3152851870fede4dde4a0df07bbcf0a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 All That Wheezes… Andrew Lipton, MD, MPH&TM MAJ, USA, MC Chief, Pediatric Pulmonology San Antonio Military Pediatric Center
All That Wheezes… Andrew Lipton, MD, MPH&TM MAJ, USA, MC Chief, Pediatric Pulmonology San Antonio Military Pediatric Center

 What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Stertor • Low-pitched, rumbling • Inspiratory • Nasopharynx, oropharynx, nasal passage • Loudest over neck, cheeks
What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Stertor • Low-pitched, rumbling • Inspiratory • Nasopharynx, oropharynx, nasal passage • Loudest over neck, cheeks
 What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Stridor • Harsh noise caused by turbulent flow • Inspiratory = larynx • Expiratory = trachea • Biphasic = fixed lesion in subglottic region
What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Stridor • Harsh noise caused by turbulent flow • Inspiratory = larynx • Expiratory = trachea • Biphasic = fixed lesion in subglottic region
 What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Wheeze • Higher-pitched expiratory noise • Monophonic, homophonous = large airway = expiratory stridor • Polyphonic, heterophonous, musical = small airways
What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Wheeze • Higher-pitched expiratory noise • Monophonic, homophonous = large airway = expiratory stridor • Polyphonic, heterophonous, musical = small airways
 What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Secretory Noise • Gurgling, polyphonic, upper or lower airway • Highly variable
What is a “wheeze” Definitions of obstructive noises § Secretory Noise • Gurgling, polyphonic, upper or lower airway • Highly variable
