 25 -1. 75) <. 001 . 09 Prior Meds . 06. 03 0 No Prior Meds 0 1 2 3 4 Years to HF 5 6 7
Cumulative Event Rates for Heart ALLHAT Failure by Prior Meds Status RR (95% CI) Cumulative HF Rate Y/N p value 1. 48 (1. 25 -1. 75) <. 001 . 09 Prior Meds . 06. 03 0 No Prior Meds 0 1 2 3 4 Years to HF 5 6 7
 ALLHAT Case-Only Analyses • Cannot do analyses on entire population since pre-ALLHAT BP meds data was only collected for HF cases. • A technique know as case-only analyses will allow us to examine if there was interaction. • Do “full” analyses and case-only analyses provide comparable results?
ALLHAT Case-Only Analyses • Cannot do analyses on entire population since pre-ALLHAT BP meds data was only collected for HF cases. • A technique know as case-only analyses will allow us to examine if there was interaction. • Do “full” analyses and case-only analyses provide comparable results?
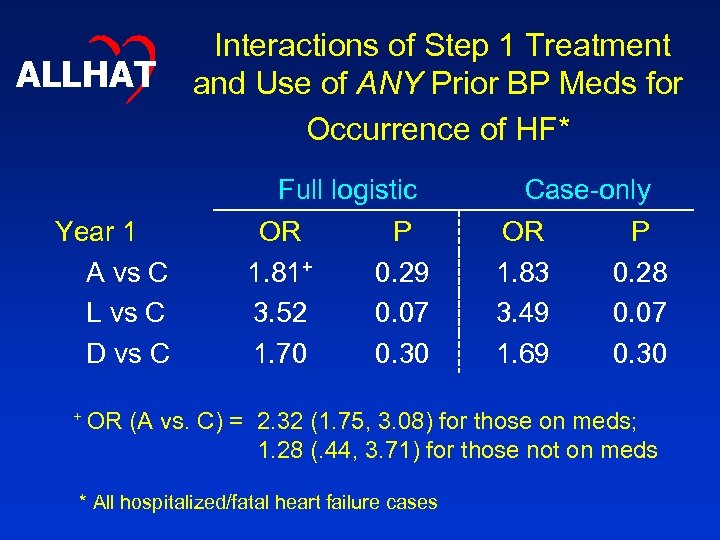 ALLHAT Year 1 A vs C L vs C D vs C + OR Interactions of Step 1 Treatment and Use of ANY Prior BP Meds for Occurrence of HF* Full logistic OR P 1. 81+ 0. 29 3. 52 0. 07 1. 70 0. 30 Case-only OR P 1. 83 0. 28 3. 49 0. 07 1. 69 0. 30 (A vs. C) = 2. 32 (1. 75, 3. 08) for those on meds; 1. 28 (. 44, 3. 71) for those not on meds * All hospitalized/fatal heart failure cases
ALLHAT Year 1 A vs C L vs C D vs C + OR Interactions of Step 1 Treatment and Use of ANY Prior BP Meds for Occurrence of HF* Full logistic OR P 1. 81+ 0. 29 3. 52 0. 07 1. 70 0. 30 Case-only OR P 1. 83 0. 28 3. 49 0. 07 1. 69 0. 30 (A vs. C) = 2. 32 (1. 75, 3. 08) for those on meds; 1. 28 (. 44, 3. 71) for those not on meds * All hospitalized/fatal heart failure cases
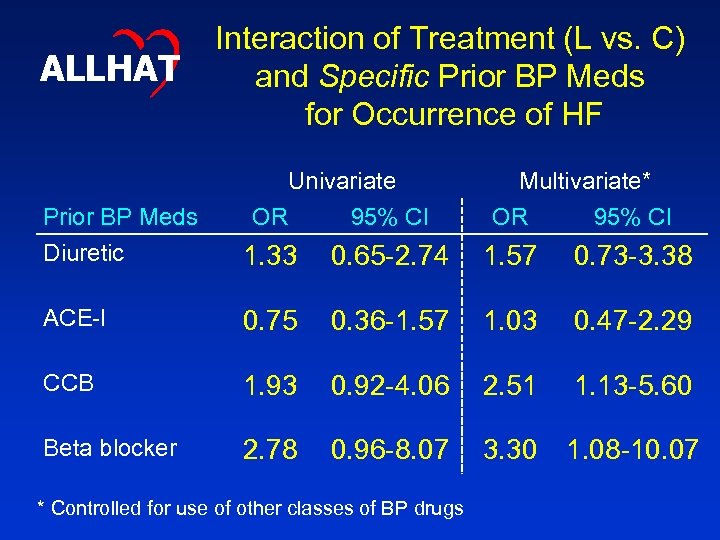 ALLHAT Prior BP Meds Interaction of Treatment (L vs. C) and Specific Prior BP Meds for Occurrence of HF Univariate OR 95% CI Multivariate* OR 95% CI Diuretic 1. 33 0. 65 -2. 74 1. 57 0. 73 -3. 38 ACE-I 0. 75 0. 36 -1. 57 1. 03 0. 47 -2. 29 CCB 1. 93 0. 92 -4. 06 2. 51 1. 13 -5. 60 Beta blocker 2. 78 0. 96 -8. 07 3. 30 1. 08 -10. 07 * Controlled for use of other classes of BP drugs
ALLHAT Prior BP Meds Interaction of Treatment (L vs. C) and Specific Prior BP Meds for Occurrence of HF Univariate OR 95% CI Multivariate* OR 95% CI Diuretic 1. 33 0. 65 -2. 74 1. 57 0. 73 -3. 38 ACE-I 0. 75 0. 36 -1. 57 1. 03 0. 47 -2. 29 CCB 1. 93 0. 92 -4. 06 2. 51 1. 13 -5. 60 Beta blocker 2. 78 0. 96 -8. 07 3. 30 1. 08 -10. 07 * Controlled for use of other classes of BP drugs
