e7c5064a68620ea886be60236cbfe6d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
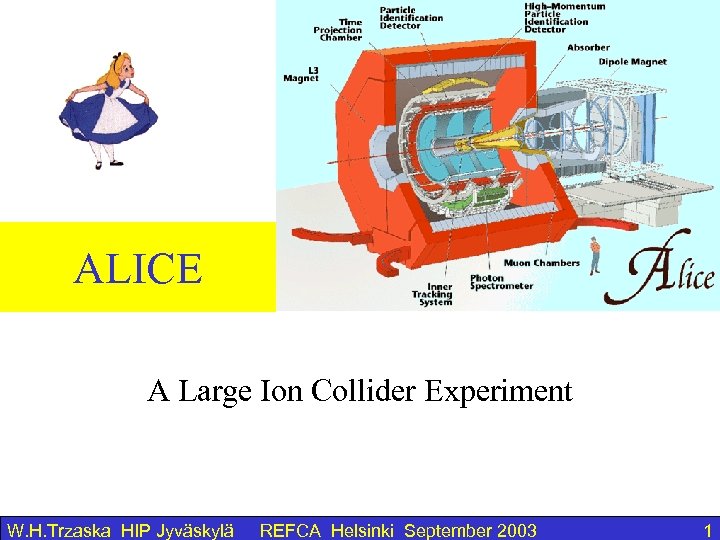 ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 1
ALICE A Large Ion Collider Experiment W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 1
 The smallest of the big LHC experiments • Dedicated to HI collisions (Pb – Pb, Ar – Ar, O – O) –Where everything is hotter, bigger, longer lived • Will also measure p – p W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 2
The smallest of the big LHC experiments • Dedicated to HI collisions (Pb – Pb, Ar – Ar, O – O) –Where everything is hotter, bigger, longer lived • Will also measure p – p W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 2
 Some of the main physics goals (QM 2002) • Global observables: multiplicities, distributions • Degrees of freedom as a function of T hadron ratios and spectra, dilepton continuum, direct photons • Early state manifestation of collective effects: elliptic flow • Energy loss of partons in quark gluon plasma: jet quenching, high pt spectra, open charm and open beauty • Deconfinement: charmonium and bottonium spectroscopy • Chiral symmetry restoration: neutral to charged ratios, res. decays • Fluctuation phenomena - critical behavior: event-by-event particle comp. and spectra • Geometry of the emitting source: HBT, impact parameter via zero-degree energy flow • pp collisions in a new energy domain W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 3
Some of the main physics goals (QM 2002) • Global observables: multiplicities, distributions • Degrees of freedom as a function of T hadron ratios and spectra, dilepton continuum, direct photons • Early state manifestation of collective effects: elliptic flow • Energy loss of partons in quark gluon plasma: jet quenching, high pt spectra, open charm and open beauty • Deconfinement: charmonium and bottonium spectroscopy • Chiral symmetry restoration: neutral to charged ratios, res. decays • Fluctuation phenomena - critical behavior: event-by-event particle comp. and spectra • Geometry of the emitting source: HBT, impact parameter via zero-degree energy flow • pp collisions in a new energy domain W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 3
