9062a4ed063d1f7ecd237b4d7d4de61a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Alert radio repeater automated backup, failover, recovery David Leader Hydro. Lynx Systems

Alert radio repeaters are critical points in a flood warning system telemetry network. l A single repeater failure can lead to major data loss during a flood warning event. – l Increased data loading can overwhelm a repeater – l System design redundancy is needed to prevent data loss. Data distribution over several repeater is needed to prevent repeater overloading. Hydro. Lynx worked with Washoe County, NV telemetry network manager to address these issues to – – Provide redundancy. Distribute radio channel use.
Washoe County, NV upgraded two Alert repeaters to automated failover. l Two repeaters in Washoe County receive Alert data on frequency f 1 and repeat data on frequency f 2. – – l One base station receives the repeated Alert data on frequency f 2. – l Peavine Peak Slide Mountain National Weather Service Office in Reno, NV Upgrade repeaters to 50386 with automated failover.
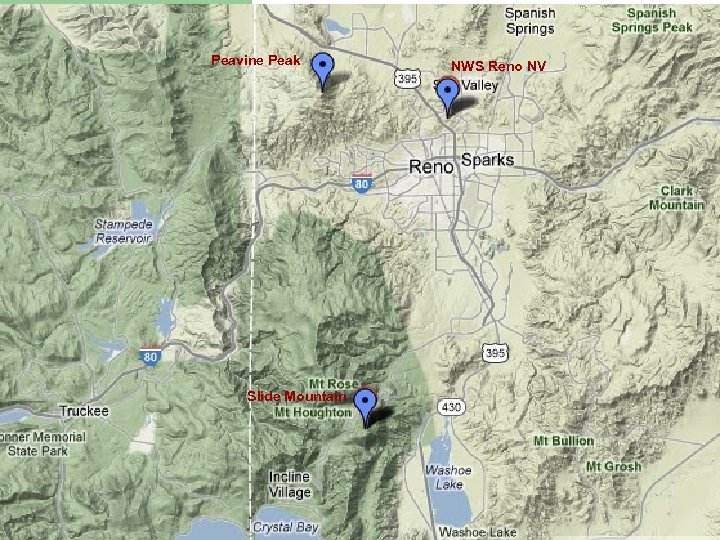
Peavine Peak Slide Mountain NWS Reno NV
Simple Solution - Paired Repeaters Pass the Same Remote Data. l Two repeaters receive all remote station data. – – – l Advantages – l Repeaters have the same pass/block list. Data received from sensor in list is repeated. Base station receives the same data from both repeaters. If one repeater fails, data is received from surviving repeater. Disadvantages – Base station incoming radio channel use is doubled.
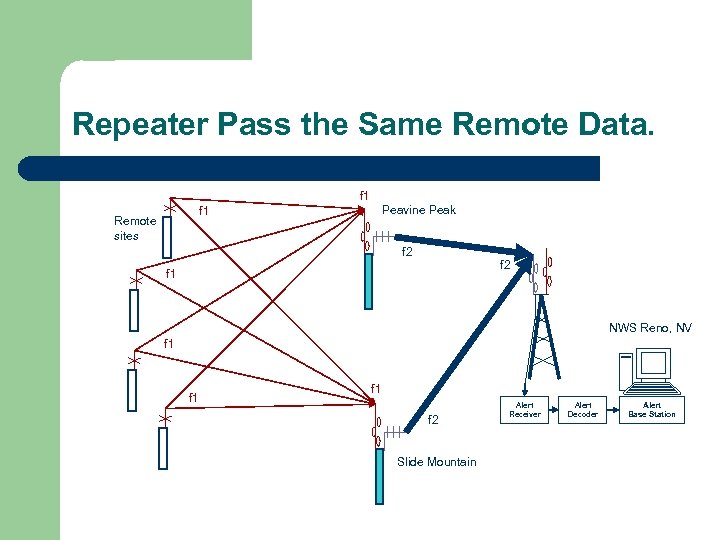
Repeater Pass the Same Remote Data. f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 2 f 1 NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station
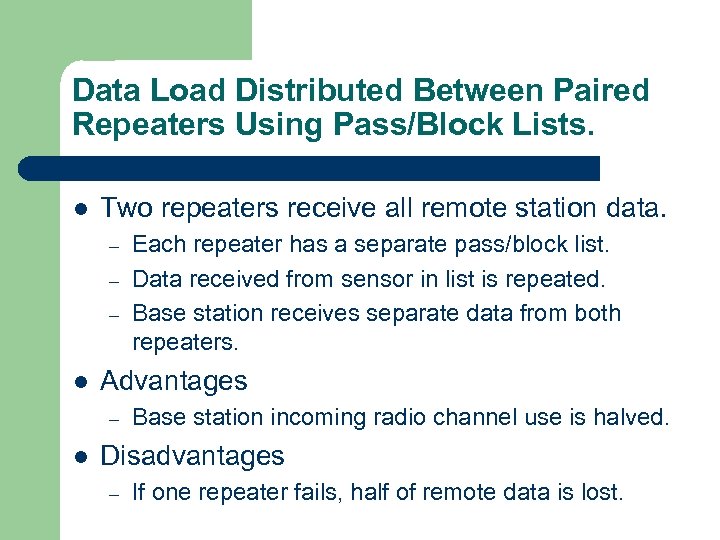
Data Load Distributed Between Paired Repeaters Using Pass/Block Lists. l Two repeaters receive all remote station data. – – – l Advantages – l Each repeater has a separate pass/block list. Data received from sensor in list is repeated. Base station receives separate data from both repeaters. Base station incoming radio channel use is halved. Disadvantages – If one repeater fails, half of remote data is lost.
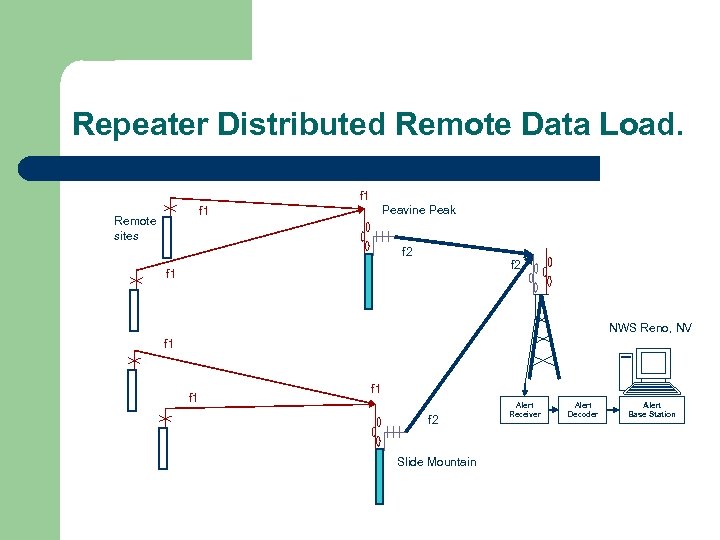
Repeater Distributed Remote Data Load. f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 2 f 1 NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station

