5907e4162221130587ad48126feffd25.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Algebra Direct Variation

Do Now §
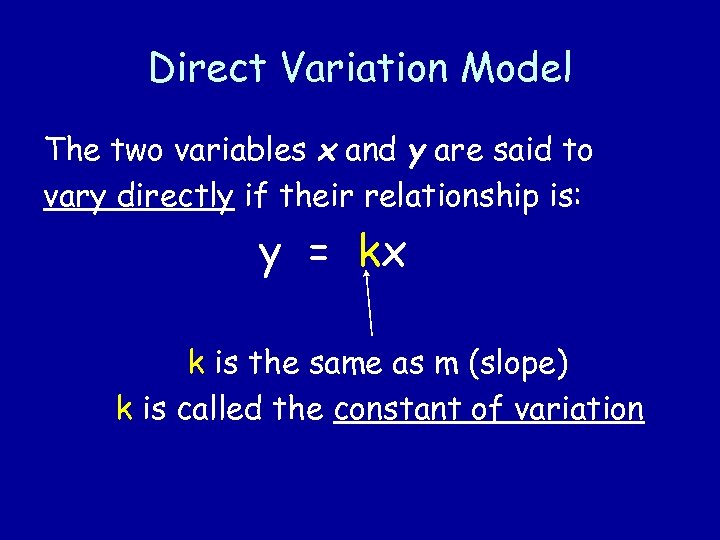
Direct Variation Model The two variables x and y are said to vary directly if their relationship is: y = kx k is the same as m (slope) k is called the constant of variation

The price of hot dogs varies directly with the number of hotdogs you buy You buy hotdogs. x represents the number of hotdogs you buy. y represents the price you pay. y = kx 21 = k(7) 7 7 Let’s figure out k, the price per hotdog. Suppose that when you buy 7 hotdogs, it costs $21. Plug that information into the model to solve for k. Now divide both sides by 7 to solve for k. k=3 The price per hotdog is $3. y = 3 x You could use this model to find the price (y) for any number of hotdogs (x) you buy.
