9b40bef91d0214827b9c58b6985dfa90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Aligning KM Market’s Top and Bottom Lines Erick Brethenoux APQC’s Fifth Knowledge Management Conference - December 8, 2000
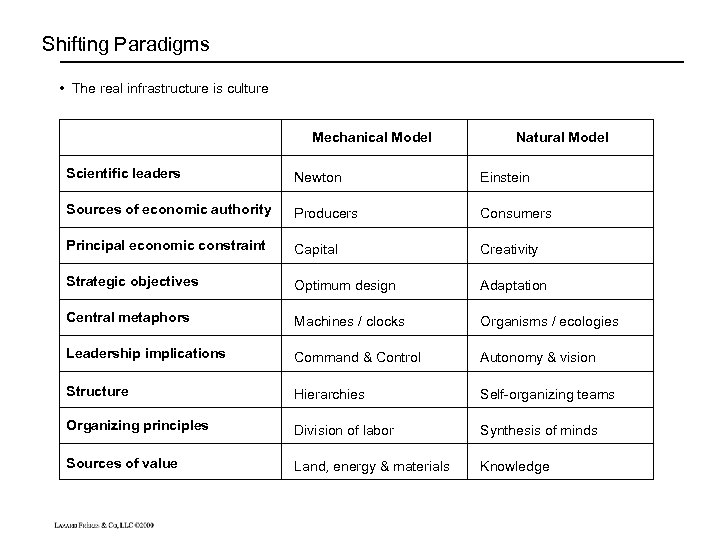
Shifting Paradigms • The real infrastructure is culture Mechanical Model Natural Model Scientific leaders Newton Einstein Sources of economic authority Producers Consumers Principal economic constraint Capital Creativity Strategic objectives Optimum design Adaptation Central metaphors Machines / clocks Organisms / ecologies Leadership implications Command & Control Autonomy & vision Structure Hierarchies Self-organizing teams Organizing principles Division of labor Synthesis of minds Sources of value Land, energy & materials Knowledge
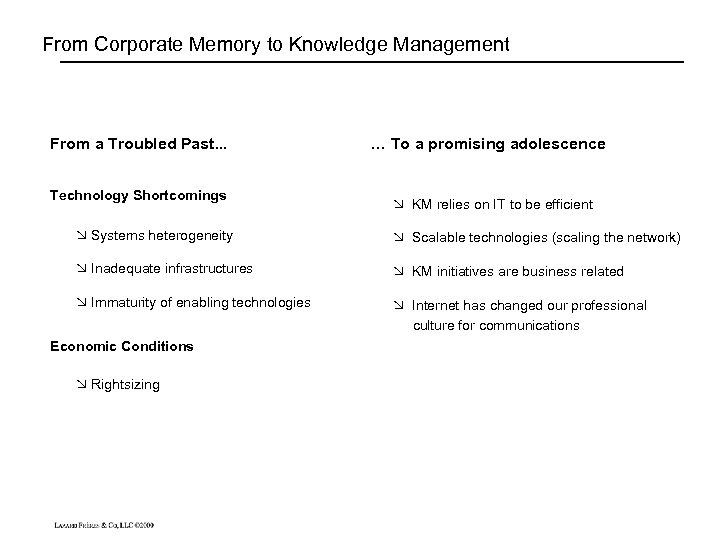
From Corporate Memory to Knowledge Management From a Troubled Past. . . Technology Shortcomings … To a promising adolescence Ø KM relies on IT to be efficient Ø Systems heterogeneity Ø Scalable technologies (scaling the network) Ø Inadequate infrastructures Ø KM initiatives are business related Ø Immaturity of enabling technologies Ø Internet has changed our professional culture for communications Economic Conditions Ø Rightsizing
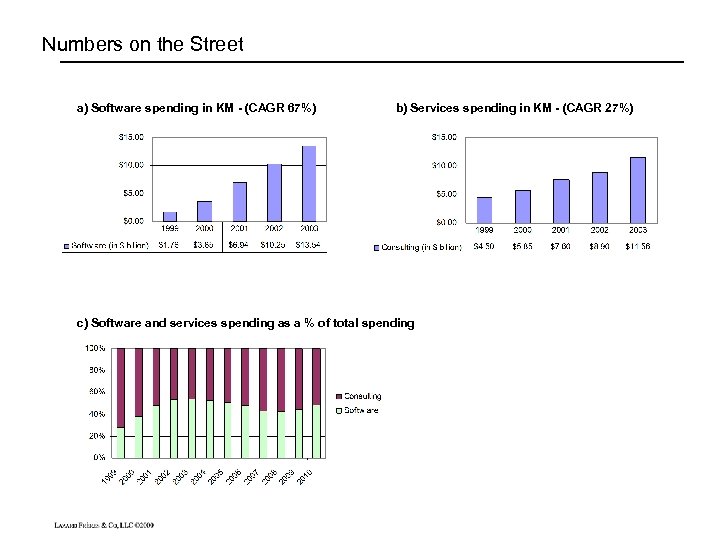
Numbers on the Street a) Software spending in KM - (CAGR 67%) b) Services spending in KM - (CAGR 27%) c) Software and services spending as a % of total spending
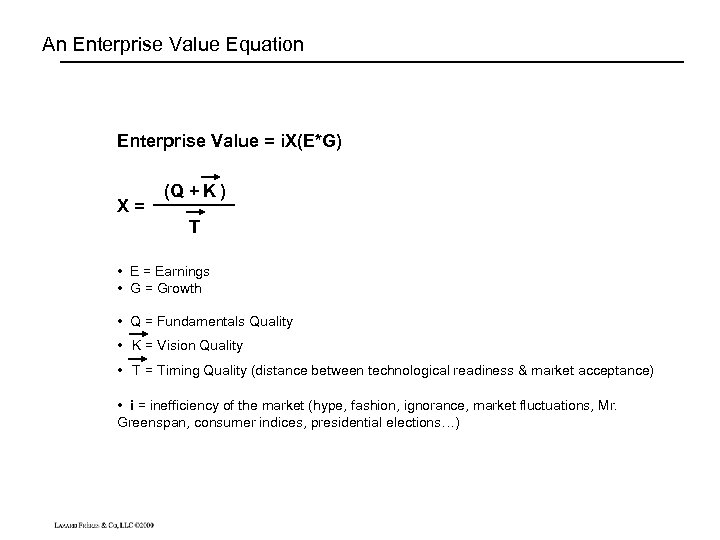
An Enterprise Value Equation Enterprise Value = i. X(E*G) X= (Q + K ) T • E = Earnings • G = Growth • Q = Fundamentals Quality • K = Vision Quality • T = Timing Quality (distance between technological readiness & market acceptance) • i = inefficiency of the market (hype, fashion, ignorance, market fluctuations, Mr. Greenspan, consumer indices, presidential elections…)