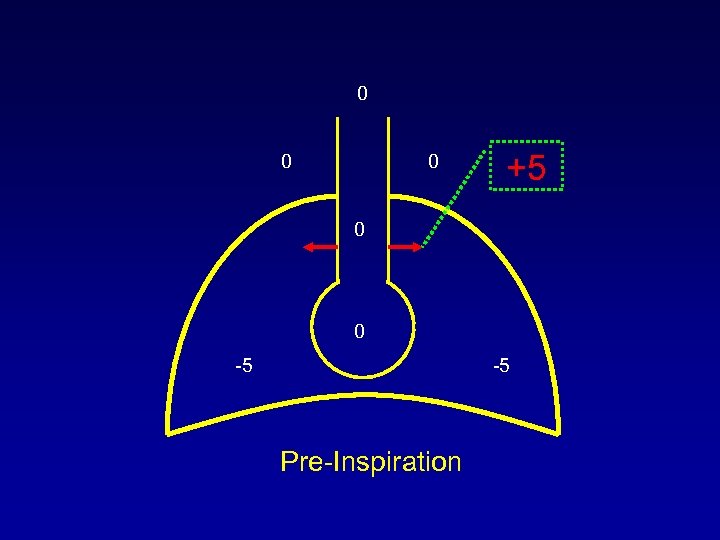 0 0 0 +5 0 0 -5 -5 Pre-Inspiration
0 0 0 +5 0 0 -5 -5 Pre-Inspiration
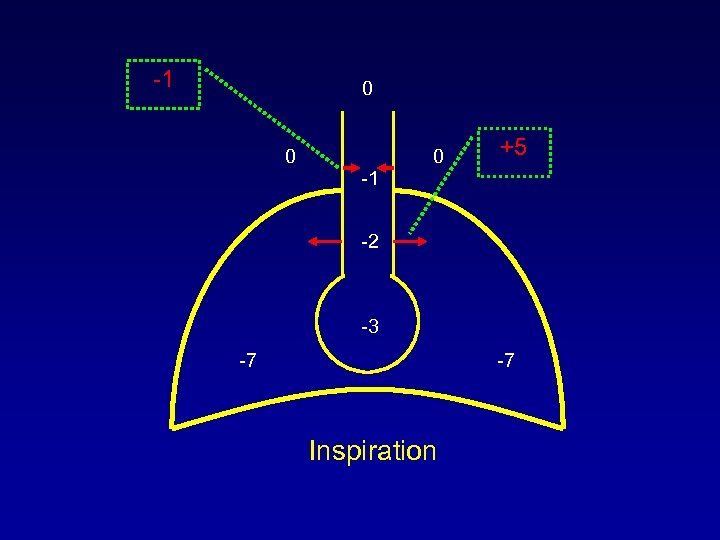 -1 0 0 0 +5 -1 -2 -3 -7 -7 Inspiration
-1 0 0 0 +5 -1 -2 -3 -7 -7 Inspiration
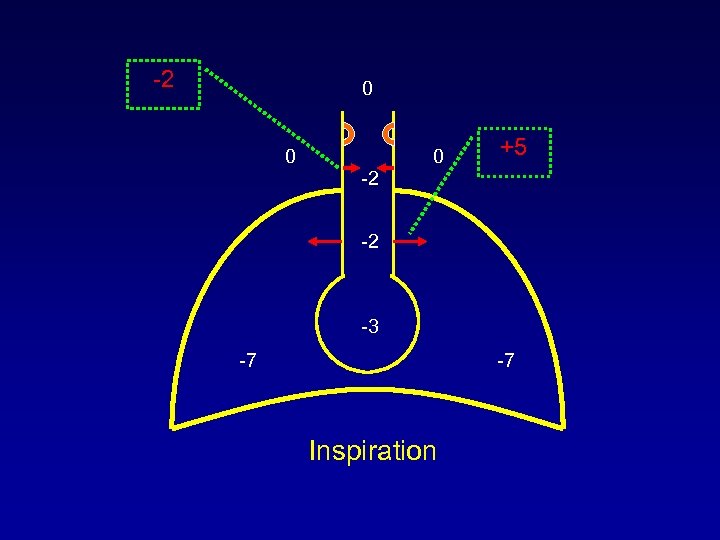 -2 0 0 0 +5 -2 -2 -3 -7 -7 Inspiration
-2 0 0 0 +5 -2 -2 -3 -7 -7 Inspiration
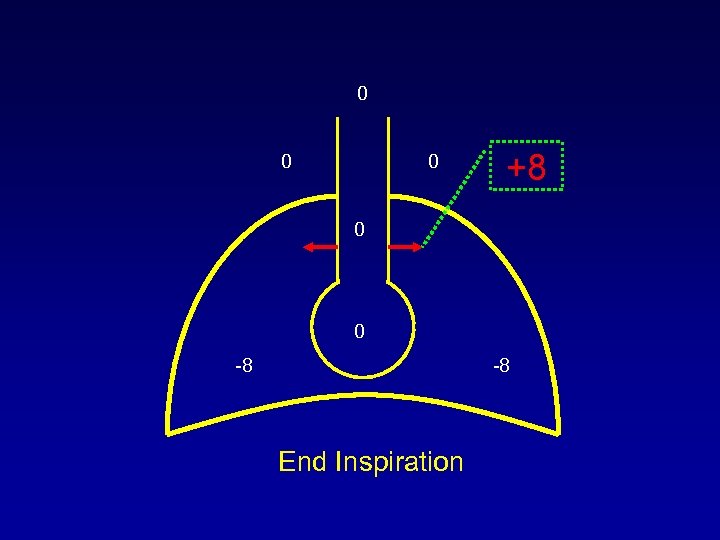 0 0 0 +8 0 0 -8 -8 End Inspiration
0 0 0 +8 0 0 -8 -8 End Inspiration
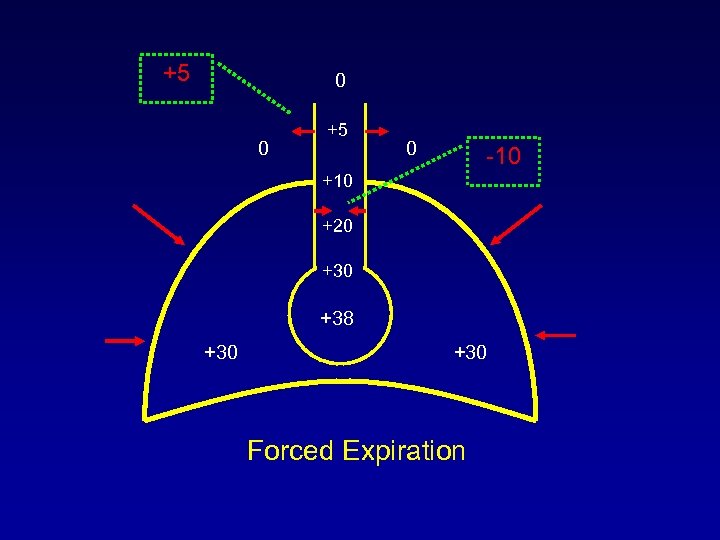 +5 0 0 +5 0 -10 +20 +38 +30 Forced Expiration
+5 0 0 +5 0 -10 +20 +38 +30 Forced Expiration
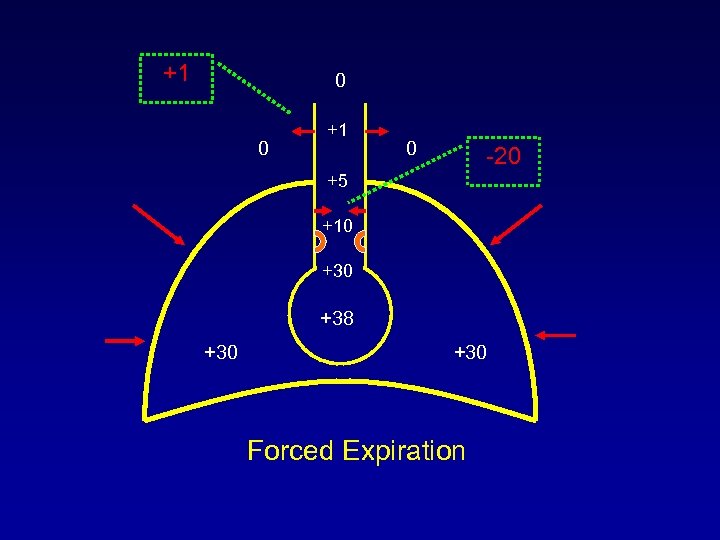 +1 0 0 +1 0 -20 +5 +10 +38 +30 Forced Expiration
+1 0 0 +1 0 -20 +5 +10 +38 +30 Forced Expiration

 Stertor Causes § Choanal atresia § Mandibular hypoplasia § Macroglossia § Nasal congestion § Adenotonsillar hypertrophy § Pharyngeal insufficiency § Encephalocele § Dermoid of base of tongue § Thyroglossal duct cyst § Lingual thyroid
Stertor Causes § Choanal atresia § Mandibular hypoplasia § Macroglossia § Nasal congestion § Adenotonsillar hypertrophy § Pharyngeal insufficiency § Encephalocele § Dermoid of base of tongue § Thyroglossal duct cyst § Lingual thyroid
 Inspiratory Stridor Causes § Laryngomalacia § Vocal cord paralysis • Unilateral – left (recurrent laryngeal nerve) • Bilateral – brainstem § Laryngotracheoesophageal cleft § Laryngocele § Laryngeal polyp § Abscess § Hypotonia
Inspiratory Stridor Causes § Laryngomalacia § Vocal cord paralysis • Unilateral – left (recurrent laryngeal nerve) • Bilateral – brainstem § Laryngotracheoesophageal cleft § Laryngocele § Laryngeal polyp § Abscess § Hypotonia
 Inspiratory Stridor Laryngomalacia § § § 60% of insp. stridor 90% require no intervention Improves when prone Worsens with activity Worsens over first 1 -6 mos, then improves Watch for FTT, apnea, cyanosis