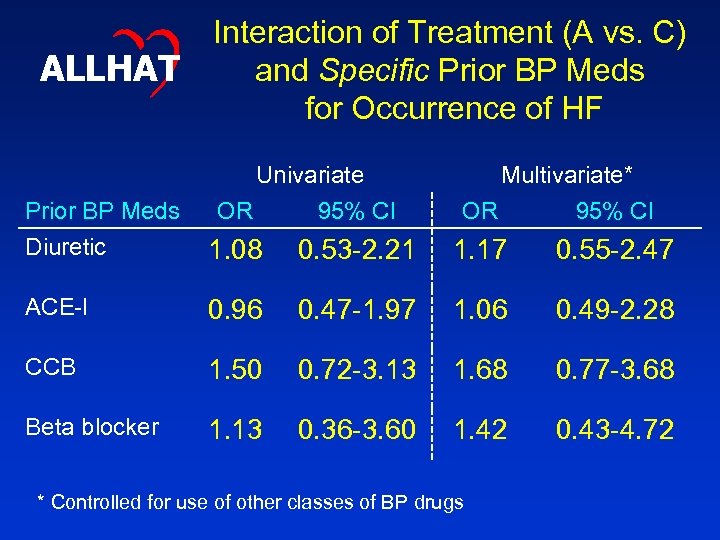 ALLHAT Interaction of Treatment (A vs. C) and Specific Prior BP Meds for Occurrence of HF Univariate OR 95% CI Multivariate* OR 95% CI Prior BP Meds Diuretic 1. 08 0. 53 -2. 21 1. 17 0. 55 -2. 47 ACE-I 0. 96 0. 47 -1. 97 1. 06 0. 49 -2. 28 CCB 1. 50 0. 72 -3. 13 1. 68 0. 77 -3. 68 Beta blocker 1. 13 0. 36 -3. 60 1. 42 0. 43 -4. 72 * Controlled for use of other classes of BP drugs
ALLHAT Interaction of Treatment (A vs. C) and Specific Prior BP Meds for Occurrence of HF Univariate OR 95% CI Multivariate* OR 95% CI Prior BP Meds Diuretic 1. 08 0. 53 -2. 21 1. 17 0. 55 -2. 47 ACE-I 0. 96 0. 47 -1. 97 1. 06 0. 49 -2. 28 CCB 1. 50 0. 72 -3. 13 1. 68 0. 77 -3. 68 Beta blocker 1. 13 0. 36 -3. 60 1. 42 0. 43 -4. 72 * Controlled for use of other classes of BP drugs
 ALLHAT Potential Confounders • Confounders by indication: why was the patient placed on a specific class of drug prior to participation in the study? • Use of additional meds during the study: what conditions developed that caused the patient to be placed on additional meds? • Possibility of misclassification of drugs used prior to study entry • Missing data: approximately one third of heart failure cases lacked information on specific drugs used prior to entry into ALLHAT
ALLHAT Potential Confounders • Confounders by indication: why was the patient placed on a specific class of drug prior to participation in the study? • Use of additional meds during the study: what conditions developed that caused the patient to be placed on additional meds? • Possibility of misclassification of drugs used prior to study entry • Missing data: approximately one third of heart failure cases lacked information on specific drugs used prior to entry into ALLHAT
 ALLHAT Conclusions • Among the HF cases, CCB’s were the most used BP drug prior to entry into ALLHAT, followed by diuretics and ACE inhibitors. • Pts on any prior BP med (vs. none) were at higher risk of developing HF. • These findings are noteworthy for those on CCB’s and BB’s at entry (confounding by indication? ). • These findings suggest that the type of BP drug at entry is not a major determinant of the HF results.
ALLHAT Conclusions • Among the HF cases, CCB’s were the most used BP drug prior to entry into ALLHAT, followed by diuretics and ACE inhibitors. • Pts on any prior BP med (vs. none) were at higher risk of developing HF. • These findings are noteworthy for those on CCB’s and BB’s at entry (confounding by indication? ). • These findings suggest that the type of BP drug at entry is not a major determinant of the HF results.