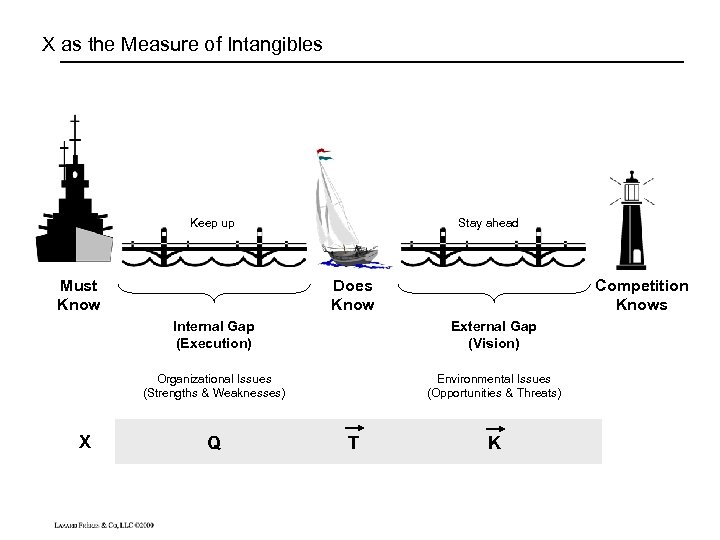
X as the Measure of Intangibles Keep up Must Know Stay ahead Does Know Competition Knows Internal Gap (Execution) Organizational Issues (Strengths & Weaknesses) X External Gap (Vision) Environmental Issues (Opportunities & Threats) Q T K
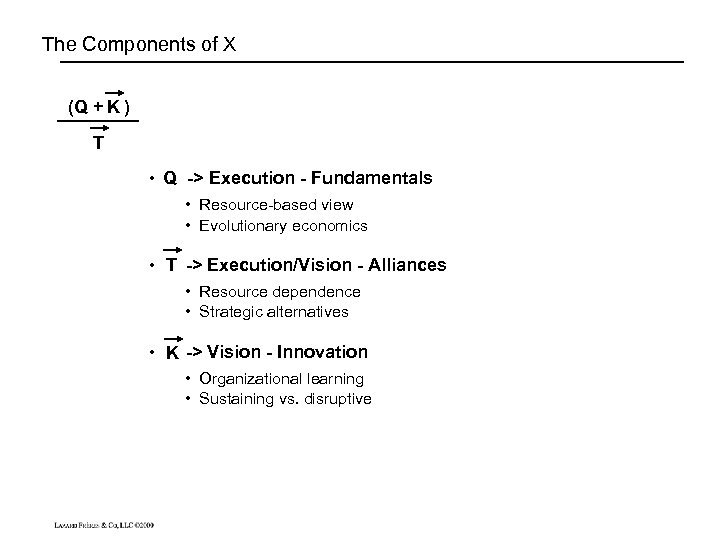
The Components of X (Q + K ) T • Q -> Execution - Fundamentals • Resource-based view • Evolutionary economics • T -> Execution/Vision - Alliances • Resource dependence • Strategic alternatives • K -> Vision - Innovation • Organizational learning • Sustaining vs. disruptive
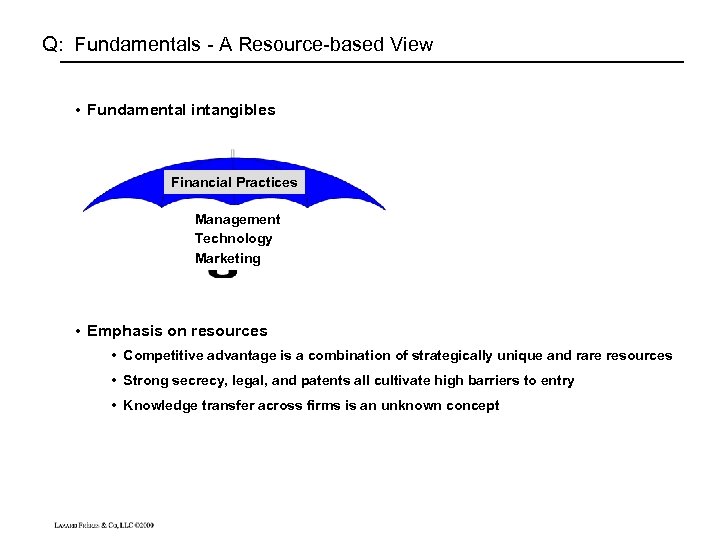
Q: Fundamentals - A Resource-based View • Fundamental intangibles Financial Practices Management Technology Marketing • Emphasis on resources • Competitive advantage is a combination of strategically unique and rare resources • Strong secrecy, legal, and patents all cultivate high barriers to entry • Knowledge transfer across firms is an unknown concept
Q: Fundamentals - Evolutionary Economics • Know-how embedded in enterprise’s business processes • Business processes evolve in response to external conditions • Internal selection for improved business processes • Breeding of best practices • Competency traps generated by sustained and repeated evolution
T : Alliances - Resource Dependence • Strategic Focus: Manage change via inter-firm relationships • Level competitive differences through alliances and standards • Manage absorptive capacity through acquisitions and controls • Knowledge resides in networks of relationships