Inspiratory Stridor Laryngomalacia § § § 60% of insp. stridor 90% require no intervention Improves when prone Worsens with activity Worsens over first 1 -6 mos, then improves Watch for FTT, apnea, cyanosis

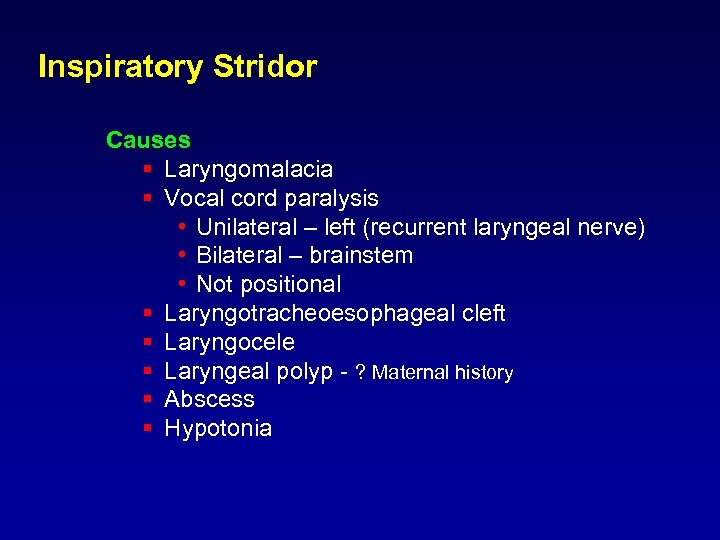 Inspiratory Stridor Causes § Laryngomalacia § Vocal cord paralysis • Unilateral – left (recurrent laryngeal nerve) • Bilateral – brainstem • Not positional § Laryngotracheoesophageal cleft § Laryngocele § Laryngeal polyp - ? Maternal history § Abscess § Hypotonia
Inspiratory Stridor Causes § Laryngomalacia § Vocal cord paralysis • Unilateral – left (recurrent laryngeal nerve) • Bilateral – brainstem • Not positional § Laryngotracheoesophageal cleft § Laryngocele § Laryngeal polyp - ? Maternal history § Abscess § Hypotonia
 Biphasic Stridor Causes § Subglottic stenosis • Congenital • Acquired – intubation, croup § Subglottic hemangioma § Laryngeal web § GERD
Biphasic Stridor Causes § Subglottic stenosis • Congenital • Acquired – intubation, croup § Subglottic hemangioma § Laryngeal web § GERD
 Biphasic Stridor Causes § Croup – acute barky cough, stridor, resp. distress • • • Low grade fever Rhinorrhea Worse at night 3 mos-3 yrs Parinfluenza 1 -3, RSV, Influenza Fall/Winter
Biphasic Stridor Causes § Croup – acute barky cough, stridor, resp. distress • • • Low grade fever Rhinorrhea Worse at night 3 mos-3 yrs Parinfluenza 1 -3, RSV, Influenza Fall/Winter
 Biphasic Stridor Causes § Recurrent Croup • Consider underlying airway anomaly • GERD • Spasmodic (reactive airways)
Biphasic Stridor Causes § Recurrent Croup • Consider underlying airway anomaly • GERD • Spasmodic (reactive airways)