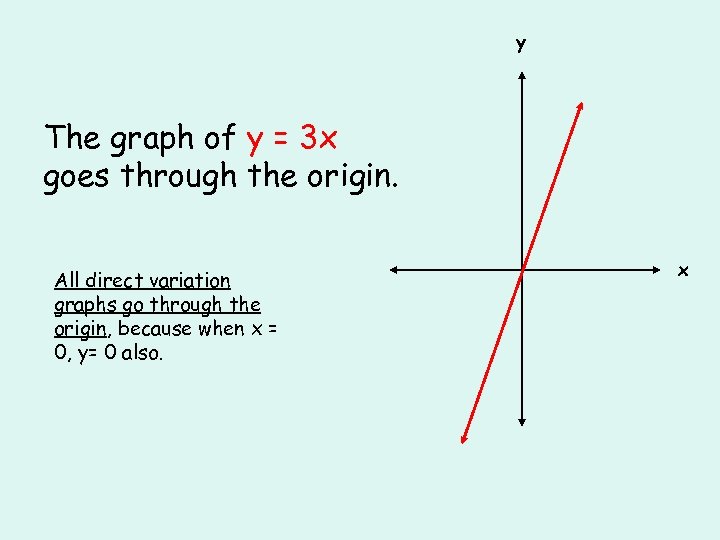
y The graph of y = 3 x goes through the origin. All direct variation graphs go through the origin, because when x = 0, y= 0 also. x
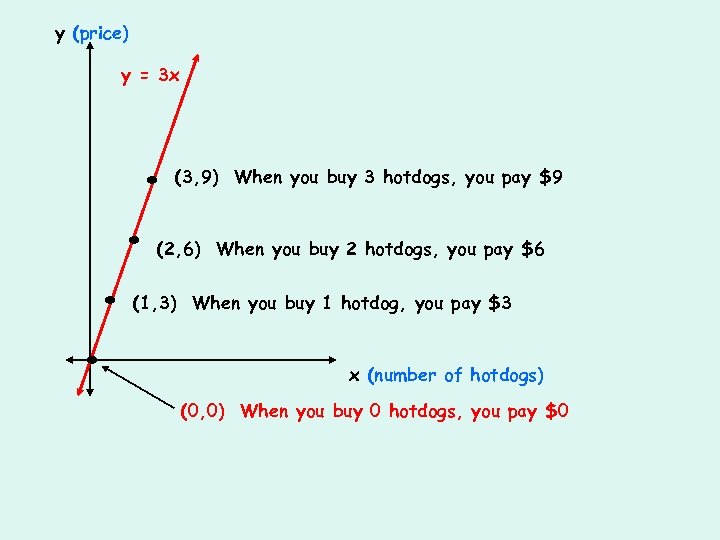
y (price) y = 3 x . . (3, 9) When you buy 3 hotdogs, you pay $9 (2, 6) When you buy 2 hotdogs, you pay $6 (1, 3) When you buy 1 hotdog, you pay $3 x (number of hotdogs) (0, 0) When you buy 0 hotdogs, you pay $0
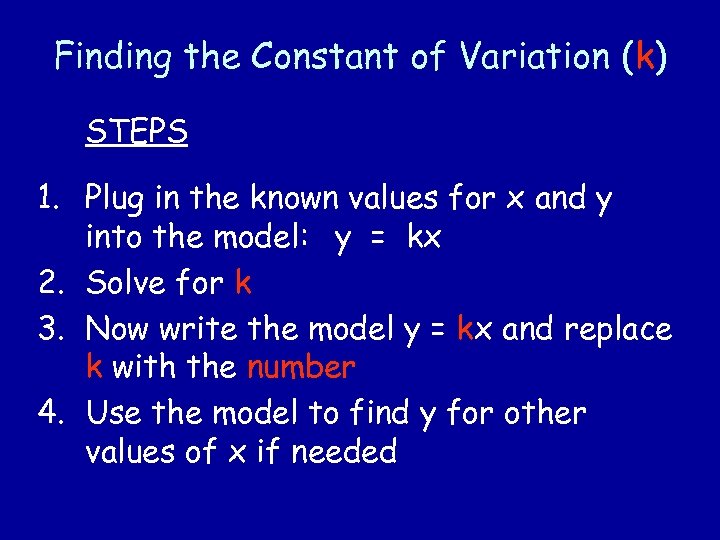
Finding the Constant of Variation (k) STEPS 1. Plug in the known values for x and y into the model: y = kx 2. Solve for k 3. Now write the model y = kx and replace k with the number 4. Use the model to find y for other values of x if needed
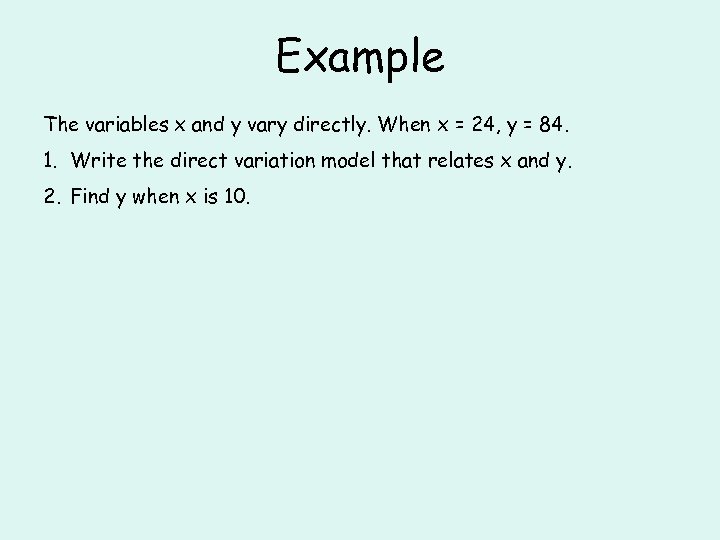
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = 24, y = 84. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 10.