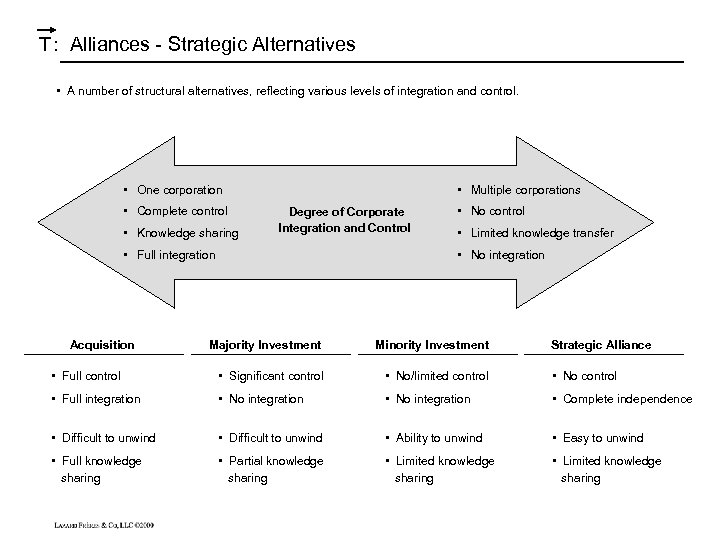
T : Alliances - Strategic Alternatives • A number of structural alternatives, reflecting various levels of integration and control. • One corporation • Complete control • Knowledge sharing • Multiple corporations Degree of Corporate Integration and Control • Full integration Acquisition • No control • Limited knowledge transfer • No integration Majority Investment Minority Investment Strategic Alliance • Full control • Significant control • No/limited control • No control • Full integration • No integration • Complete independence • Difficult to unwind • Ability to unwind • Easy to unwind • Full knowledge sharing • Partial knowledge sharing • Limited knowledge sharing

K : Innovation - Organizational Learning • Enterprise’s adaptation is dynamic • Learning as part of the corporate culture - directed / non-directed • Failure to achieve goals stimulates new learning • Limited resources - necessary condition for innovation • Incremental, sustaining innovation leads to myopic learning • Knowledge creation requires strategic intent to invest resources • Institutionalization of change and “technology watch” strategy
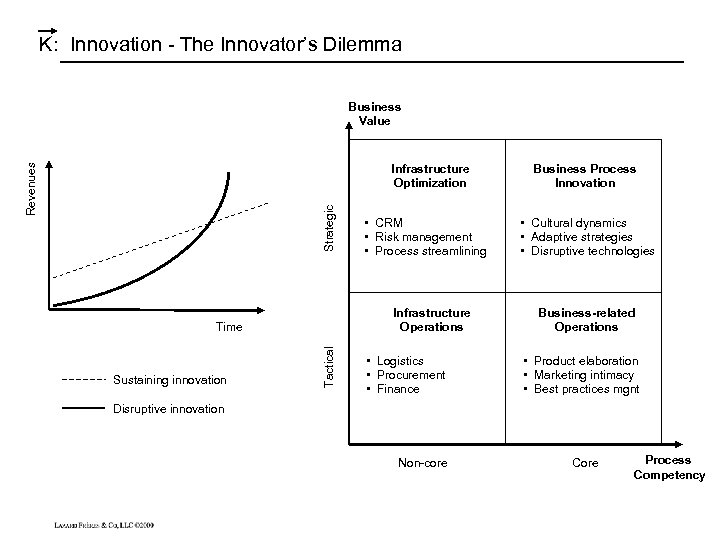
K : Innovation - The Innovator’s Dilemma Business Value Strategic Revenues Infrastructure Optimization Infrastructure Operations Tactical Time Sustaining innovation • CRM • Risk management • Process streamlining • Logistics • Procurement • Finance Business Process Innovation • Cultural dynamics • Adaptive strategies • Disruptive technologies Business-related Operations • Product elaboration • Marketing intimacy • Best practices mgnt Disruptive innovation Non-core Core Process Competency