 Expiratory Stridor Causes § § § § § Tracheomalacia Bronchomalacia Vascular Ring/Sling Complete Tracheal Ring Tracheoesophageal Fistula Bronchogenic Cyst Mediastinal Mass Foreign Body GERD
Expiratory Stridor Causes § § § § § Tracheomalacia Bronchomalacia Vascular Ring/Sling Complete Tracheal Ring Tracheoesophageal Fistula Bronchogenic Cyst Mediastinal Mass Foreign Body GERD
 Expiratory Stridor Causes § Tracheobronchomalacia • • • Deficient cartilage rings Worse with exertion, agitation Prolonged expiratory phase Narrow trachea on expiratory lateral films Primary vs. Secondary § BPD, TEF, vascular anomalies
Expiratory Stridor Causes § Tracheobronchomalacia • • • Deficient cartilage rings Worse with exertion, agitation Prolonged expiratory phase Narrow trachea on expiratory lateral films Primary vs. Secondary § BPD, TEF, vascular anomalies



 Wheezing Causes § § § § Asthma Bronchiolitis Pneumonia GERD – inflammation, bronchospasm Heart Failure – often presents around 2 mos BPD Other: CF, Ciliary Dykinesia, Food Allergy
Wheezing Causes § § § § Asthma Bronchiolitis Pneumonia GERD – inflammation, bronchospasm Heart Failure – often presents around 2 mos BPD Other: CF, Ciliary Dykinesia, Food Allergy
 History § § Congenital or acquired Acute, Chronic, or intermittent Positional? Feeding – gag/choke/cough, suck, emesis, fatigue § Voice/cry quality
History § § Congenital or acquired Acute, Chronic, or intermittent Positional? Feeding – gag/choke/cough, suck, emesis, fatigue § Voice/cry quality
 History § FTT – increased WOB, poor feeding • >90% - think of GERD § § § Cyanosis Apnea Fever Cough Nocturnal Sxs
History § FTT – increased WOB, poor feeding • >90% - think of GERD § § § Cyanosis Apnea Fever Cough Nocturnal Sxs