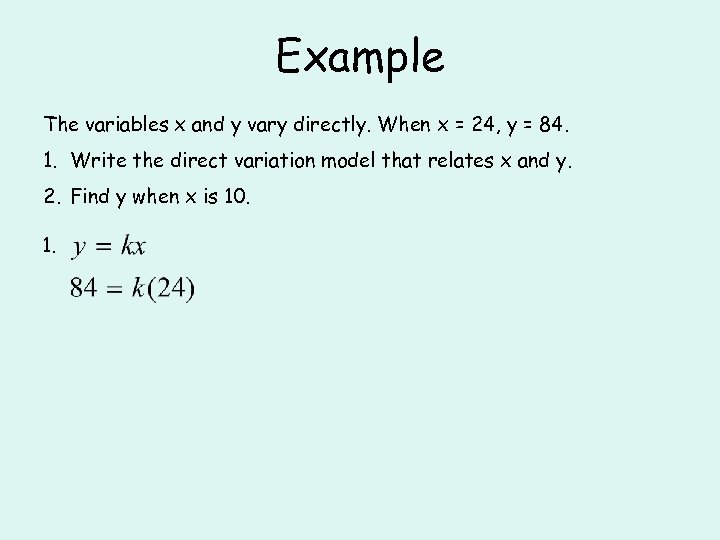
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = 24, y = 84. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 10. 1.
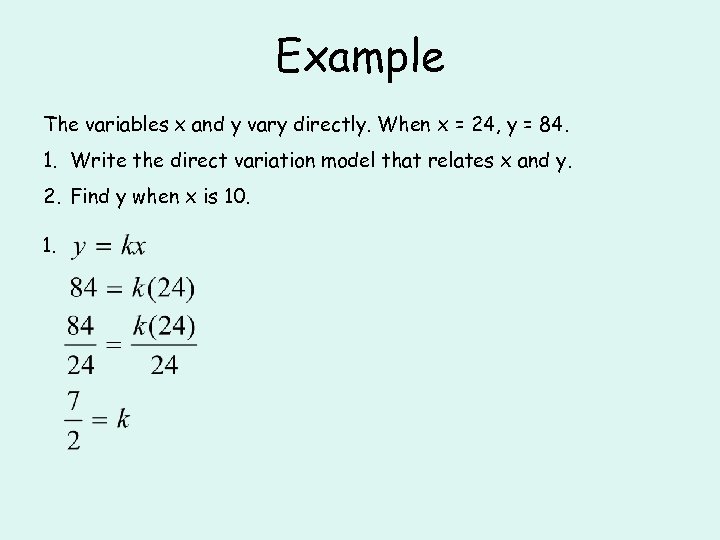
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = 24, y = 84. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 10. 1.
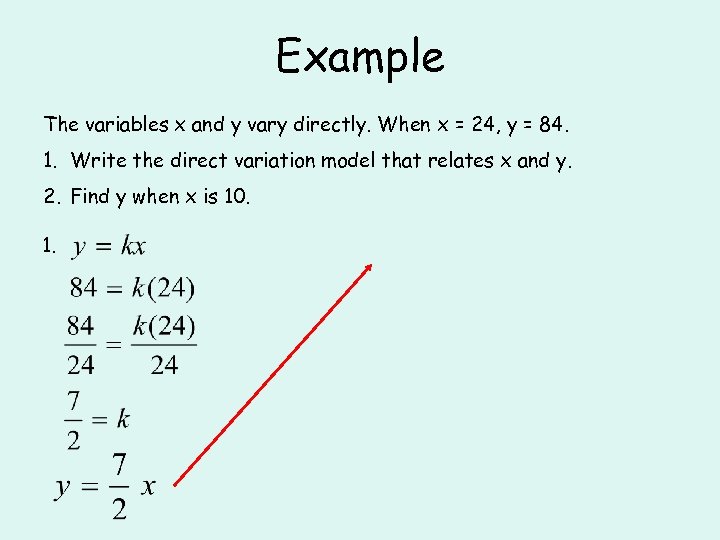
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = 24, y = 84. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 10. 1.