Manual remote repeater failover controls repeat function and pass/block lists. l Two repeaters receive all remote station data. – – – l Advantages – l Each repeater has a separate pass/block list. Data received from sensor in list is repeated. Base station receives separate data from both repeaters. If one repeater fails, control sent to surviving repeater to repeat all data. Disadvantages – Operator action required to send remote control failover command.
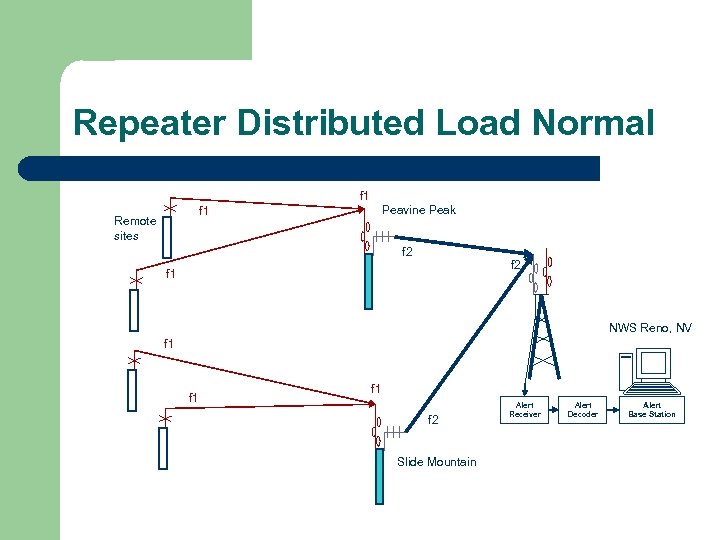
Repeater Distributed Load Normal f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 2 f 1 NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station
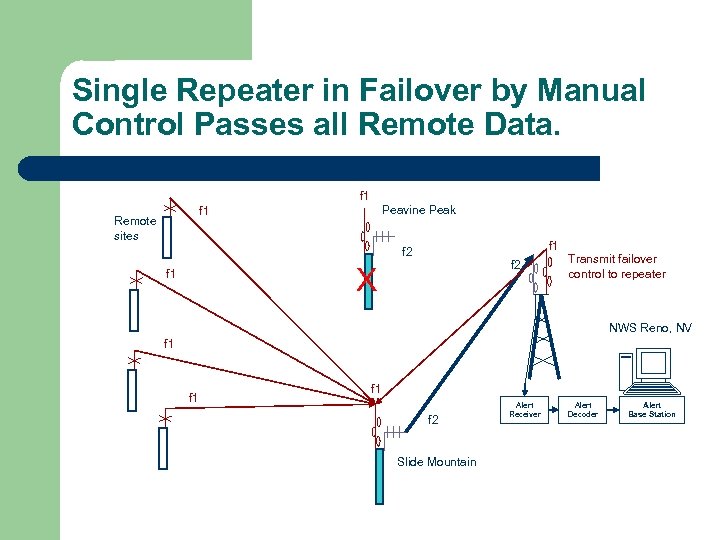
Single Repeater in Failover by Manual Control Passes all Remote Data. f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 1 f 2 X f 1 Transmit failover control to repeater NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station