 …and the resulting Detector Challenge • ALICE is expected to be a multipurpose experiment – – with excellent tracking and secondary vertex capability with electron and muon detection with a high resolution gamma spectrometer and provide unique Particle Identification • ALICE is still evolving! – we are improving the ability to handle rare, hard signals (more sophisticated triggering, HLT) – building a large TRD (approved in 2001) – planning a single arm EM calorimeter (expected US contribution) W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 4
…and the resulting Detector Challenge • ALICE is expected to be a multipurpose experiment – – with excellent tracking and secondary vertex capability with electron and muon detection with a high resolution gamma spectrometer and provide unique Particle Identification • ALICE is still evolving! – we are improving the ability to handle rare, hard signals (more sophisticated triggering, HLT) – building a large TRD (approved in 2001) – planning a single arm EM calorimeter (expected US contribution) W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 4
 Finnish contribution to ALICE • Full member of the collaboration since 1998 – HIP & JYFL (University of Jyväskylä) • Core contribution – 1 M CHF (~ 0. 7 M€) • Substantial non-core contribution – Salaries, infrastructure, beam tests at Jyväskylä, etc. – Software, event generation, SDD test experiments and data analysis, mechanics, etc. • Currently the full focus of our group is on – Bonding of SSD modules (70% core) – T 0 detector (20% core) – Tracking W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 5
Finnish contribution to ALICE • Full member of the collaboration since 1998 – HIP & JYFL (University of Jyväskylä) • Core contribution – 1 M CHF (~ 0. 7 M€) • Substantial non-core contribution – Salaries, infrastructure, beam tests at Jyväskylä, etc. – Software, event generation, SDD test experiments and data analysis, mechanics, etc. • Currently the full focus of our group is on – Bonding of SSD modules (70% core) – T 0 detector (20% core) – Tracking W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 5
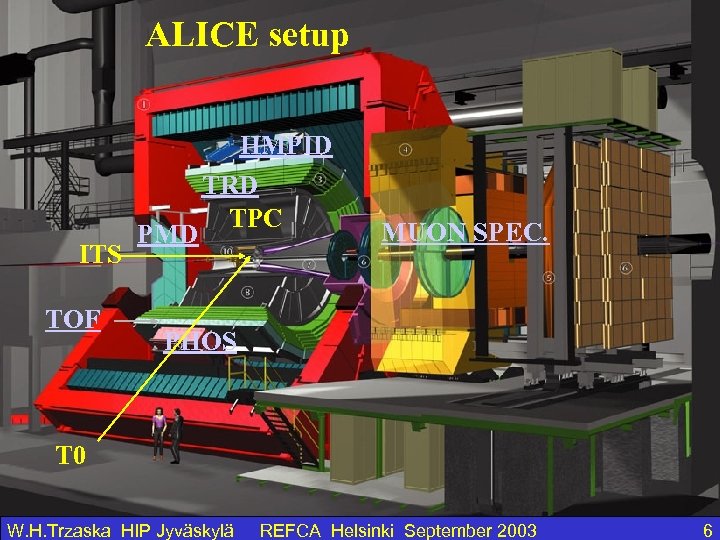 ALICE setup ITS TOF PMD HMPID TRD TPC MUON SPEC. PHOS T 0 W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 6
ALICE setup ITS TOF PMD HMPID TRD TPC MUON SPEC. PHOS T 0 W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 6
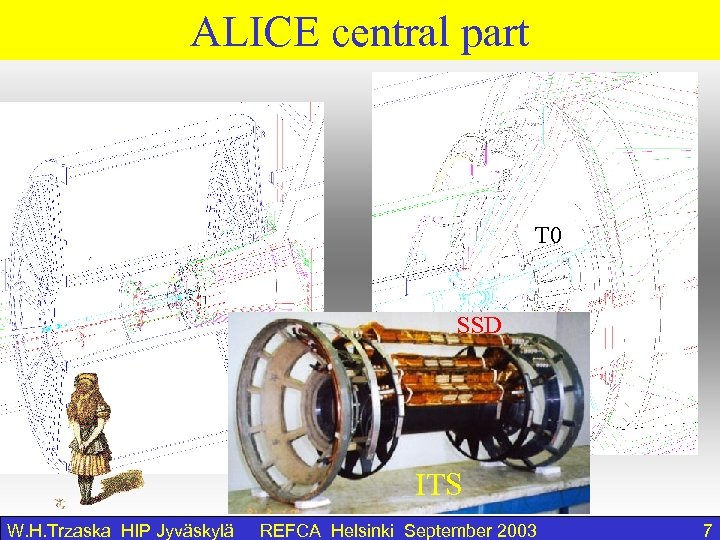 ALICE central part T 0 SSD ITS W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 7
ALICE central part T 0 SSD ITS W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 7
 SSD module • Each SSD is 75 x 42 mm in size, double -sided, 768 strips on each side • Each strip is bonded to the microcables with front-end electronics • 2000 modules must be produced • 500 for the Finnish core money and in Finland W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 8