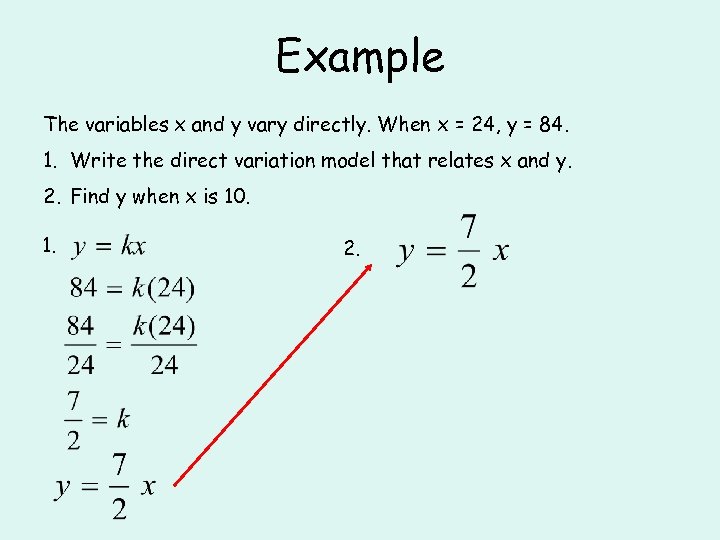
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = 24, y = 84. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 10. 1. 2.
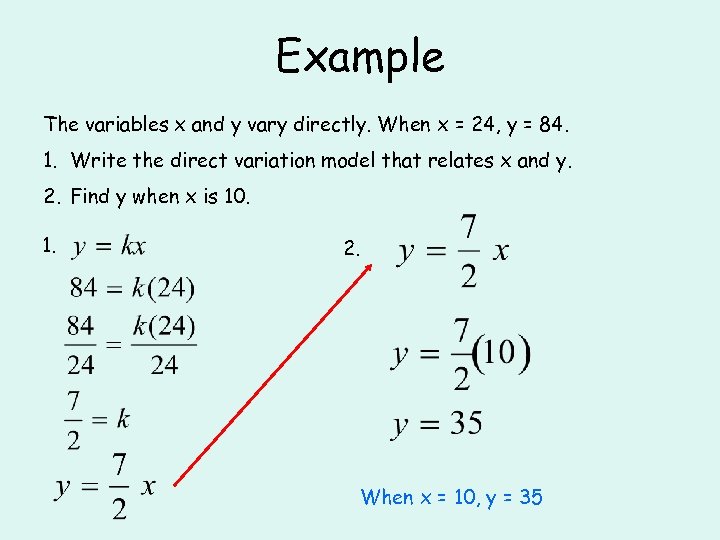
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = 24, y = 84. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 10. 1. 2. When x = 10, y = 35
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5.