Value Innovation: The Strategic Logic of High-Growth Companies • High-growth companies do not compete - they make their competitors irrelevant • They build on the powerful commonalities in features that customers value • They think in terms of total solutions (rather than merely overcome compromises enforced by the industry) • They build fundamentally different value curves for what customers value • Enterprise value in Pioneers, sizeable Migrators, but never in Settlers
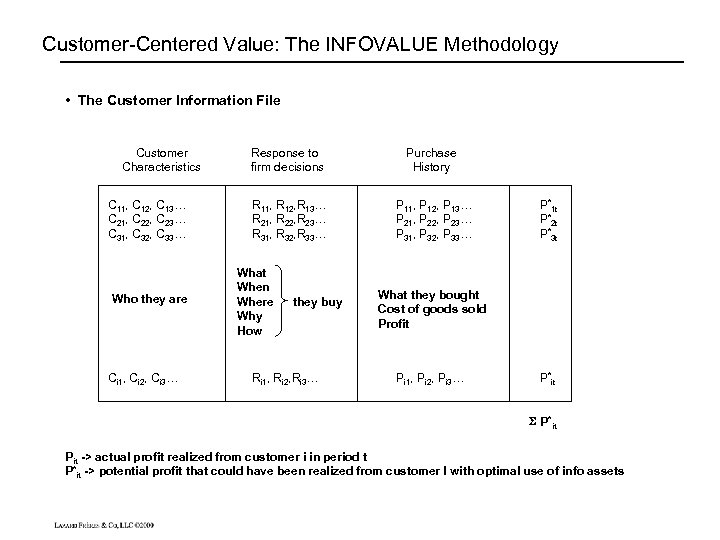
Customer-Centered Value: The INFOVALUE Methodology • The Customer Information File Customer Characteristics C 11, C 12, C 13… C 21, C 22, C 23… C 31, C 32, C 33… Who they are Ci 1, Ci 2, Ci 3… Response to firm decisions Purchase History R 11, R 12, R 13… R 21, R 22, R 23… R 31, R 32, R 33… P 11, P 12, P 13… P 21, P 22, P 23… P 31, P 32, P 33… What When Where Why How they buy Ri 1, Ri 2, Ri 3… P*1 t P*2 t P*3 t What they bought Cost of goods sold Profit Pi 1, Pi 2, Pi 3… P*it Pit -> actual profit realized from customer i in period t P*it -> potential profit that could have been realized from customer I with optimal use of info assets

Investing in Value: Technology Strategies “Build vs. Buy” strategy beyond technologies • Proactive management of intellectual properties • Innovation does not imply reinventing the wheel • Greater attention to external monitoring of technologies & business processes • Organizational changes to support technology licensing, joint ventures and acquisition of external technologies and business processes Bottom Line: Uncompromising with Q, practical with K, aggressive with T
The Knowledge Management Quest Approaching Infinity
9b40bef91d0214827b9c58b6985dfa90.ppt