 History § Birth/Neonatal History § Other anomalies: cardiac, hemangiomas, eczema, CHARGE, VACTERL, Arnold-Chiari, hypotonia, etc. § Family Hx – anomalies, CF, immunodeficiency, asthma, GERD, atopy § Exposure – smoke, pollutants, irritants, Foreign body: toys, foods, older sibs
History § Birth/Neonatal History § Other anomalies: cardiac, hemangiomas, eczema, CHARGE, VACTERL, Arnold-Chiari, hypotonia, etc. § Family Hx – anomalies, CF, immunodeficiency, asthma, GERD, atopy § Exposure – smoke, pollutants, irritants, Foreign body: toys, foods, older sibs
 Exam § § § Nose Pharynx, tonsils, tongue, face, mandible, palate Neck Cardiac Chest Respiration: • Pattern, rate, accessory muscle use, sounds, change with position, oxygenation § Abdomen – hepatomegaly, masses § Tone § Skin – eczema, hemangiomas, cyanosis
Exam § § § Nose Pharynx, tonsils, tongue, face, mandible, palate Neck Cardiac Chest Respiration: • Pattern, rate, accessory muscle use, sounds, change with position, oxygenation § Abdomen – hepatomegaly, masses § Tone § Skin – eczema, hemangiomas, cyanosis
 Radiographs § § § Lateral neck Chest PA/Lateral CT Head/Neck/Chest UGI, Videofluoroscopic swallowing study Airway fluoroscopy MRI/MRA – chest, brainstem
Radiographs § § § Lateral neck Chest PA/Lateral CT Head/Neck/Chest UGI, Videofluoroscopic swallowing study Airway fluoroscopy MRI/MRA – chest, brainstem
 Other Studies § Bronchoscopy • Flexible • Rigid § Laryngoscopy § Polysomnography (sleep study) § Echocardiography § Infant PFTs § p. H Probe, scan § ABG
Other Studies § Bronchoscopy • Flexible • Rigid § Laryngoscopy § Polysomnography (sleep study) § Echocardiography § Infant PFTs § p. H Probe, scan § ABG
 Other Studies § § § Allergy testing Immunoglobulins CBC ABG Sweat Cl Ciliary Bx
Other Studies § § § Allergy testing Immunoglobulins CBC ABG Sweat Cl Ciliary Bx