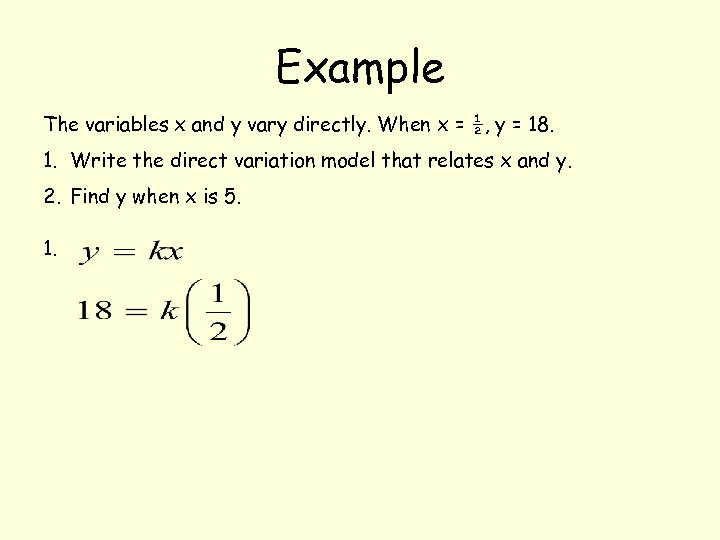
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5. 1.
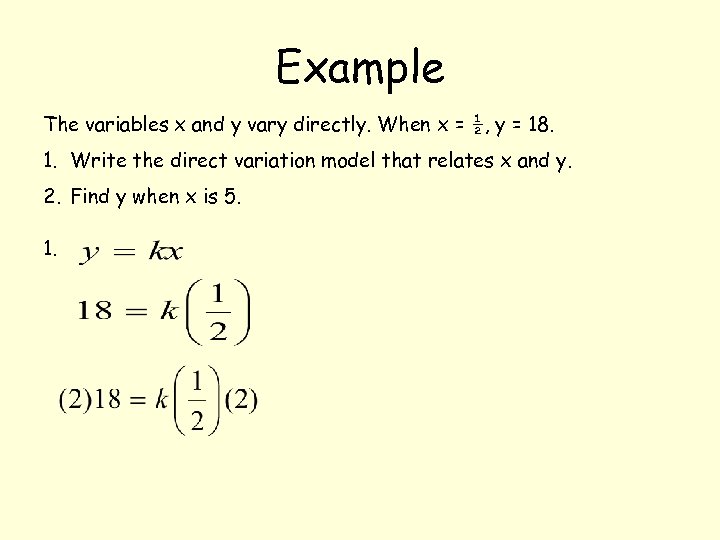
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5. 1.
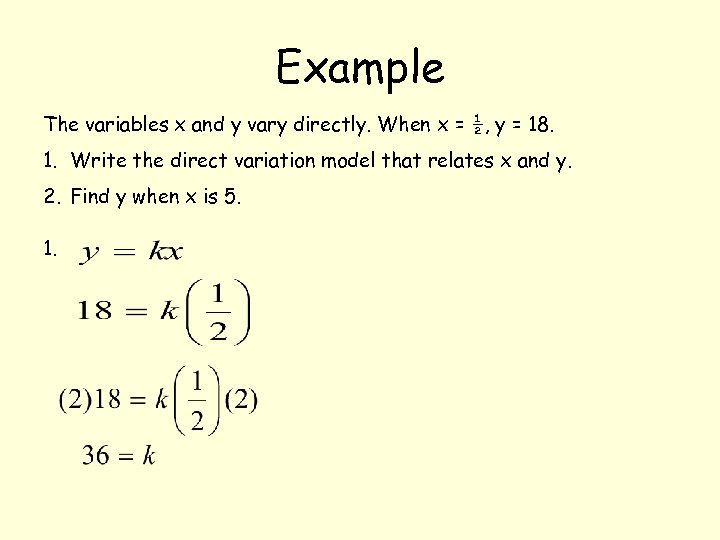
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5. 1.