Automated local repeater failover was the next step in repeater control. l Two repeaters receive all remote station data. – – – l Each repeater has a separate pass/block list. Data received from sensor in list is repeated. Base station receives separate data from both repeaters. Advantages – – If one repeater fails, surviving repeater takes local control and repeats all data. No operator action required to execute local failover command.

Teamed repeaters continuously check each others health. l Health check must use radio. – – l Multiple check-in failure required for failover – – l Test receiver on other repeater. Test transmitter on other repeater. Transmit check-in every 15 minutes. Execute failover if no check-in for 1 hour. Repeater check-in not repeated. – Base station does not receive repeater check-in reports.
Repeater Health Radio Check-in l Repeater 1 transmits a check-in ID. – – – l Check-in ID (903) transmitted every 15 minutes. Repeater 2 responds by transmitting a check-in received response ID (904) back to repeater 1. Repeater 1 resets the failover timeout counter. Repeater 2 transmits a check-in ID. – – – Check-in ID (913) transmitted every 15 minutes. Repeater 1 responds by transmitting a check-in received response ID (914) back to repeater 2. Repeater 2 resets the failover timeout counter.
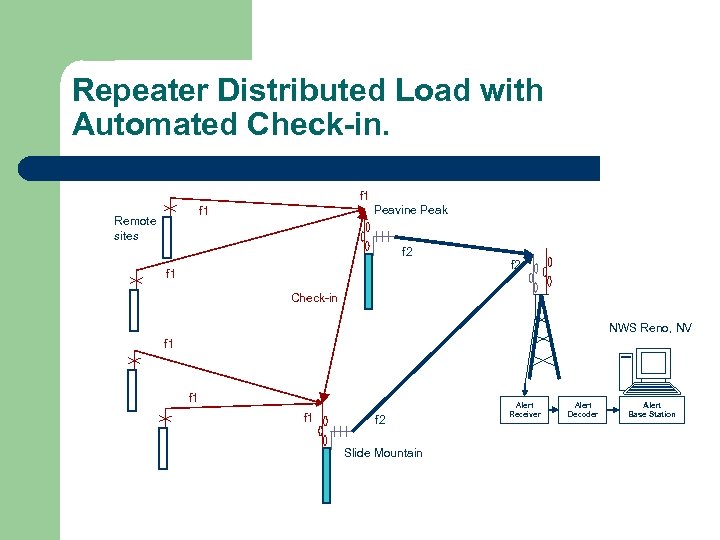
Repeater Distributed Load with Automated Check-in. f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 2 f 1 f 2 Check-in NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station
Repeater Failover l Failover repeater on check-in timeout (1 hour) – – – l Load failover configuration. Failover state ID (902) transmitted to base station. Failover configuration repeats all sensor data. Monitor other repeater check-in for recovery. – – – Increment recovery count for each check-in. After 4 check-in reports received, restore repeater teaming. After timeout on check-in report, reset restore count.
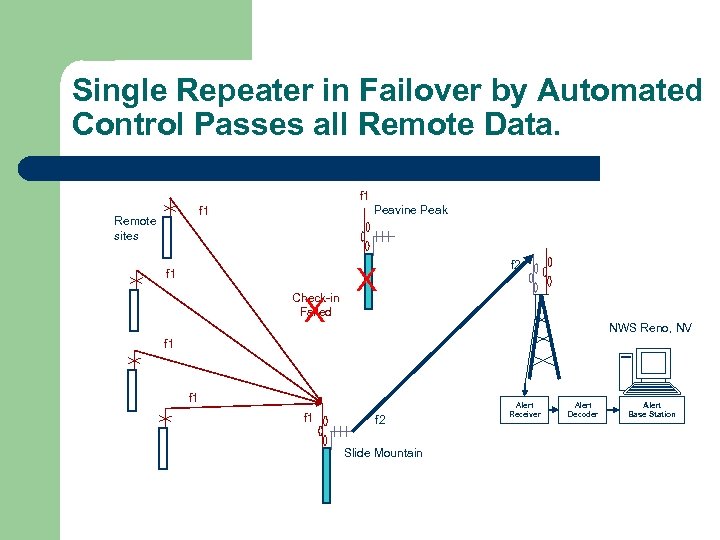
Single Repeater in Failover by Automated Control Passes all Remote Data. f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 1 Check-in Failed X X f 2 NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station