SSD module • Each SSD is 75 x 42 mm in size, double -sided, 768 strips on each side • Each strip is bonded to the microcables with front-end electronics • 2000 modules must be produced • 500 for the Finnish core money and in Finland W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 8
 SSD module close-up W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 9
SSD module close-up W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 9
 Microcable – Detector Bonding W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 10
Microcable – Detector Bonding W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 10
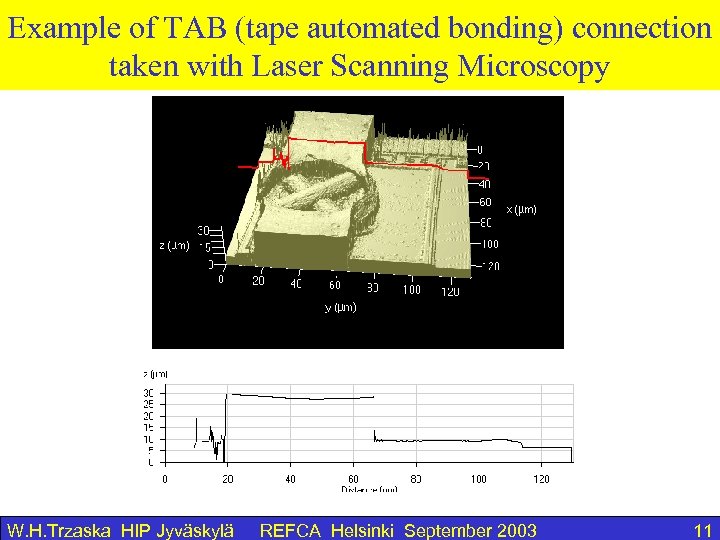 Example of TAB (tape automated bonding) connection taken with Laser Scanning Microscopy W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 11
Example of TAB (tape automated bonding) connection taken with Laser Scanning Microscopy W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 11
 Progress in bonding since 2002 • First complete modules have already been assembled and tested in-beam at CERN (September 2003) 4 modules in beam • Excellent work by Markku Oinonen, Zoran Radivojevic and Henri Seppänen • Support and help from ALICE • We have started from collaboration (Ukraine, an empty Lab in Helsinki Holland, France) (28 August 2001) Trigger scintillators Beam, 7 Ge. V/c p’s W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 12
Progress in bonding since 2002 • First complete modules have already been assembled and tested in-beam at CERN (September 2003) 4 modules in beam • Excellent work by Markku Oinonen, Zoran Radivojevic and Henri Seppänen • Support and help from ALICE • We have started from collaboration (Ukraine, an empty Lab in Helsinki Holland, France) (28 August 2001) Trigger scintillators Beam, 7 Ge. V/c p’s W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 12
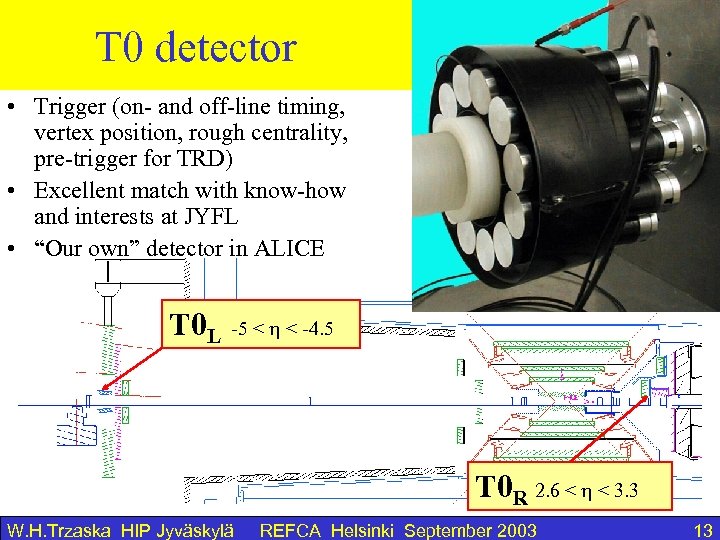 PMD pre. T 0 detector shower • Trigger (on- and off-line timing, vertex position, rough centrality, pre-trigger for TRD) • Excellent match with know-how and interests at JYFL • “Our own” detector in ALICE T 0 L -5 < < -4. 5 T 0 R 2. 6 < < 3. 3 W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 13
PMD pre. T 0 detector shower • Trigger (on- and off-line timing, vertex position, rough centrality, pre-trigger for TRD) • Excellent match with know-how and interests at JYFL • “Our own” detector in ALICE T 0 L -5 < < -4. 5 T 0 R 2. 6 < < 3. 3 W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 13