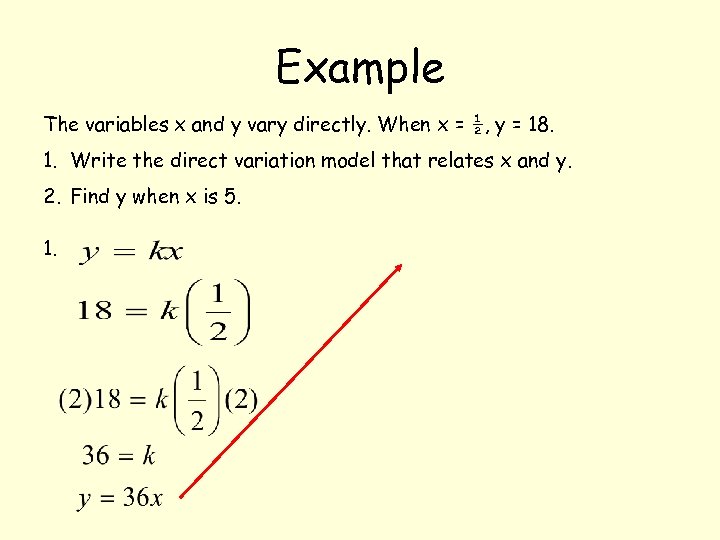
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5. 1.
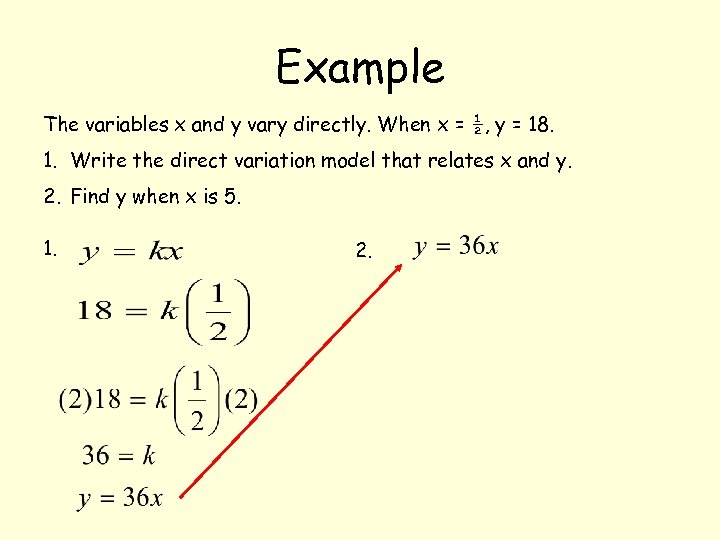
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5. 1. 2.
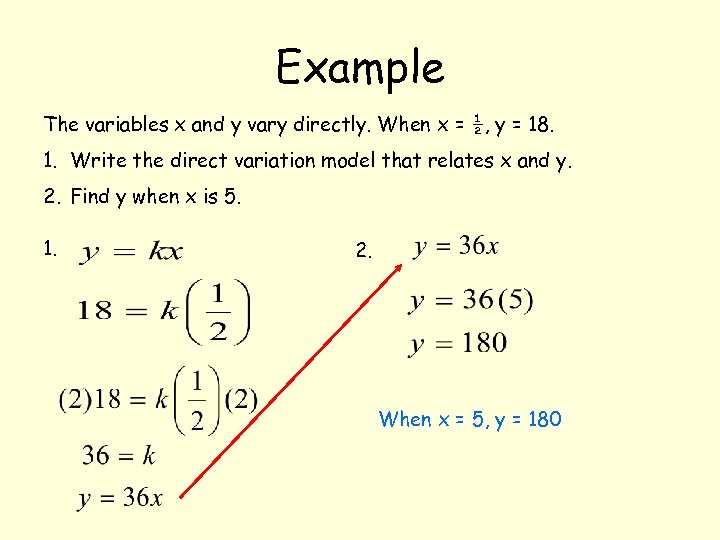
Example The variables x and y vary directly. When x = ½, y = 18. 1. Write the direct variation model that relates x and y. 2. Find y when x is 5. 1. 2. When x = 5, y = 180

Work Rookie-Pg. 302 # 9, 11 Veteran-Pg. 302 # 15, 17 All Star-Pg. 302 # 21, 25
5907e4162221130587ad48126feffd25.ppt