Repeater Recovery l Repeater recovery after 4 check-ins succeed. – – l Load normal configuration. Repeater status set to normal. Repeater status transmit to base station. Normal configuration repeats selected sensor data. Restart repeater health radio check-in. – – Transmit check-in every 15 minutes. Execute failover if no check-in response after 1 hour.
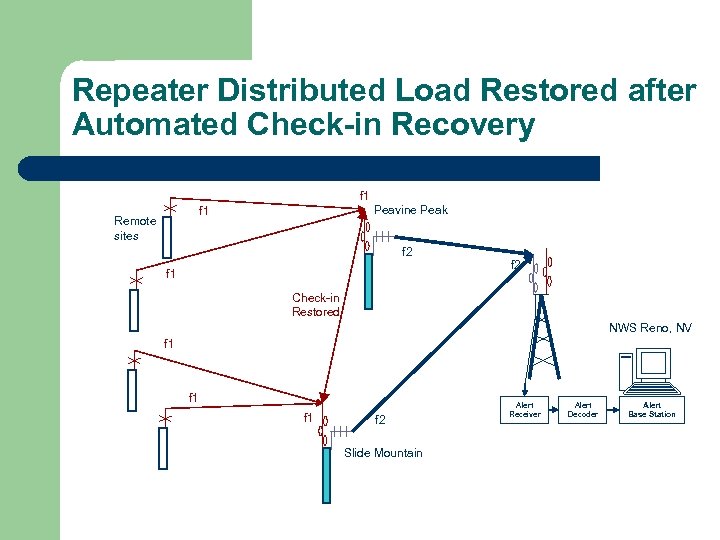
Repeater Distributed Load Restored after Automated Check-in Recovery f 1 Peavine Peak f 1 Remote sites f 2 f 1 f 2 Check-in Restored NWS Reno, NV f 1 f 1 f 2 Slide Mountain Alert Receiver Alert Decoder Alert Base Station
Repeater Radio Check-in Control l Repeaters have two radios and two antennas. – – l Repeater check-in on receive frequency. – – l Receive on omni radio antenna using frequency f 1. Transmit on directional antenna using frequency f 2. Repeater 1 transmits check-in on receive radio using frequency f 1. Repeater 2 responds to check-in on receive radio using frequency f 1. Repeater receive radio control. – Use repeater digital output to switch transmit to receive radio.

Future Enhancements Planned l 50386 Repeaters are Alert 2 ready – – Use Alert 2 protocol to transmit repeated data to base station. When low power Alert 2 receiver available, switch remote transmitters and repeater receive protocol to Alert 2.

Other Enhancements Possible l Add wired or wireless internet access to repeaters. – – – Provide an alternate communication pathway to the base station. Allow remote repeater testing and configuration programming. Retrieve received data logged in repeater.

Thank you You can download this presentation from: http: //hydrolynx. com/presentations/Hydro. Lynx. Automated. Repeater. Failover. ppt Hydro. Lynx Systems, Inc. 950 Riverside Pkwy. , #10 West Sacramento, CA 95605 916 -374 -1800 hydro@hydrolynx. com www. hydrolynx. com
9062a4ed063d1f7ecd237b4d7d4de61a.ppt