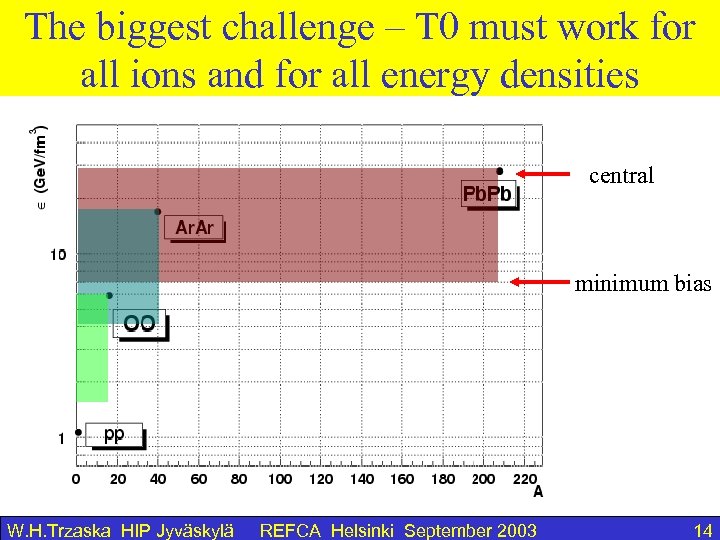 The biggest challenge – T 0 must work for all ions and for all energy densities central minimum bias W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 14
The biggest challenge – T 0 must work for all ions and for all energy densities central minimum bias W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 14
 T 0 progress since 2002 • Complete 1: 1 prototype ready • Prototypes of all the key electronics modules of T 0 have been build and tested in-beam at CERN – – Mean timer stability 0 ± 10 ps Time resolution T 0 = 37 ps Vertex resolution = 1. 3 cm Dynamic range 1: 500 • Prototype of the laser calibration system nearly completed • TDR nearly completed W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 15
T 0 progress since 2002 • Complete 1: 1 prototype ready • Prototypes of all the key electronics modules of T 0 have been build and tested in-beam at CERN – – Mean timer stability 0 ± 10 ps Time resolution T 0 = 37 ps Vertex resolution = 1. 3 cm Dynamic range 1: 500 • Prototype of the laser calibration system nearly completed • TDR nearly completed W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 15
 NA 49 Pb – Pb event W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 16
NA 49 Pb – Pb event W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 16
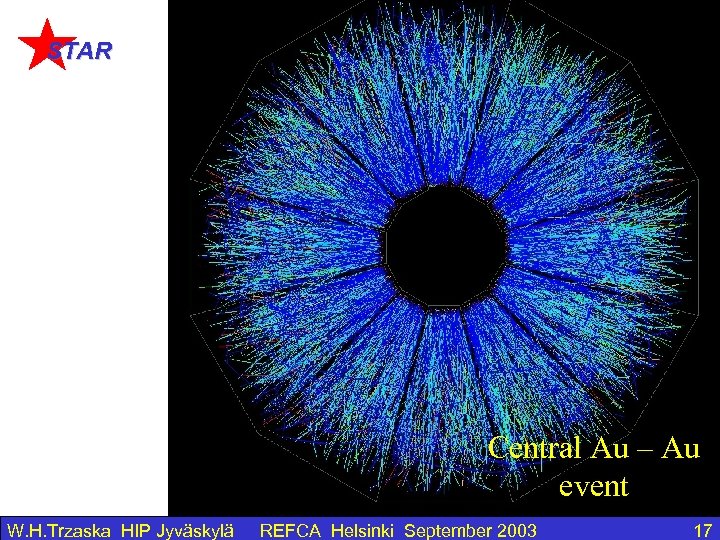 STAR Central Au – Au event W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 17
STAR Central Au – Au event W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä REFCA Helsinki September 2003 17
 ALICE tracking challenge • Can it be done? • Yes, but the question is when (speed) & how (efficiency) • In fact ALICE tracking is doing very well Simulated ALICE central event – Already tested with real data (cosmic+TPC) • Excellent work by Mariana Bondila together with people from CERN and Krakow W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä Nch(-0. 5< <0. 5) = 8000 REFCA Helsinki September 2003 18
ALICE tracking challenge • Can it be done? • Yes, but the question is when (speed) & how (efficiency) • In fact ALICE tracking is doing very well Simulated ALICE central event – Already tested with real data (cosmic+TPC) • Excellent work by Mariana Bondila together with people from CERN and Krakow W. H. Trzaska HIP Jyväskylä Nch(-0. 5< <0. 5) = 8000 REFCA Helsinki September 2003 18


